StemUp: OCR A A level Biology 5.1.4 Hormonal communication
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
How does endocrine communication occur? (4)
1. Specialised glands secrete hormones into bloodstream
2. Circulatory system carries hormone to target cell / tissue
3. Hormones will diffuse into cell and bind to complementary receptor in cytoplasm
4. Peptide hormones will bind to complementary receptor on cell-surface membrane
Draw and label the structure of the adrenal glands (3)
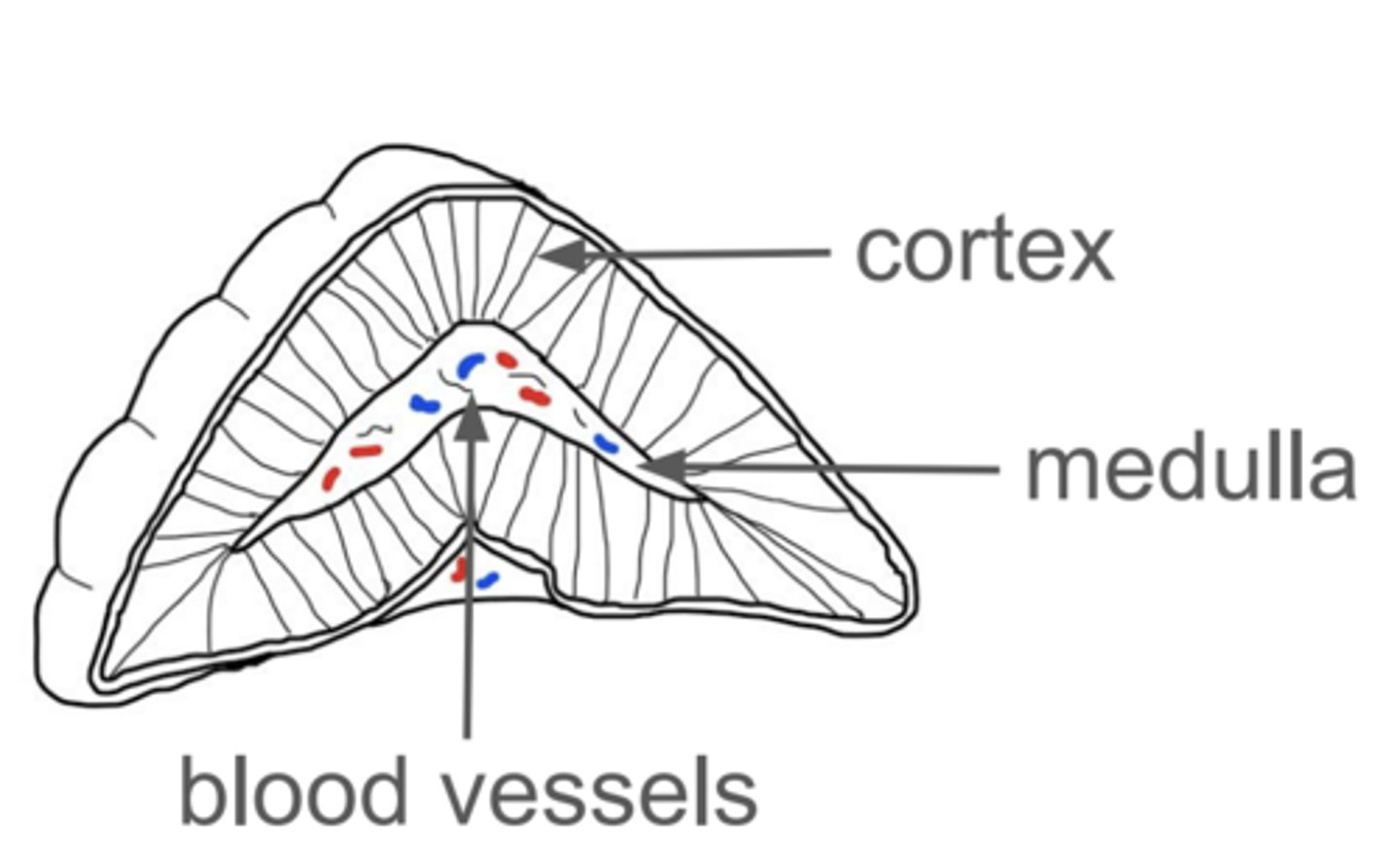
What hormone does the medulla secrete and why? (2)
- Adrenaline
- In response to danger or stress - fight or flight
Which hormones does the cortex secrete and what is their functions? (4)
- Mineralocorticoids - e.g. aldosterone
- Which targets kidney and gut to control the concentration of sodium + potassium ions in blood
- Glucocorticoids - e.g. cortisol and corticosterone
- Which stimulate an increase in blood glucose concentration
What are the two main functions of the pancreas? (3)
- The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions
- Exocrine = produces digestive enzymes that are secreted into the small intestine
- Endocrine = produces hormones like insulin and glucagon in the Islets of Langerhans to regulate blood glucose levels
What are the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas? (2)
- The endocrine tissues in the pancreas
- That are responsible for producing hormones like insulin and glucagon
What cells are found in the Islets of Langerhans? (2)
- Alpha cells = produce glucagon
- Beta cells = produce insulin
How can the Islets of Langerhans be identified in a stained section of the pancreas? (3)
- Appear lighter in color
- Are scattered throughout the darker exocrine tissue
- They contain both alpha and beta cells
How does the hormone insulin regulate blood glucose levels? (3)
- Insulin is released from beta cells in the pancreas when blood glucose levels are high
- It stimulates the liver to convert glucose to glycogen (glycogenesis) and increases the uptake of glucose by cells
- Lowering blood glucose levels
How does the hormone glucagon regulate blood glucose levels? (3)
- Glucagon is released from alpha cells in the pancreas when blood glucose levels are low
- It stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose (glycogenolysis) and release glucose into the blood
- Raising blood glucose levels
What is the role of the liver in regulating blood glucose levels? (2)
- Stores excess glucose as glycogen in response to insulin
- And breaks it down into glucose when stimulated by glucagon
How does insulin secretion occur in beta cells of the pancreas? (5)
1. Glucose enters the beta cell through glucose transporters.
2. ATP is produced from glucose metabolism, causing potassium channels to close
3, The cell becomes depolarised, triggering calcium channels to open
4. Calcium ions enter the cell and cause vesicles containing insulin to fuse with the cell membrane
5. Releasing insulin into the blood
What causes Type 1 diabetes mellitus? (2)
- Caused by the immune system attacking and destroying the beta cells in the pancreas
- Preventing insulin production
What causes Type 2 diabetes mellitus? (2)
- Occurs when beta cells do not produce enough insulin
- Or the body's cells become resistant to insulin
How is Type 1 diabetes treated? (2)
- Insulin injections
- Insulin pumps
How is Type 2 diabetes treated? (2)
- Treated with a combination of lifestyle changes (diet and exercise)
- Sometimes medication like metformin or insulin
How is insulin for diabetes treatment produced? (2)
- Using genetically modified bacteria
- These bacteria contain the human insulin gene and produce insulin in large quantities
How might stem cells be used to treat diabetes in the future? (2)
- Could potentially be used to replace damaged or destroyed beta cells in the pancreas
- Allowing patients to produce insulin naturally