Chapter 23 - Global Ecology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is ENSO?
The oscillation between El Nino and La Nina in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific
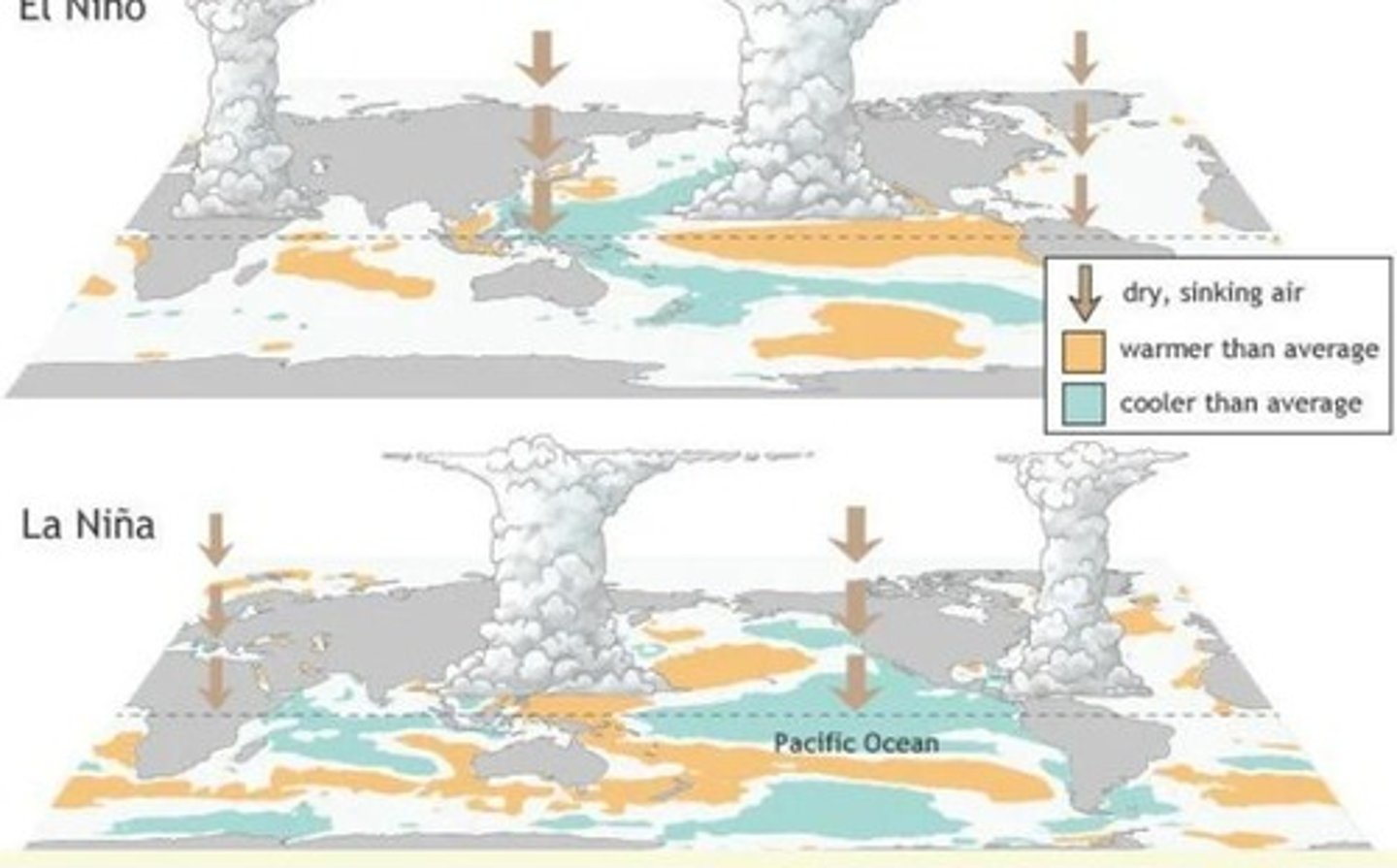
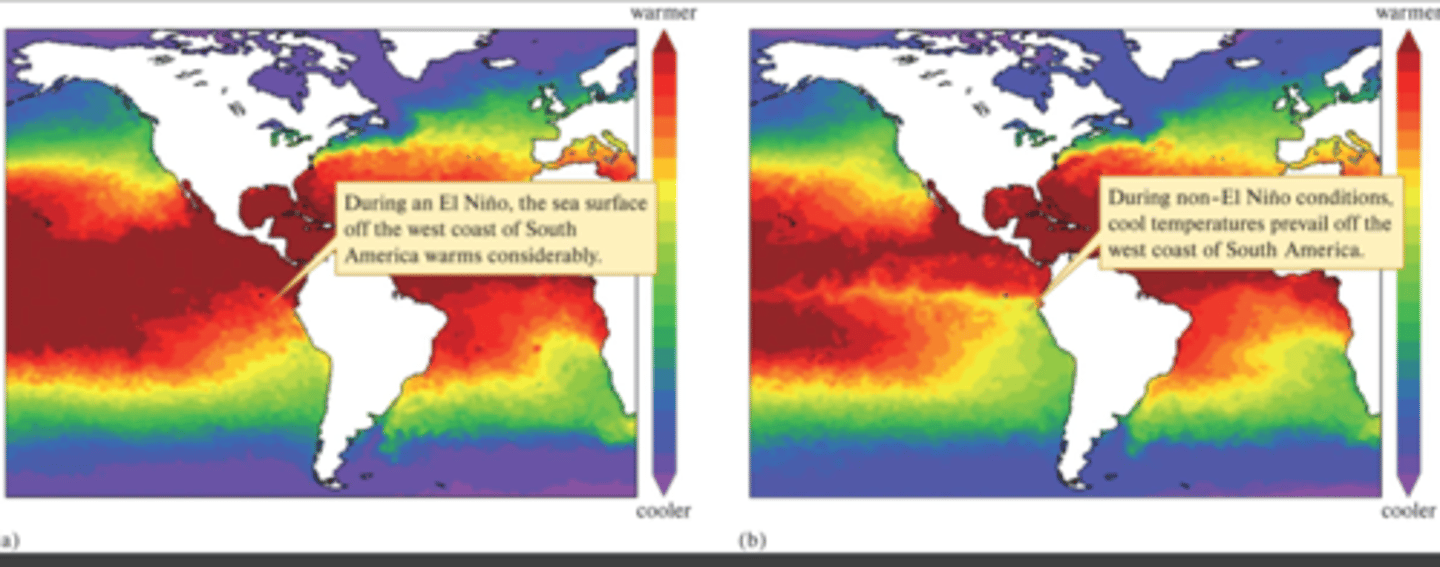
What is El Nino
A climate phenomenon where the eastern equatorial pacific is abnormally warm
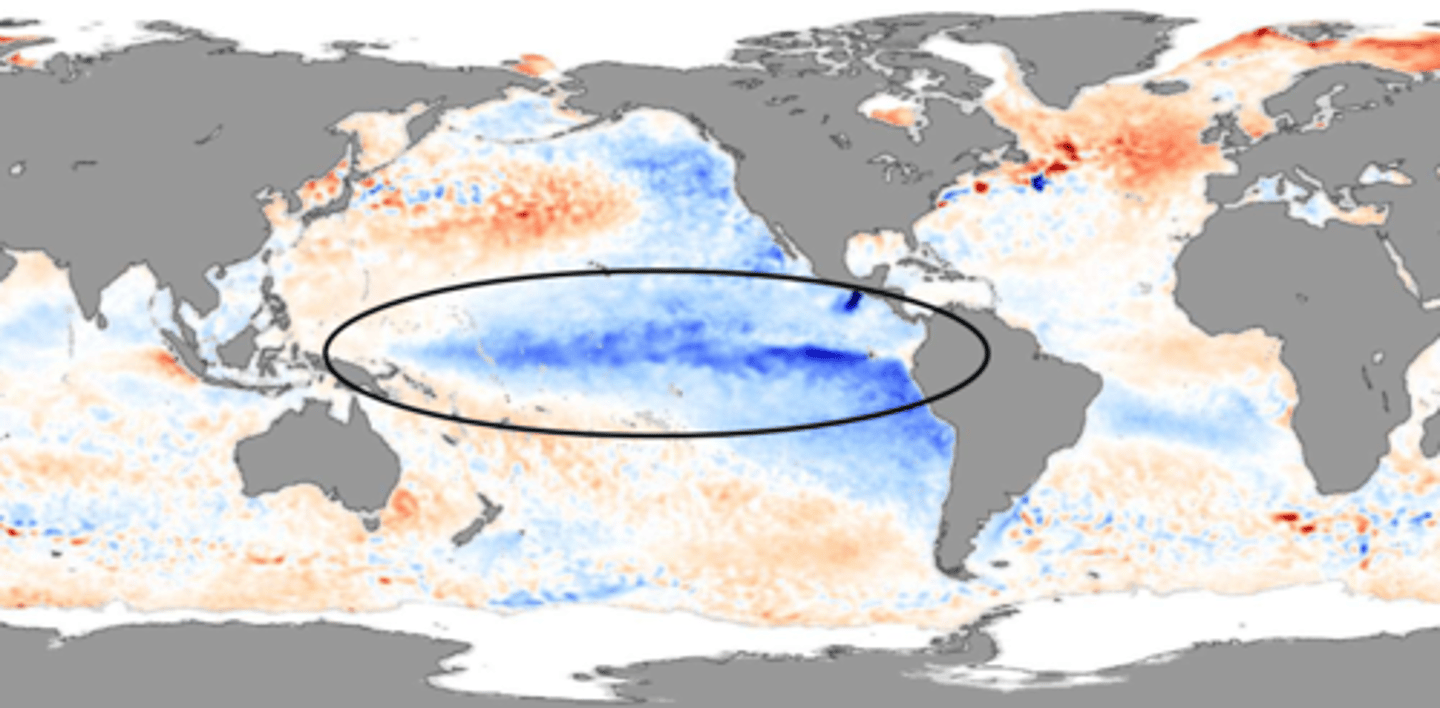
