BIO FINAL FALL 2025
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
what is the evaluation technique for truth claims?
examine the individual’s credentials, examine the presented data (does it follow the scientific method?), are there other studeis to confirm this data, are there any biases from the individual or organization funding
deoxyribose
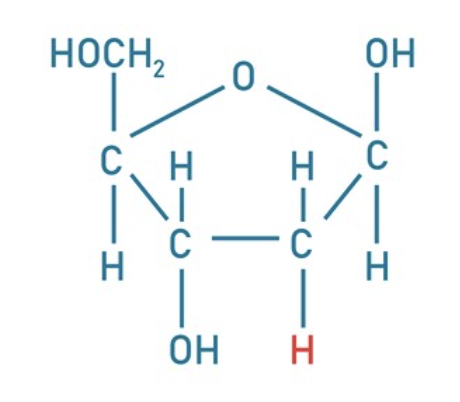
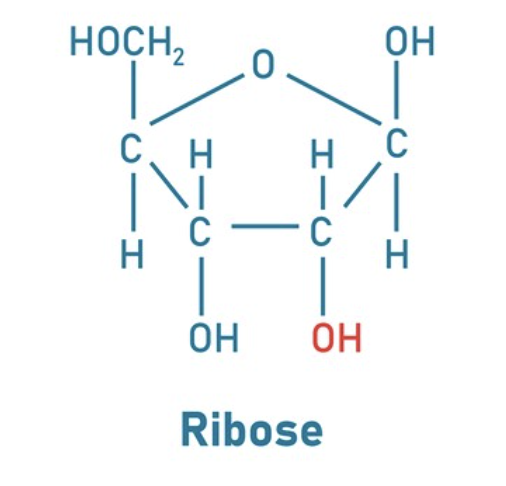
oxyribose
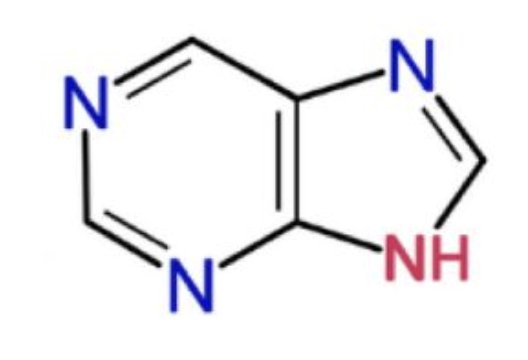
purine
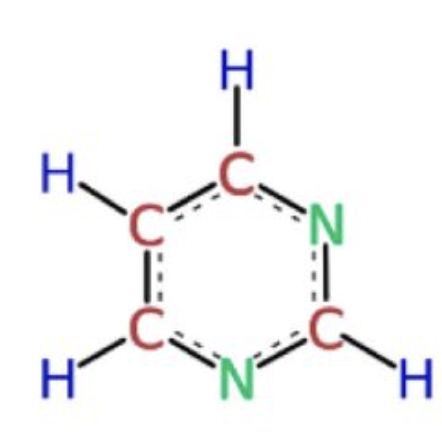
pyrimidine
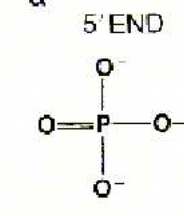
5’ phosphate
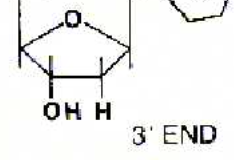
3’ OH
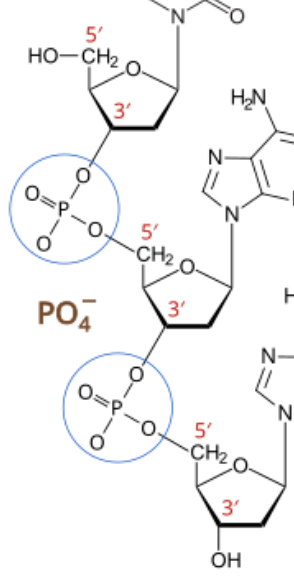
phosphodiester bonds
what is the function of DNA?
stores and copies genetic information in its cells. this information is ultimately used to create the body’s structural, regulatory, and functional proteins
what is the function of RNA?
assists with gene expression by helping to build proteins. it carries genetic instruction across a cell, it transfers amino acids, and it structurally makes up ribosomes.
what is the monomer of DNA and RNA?
nucleotides
phospholipid

