How the Earth Works Exam 2
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
continental jigsaw, fossils match across the seas, rock types and structures match, ancient climates
Continental drift evidence
Pangea
supercontinent
Alfred Wegner
creator of continental drift hypothesis

lithosphere
strong, rigid layer, made of broken plates
crust and uppermost solid mantle
oceanic lithosphere
basalt, thin, but thicker with age
oceanic
mafic crust
continental lithosphere
granitic, thicker
continental
felsic crust
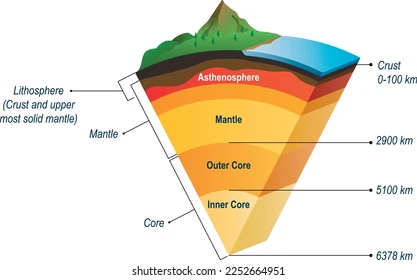
asthenosphere
upper mantle, weak, hot and pressure, able to flow, allows outer sphere to move
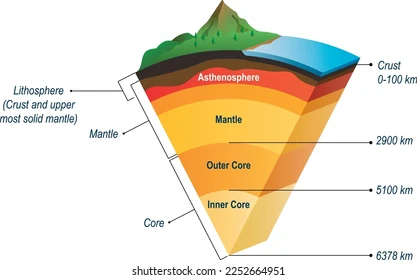
mesosphere
lower mantle, pressure counteracts temperature to create strong rocks
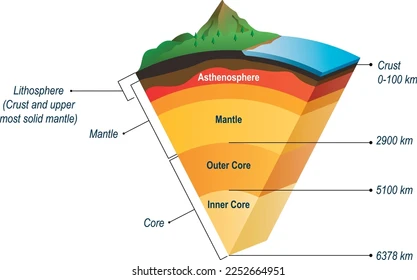
outer core
liquid layer of the core that generates earth’s magnetic field
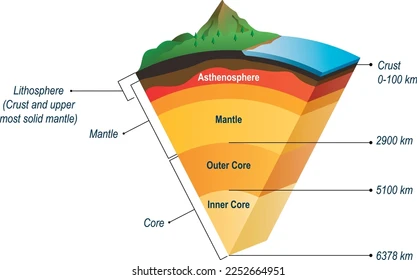
inner core
solid (iron) layer of the core because of immense pressure
tectonic plates
Large sections of the Earth's lithosphere that move and interact with each other, responsible for earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountains
plate boundary
where tectonic plates meet and interact, causing geological activity
divergent boundary
constructive, plates moving apart
oceanic divergent boundary
causes seafloor spreading
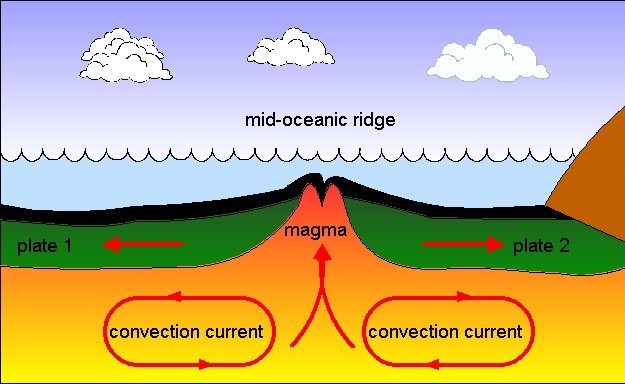
seafloor spreading
Process where new oceanic crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges and spreads outward, pushing older crust aside. Driven by convection currents in the mantle.
mid-ocean ridges
Underwater mountain ranges that form at divergent plate boundaries. They have volcanic activity and the upwelling of molten rock from the Earth's mantle.
5
The sea floor moves about __ cm per year.
180 million
None of the ocean floor exceeds __ years old.
slower
The __ the spreading of magma, the more even and smooth the surface becomes.
continental divergent boundary
causes continental rifting
convergent boundary
destructive, plates moving towards each other
subduction zone
where one plate bends and sinks down into the asthenosphere beneath another plate
oceanic
Which crust is denser: oceanic or continental?
deep-ocean trenches
form at oceanic subduction zones
older
The __ the crust, the steeper the angle of subduction.
younger
The __ the crust, the warmer and less dense it will be.
downgoing plate
plate being subducted
overriding plate
plate going overtop
oceanic; continental
The __ plate always subducts under the __ plate.
accretionary prism
A wedge-shaped mass of sediment and rock scraped off the top of a downgoing plate that accumulates at the boundary
partial melting
when the minerals with the lowest melting temperatures inside a rock melt first while the other minerals remain solid
water
Subduction zones allow __ to be brought into the mantle, which heats up, allowing the mantle to melt and magma to form.
oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary
creates volcanic island arcs
back-arc basin
depression formed by subduction zones behind a volcanic island arc
continental-continental convergence
Type of convergence where neither plate can subduct, causing a collision and forming a mountain belt
transform boundary
neither constructive nor destructive, plates sliding past each other
San Andres Fault
an active transform fault in the United States that produces frequent earthquakes
offset of mid-ocean ridge
series of transform faults that are present along a ridge axis causes this
continental margin
edges of continents where they meet the ocean
active continental margin
continental margin where there is a plate boundary
passive continental margin
continental margin where there is no plate boundary
hot spots
record the movement of plates over time through the formation of volcano chains
seamount
extinct volcanoes that sink below the sea level
Earthquake
a vibration caused by the sudden breaking or frictional sliding of rock in the Earth
fault
a fracture on which one body of rock slides past another
focus/hypocenter
location where a fault slips during an earthquake underground
epicenter
point above ground directly above the focus of an earthquake
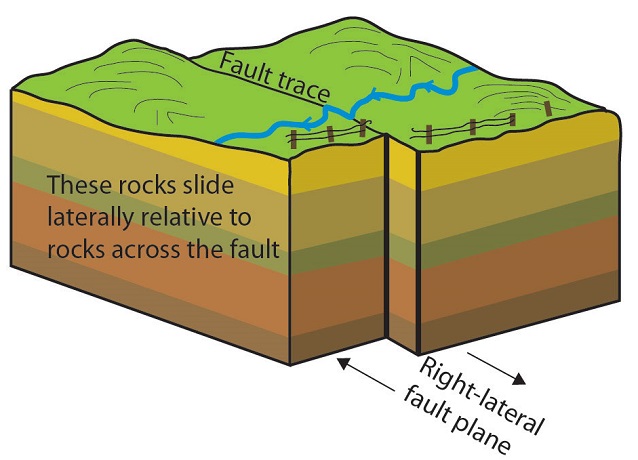
fault trace
The visible line on the Earth's surface where a fault is exposed due to movement of tectonic plates
fault creep
fault displacement without large earthquakes, movement that occurs slowly and relatively smoothly
rapid release of elastic energy stored in rock that has been subjected to great stress
Why do Earthquakes occur?
Elastic rebound
springing back of a rock to its original shape once an earthquake has occured
footwall
rock mass that lies below the fault plane
hanging wall
rock mass above the fault plane
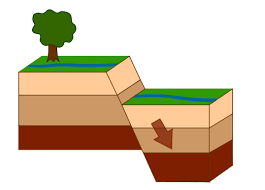
normal fault
hanging wall moves down, divergent plate
extension
a normal fault is caused by __
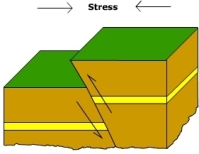
reverse/thrust fault
hanging wall moves up, convergent
compression
thrust and reverse faults are caused by __
steeper
the reverse fault has a __ angle than the thrust fault
transform fault
horizontal movement
shear
transform faults are caused by
right or left lateral
directions of transform fault movement
look at opposite plate from the other side
how to determine transform fault movement
seismic waves
waves that travel through the crust generated by earthquakes
surface waves
seismic waves that travel on the surface of the Earth
greatest; slowest
surface waves cause the __ damage and have the __ velocity
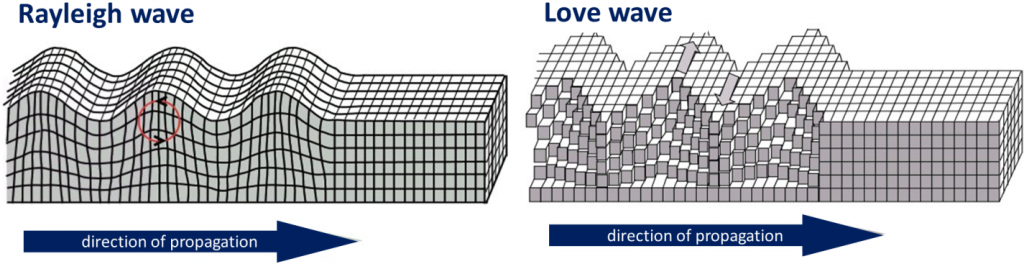
Rayleigh/r-wave
surface wave that creates an up and down motion
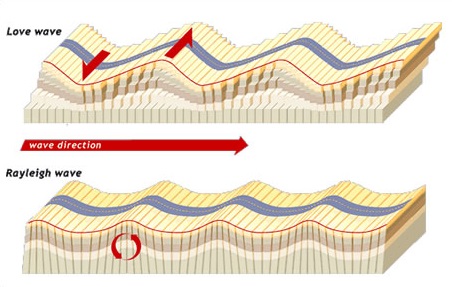
Love/l-wave
surface wave that creates a back and forth motion