What is La Nina
A climate phenomenon where the eastern equatorial pacific is abnormally cool
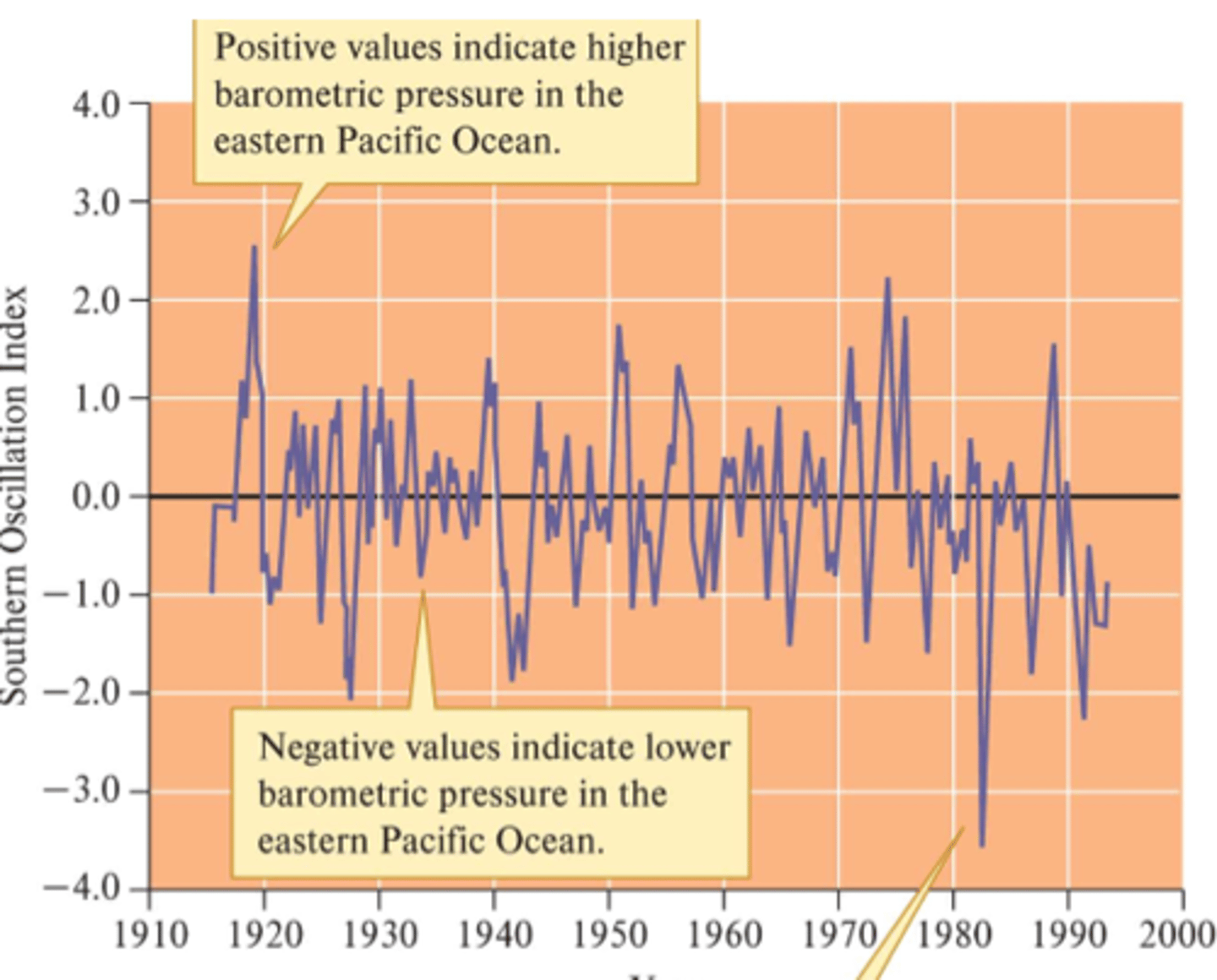
What is the ENSO Index, what do the negative and positive values mean?
A way to quantify the ENSO oscillation; negative values are typically associated with El Nino and positive values are typically associated with La Nina
What do the ENSO oscillations do to climate globally?
