physiology final 2.0
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
password
alec
What is the funtion of muscle tissue
contraction
The skeltal muscle cell is called a
muscle fiber
group of muscle fibers is called a
fasicle
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber is called
sarcolemma
The endomysium is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the
muscle fiber
Which connective tissue layer in the muscle contains the blood vessels and nerves
perimysium
Which structure in a muscle fiber stores calcium
sarcoplasmic reticulum
This line separates one sarcomere from another
z disc
The line that connects the thick filament
m line
The area of the sarcomere where there is only thin filaments
I band
When calcium binds to troponin, troponin changes the shape removing____ from the active binding sites of actin
tropomyosin
For relaxation to occur
sarcoplasm calcium levels fall calcium is removed from troponin and tropomyosin blocks binding sites on actin
A power stroke involved
a myosin head polling a thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere
When myosin breaks down the ATP into ADP and Phosphate, it causes the myosin to do what
stretch
At the end of the power stroke, if calcium stays bound to troponin
cross bridging continues
The muscle fiber type that is used for speed and strength
fast twitch (fast glycolytic)
the muscle fiber type that is used for endurance
slow twitch
The muscle fiber type that uses aerobic repiration
slow twitch
In the creatine phosphate pathway, ____ creates and ATP from and ADP and creatine phosphate molecule
creatine kinase
Which of the following describes the set up of actin and myosin in smooth muscle
lined along intermediate filaments and anchored in dense plaques
Due to ___ smooth muscle is fatigue resistant
latch bridging
Which of the following causes skeletal muscle to fatigue out
Running out of Atp, neuron running out of ach
an increase in phosphate
How would calcium play a role in skeletal muscle fatigue
the neuron can not release the neurotransmitter without calcium
___ produces osteoid
osteoblast
___. maintains the bone matrix
osteocyte
___ breaks down the bone matrix
osteoclast
What is the structural unit of spongy bone
trabeculae
What is the structural unit of compact bone
osteon
The shaft of a long bone is called the ___
Diaphysis
The medullary cavity is filled with
yellow bone marrow
The part of the osteon where the blood vessels and nerves are found
central canal
The part of the compact bone that fills in the spaces left between the osteon
intersitital lamellae
____- ossification forms flat bones, where as____ossification forms long bones
Intramembranous, endochondral
When a bone grows in length it is called
interstitial growth
____ the area where chondrocytes quit dividing and begin to enlarge
Zone of hypertrophic cartlige
___ secures the epiphysis to the epiphyseal plate,looks like normal hyaline cartlage
zone of resting cartilage
___ minerals are deposited in the matrix, appears opague
zone of calcified cartilage
____ chondrocytes undergo rapid mitotic division
zone of the proliferating cartilage
___ walls break down between lacunae and osteoprogenitor cells form the medullary cavity migrate in and become osteocytes
Zone of ossification
When normal stress is applied to an abnormal bone, it can break. when the bone is abnormal or weakened by disease it is called a ___ fracture
pathologic
the rings of osteoid that encircle the central canal
lamella
The chondrocytes can be found in _____ within the cartilage
lacunae
In resorption which cell type releases digestive enzymes
Osteoclast
nodal cells are specialized cells that are found in the____
SA nod
to increase heart rate and decreased blood pressure, ____ is released
norepinephrine
after threshold is met in nodal cells, what channels open?
voltage gated Ca++
why does AV node hold onto action potential for a brief second before letting it enter the ventricles?
to make sure ventricles are relaxed so they can fill up
what delivers the action potential to cardiac muscle in ventricular walls?
the purkinje fibers
what represents atria contraction?
P
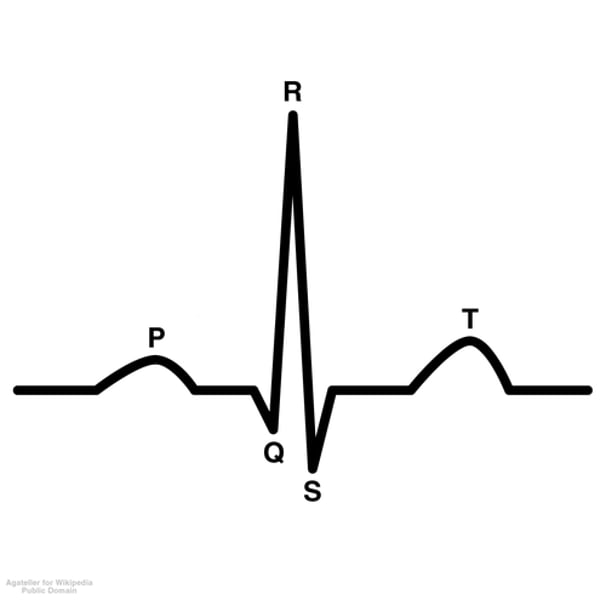
for the complex that's labeled QRS, what valves are open?
