Sound and Properties of Waves
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science GACE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Longitudinal Wave
a wave in which the direction of the vibration is parallel to the direction the energy travels
Period
the time it takes to complete one full wave cycle, measured in seconds
Threshold of Hearing
0 dB, the softest sound a human can hear
Mechanical Waves
Physical waves that travel through a medium.
Electromagnetic Waves
Waves consisting of vibrating electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum because they do not require a medium. Emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero.
Amplitude
the maximum displacement of a particle of the medium during a vibration (measured from non-vibrating position to one crest)
Wave
a disturbance that transports energy as it moves through space and time
Doppler Effect
an increase in the frequency of a wave when an emitter and/or an observer move toward each other and a decrease in the frequency when the objects move apart
Compression Wave
a longitudinal wave with areas of high and low pressure, or density
Frequency
the number of ocurrences of an observed behavior over a set time period
Pitch
a description of the frequency of a sound wave; high-pitched sounds have high-frequency waves
Decibel
The unit for the loudness of sound and is abbreviated dB.
Crests
the peaks, or highest points, of a vertically vibrating transverse wave
Threshold of Pain
sound at 120 dB
Loudness
human perception of the intensity of a sound
Wave Speed
a measure of how fast the wave energy moves from one place to another
Wavelength
the length (in space) of one complete wave cycle, measured in distance units
Intensity
a measure of the severity or volume of a behavior when it occurs
Medium
the material that carries a mechanical wave
Troughs (of a Wave)
the valleys, or lowest points, of a vertically vibrating transverse wave
Transverse Wave
a wave in which the direction of the vibration is perpendicular to the direction the energy travels
Which of the following devices does NOT need waves in order to function?
water filter
The amplitude of a transverse wave is:
half of the distance between the top of a crest and the bottom of a trough.
A sound wave consists of alternating regions of high and low pressure. The wavelength of a sound wave would be the length between:
one high pressure region to the next.
A remote-controlled toy boat vibrates on the surface of a ripple tank and is the source of waves. The waves have a frequency of 30 Hz and a speed of 60 cm/s. If the toy boat, marked S in the diagram, is moving 20 cm/s east, at which marked point on the diagram would an observer measure the greatest frequency?
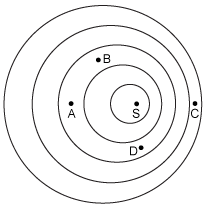
Point C
Which of the following determines the frequency of a sound wave?
the vibration rate of the source
Pitch is a characteristic of sound that is related to which of the following properties of a sound wave?
frequency
The middle school science and orchestra teachers collaborated during a science unit on sound. They set up an oscilloscope attached to a microphone and projected the oscilloscope image onto a screen. This setup allowed students to view the waveform of the sound waves on the screen.
During the lesson, the orchestra teacher then explained the concept of pitch and connected pitch to the sounds made by a flute and a piccolo. Then the teacher played pure instrumental tones into the microphone while the class recorded the pitch and the data from the waveforms displayed across the screen.
During this investigation, the students were most likely studying the relationship between pitch and which of the following properties of sound?
frequency
As you ride a train, it passes a stationary warning horn. Which of the following causes you to hear the horn's frequency shift from high to low?
Doppler effect
Students in a seventh-grade science class use computer software to observe the patterns of the sound waves formed by various tuning forks. Students measure the length of each wave and keep records showing the appearance of the wave pattern, the dimensions, and the observed pitch of the sound made by each tuning fork they use.
Which of the following is most likely being investigated by the students?
how the wavelength of a sound varies with the frequency
The table shown compares two properties of sound by listing a few characteristics of each property and an example. Which term would best replace the letter X in the table?
Intensity | X |
Characteristics: | Characteristics: |
1. Related to the amount of energy transported by a sound. | 1. Related to the human perception of a sound. |
2. Y | 2. Measured in descriptive words. |
Example: | Example: |
The softest sound intensity that can be heard is 0 dB. | Z |
loudness
wave speed (equation)
wave speed = wavelength * frequency
wave period (equation)
wave period = 1 / frequency