They can bring exceptionally wet or exceptionally dry climates to large parts of the globe
El Nino years typically cause what in the SW United States? What about La Nina?
Above-average precipitation during El Nino and below-average precipitation (droughts) during La Nina
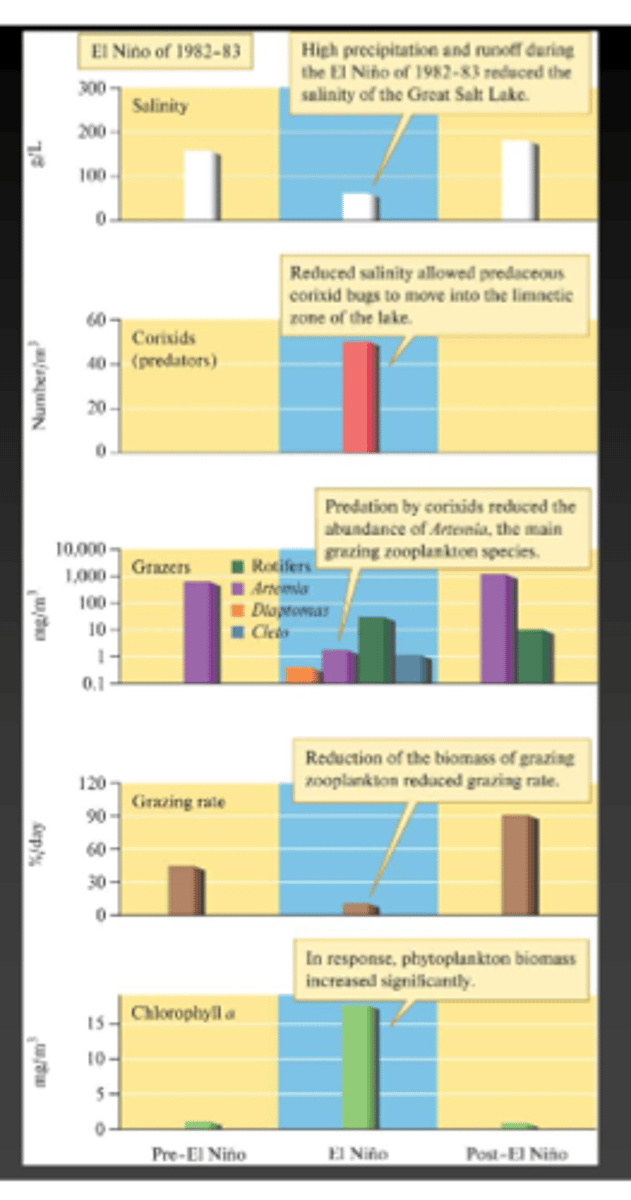
What happened to the Great Salt Lake after the El Nino years of 1982-83?
