chem 4 (kinetics/equilib)
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
what is a reaction rate equation
Δ[ ] / Δtime
[ ] is molarity of whatever’s inside
4 factors that increase the rate of a chemical reaction
1) Increasing temp ( more KE, faster, more collisions, reacts faster)
2) Add a catalyst (new pathway that is a faster reaction)
3) Increasing molarity of reactants (more reactants means more collisions and reactions, so faster)
4) decreasing the particle size of reactant (smaller particle size is more surface area, so more collisions) (the powder form of a metal will be much faster than a solid chunk) this is for heterogeneous mixtures (diff phases)
5) stirring a mixture of different phases (heterogeneous) will increase interaction and access
Differentiate law eqn
rate = k[ X ]^m
k is rate constant
[ X ] is reactant concentration
n, m, etc is the e order of reactants (how rate is affected by the reactant)
when do you use differential rate laws
when you have concentrations and rate, and only works for forward rxns
How do you solve for order of reactants (m, n, etc)
Find rate law for different experiments where one of the reactants is the same for both experiments
Set up a ratio of the different equations and cancel out what’s the same
You’ll have something like: 2 = 2^n
and then figure out n based on this
Repeat for order of each reactant

how do you find overall reaction order
sum of the reactant orders (sum of exponents m, n, etc)
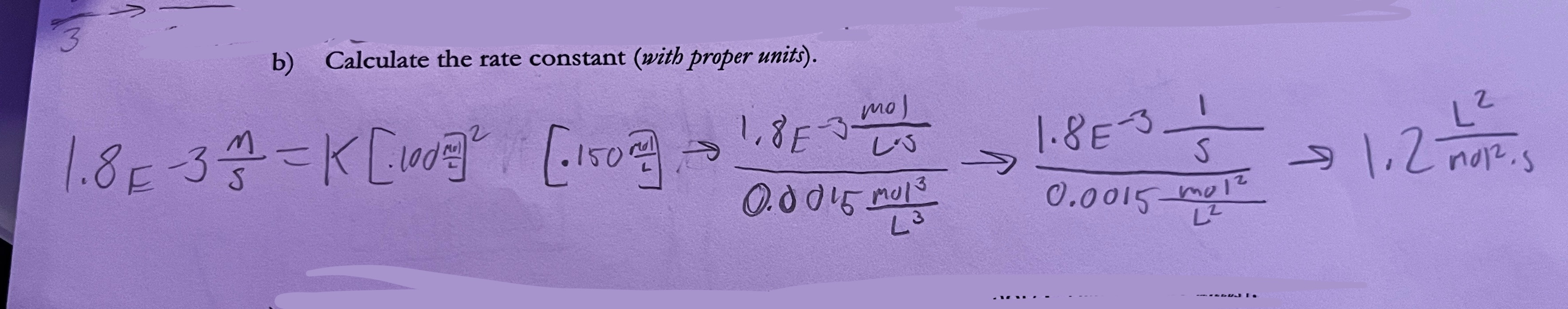
How do you determine k (and units) for differential rate laws
choose any experiment’s rate law and plug in numbers!
to find units include units for the rate and the concentrations (exponents apply to labels too!!) and then solve to find what the units are (may need to cancel stuff from fraction, or multiply reciprocal from bottom, etc)
1) 2 = 2^n ; n=?
2) 8 = 2^m ; m=?
3) 4=2^o ; o=?
n=1
m=3
o=2
What happens with a zero order reaction
The rate doesn’t change, thus the reactant doesn’t appear in the rate law (if [reactant] changes and rate doesn’t, it’s zero order
When are integrated rate laws used?