triglyceride
cholesterol

what is the function of lipids in a cell
to form the protective cell membrane, store the organism’s long-term energy, insulate and protect the cells, and relay hormonal signals
what is the monomer of a lipid
fatty acids and glycerol
primary protein structure
amino acid sequence in a polypeptide chain
secondary protein structure
local folding from backbone hydrogen bonds (alpha helix spirals and beta pleated sheets)
tertiary protein structure
overall 3D shape formed of a single polypeptide chain formed from R-group interactions
quaternary protein structure
association of multiple polypeptides into one functional unit
lactose
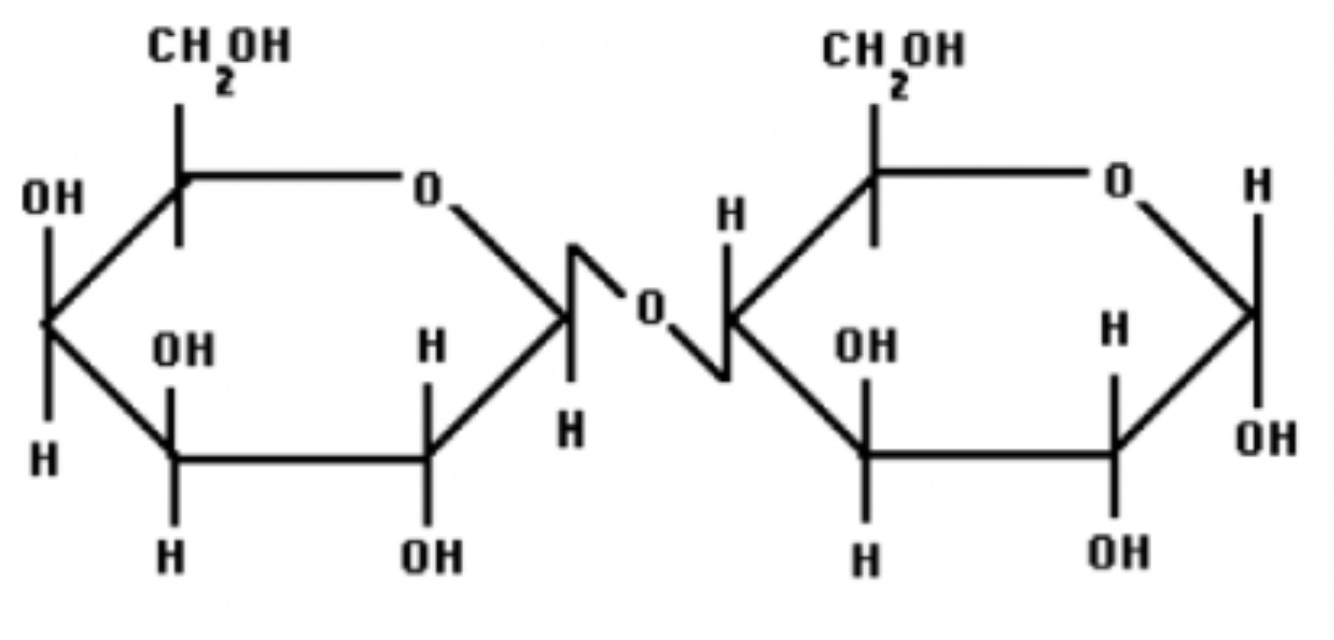
glucose
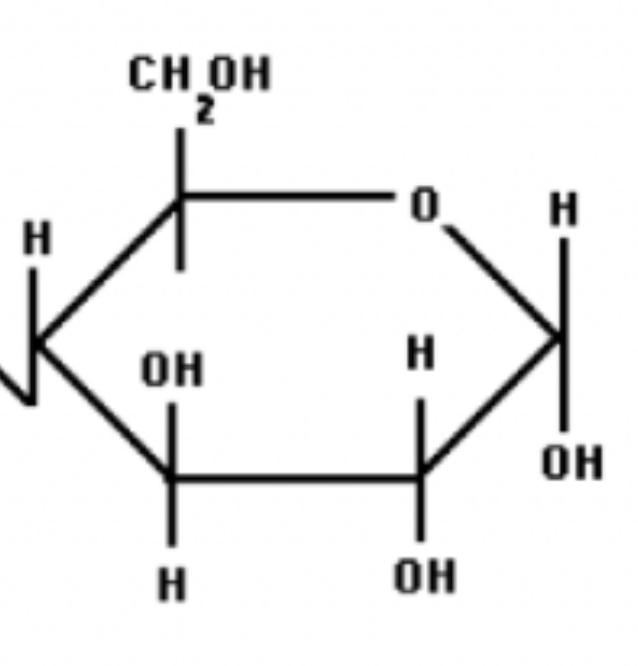
what is the function of carbohydrates?
providing cells with energy that can be immediately used or stored, and offering some structural support in plants and fungi
describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
photosynthesis and cellular respiration form a cycle of energy circulation. in photosynthesis (chloroplast), energy from light drives the production of glucose and oxygen from the atmosphere’s CO2 and H2O. cellular respiration (mitochondria) uses glucose and oxygen to generate ATP, and it releases CO2 and water as by-products into the atmosphere, which will be used again in photosynthesis. The two systems rely heavily on each other to create a continuous energy flow from continuous opposite redox reactions.
what is the equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H20 + energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
where do light dependent reactions occur?
the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast
what are the inputs of a light dependent reaction?
light energy, H2O, ADP and Pi, and NADP+
what are the outputs of a light dependent reaction?
O2, ATP, NADPH
where does the calvin cycle take place?
the stroma of the chloroplast
what are the inputs of the calvin cycle?
CO2, ATP, NADPH
what are the outputs of the calvin cycle?
