Multiple Comparison Tests and ANOVA Analysis
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
ANOVA
Analysis of variance for comparing means.
Null hypothesis
Assumes no difference between group means.
Alternate hypothesis
Indicates at least one mean differs.
Significant F
Indicates at least one mean differs.
Multiple comparison tests
Post hoc tests for pairwise mean comparisons.
Post hoc tests
Conducted after ANOVA to explore differences.
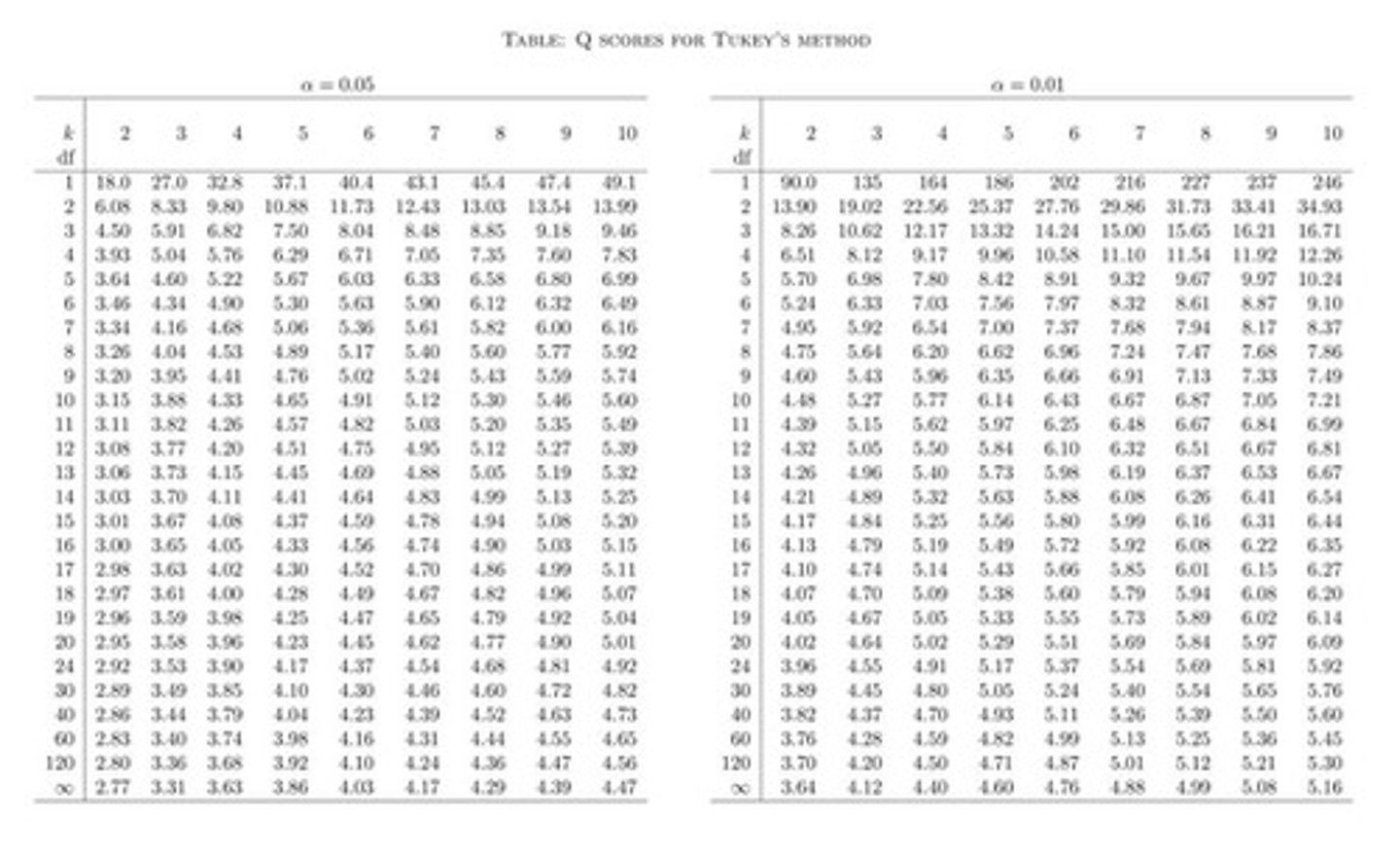
Tukey's HSD test
Honestly significant difference for multiple comparisons.
