TERM 1 BIOLOGY- Sem 1 24'
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A1 Water, D2.3 Water Potential, B2.1 Membrane structure and transport, A2.2 Cell Structure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
phospholipids spontaneously form vesicles due to
hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties
hypertonic solutions can damage human cells by
dehydrating them
example of a medical isotonic sodium chloride solution
normal saline
normal saline can be used for
rinse wounds, basis for eye drops, frozen for cooling organs, introduced into patient’s blood system via intravenous drip
used medical procedures so cell stay healthy
isotonic solutions
hypotonic solutions can cause human cells to
swell and burst
membrane structure
magnification formula
image size/ actual size
spontaneous formation of vesicles helped
the first cell form a compartmentalised region, semi-permeable
polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons
cohesion
water molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonding
adhesion
water sticking to a solid surface in the form of capillary action
water as a solvent
can only dissolve hydrophilic things such as polar molecules or ions
physical properties of water
buoyancy, viscosity and thermal conductivity
example of water being a good thermal conductor
water is good at maintaining body temperature
osmosis
passive movement of water from low concentration to high concentration
passive
no energy required
isotonic
same concentration
hypotonic
lower concentration
hypertonic
higher concentration
aquaporin
channel protein that allows water to pass through more easily
plant cells have a
cell wall that prevents excess water
animals have
no cell wall
what do other eukaryotes do when they have no cell wall
they have adaptations
turgid
plants are in hypotonic medium
flaccid
when pressure inside drops to atmospheric levels
plasmolysis
in hypertonic solution, membrane shrinks away from cell
lysed
cell bursts in hypotonic solution
shriveled
shrinks in hypertonic solution
normal
when in isotonic solution
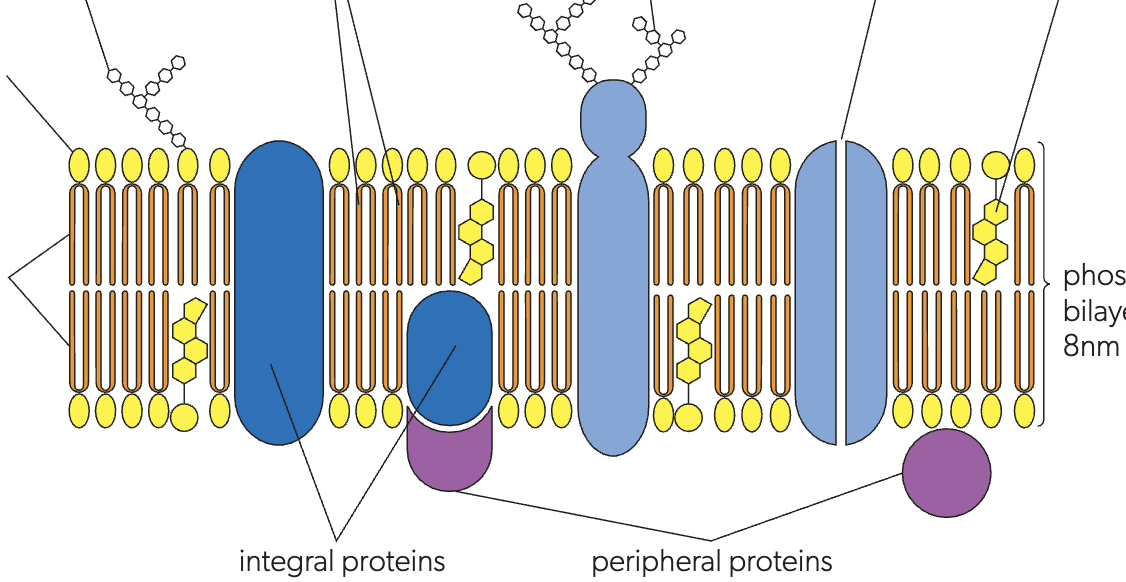
the lipid bilayer
two layers of lipids, controls what enters and leaves the cell
larger molecules are
not as permeable
membrane is not permeable
to polar/charged particles
diffusion
passive movement from high concentration to low concentration
JETRAT
junction, enzymes, transport, recognition, attachment, transduction of hormonal signals
integral proteins
transmembrane proteins, full length of bilayer
peripheral proteins
only attached to the surface
facilitated diffusion
movement of particles from area of low concentration to high concentration through a channel protein