body waves
seismic waves that travel within the Earth’s interior
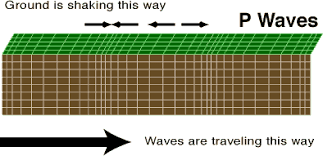
primary/p-wave
body wave that can travel through any substance
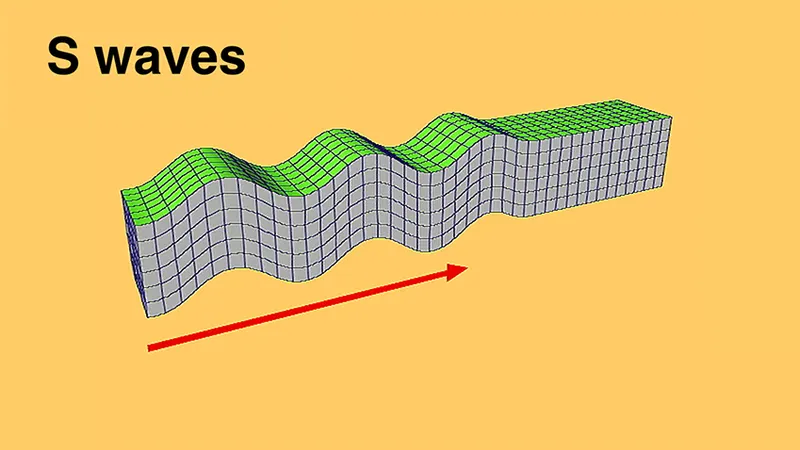
secondary/s-wave
body wave that can only travel through solids
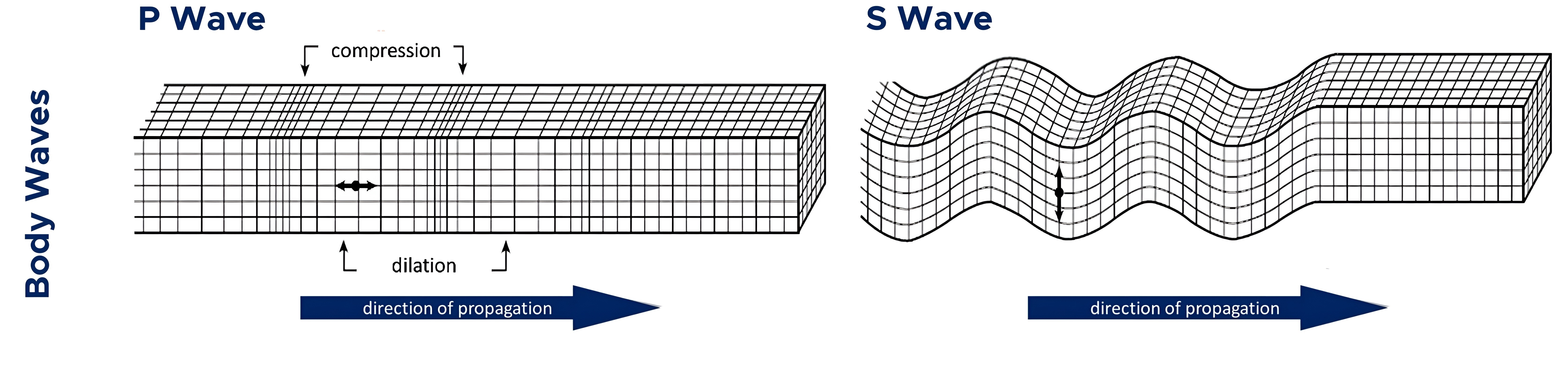
compression; shear
p-waves use __ to make an push/pull motion, while s-waves use __ to make a up/down motion
p-waves, s-waves, surface waves
seismic waves from fastest to slowest
arrival times of different waves
What do seismographs use to determine the distance to an earthquake’s epicenter?
foundation conditions, building standards, population density
Factors influencing the damage caused by an Earthquake
less
hard igneous rock will have __ ground shaking than silt and mud during an earthquake
liquefaction
Earthquakes can cause __ which is the process where water mixes with sand and clay to make a slurry
foundation damage
Earthquakes can cause __ where the shaking causes the soil and sand in the ground to loose cohesion so that the particles stop touching, making the ground and foundation unstable. Mass wasting also occurs.
tsunamis
Earthquakes can cause __ where large waves surge on the shore.
shadow zone
an area inside the Earth where seismic waves do not reach because of the bending and reflection of waves by the Earth's core, which helps scientists understand the structure and composition of the Earth's interior
Temperature, magma composition, dissolved gases
How violently or gently a volcano erupts is determined by these three things
magma chamber
Where the magma is held inside the volcano
conduit
the pipe that connects the magma chamber to the opening
higher
a material __ in viscosity will flow with greater difficulty
lower
Mafic magmas have __ viscosity than felsic ones
basaltic lava
example of a mafic magma, which is found on the seafloor
less
Hotter magmas are __ viscous
increase
dissolved gases (volatiles) __ the fluidity of magma
most
felsic magma has the __ silica and gas content, so it is also has the __ viscosity
rhyolitic lava
Example of a felsic magma
andesitic lava
example of an intermediate magma
50-60; 1-6
magmas range from __ to __ percent in silica content, and __ to __ percent in gas content
Pahoehoe
basaltic lava that forms relatively smoothly with some wrinkles
Aa
basaltic lava that flows slower than Pahoehoe and has rough and jagged edges
lava tubes
tunnel underneath hardened lava where lava still flows
effusive eruption
type of eruption where the magma flows gently
explosive eruption
violent eruption filled with pyroclastic material
fissure eruption
eruption from a linear tear in Earth’s surface, creating a curtain of lava and stair-step topography
shield volcanoes
volcanoes that have effusive eruptions