When given concentration and time (when conc. depends on time)
We will only be dealing with zero, first, and second order reactions
integrated rate law for 0 order reaction
[A]t - [A]0 = -kt
integrated rate law for 1st order reaction
ln[A]t - ln[A]0 = -kt
integrated rate law for 2nd order reaction
1/[A]t - 1/[A]0 = -kt
how do you know which order it is based on integrated rate law graph?
if the equation for the rate law produces a linear graph (NOT curved)
what is a half life (for a 1st order reaction(only one you need))
time required for a reactant to reach HALF its original concentration
formula for half life
t ½ = 0.693 / k IN AP PACKET
While you don’t need to know the equation for a 0 or 2nd order half life, how can you determine if it is NOT first order
If the half lives vary (different time for it to go from 100→50 than 50→25) for second and 0 order, so if it is not half for SAME amount of time it is not first order
how do you solve for k using integrated rate law when given time vs concentration?
plug in the times and concentrations into specific equation for order of reaction and solve for k
What are units for k in an integrated rate law?
1/units of time (1/sec, 1/hr, etc)
how do you rearrange half life to solve for k?
k = 0.693/t ½
0 order differential rate law eqn
Rate = k
1st order differential rate law eqn?
rate = k[A]
what is the eqn for second order differential rate law?
rate = k[A]²
how do you determine the rate law for a reaction if you know the elementary steps and slow step?
use the coefficients of reactants in the slow step to determine the exponent of said chemical in the rate law. reactants to power of coefficients of SLOW STEP
what is the rate determining step of elementary steps in a chemical reaction?
the slow step (the reaction rate can only go as fast as the slowest step)
For a reaction mechanism to be “correct” what two criteria need to be met?
sum of elementary steps must add up to overall reaction (hess law kind of canceling if something is on both sides of diff elem. steps)
the rate law for the overall r n must agree with the rate determining (slow) step
rates are ALWAYS
positive!
to determine the rate of consumption of a particular chemical
