AP US Gov & Pol | Unt 1: Chapters 1-3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary an other information that could be important
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
Natural Rights
the idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property
2
New cards
Limited Goverment
The idea that certain restrictions should be placed on government to protect the natural rights of citizens.
3
New cards
John Locke
English philosopher who advocated the idea of a "social contract" in which government powers are derived from the consent of the governed and in which the government serves the people; also said people have natural rights to life, liberty and property.
4
New cards
Social Contract
A voluntary agreement among individuals to secure their rights and welfare by creating a government and abiding by its rules.
5
New cards
Popular Sovereignty
A goverment in which people rule by there own consent
6
New cards
Declaration of Indapendence
Signed in 1776 by US revolutionaries; it declared the United States as a free state.
7
New cards
Articles or Confederation
the original constitution of the US, ratified in 1781, which was replaced by the US Constitution in 1789.
8
New cards
U.S Constitution
The document written in 1787 and ratified in 1788 that sets forth the institutional structure of the U.S. government and the tasks these institutions perform. It replaced the Articles of Confederation.
9
New cards
Repersentitive Democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect representatives, or leaders, to make decisions about the laws for all the people.
10
New cards
participatory democracy
a system of democracy in which all members of a group or community participate collectively in making major decisions
11
New cards
Pluralist Democracy (Pluralism)
a model of democracy in which no one group dominates politics and organized groups compete with each other to influence policy
12
New cards
Elite democracy
a model of democracy in which a small number of people, usually those who are wealthy and well-educated, influence political decision making
13
New cards
Federalist #10
By James Madison, says how to guard against factions, special interest groups, by extending the sphere and making sure nobody gets too much power
14
New cards
Brutus #1 (1787)
Written by Yates (Anti Federalist)
Constitution gives too much power to central government
Necessary and Proper Clause
Supremacy Clause
Can do away with State Governments
Standing Army in peacetime is a destruction of liberty
Once you give up power the only way to get it back is by force- "Many instances can be produced where the people have voluntarily increased the powers of their rulers; but few, if any, in which rulers have willingly abridged their authority."
Constitution gives too much power to central government
Necessary and Proper Clause
Supremacy Clause
Can do away with State Governments
Standing Army in peacetime is a destruction of liberty
Once you give up power the only way to get it back is by force- "Many instances can be produced where the people have voluntarily increased the powers of their rulers; but few, if any, in which rulers have willingly abridged their authority."
15
New cards
Federalists
A term used to describe supporters of the Constitution during ratification debates in state legislatures.
16
New cards
Anti-Federalists
Anti-Federalists rose up as the opponents of the Constitution during the period of ratification. They opposed the Constitution's powerful centralized government, arguing that the Constitution gave too much political, economic, and military control. They instead advocated a decentralized governmental structure that granted most power to the states
17
New cards
central government
a form of government in which the national government has most of the power, while the states have little power
18
New cards
Reserved Powers (10th Amendment)
The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.
19
New cards
Republic
A form of government in which the people select representatives to govern them and make laws.
20
New cards
Factions
Groups such as parties or interest groups, which according to James Madison arose from the unequal distribution of property or wealth and had the potential to cause instability in government.
21
New cards
Shay's Rebellion (1786)
This MA conflict caused criticism of the Articles of Confederation; weak govt; increased calls for a Constitutional Convention to revise the Articles
22
New cards
Virgina Plan
Virginia delegate James Madison's plan of government, in which states got a number of representatives in Congress based on their population
23
New cards
New Jersey Plan
The proposal at the Constitutional Convention that called for equal representation of each state in Congress regardless of the state's population.
24
New cards
The Great Compromise
Compromise made by Constitutional Convention in which states would have equal representation in one house of the legislature and representation based on population in the other house
25
New cards
Three-Fifths Compromise
Compromise between northern and southern states at the Constitutional Convention that three-fifths of the slave population would be counted for determining direct taxation and representation in the House of Representatives.
26
New cards
Slave Trade Compromise
Congress could not regulate or outlaw slavery or slave trade until 1808
27
New cards
ex post facto law
a law that makes an act criminal although the act was legal when it was committed
28
New cards
Electoral College
a body of people representing the states of the US, who formally cast votes for the election of the president and vice president.
29
New cards
Amendment Process
step 1: amendment proposed by 2/3 vote of both houses of congress OR a constitutional convention called by congress on petition of 2/3 out of 50 states. THEN amendment ratified by 3/4 of the 50 state legislatures OR 3/4 of special constitutional conventions called by 50 states THEN the new amendment!
30
New cards
Supremacy Clause
It establishes that the federal constitution, and federal law generally, take precedence over state laws, and even state constitutions.
