AP Bio Vocab Chapters 3 and 4
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms

chemical reaction
when atoms combine or change bonding partners
reactants
substances that participate in a chemical reaction
products
substances formed by the chemical reaction
organic molecule
molecules with a chemical skeleton composed primarily of carbon
hydrocarbon
molecule containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms

structural isomers
molecules with the same chemical formula but differ how the atoms are arranged

functional groups
a characteristic combination of atoms that contribute specific properties when attached to other molecules
macromolecules
giant molecules

polymers
large molecules made up of repeating subunits
monomers
building blocks
monomer of carbs
simple sugars
monomer of proteins
amino acids
dehydration synthesis
process in which water is removed to join two monomers

hydrolysis
process in which polymers are broken and water is added
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond that joins two sugars
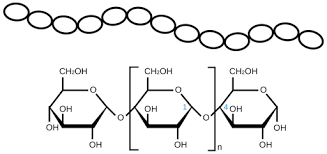
starch
energy storage molecule in plants composed of alpha glucose molecules (H above plane on carbon 1)
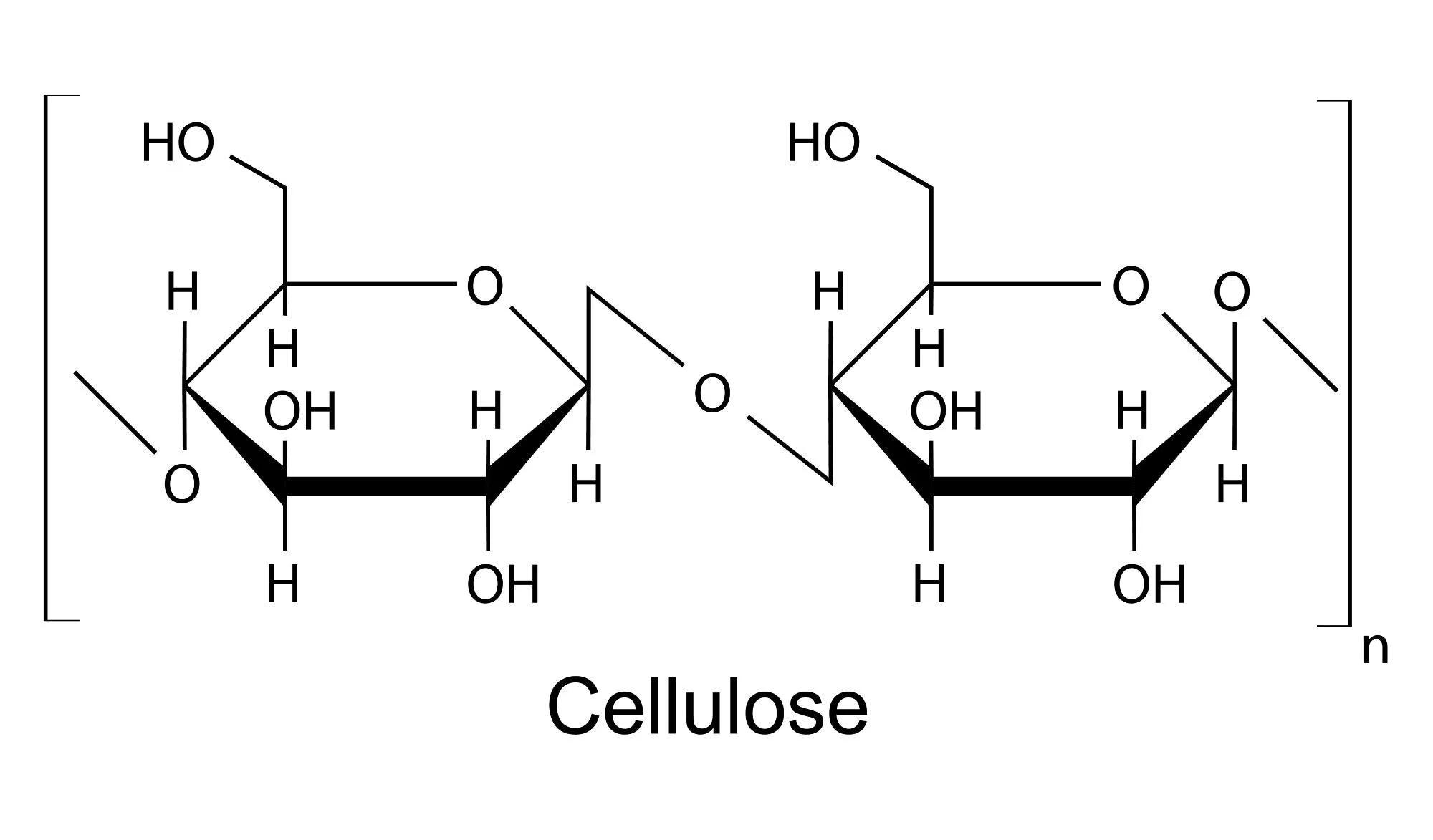
cellulose
structural support in plants composed of beta glucose (H below plane on carbon 1)