John Tukey
Statistician who developed Tukey's HSD test.
Type I error
Incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis.
Type II error
Failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
Placebo
Control treatment with no active ingredient.
Mean driving ability
Average driving scores across treatment groups.
Degrees of freedom (df)
Number of independent values in a calculation.
HSD value
Critical value for Tukey's HSD test.
Effect size (ω²)
Measure of variance explained by treatment.
Significant difference
Difference exceeding critical HSD value.
Common superscripts
Indicate no significant difference between groups.
Absolute difference
Numerical difference between two means.
Mean (M)
Average of a set of values.
Standard deviation (SD)
Measure of data dispersion around the mean.
Computation of Tukey's HSD
Calculating HSD using q and MSW.
Experimentwise error
Cumulative probability of Type I error across tests.
Replication
Repetition of study for validation.
Control Group
Group with no guidance on exam preparation.
Study Group
Group receiving study guidance for exams.
Exam Group
Group receiving exam writing guidance.
Mean Score
Average performance score across groups.
Ho (Null Hypothesis)
Assumes no difference in group means.
Ha (Alternative Hypothesis)
At least one group mean is different.
MSB (Mean Square Between)
Variance among group means calculated.
MSW (Mean Square Within)
Variance within groups calculated.
Degrees of Freedom Total
Total cases minus one; df=29.
Degrees of Freedom Between
Number of groups minus one; df=2.
Degrees of Freedom Within
Total df minus between df; df=27.
F-Statistic
Ratio of MSB to MSW; F=3.63.
F-critical Value
Threshold to compare against F-calc; F=3.35.
Reject Ho
Decision made when F-calc exceeds F-critical.
ANOVA Table
Summarizes variance sources and statistics.
Effect Size (ω²)
Measures strength of group differences; ω²=0.15.
Tukey's HSD Test
Post-hoc test for multiple comparisons.
q Value
Critical value from Tukey's table; q=3.53.
HSD (Honestly Significant Difference)
Minimum difference to declare significance.
Absolute Difference
Difference in means between groups.
Significant Effect
Advice type significantly influenced exam performance.
Presentation of Results
Visual representation of mean test scores.
F-test
Statistical test for comparing variances.
Significant F
Indicates at least one group mean differs.
Multiple comparison tests
Post hoc tests after significant ANOVA results.
Tukey's HSD test
Used for comparing means across groups.
ANOVA
Analysis of variance for comparing multiple groups.
Within-subjects design
Same subjects tested under all conditions.
Between-subjects design
Different subjects tested under different conditions.
Null hypothesis
Assumes no effect or difference exists.
Alternate hypothesis
Assumes an effect or difference exists.
Degrees of freedom (d.f.)
Number of independent values in a calculation.
MSB
Mean square between groups in ANOVA.
MSW
Mean square within groups in ANOVA.
Q statistic
Used in Tukey's HSD for mean comparisons.