find the concentration of a certain chemical and then use the coefficients to determine if the concentration of OTHER chemicals are same, half, double, etc. based on coefficients, and compare products and reactants to determine how fast a certain chemical disappears
Zero order reactions have a (pos/neg) slope
negative (-k)
First order reactions have a (pos/neg) slope
negative (-k)
second order reactions have a (pos/neg) slope
positive (+k)
What is the molecularity and rate law for a mechanism with an elementary step: A → products
unimolecular, Rate = k[A]
What is the molecularity and rate law for a mechanism with an elementary step: A + A → products or 2A → products
bimolecular, Rate = k[A]²
What is the molecularity and rate law for a mechanism with an elementary step: A + B → products
bimolecular, Rate = k[A][B]
What is the molecularity and rate law for a mechanism with an elementary step: A + A + B → products (2A + B → products)
termolecular, Rate = k[A]²[B]
What is the molecularity and rate law for a mechanism with an elementary step: A + B + C → products
termolecular, Rate = k[A][B][C]
If the fast step comes before a rate determining (slow) step
it will start to reverse while the slow step occurs, and if the product of this step is a reactant in the next (it’s an intermediate) sub the reactants in the fast step for the intermediate reactant in the slow step

Chemical reactions _____ when temp is increased
speed up
what is activation energy
the minimum amount of energy that must be overcome to produce a chemical reaction
What two conditions must be met for an effective collision to occur
collisions must have enough activation energy
reactants must be oriented correctly

More activation energy means a _____ rxn rate
slower
less activation energy means a ____ rxn rate
higher
Why does a higher temp increase the rxn rate
more molecules have enough energy to overcome activation energy threshold and will therefore have more successful
collisions faster
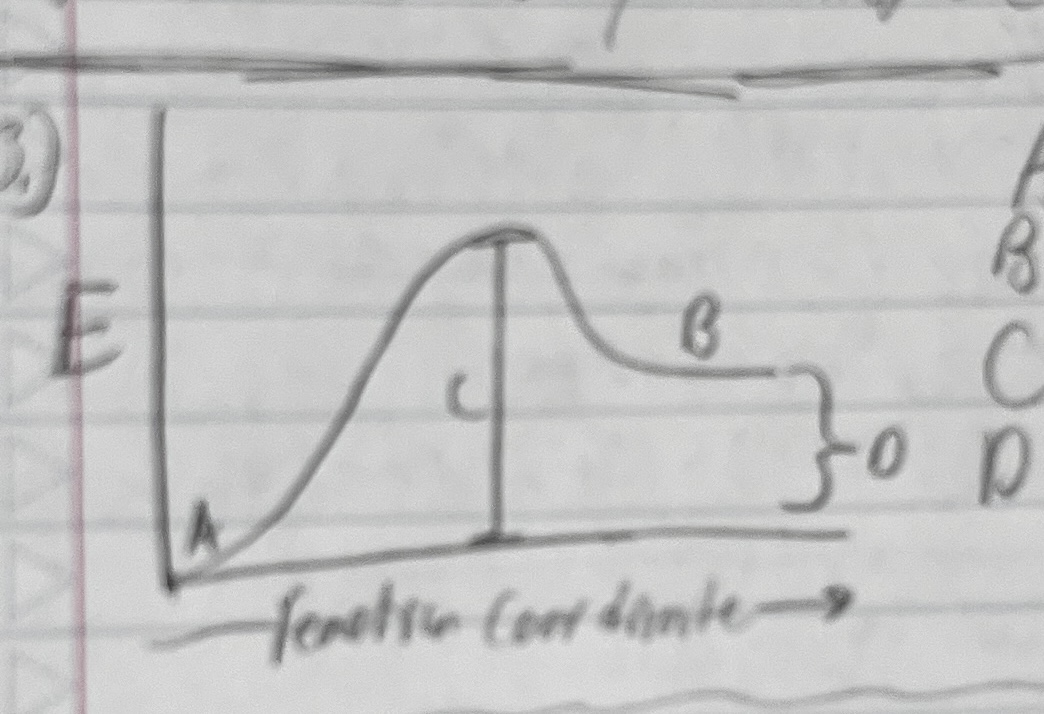
what does each letter represent in the following graph:
A: reactants
B: products
C: Activation energy
D: Overall ΔE (positive, but can be negative)
what is an activated complex, where is it on a reaction progress graph
an aggregate of all of the reactant atoms in one big clump, located at the top of the hump of activation energy
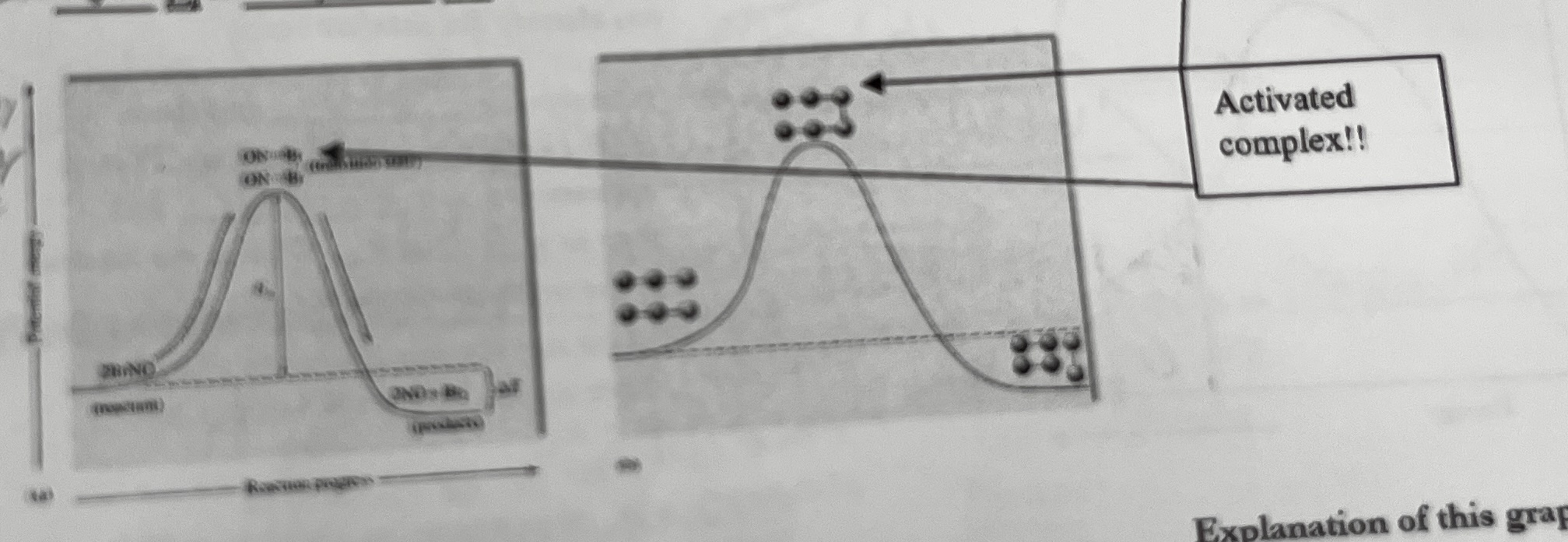
What is an intermediate?