polypeptide
long chain of amino acids
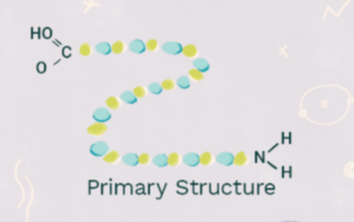
primary structure
sequence of amino acids
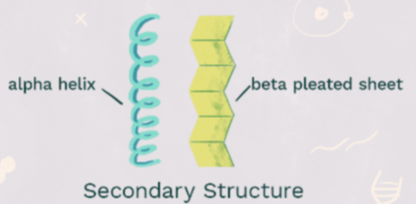
secondary structure
maintained by hydrogen bonds between polar sections

tertiary structure
caused by interactions between R groups

quaternary structure
results from ways subunits bind together and interact
denature
process in which tertiary structure is lost and therefore the function of the protein
monomer of nucleic acid
nucleotides
monomer for lipids
fatty acids
hydrophobic
unable to dissolve in water
triglyceride
one glycerol + three fatty acids
saturated fats
all carbons in fatty acid chain are bonded by single bonds except for carboxyl group at the top
unsaturated fats
some of the carbons in fatty acids have double covalent bonds
phospholipid
one glycerol + two fatty acids with a phosphate group on each

steroid
composed of four ring structure
molecules:
vary in shape and size, have specific 3D shapes, are characterized by specific chemical properties
4 important classes of organic molecules found in L.O
carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids
general chemical formula for all amino acids:
a central carbon with four different groups attached where R is a variable group that determines the reactivity of the molecule
3 parts of nucleotides:
Five carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base
Purines
double ringed, adenine, guanine
Pyrimidines
single ringed, thymine, cytosine
RNA
ribose, single stranded, A,U,C,G
DNA
deoxyribose, double stranded, A, T, C, G
Lipids are:
composed of C, H, O, unable to dissolve in water, include fats, oils and waxes
3 families of lipids:
fats, phospholipids, steroids
light microscope
microscope that uses glass lenses and visible light to form a magnified image of an object
electron microscope
uses magnets to focus an electron beam to create a visible image on film
cytoplasm
material inside plasma membrane may contain H2O, NaCl, or organelles
What are the differences between prokaryotes from eukaryotes?
before nucleus, kingdoms eubacteria and archaebacteria, small, simple, lack membrane bound organelles
What are the differences between eukaryotes from prokaryotes?
true nucleus, kingdoms protista + animalia + plantae + fungi, larger, complex, animal + plant cells
nucleus
center of genetic activity in eukaryotic cells that is called the “control center” because it houses DNA
nucleolus
region in which RNA is synthesized in eukaryotic cells
nuclear envelope
a double membrane that encloses the nucleus, there by separating the contents from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells
nuclear pore
a small opening in which the RNA can pass through to be interpreted by the ribosomes in eukaryotic cells
plasma membrane
membrane made up of phospholipids and proteins that surrounds a cell protecting it and controls what crossed the membrane
cilia
hair-like extensions in eukaryotic cells used to trap unwanted waste materials in multicellular organisms or specializing in locomotion in unicellular organisms
flagellum
a tail-like structure that helps the cell move
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
molecules that transfers, transmits, and expresses genetic information
mitochondrion
organelle in eukaryotic cells that produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy currency of the cell, and is also known as the “powerhouse of the cell”
ribosome
organelle in cells that is the site of protein synthesis
lysosome
organelle in eukaryotes that store digestive enzymes
vesicle
a sac composed of membrane inside cells that transport materials
golgi apparatus
organelle in eukaryotes that sorts and packages protein for export or use in the cells
smooth er
organelle in eukaryotes composed of connected channels of membranes in the cytoplasm which do not have ribosomes and synthesize lipids
rough er
organelle in eukaryotes composed of connected channels of membranes covered in ribosomes and involved in protein synthesis
centriole
membrane converted organelles in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes composed of microtubules and involved in mitosis
cell wall
surrounds cell membrane composed of cellulose
chloroplast
organelle surrounded by 2 membranes green from chlorophyll
central vacuole
large membrane bound sac
3 plant specific structures
cell wall, chloroplast, central vacuole
symbiosis
two or more living organisms of different species living in close association
endosymbiosis
process by which eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotes
cytoskeleton
a network of protein fibers in the cytoplasm that gives a cell shape, holds and moves organelles, and is involved in cell