Lake levels rose (3.7 Meters), salinity dropped (to 50 g/L), Trichocorixa verticalis invaded the lake and caused a trophic cascade.
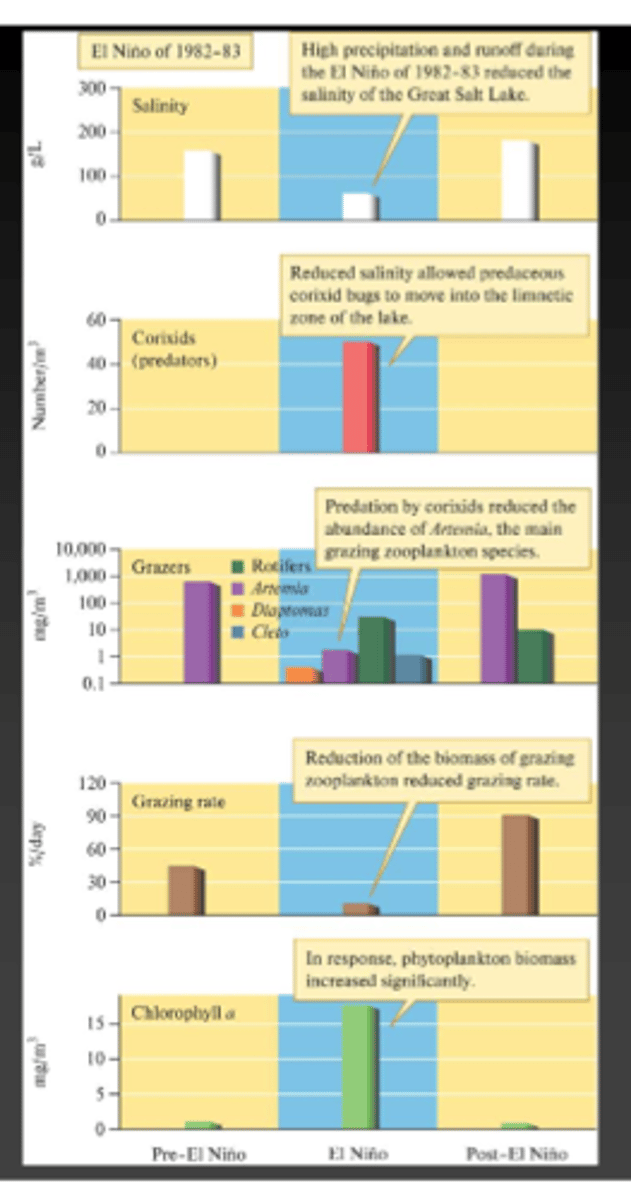
Why did the introduction of Trichocorixa verticalis cause a trophic cascade?
It reduced the population of brine shrimp from 12,000 to 74 per m^3 which caused Phytoplankton to increase significantly
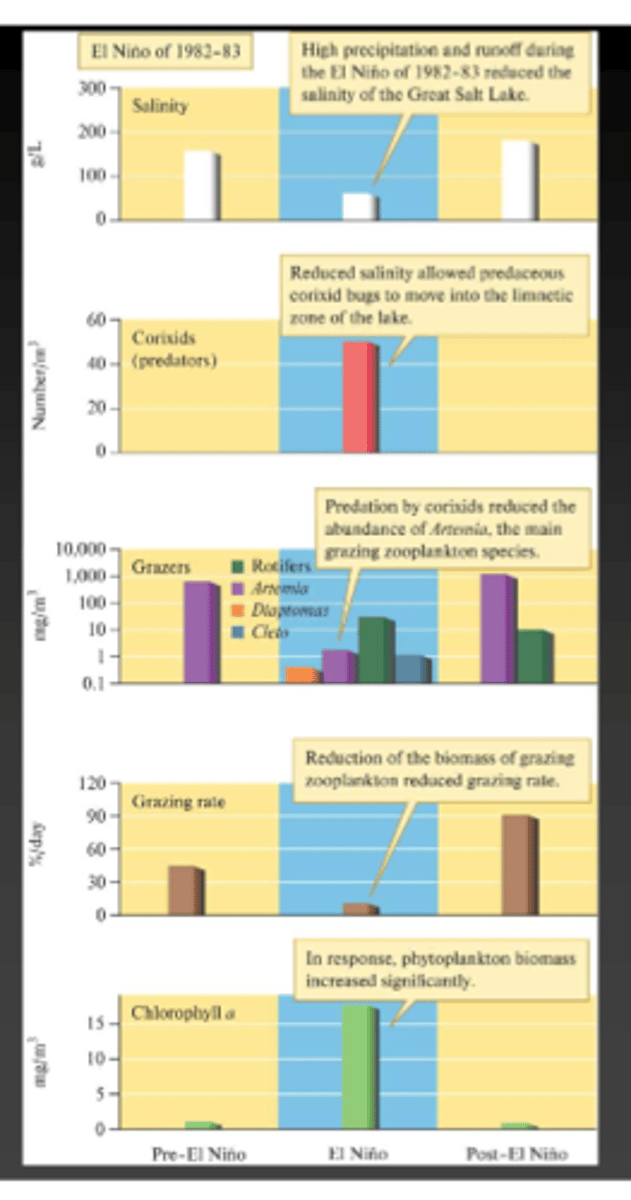
What happened to the Great Salt Lake during 1990?