something that appears in elementary steps of a mechanism first as a product and then again as a reactant
what is a catalyst?
Substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed itself, gives another pathway for a reaction that has a lower activation energy
how do you determine a catalyst in a mechanism
it appears over multiple elementary steps, first as a reactant, then as a product
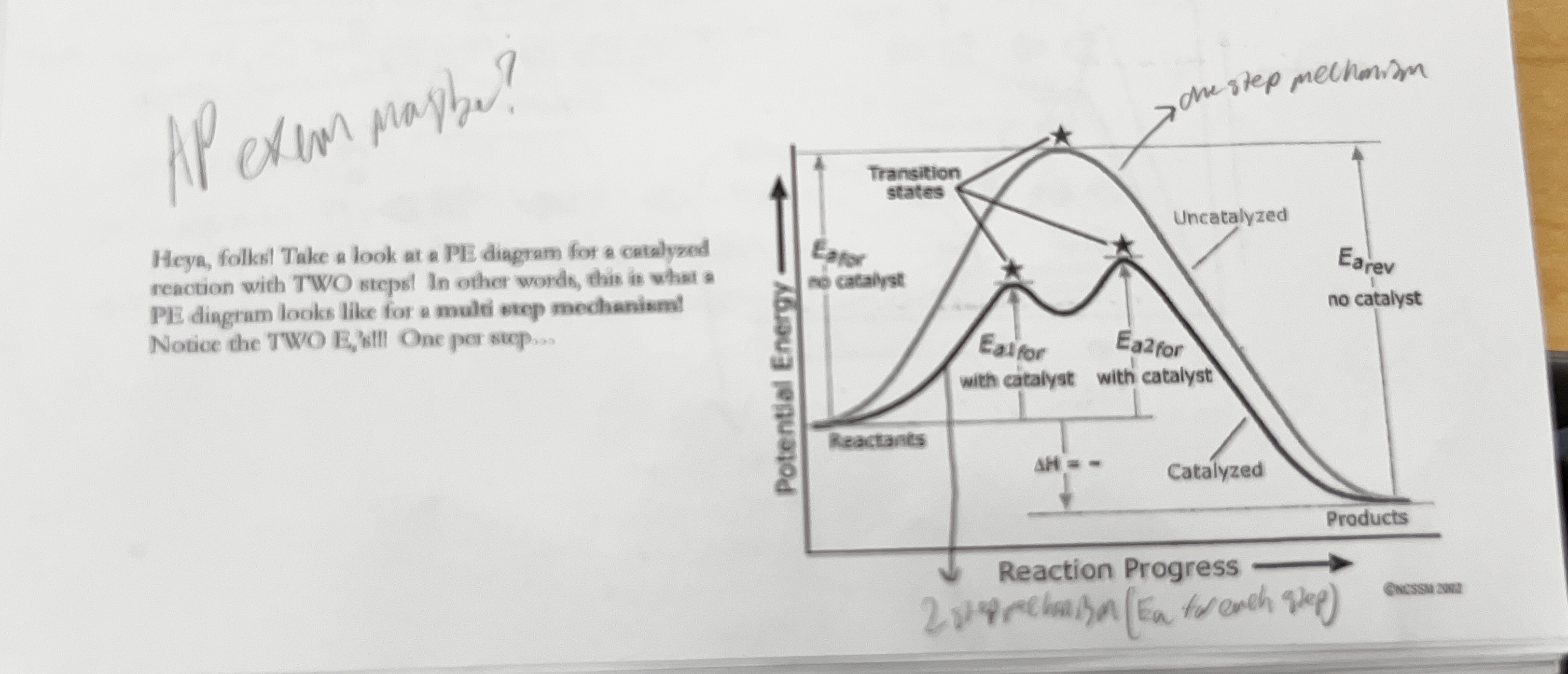
what does a reaction progress and energy graph look like for a multi step mechanism
it will have two humps compared to one big one with two different steps
What is chemical equilibrium
The state where concentrations of reactants and products are constant with time (rate of forward reaction proceeeds at same rate as reverse reaction), a system is at equilibrium when it can no longer do work ΔG = 0
What is the equilibrium constant?