31
New cards
Ratification
Formal of approval
32
New cards
Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power
33
New cards
Separation of Powers
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law
34
New cards
Federalist #51 (Madison)
1. "If men were angels, no government would be necessary"
2. Republican Govt. = Legislature is the Strongest Branch
\-potential to become tyrannical
3. Three Auxiliary Precautions = Safeguard Against Tyranny
\-Separation of Powers
\-Checks and Balances
\-Federalism
35
New cards
tyranny of the majority
the tendency in democracies to allow majority rule to neglect the rights and liberties of minorities
36
New cards
exclusive powers
Those powers that can be exercised by the National Government alone
37
New cards
concurrent powers
Powers held jointly by the national and state governments.
38
New cards
conditions of aid
terms set by the national government that states must meet if they are to receive certain federal funds
39
New cards
Grants
money given by the national government to the states
40
New cards
revenue sharing
federal sharing of a fixed percentage of its revenue with the states
41
New cards
Mandates
terms set by the national government that states must meet whether or not they accept federal grants
42
New cards
categorical grants
Federal grants for specific purposes
exp: building an airport
exp: building an airport
43
New cards
Block Grants
Federal grants given more or less automatically to states or communities to support broad programs in areas such as community development and social services
44
New cards
Necessary and Proper Clause
Clause of the Constitution (Article I, Section 8, Clause 3) setting forth the implied powers of Congress. It states that Congress, in addition to its express powers, has the right to make all laws necessary and proper to carry out all powers the Constitution vests in the national government
45
New cards
Commerce Clause
The clause in the Constitution (Article I, Section 8, Clause 1) that gives Congress the power to regulate all business activities that cross state lines or affect more than one state or other nations.
46
New cards
enumerated powers
The powers explicitly given to Congress in the Constitution.
47
New cards
Implied Powers of Congress
Powers not specifically written in the Constitution.
48
New cards
inherent powers
Powers the Constitution is presumed to have delegated to the National Government because it is the government of a sovereign state within the world community
49
New cards
state sovereignty
the concept that states have the right to govern themselves independent of the federal government
50
New cards
Supreme Court of the United States
The highest court in the federal judiciary specifically created by the Constitution. It is composed of nine justices and has appellate jurisdiction over lower federal courts and the highest state courts. It also possesses a limited original jurisdiction.
51
New cards
McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
Maryland was trying to tax the national bank and Supreme Court ruled that federal law was stronger than the state law (result/significance: Congress has IMPLIED powers to create a necessary and proper bank)
52
New cards
United States v. Lopez (1995)
Congress may NOT use the commerce clause to make possession of a gun in a school zone a federal crime
53
New cards
Which is the most democratic institution of goverment that repersennts the farmers commitment to a limited repubic
A- U.S. Senate
B-Supreme Court
C-U.S. House of Repersentives
D-Electoral Collage
A- U.S. Senate
B-Supreme Court
C-U.S. House of Repersentives
D-Electoral Collage
C-U.S. House of Repersentives
54
New cards

Which of the following is an acurate comparison of political philosophies of John Locke and Thomos Hobbes?
B
55
New cards
Which of the following is a chief argument in James Masisons Federalist 10
A- A bill of rights is necessary to secure liberty
B- Free speech be added to the constitution
C- Judicial review will prevent harsh laws against the citizenry
D-A large, diverse republic will tame the mischiefs of factions
A- A bill of rights is necessary to secure liberty
B- Free speech be added to the constitution
C- Judicial review will prevent harsh laws against the citizenry
D-A large, diverse republic will tame the mischiefs of factions
D-A large, diverse republic will tame the mischiefs of factions
56
New cards
“We . . . do by these presents, solemnly and mutually, in the presence of God and one another, covenant and combine ourselves together into a civil body politic, for our better ordering and preservation . . . \[and\] do enact, constitute, and frame, such just and equal laws, ordinances, acts, constitutions, and officers, from time to time, as shall be thought most meet and convenient for the general good of the colony.”
\
Which of the following statements best reflects the authors’ perspective? (A) The authors believed faith is the strongest guiding principle to maintain social order.
(B) The authors recognized their right to collective self-rule even as British subjects.
(C) The authors created their pact in order to break away from British religious persecution.
(D) The authors believed that everyone in the colony should share the same religion.
\
Which of the following statements best reflects the authors’ perspective? (A) The authors believed faith is the strongest guiding principle to maintain social order.
(B) The authors recognized their right to collective self-rule even as British subjects.
(C) The authors created their pact in order to break away from British religious persecution.
(D) The authors believed that everyone in the colony should share the same religion.
(B) The authors recognized their right to collective self-rule even as British subjects.