(After effect recovered)
All ecosystem changes were reversed to its original condition
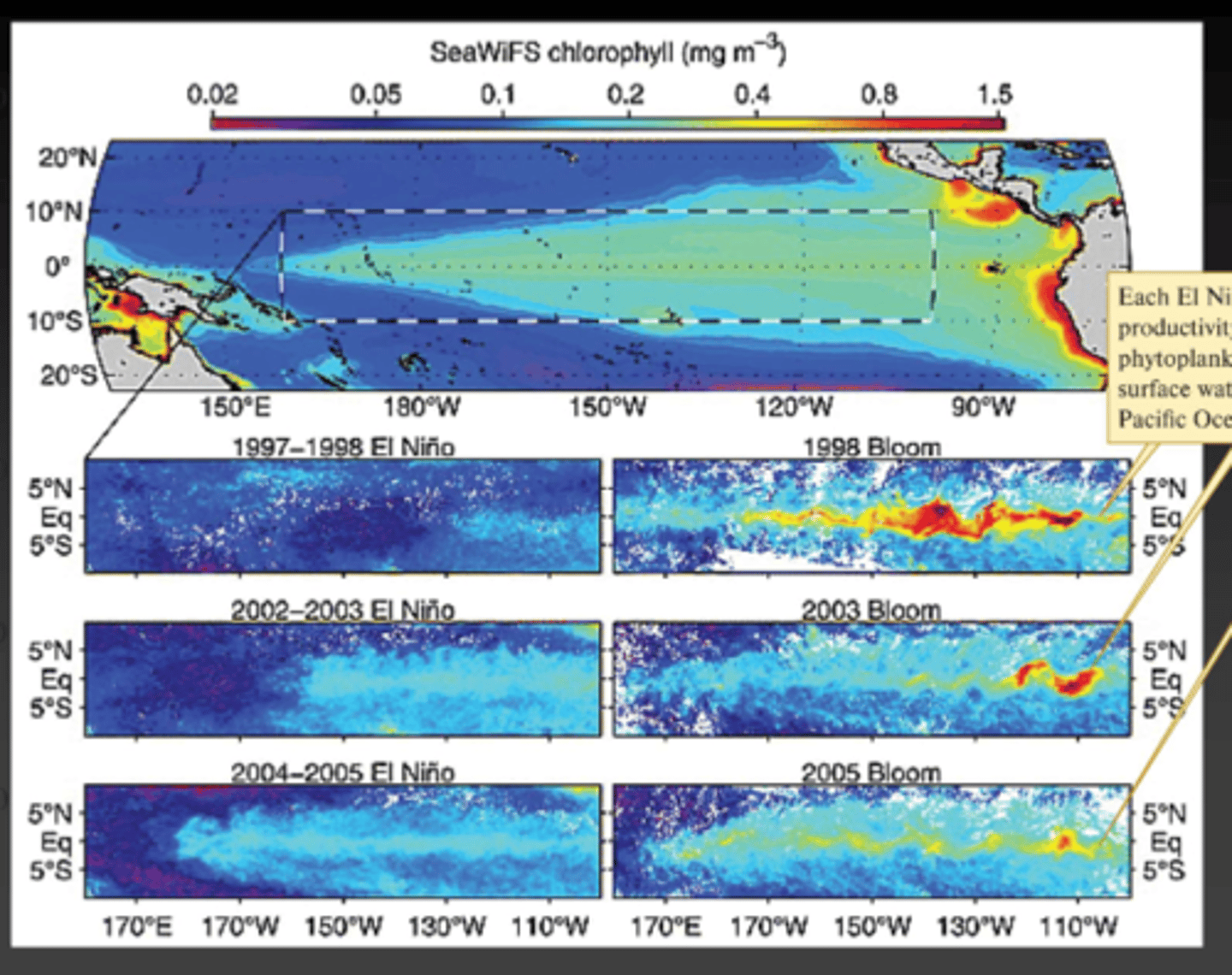
Under normal conditions cold nutrient-rich water upwells off South America and results in high phytoplankton productivity, what happens during El Nino years?
The warm water suppresses upwellings and causes a reduction in nutrients and phytoplankton production, this causes Reproductive failure, starvation, and migration of fish, birds, and other marine animals.