CAPITAL K, tells you the rate at which a reaction will proceed to completion
what is the equilibrium expression formula if
jA + kB ⇌ lC + mD
K = [C]^l [D]^m / [A]^j [B]^k
PRODUCTS OVER REACTANTS (concentrations to power of coefficients)
if K > 1 then ____ are favored
products are favored (forward reaction is favored)
if K < 1 then _____ are favored
reactants are favored (reverse rxn is favored)
Kc is
Equilibrium constant for molar concentrations
Kp is
Equilibrium constant for partial pressures
Ksp is
solubility product (no denominator because the reactants are solid)
Ka is
acid dissociation constant for weak acids
Kb is
base dissociation constant for weak bases
Kw describes
ionization of water (Kw = 1E-14)
K modifications:
if the rxn is reversed, K will be
1/K (reciprocal)
K modifications:
if coefficients are changed by n, K is
raised to the power of n
halved: K^1/2
doubled: K²
K modifications:
when reactions are ADDED together then K overall will be…
the product of K for each individual step (K overall = K1 * K2)
for the rxn jA + kB ⇌ lC + mD, Kp = ?
(Pc)^l (PD)^m / (PA)^j (PB)^k
if pure solid or pure liquids are in a chemical equation, for equilibrium expressions they are…
NOT USED (concentrations stay the same)
What is Q
the constant that is used for initial concentrations (K but when the system is NOT in equilibrium)
if something says [H2]0 that means
initial concentration
determining which way a reaction will shift:
Q = K
no shift (already at equilibrium)
determining which way a reaction will shift:
Q > K
Left shift, initial has too much product and a larger numerator
determining which way a reaction will shift:
Q < K
right shift, because there is too much initial reactant and a larger denominator
In a chemical reaction, equilibrium occurs when (using G):
Gproduct = Greactant
Gproduct - Greactant = 0
or 🔺G = 0
(when it no longer does work because nature is lazy and wants the lowest possible energy state which is 🔺G = 0)
not every reaction has to reach completion (all product) in order to be at equilibrium
formula for ΔG involving K
ΔG = -RTln(K)
if ΔG = 0 (at equilibrium), K=?
K=1 (equal concentrations of reactants and products, equilibrium)
if ΔG < 0 (-ΔG or SPONTANEOUS (reacts readily)) then K is
K > 1, there is more product
if ΔG > 0 (POSITIVE ΔG or non spontaneous) then K is
K < 1, more reactant

What are the steps to this problem?