G3P, ADP and Pi, and NADP+
what is the equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy
where does glycolysis take place?
the cytosol (outside the mitochondria)
what are the inputs of glycolysis?
glucose, 2 ADP + Pi, 2 NAD+
what are the outputs of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 2 net ATP, and 2 NADH
where does the krebs cycle take place?
the mitochondrial matrix
what are the inputs for the krebs cycle?
2 acetyl-CoA, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD, 2 ADP + Pi
what are the outputs of the krebs cycle?
4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP
where does oxidative phosphorylation take place?
the inner mitochondrial membrane
what are the inputs of oxidative phosphorylation?
NADH, FADH2, O2, ADP + Pi
what are the outputs of oxidative phosphorylation?
approx. 30 ATP, H2O, NAD+ and FAD
what is the structure of the sodium-potassum pump?
it consists of binding sites for 3Na+ ions, 2 K+ ions, and ATP.
what is the functionality of the sodium-potassium pump?
3 Na+ ions from inside of the cell bind to the pump, ATP is broken down and phosphorylates the pump, the pump moves and pushes the Na+ out of the cell. while facing the outside, 2 K+ ions bind, the phosphate detatches from the pump, it goes back to its original state and releases 2 K+ inside of the cell.
what is the purpose of the sodium potassium pump
to keep the cell’s inside slightly negative, and to control the sodium and water ratio to prevent swelling and bursting (Na+ naturally wants to come in and water will follow)
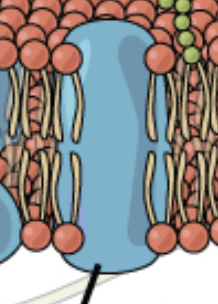
identify the components of a phospholipid
a glycerol backbond, two hydrophobic fatty acid tails (unsaturated is kinked), and a phosphate and R-group head.
explain how the chemical composition of phospholipids creates a lipid bilayer
the hydrophilic heads face the watery extracellular fluid and cytoplasm, and the tails face each other to create a dry bilayer that forms the structure for the cell membrane.
glycoprotein
glycolipid
protein channel