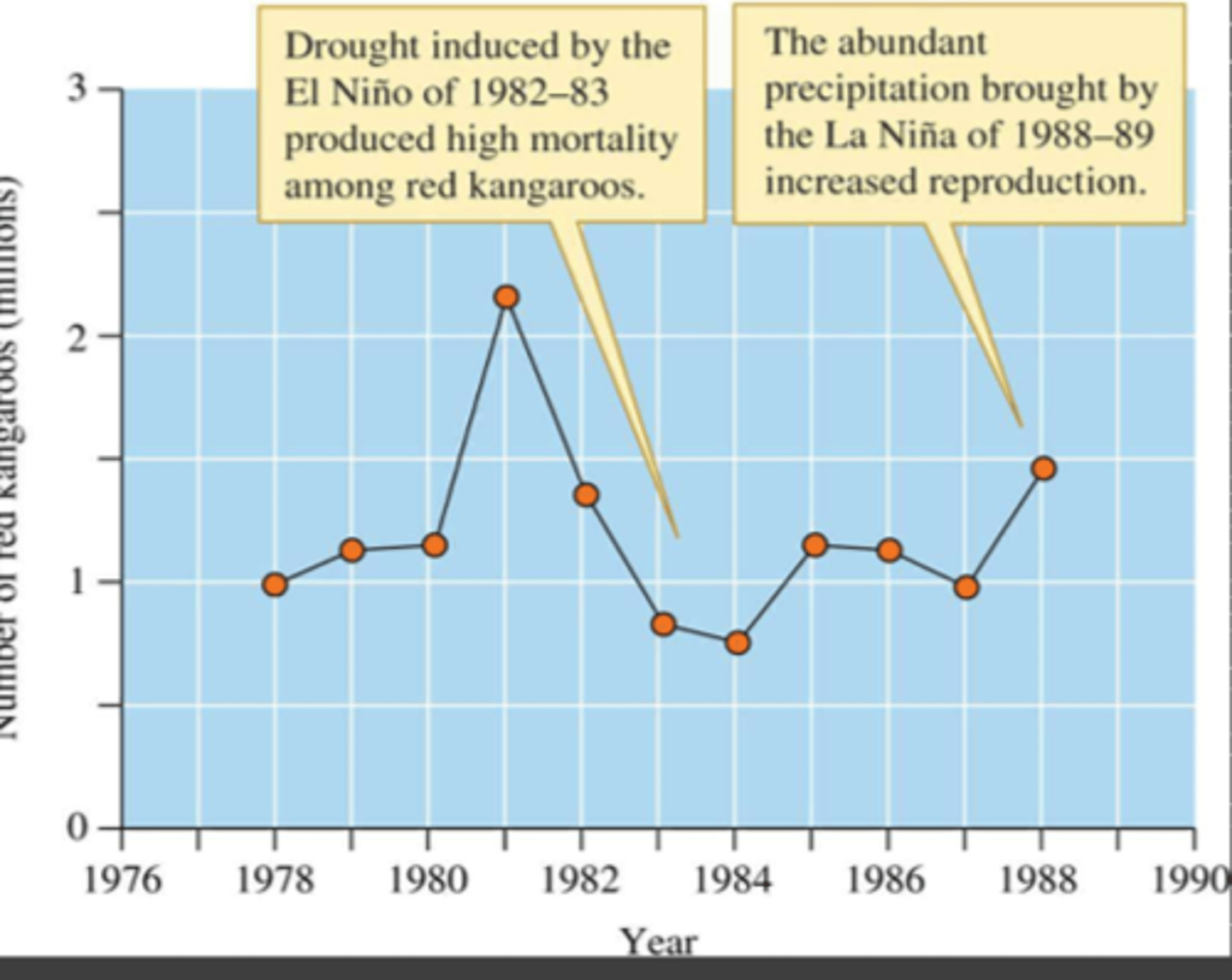
What do Kangaroo populations in Australia do during wet El Nino years? Why do they do this?
They breed rapidly, this is so that there is a large cohort of adults that will face the droughts caused by El Nino later on
How do humans affect the global Nitrogen Cycle?
Humans input about 130 TERAGRAMS of Nitrogen into the cycle, this is larger than any natural source
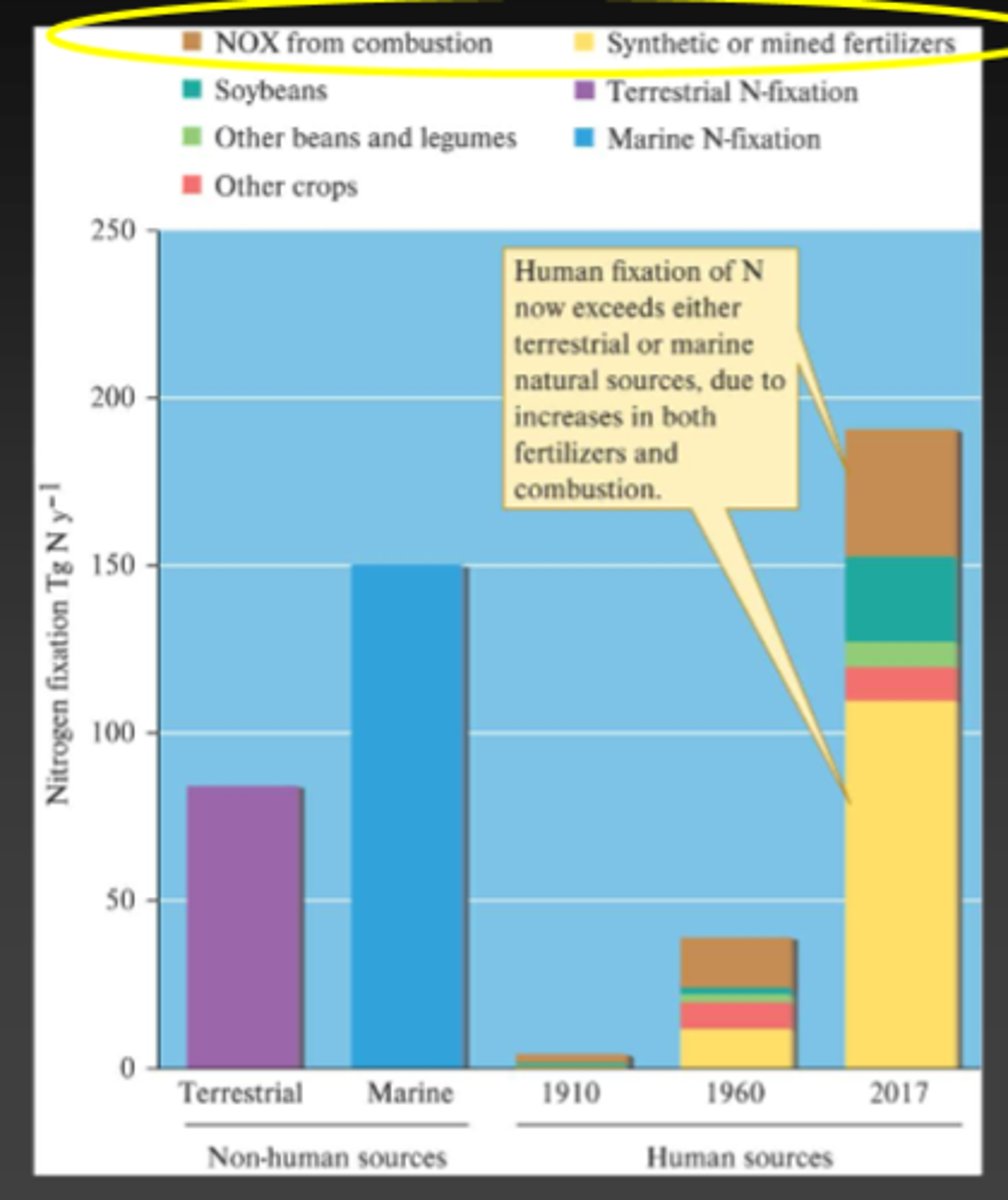