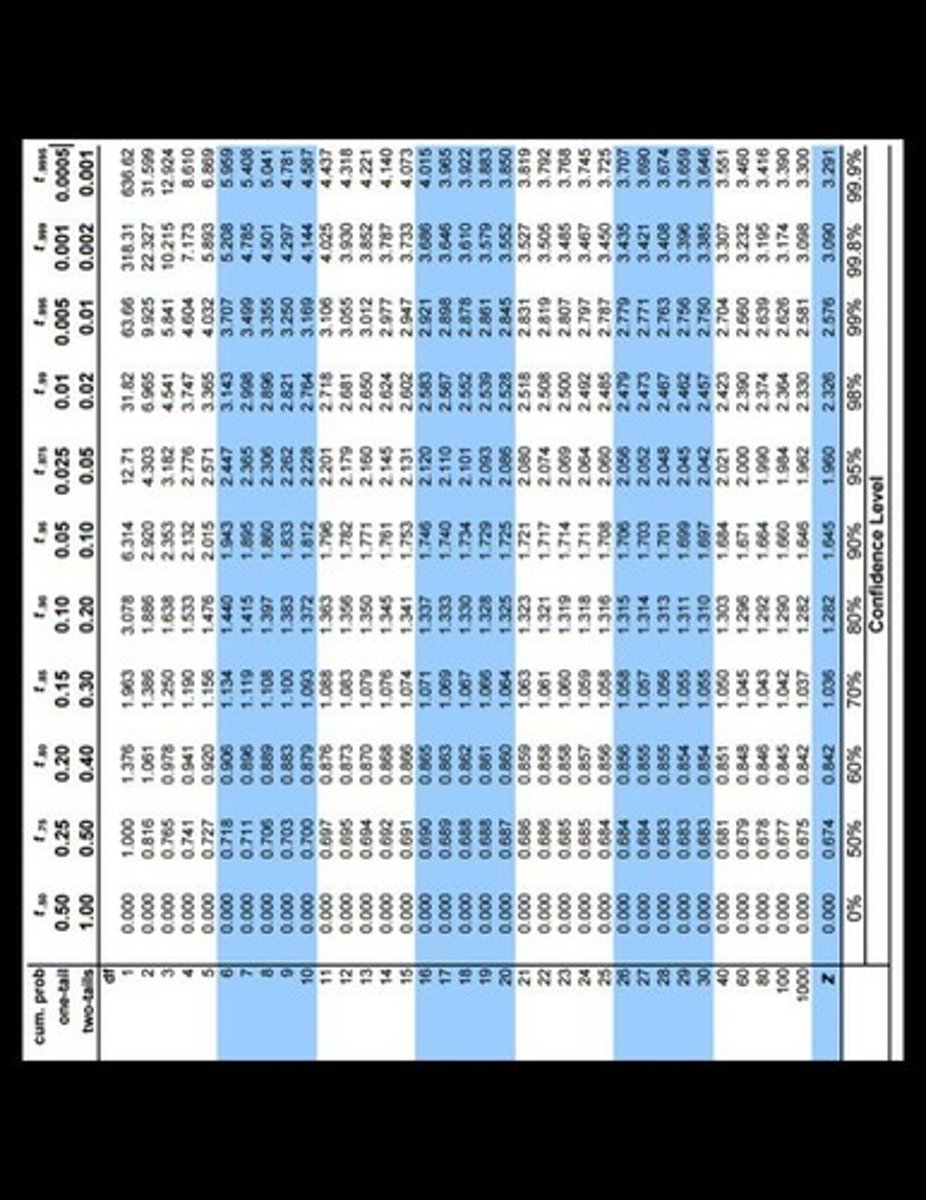
Critical t table
Table for determining t-test significance.
