Cell Structure
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
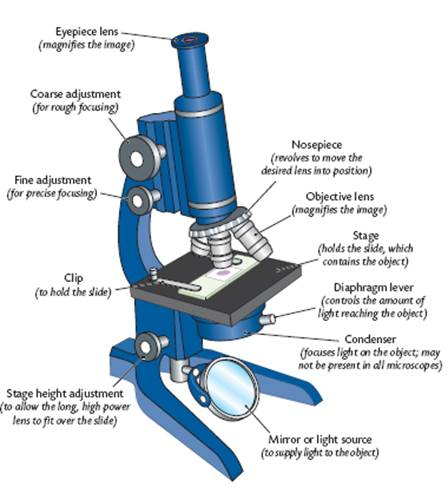
Microscopes (Light Microscope)
Uses 2 lenses.
Magnification = Power of eyepiece lens x Objective lens
Light Microscope (Diagram)
Microscope (Electron Microscope)
Electron instead of light
Transmission electron microscope: A beam of electrons passes through a thin specimen to show the internal structure.
Scanning electron microscope: Shows the surface structure.
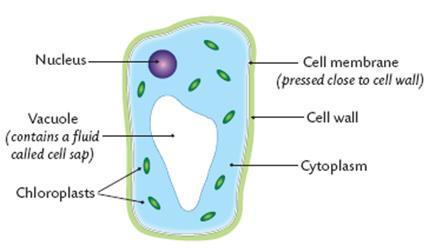
Cell structure (Plant cell Diagram) under (light) microscope
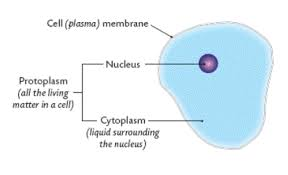
Cell Structure (Animal cell Diagram) under (light) microscope
Cell Structure (Functions)
Selectively Permeable
Regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell
Cell Ultrastructure
The detailed structure as seen using an electron microscope
Cell Components (7)
Cell membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cell wall (Plant Only)
Chloroplasts (Plants Only)
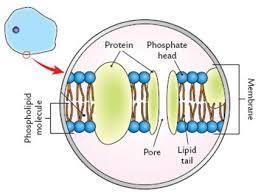
Cell Membrane (plasma)
Composed of phospholipid bilayer and proteins.
Phospholipids have a water loving (hydrophilic) and a water hating (hydrophobic) lipid group.
Functions:
Retain the cell contents.
Some support.
Control what enters and exits the cell.
Nucleus
made up of a double membrane.
The nucleolus contains RNA, DNA and proteins and makes ribosomes.
Chromatin = elongated chromosome
Cytoplasm
= The jelly-like liquid that surrounds the nucleus.
Mitochondria
= Where respiration occurs
Ribosomes
= Tiny structures made of RNA and protein
Function: protein synthesis - combine amino acids to make proteins.
Cell wall (Plants Only)
Made of cellulose
Function: Strength and support
Chloroplasts (Plants Only)
Double membrane. contain a green pigment
Function: Photosynthesis
Differences between plant and animal cell
Has a cell wall - does not have a cell wall
May have chloroplasts - Do not have chloroplasts
Has a large vacuole - Does not have a large vacuole
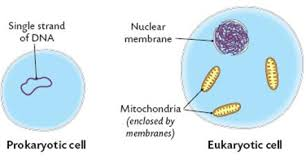
Prokaryotic Cell
Does not have a nucleus or membrane enclosed organelles. e.g. bacteria.
Eukaryotic Cell
Have a nucleus and a membrane. e.g. plants, animals and fungi.
Prokaryotic + Eukaryotic Diagrams
To prepare and examine plant cells using the light microscope.
Step 1: Use a forceps to pull a thin, transparent strip of onions epidermis from between the onion leaves.
Step 2: Place strip on a glass slide.
Step 3: Add a few drops of iodine (makes cells visible).
Step 4: Lower coverslip at an angle to prevent air bubbles.
Step 5: Blot off excess iodine.
Step 6: Examine and draw results.
(Check Booklet for Diagram)
To prepare and examine animal cells using the light microscope.
Step 1: Rinse your mouth out with water.
Step 2: Scrape the inside of your cheek gently with a cotton swap.
Step 3: Spread the smear of cells thinly onto a glass slide.
Step 4: Add a few drops of methylene blue (Stains nucleus dark blue making it visible).
Step 5: Add a cover slip at an angle to avoid air bubbles.
Step 6: Blot off excess stain.
Step 7: Examine under low and high power and draw a labelled diagram of results.
(Check booklet for diagram)
Vacuole
Function = Waste disposal and Support
Cell wall + Cell Membrane (Permeability)
Cell Wall - Fully permeable
Cell Membrane - Selectively permable
Components of Cell Membrane (2)
Phospholipid + Protein