Resultant Forces and Balanced/Unbalanced Forces
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is resultant force?
The single force that could replace all the forces acting on an object, found by adding these together. If all the forces are balanced, the resultant force is zero
Balanced forces
no change in motion (stationary or moving at constant speed)
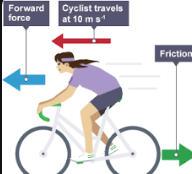
What are unbalanced forces?
Unbalanced forces occur when the net force acting on an object is not zero, causing the object to accelerate

List some scalar quantities
speed, temp, distance, area, entropy, volume
list some vector quantities
velocity, acceleration, displacement force momentum, drag
What is a free body diagram?
A free body diagram represents all forces acting on an isolated object.

Calculate the resultant force of more than one forces acting on a object in different directions
General Steps (for forces in different directions):
Break angled forces into components (horizontal & vertical).
Add all horizontal components together(if they a different directions you minus the smaller from the greater Force)
Add all vertical components together.(same as brackets from step 2)
Use Pythagoras to find the resultant force.
Use trig (tan⁻¹) to find the angle of the resultant.(optional)
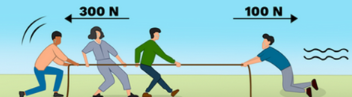
How to work out the resultant force(opposite directions)
Minus the force with the lower N from the from the force with the higher N to get the resultant force
e.g. Tug of war:
300N(right) - 100N(left)= 200N(right)= resultant force
How to work out the resultant force(Right angle triangle)
use Pythagoras theorem to work out the resultant when the 2 vectors form a right angle.
e.g.
↑ 8 N
| R= √(82+62)=√100=10N
| R=10 N
•--------→ 6 N
Force that act on a plane
An airplane in flight experiences four fundamental forces: lift (upward), weight (downward), thrust (forward), and drag (backward).
The effect of forces on objects
Effect of Force | Example |
|---|---|
Change speed | Car accelerates or brakes |
Change direction | Football changes path mid-air |
Change shape | Spring stretches |
Start motion | Pushing a trolley |
Stop motion | Braking a bike |