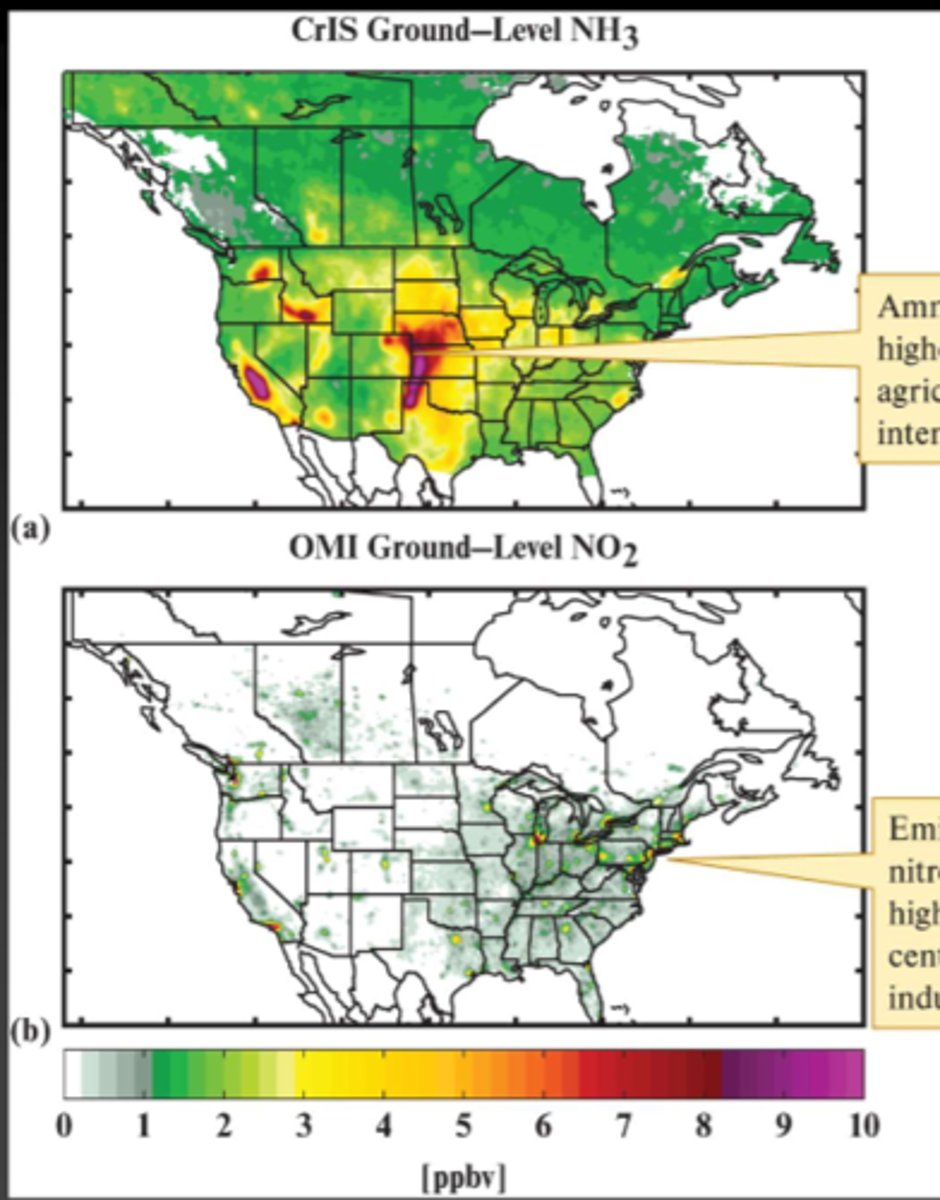
Why do humans release so much Nitrogen, where does this come from?
The use of Industrial fertilizers from agriculture and fossil fuel emissions from cities and smokestacks
Tropical forests support more than 50% of earth's species and occurs within 73 countries, lots of these forests are being deforested to be used for agriculture. What is this type of deforestation called?