57
New cards
“We . . . do by these presents, solemnly and mutually, in the presence of God and one another, covenant and combine ourselves together into a civil body politic, for our better ordering and preservation . . . \[and\] do enact, constitute, and frame, such just and equal laws, ordinances, acts, constitutions, and officers, from time to time, as shall be thought most meet and convenient for the general good of the colony.”
\
Which of the Enlightenment philosophies is most consistent with the ideas in the passage?
\
(A) Hobbes’s state of nature
(B) Locke’s consent of the governed
(C) Rousseau’s refusal to accept a social contract
(D) Montesquieu’s belief in limited government
\
Which of the Enlightenment philosophies is most consistent with the ideas in the passage?
\
(A) Hobbes’s state of nature
(B) Locke’s consent of the governed
(C) Rousseau’s refusal to accept a social contract
(D) Montesquieu’s belief in limited government
(A) Hobbes’s state of nature
58
New cards
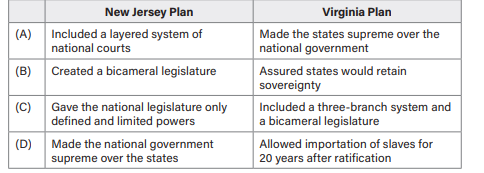
Which of the following is an accurate comparison of the New Jersey Plan and the Virginia Plan?
C
59
New cards
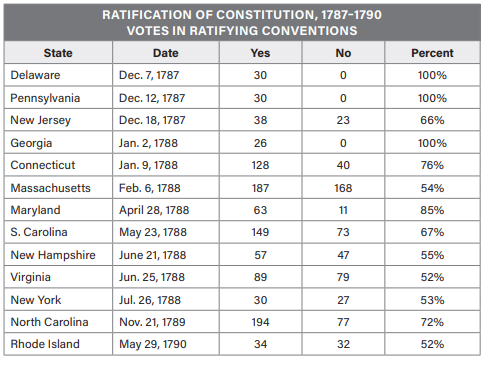
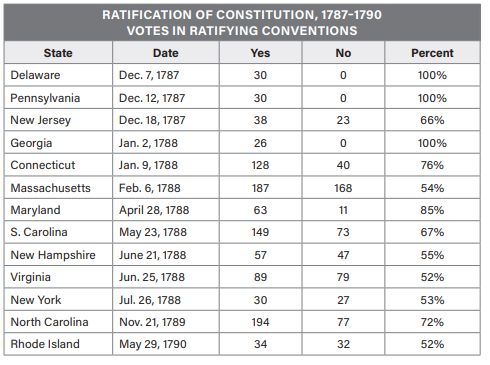
Which statement most accurately reflects the data in the table?
\
(A) The Great Compromise had little influence on states’ votes.
(B) The number of states required by Article VII to ratify the Constitution was reached by June 1788.
(C) The Articles of Confederation had more support than the Constitution.
(D) The highest Anti-Federalist sentiment was seen in New Jersey, Delaware, and Georgia.
\
(A) The Great Compromise had little influence on states’ votes.
(B) The number of states required by Article VII to ratify the Constitution was reached by June 1788.
(C) The Articles of Confederation had more support than the Constitution.
(D) The highest Anti-Federalist sentiment was seen in New Jersey, Delaware, and Georgia.
(B) The number of states required by Article VII to ratify the Constitution was reached by June 1788.
60
New cards
The process depicted in the above chart reflects which governmental concept?
\
(A) Direct democracy
(B) Representative republic
(C) Checks and balances
(D) Judicial review
\
(A) Direct democracy
(B) Representative republic
(C) Checks and balances
(D) Judicial review
(B) Representative republic
61
New cards
Which of the following is the best example of results from political negotiation and compromise at the Constitutional Convention?
\
(A) The creation of the House and Senate
(B) Establishing a federal court system
(C) Protecting individual property rights
(D) Determining which citizens could vote in elections
\
(A) The creation of the House and Senate
(B) Establishing a federal court system
(C) Protecting individual property rights
(D) Determining which citizens could vote in elections
(A) The creation of the House and Senate
62
New cards
Each State shall appoint, in such Manner as the Legislature thereof may direct, a Number of Electors, equal to the whole Number of Senators and Representatives to which the State may be entitled in the Congress: but no Senator or Representative, or Person holding an Office of Trust or Profit under the United States, shall be appointed an Elector . . . The Congress may determine the Time of choosing the Electors, and the Day on which they shall give their Votes; which Day shall be the same throughout the United States.
\
The above passage defines which of the following constitutional structures or procedures?
\
(A) Lawmaking requirements
(B) The presidential selection process (C) The necessary and proper clause (D) Ratification requirements
\
The above passage defines which of the following constitutional structures or procedures?
