Resistivity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What does resistance of a conductor depend on?
Length
Cross sectional area
Material
Temperature
Resistivity
Electrical resistance of a conductor of unit cross sectional area and unit length
Formula for resistivity
rho = RA/l
Where R is resistance, A is cross sectional area(m²) and l is length(m)
Micrometer
A device used to measure small distances - i.e the diameter of a wire.
A resistor
A device that converts electrical potential energy into some other form.
Multimeter
Electrical instrument which can be used to measure voltage, current or resistance.
Purpose of a Wheatstone bridge
To find resistance of an unknown resistor.
Formula and setup of a Wheatstone bridge:
R1/R2 = R3/R4
Galvanometer
Very sensitive analogue ammeter which registers whether or not there is any potential difference between two points. If a Galvanometer is balanced there will be no deflection of the pointer.
Uses of a Wheatstone bridge
Temperature control (the resistance increases when it heats up)
A stress gauge (The resistance of a conductor in a strain gauge increases when a force is applied to it.)
The Metre Bridge
Same as Wheatstone bridge except two of the resistors are replaced by a single strip of uniform resistance wire.
The balance point can be reached by simply sliding the contact wire along this lower uniform resistance wire
One of the resistors is known and the two lengths can be measured.
Resistance is proportional to length so instead of using R3/R4 we can use l1/l2.
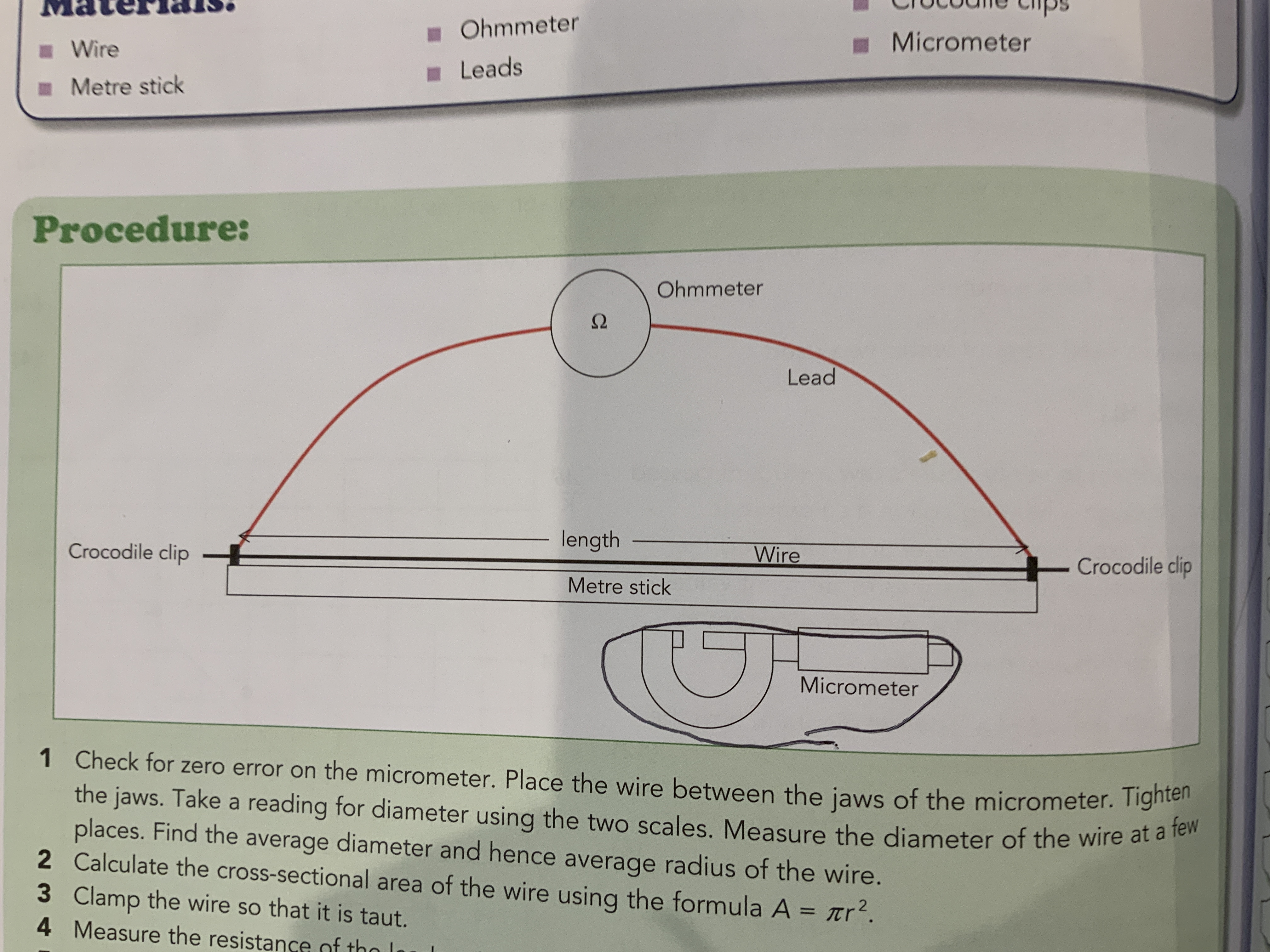
Measurement of the resistivity of the resistivity of a wire diagram