solve for overall ΔH (sum ΔH products times coefficients) minus (sum of ΔH reactants times coefficients
Solve for overall ΔS (same as ΔH, sum of products - reactants)
Solve for ΔG (ΔG = ΔH-TΔS)
Solve for K (ΔG = -RTlnk, plug in G, R and T)
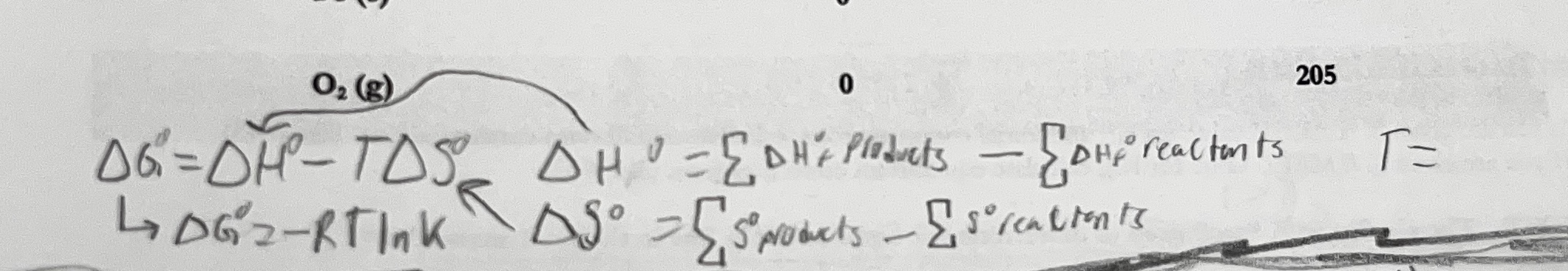
Steps to solve equilibrium problems (ICE problems)
if you have nonzero initial concentrations for everything, find Q and compare to K to determine left or right shift
Complete ICE table (initial concentrations, change (-x, 2x, x, -2x, etc), equilibrium (take the initial plus or minus the change)
solve for x (based on K or based on info given for equilibrium concentrations)
Substitute in X into final row of ice table
Three types of ice problems
Solve for K (find equilibrium concentrations with ice table and plug into equilibrium expression)
If you are given a larg K value and initial concentrations, and asks to calculate equilibrium concentrations
if you are given a small K value and asks to calculate equilibrium concentrations
What is a TINY K value?
K< x10^-2
what does a tiny K value mean
when you see +x, - x, +2x, -2x, etc, cross them out when solving for x they won’t impact answer
What is Le Chateliers principle
If a system AT equilibrium is subject to stress, it will shift to reduce that stress
Le chateliers:
Add a substance, how will it shift
it will shift AWAY from added substance to “use it up”
substances can include chemicals or energy (temp)
Le chateliers:
Remove a substance and it will shift
TOWARD that substance to replace what was removed
substances can include chemicals or energy (temp)
Le chateliers:
if a pure solid or liquid is affected, there will be ____ shift
NO SHIFT (concentrations are constant)
Le chateliers (pressure):
Add or remove a gaseous substance, shift or no
YES SHIFT, away/toward affected substance
Le chateliers (pressure):
Change in volume of container, yes or no shift
YEA SHIFT, will shift to undo this
Le chateliers (pressure):
Add an INERT (last column) gas, yes or no shift?
NO SHIFT
Le chateliers (pressure):
Volume of container decreases, how will it shift
it will shift to DECREASE PRESSURE (less space=more pressure on gasses, so it wants to undo that) it will go towards side with LESS mols of gas
Le chateliers (pressure):
Volume of container increases, how will it shift?
it will shift to INCREASE pressure, more space means less pressure in gasses so it will want to undo this, thus shifting toward the side with MORE mols of gas
Le chateliers (pressure):
How do you determine HOW to increase or decrease pressure
Look at the gaseous species in the reaction and their coefficients, find out which side has more coefficients (mols), and to inc pressure it will shift toward larger mol side and to dec pressure it will shift toward smaller mol side
If there is an endothermic process (+ΔH) energy is a…
Reactant
If there is an exothermic process (-ΔH) energy is a…
product
ONLY a ______ causes the value of K to change
CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE, because Energy (temp) is not a Chemical that is inducing a shift, therefore when the reaction shifts to change the energy, the amount of chemicals are the same, and it will affect the overall ratio of reactants and products when it shifts which will affect K
When a stress is placed on a system, even when equilibrium is re established, the stress is..
never FULLY eliminated
Pressure changes only affect…
gas
good luckkkk
😝
what would a graph look like for the effect of a catalyst on a reaction with activation energy
one higher hump and one smaller hump, representing with and without a catalyst
K (equilibrium constant) will ONLY change from a…
CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE, there is one value for K for a system at a certain temp, change the temp and the K will change, otherwise the equilibrium will be maintained at the same constant