\
(A) Lawmaking requirements
(B) The presidential selection process (C) The necessary and proper clause (D) Ratification requirements
(B) The presidential selection process
63
New cards
Each State shall appoint, in such Manner as the Legislature thereof may direct, a Number of Electors, equal to the whole Number of Senators and Representatives to which the State may be entitled in the Congress: but no Senator or Representative, or Person holding an Office of Trust or Profit under the United States, shall be appointed an Elector . . . The Congress may determine the Time of choosing the Electors, and the Day on which they shall give their Votes; which Day shall be the same throughout the United States.
\
The above procedure explained in Article II resulted from which of the following?
\
(A) The drafting of the Bill of Rights
(B) A belief that the popular vote should elect the president
(C) A compromise necessary for the adoption of the Constitution
(D) The successful war against Great Britain
\
The above procedure explained in Article II resulted from which of the following?
\
(A) The drafting of the Bill of Rights
(B) A belief that the popular vote should elect the president
(C) A compromise necessary for the adoption of the Constitution
(D) The successful war against Great Britain
(C) A compromise necessary for the adoption of the Constitution
64
New cards
Which of the following statements accurately describes federalism?
\
(A) It is a governing system that places a national authority above regional authority.
(B) It ranks the sovereignty of the states over the power of the national government.
(C) It is a balance of powers between state and local governments.
(D) It is a sharing of powers between national and state governments.
\
(A) It is a governing system that places a national authority above regional authority.
(B) It ranks the sovereignty of the states over the power of the national government.
(C) It is a balance of powers between state and local governments.
(D) It is a sharing of powers between national and state governments.
(D) It is a sharing of powers between national and state governments.
65
New cards
In the McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) decision, which two provisions in the Constitution were upheld and strengthened?
\
(A) Congress’s power to regulate commerce and its power to levy taxes (B) The necessary and proper clause and the supremacy clause
(C) The First and Tenth amendments (D) The president’s power to nominate justices and negotiate treaties
\
(A) Congress’s power to regulate commerce and its power to levy taxes (B) The necessary and proper clause and the supremacy clause
(C) The First and Tenth amendments (D) The president’s power to nominate justices and negotiate treaties
(B) The necessary and proper clause and the supremacy clause
66
New cards
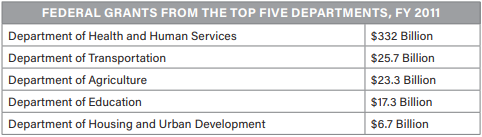
Which of the following statements is reflected in the table above?
\
(A) Education and agricultural needs receive the most federal grant money. (B) Federalism prevents the national government from assisting with state responsibilities.
(C) Grants appear to assist urban development, not agricultural interests.
(D) Medical and social needs receive the most federal grant money.
\
(A) Education and agricultural needs receive the most federal grant money. (B) Federalism prevents the national government from assisting with state responsibilities.
(C) Grants appear to assist urban development, not agricultural interests.
(D) Medical and social needs receive the most federal grant money.
(D) Medical and social needs receive the most federal grant money.
67
New cards
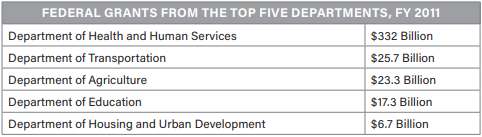
Which governmental concept most likely results in lower funding for Education and Housing and Urban Development than for the other departments?
(A) Checks and balances prevent funding of these concerns.
(B) Federalism encourages states and localities to provide primary support for these services.
(C) Judicial review and court decisions have rendered government unable to provide these services.
(D) Separation of powers results in lower funding of these concerns.
(A) Checks and balances prevent funding of these concerns.
(B) Federalism encourages states and localities to provide primary support for these services.
(C) Judicial review and court decisions have rendered government unable to provide these services.
(D) Separation of powers results in lower funding of these concerns.
(B) Federalism encourages states and localities to provide primary support for these services.
68
New cards
69
New cards

Which of the following statements best describes the message expressed in the cartoon?
\
(A) Government overlap creates too many taxes and fees at multiple levels.
(B) Taxpayers are obligated to support multiple levels of government.
(C) Regulations for transportation and safety should be at the state level.
(D) Taxes and fees will be collected at convenient times.
\
(A) Government overlap creates too many taxes and fees at multiple levels.
(B) Taxpayers are obligated to support multiple levels of government.
(C) Regulations for transportation and safety should be at the state level.
(D) Taxes and fees will be collected at convenient times.
(A) Government overlap creates too many taxes and fees at multiple levels.
70
New cards

Which of the following concepts would the cartoonist most likely support?
(A) Commercial development
(B) Devolution
(C) Categorical grants
(D) Mandates
(A) Commercial development
(B) Devolution
(C) Categorical grants
(D) Mandates
(B) Devolution