cholesterol
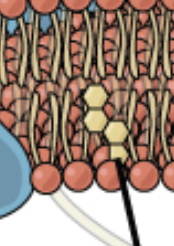
cytoskeletal filaments

integral membrane protein
peripheral membrane protein

what is the dna like in a prokaryotic cell?
single, circular chromosome in the nucleoid
pillus

capsule

cell wall

cell membrane
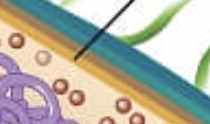
ribosomes

chromosome

flagelli

describe the structure of eukaryotic dna
long, linear DNA double helices tightly wound around histone proteins to form chromatin, which is compacted into multiple chromosomess within the cell’s nucleus
state the function of the nucleus
stores the cell’s DNA, controls cell activity by regulating gene expression
state the function of the mitochondria
produces ATP through cellular respiration, regulates metabolism and apoptosis
state the function of the rough ER
studded with ribosomes, so it helps synthesize proteins
state the function of the smooth ER
synthesizes lipids (fats, phospholipids, steroids) ,detoxifies drugs/toxins, and stores calcium
state the function of the golgi apparatus
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids, and sends them to their final destination in the cell
state the function of chloroplasts
the site of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted to chemical energy (and O2g); contains chlorophyll
describe what happens in the G1 phase
cell grows, organelles replicate, the cell prepares the materials that will be needed for DNA replication, and normal metabolic activities continue
describe what happens in the S phase
DNA replication occurs— each chromosome duplicates into 2 sister chromatids
describe what happens in the G2 phase
additional cell growth, production of special proteins for mitosis, and checking for DNA damage/incomplete replication
describe what happens in the M phase
mitosis: prophase (chromosomes condense and spindles form), metaphase (chromosomes line up at the cell’s equator), anaphase ( sister chromatids separate to opposite poles), and telophase (new nuclei form around separated chromatids). cytokinesis: the cell splits into two genetically identical daughter cells.
what is the purpose of the G1 checkpoint?
to prevent unhealthy cells from replicating their DNA
what is the purpose of the G2 checkpoint?
to ensure that the DNA was replicated correctly and to prevent cells with mutations or incomplete DNA from entering mitosis
what is the purpose of the M checkpoint?
to ensure that the sister chromatids will separate accurately so each daughter cell gets a full set of chromosomes.
what is the purpose of mitosis?
to make two identical diploid cells for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction
what is the purpose of meiosis?
to make four genetically unique haploid gametes for sexual reproduction
describe the parent cell in mitosis
diploid with a full set of chromosomes (46 in humans); each chromosome has 2 sister chromatids (it has already been replicated)
describe the daughter cells in mitosis
2 diploid daughter cells are identical to each other and to the parent cell; each chromosome is now a single chromatid, just like the parent before prophase
describe the parent cell in meiosis
diploid with a full set of chromosomes (46 in humans); each chromosome is 2 sister chromatids (it has already been replicated)
describe the daughter cells after meiosis I
2 haploid daughter cells → they now have one chromosome from each homologous pair. each chromosome has two sister chromatids.the cells are not identical because homologous chromosome pairs were separated and crossing over may have occurred.
describe the daughter cells after meiosis II
4 haploid daughter cells → each chromosome is one chromatid. all four cells are genetically different due to crossing over and independent assortment in meiosis I.
what makes up the central dogma of biology
translation (DNA to RNA) and transcription (RNA to a protein)
write a small overview of DNA replication (include semi-conservative, DNA template strand, separating DNA strands, DNA polymerase, 5’ to 3’ synthesis, leading strand, lagging strand)
a semi-conservative process— each new DNA molecule contains one original DNA template strand and one newly synthesized strand. replication begins by separating the DNA strands, allowing enzymes to have access to each strand. DNA polymerase then builds new DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Since the two strands will run in opposite orientations, synthesis occurs differently on each. on the leading strand, DNA polymerase continuously adds nucleotides. on the lagging strand, it must synthesize DNA in short fragments because of its 5’ to 3’ reading orientation.
write a small overview of transcription (include RNA polymerase, DNA template strand, 5’ to 3’ synthesis, and non-template strand)
a process in which RNA polymerase uses a DNA template strand to build the complementary RNA molecule. after the DNA is unwound, RNA polymerase binds to the template strand and carries out 5’ to 3’ synthesis, adding RNA nucleotides that pair with the template’s bases. the opposite DNA strand (non-template strand) has the same sequence as the newly made RNA, with thymines instead of uracil. this process produces an rna copy of a gene.
write a small overview of translation (include ribosome, RNA template, codon, tRNA, anticodon, A site, P site, and E site)
a process in which a ribosome reads an RNA template to build a protein. the ribosome moves along the mRNA one codon at a time. each codon specifies an amino acid. tRNA molecules bring these amino acids to the ribosome, each amino acid carrying an anticodon complementary to the mRNA. the ribosome cycles through three binding sites: the A site (where tRNA enter), the P site (where the growing polypeptide chain is growing), and the E site (where uncharged tRNA exit). through this, amino acids are linked to form a polypeptide chain.
which way is a DNA template READ?
3’ to 5’
which way is a DNA template MADE?
5’ to 3’
which way is an RNA template READ?
5’ to 3’
what happens in mutation to change allelic frequencies
single alleles can sometimes change randomly. if there is no survival advantage present, it becomes lost
what happens in gene flow to change allelic frequencies
certain portions of a species may migrate, therefore changing available populations
what happens in genetic drift to change allelic frequencies
largely devastating natural event changes the numbers of a population
what happens in selection to change allelic frequencies
adaptive changes become more common over time
explain how allopatric speciation causes evolution
a population is physically separated into two or more isolated groups. different mutations, natural selection pressures, and genetic drift act independently on these species, which causes evolution over a long period of time
explain how sympatric speciation causes evolution
a new species forms without physical separation. this is done through commonalities like polyploidy (extra chromosomes) or behavioral isolation (mating preferences change) that make it impossible for a species to interbreed with its original species.
explain how to combat the misconception that evolution is just a theory
it is not “just” a theory— theories are thoroughly tested and verified
explain how to combat the misconception that evolution means that individuals can evolve
an individual cannot change over time— a population can
explain how to combat the misconception that evolution is trying to explain the origins of life
evolution describes a change in allelic frequency— not the origins of life
explain how to combat the misconception that organisms evolve on purpose
mutations are completely random. certain mutations can be selected if there is a fitness advantage with them. mutations cannot be willed.