Slash and Burn
Why is the Slash and Burn method of agriculture unsustainable?
This method is used to clear out forests to use up all of the nutrients present, tropical soils are nutrient poor so after 2-5 years they will become infertile and no longer support life.
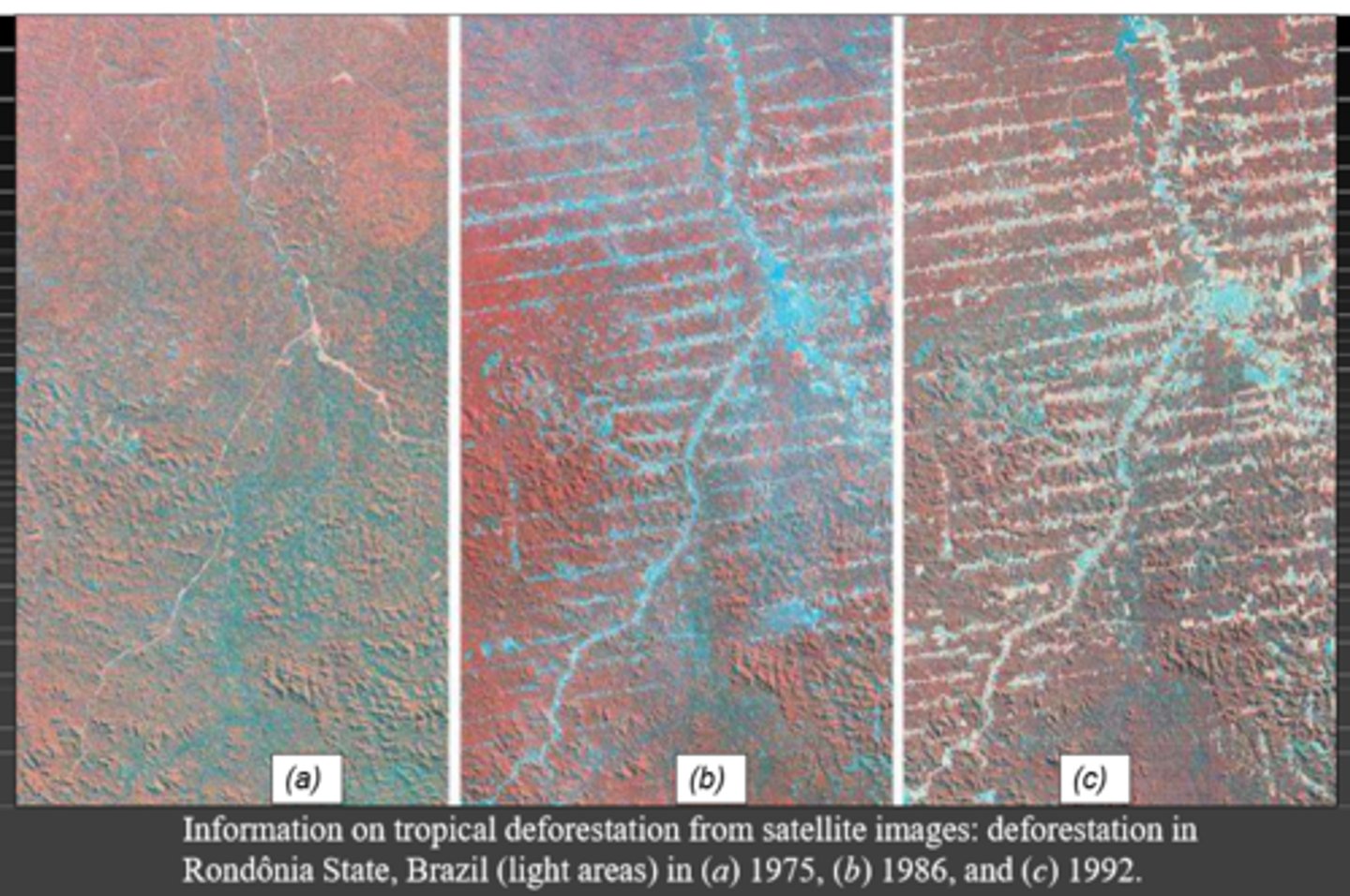
Large areas of the Amazon Rainforest is was deforested in 2019-2024, this causes fragmentation of the forests and forms many edges. Why is this bad for the forests?
Forest edges are:
hotter, drier, and has high solar exposure and wind which causes a decreases in the diversity of many animal groups.
What is the chemical composition of the Surface Air?
(78%) Nitrogen,
(21%) Oxygen,
(.9%) Argon,
(.03%) Carbon Dioxide
What is the greenhouse effect?
The trapping of heat in the Earth's atmosphere
How is the greenhouse effect amplified by humans?
The release of greenhouse gasses such as CO2, Methane, NO2, Refrigerants, and surface Albedo.
According to Ice Core Records what is the relationship between CO2 concentration and temperature?
CO2 concentration and Temperature are directly related to one another.
What were the 3 major human events that halted the rise of CO2
WW1, WW2, and the Great Depression
What is the Suess Effect?
The ratio of Carbon 14 (Naturally Occurring Carbon) is decreasing compared to other Carbon Isotopes (Decayed Carbon), this indicates that humans have become the primary source of atmospheric carbon dioxide
What was the primary cause of the giant fking ozone hole in the fking atmosphere 1985? What was the fix?
The use of CFCs, fixed by switching to alternative refrigerants
What are Zombie Fires?
Fires that overwinter underground and reignite later.
National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON)
Large-scale long-term ecological monitoring across the US