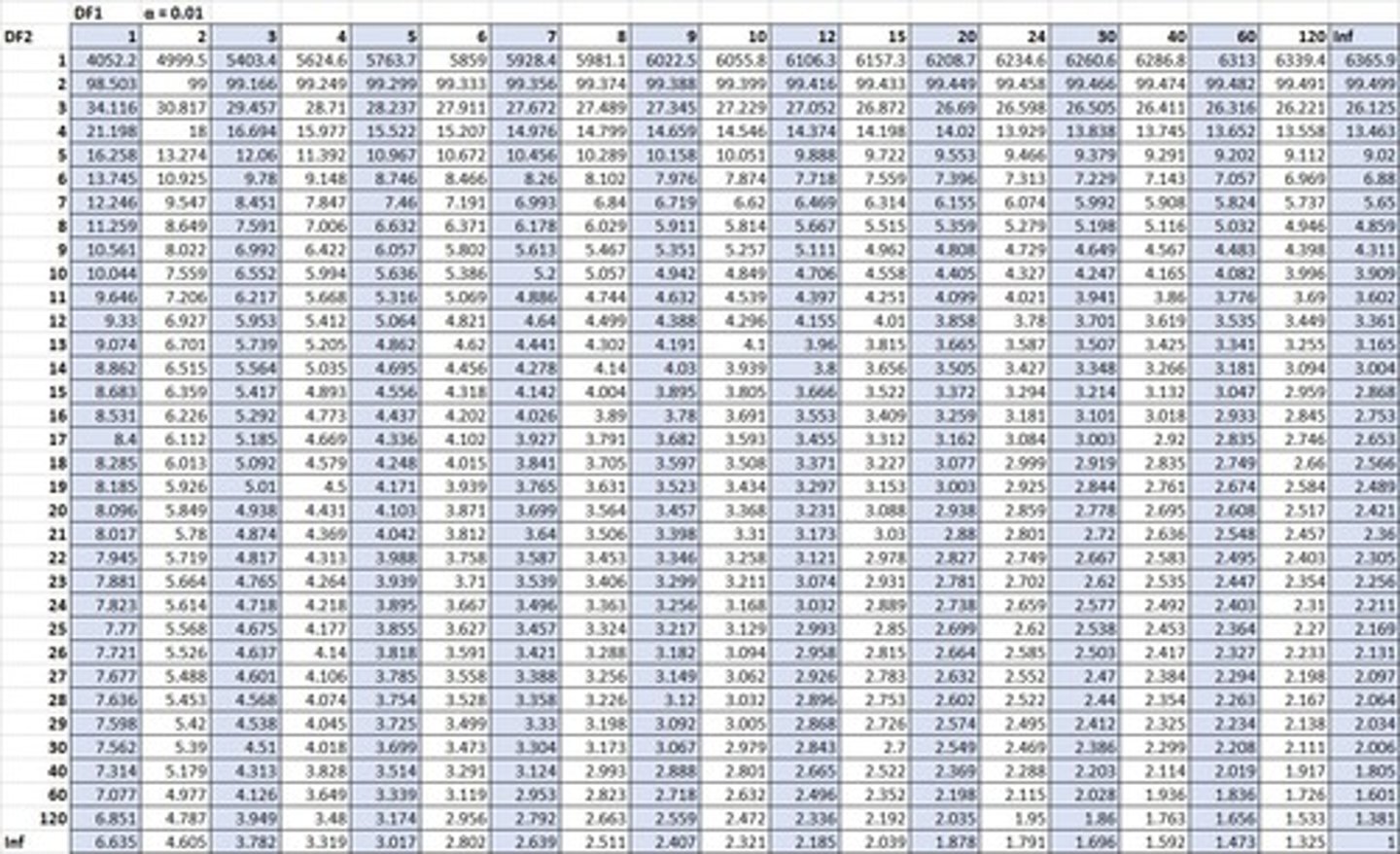
Critical F table
Table for determining ANOVA significance.
Pooled variance
Combined variance estimate from multiple samples.
Effect size
Quantifies the magnitude of a treatment effect.
Anxiety rating scale
Scale from 1 (no anxiety) to 10 (high anxiety).
Practice problem set
Exercises to prepare for midterm calculations.
Jamovi
Statistical software for data analysis.
Reporting decimal answers
Final answers should be to two decimal places.
Compelling reason
Justification for choosing an alternative test.
Random selection
Participants chosen randomly for study conditions.
Meditation intervention
Treatment involving meditation to assess anxiety effects.
Anxiety differences
Variations in anxiety ratings between meditation conditions.