active transport
movement of particles from low concentration to high concentration, requires energy
glycoprotein
protein + carbohydrate, chain extending outside, important for recognition and joining of cells
glycolipids
liquids + carbohydrates, sticking outside, important to eukaryotes and recognition in immune system
fluidity
how easily something can move around
saturated fatty acids
less fluid than unsaturated fatty acids
osmosis
diffusion of water or other solvents through a semipermeable membrane
endocytosis
process of bringing material into the cell by engulfing it
endocytosis process
IPF
IPF definition
indentations, pinches off, forms a vesicle
vesicles are used in the cell to transport
SWFM
SWFM definition
protein synthesis by ribosomes, wrapped in a vesicle, fuses with golgi membrane, golgi modifies it and repackages
exocytosis
process of moving material out of the cell
exocytosis process
OIF
OIF definiton
materials out of the cell, inside a vesicle, fuses with membrane
cell growth process
GPFB
GPFB
membrane growth, vesicles pinch off, fuse with membrane, results in bigger membrane
what bonds are responsible for the cohesive properties of water molecules
hydrogen bonds between water molecules
most enzyme molecules are
hydrophilic and soluble
water molecule diagram
oxygen = slightly negative, hydrogen= slightly positive
why are lipid tails hydrophobic
they and insoluble and non-polar and they provide a barrier between the cell, cytoplasm and external liquids
what is an animal example of buoyancy
black throated loon being able to float on water with feathers
what is an animal example of thermal conductivity
polar bears keeping warm in cold air with better insulation
what is an animal example of low viscosity
animals are more easily able to move in water
what causes rates of diffusion to differ
different concentration gradients at the start
uptake of water by cells in the wall of the intestine and loss of water from a plant cell in a hypertonic environment are
processes that occur by osmosis
cell walls are
structures only found in prokaryotic cells
water molecules are highly cohesive which is
important for transport in xylem
where do hydrogen bonds form
between the slight positive charge of hydrogen and slight negative charge of oxygen in different water molecules
nucleus
Rough ER
Smooth ER
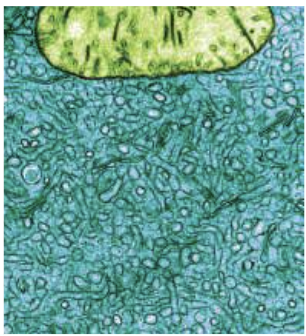
Golgi App
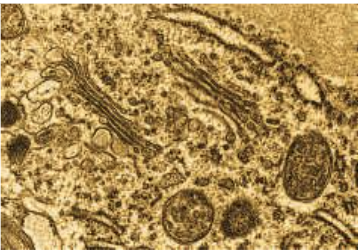
Lysosome
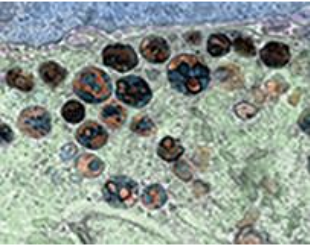
Mitochondrion
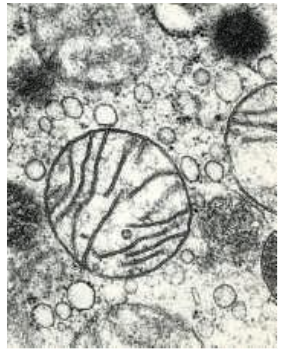
free ribosomes
chloroplast
vacuoles and vesicles
microtubules and centrioles
cytoskeleton
cilia and flagella