pulmonary and aortic (Semilunar)
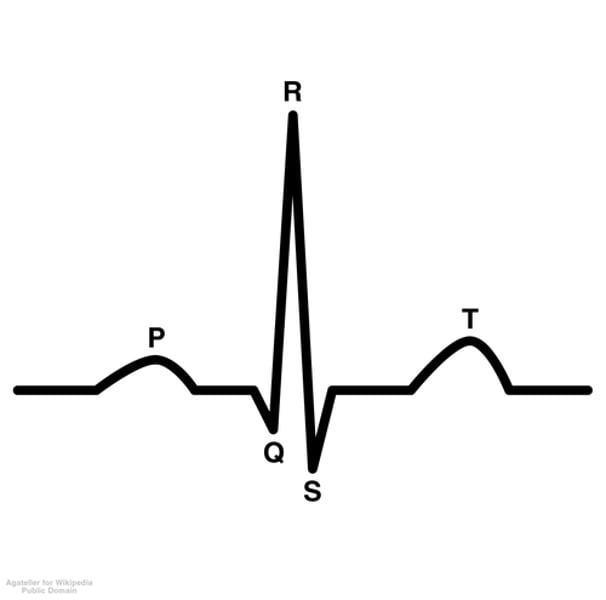
which chambers are relaxed at T?
atria
what affects resistance of blood flow?
blood viscosity, vessel length, vessel diameter
what is the receptor for epinephrine (responsible for vasodialation)?
beta 2
what does norepinephrine cause in heart muscle?
increase in strength of contraction
what increases the sensitivity of the nodal cells to norepinephrine and epinephrine?
thyroid hormone
what two things can you do to decrease blood pressure?
cardiac output and resistance
what is the pulmonary ventilation stage of respiration dependent on?
pressure differences between atmospheric pressure and pressure inside lungs
during inspiration, ribs move ____ and ____
up and out
during expiration, the diaphragm moves ____
up
space for conducting airflow is _____
anatomical dead space
what is tidal volume?
amount of air in one breath
what is used to measure compliance?
inspiratory reserve volume
what increases the sensitivity of the nodal cells to norepinephrine and epinephrine?
Thyroid hormone (postive chronotropic)
in alveoli gas exchange, partial pressure of carbon dioxide drives movement in which direction?
capillaries to alveoli
what is the definition of cooperative binding effects?
if an oxygen binds to hemoglobin, it makes it easier for other oxygen's to bind
what is the main way carbon dioxide is transported in blood?
bicarbonate
in systemic gas exchange, partial pressure for carbon dioxide drives the flow of carbon dioxide in what direction?
into the capillary
in systemic gas exchange, partial pressure for oxygen drives the flow of oxygen in what direction?
into tissue
peripheral chemoreceptors monitor ___ in the blood
carbon dioxide, Hydrogen, O2
where is the depth of breathing controlled?
anterior medulla
what is the average rate of breaths per minute in persons with eupnea?
12-15
what is the ability of bronchioles to regulate airflow and arterioles to regulate blood flow in the lungs?
ventilation-profusion coupling
where does blood flow after it leaves the right ventricle?
pulmonary trunk
after voltage gated calcium channels open in nodal cells, what channels open next?
voltage gated potassium
for air to enter the lungs, pressure must be ___ than atmospheric pressure
lower
in alveoli gas exchange, partial pressure of oxygen is higher in ___
alveoli
what is the basic unit of life?
the cell
when an unequal sharing of electrons occurs in a molecule, it makes one end slightly positive and the other slightly negative. this molecule would be said to be ______?
polar
when looking at the pH scale, which range is considered neutral?
6-8
when dissolved in water, ____ give off hydrogen ions
acid
transitional epithelium is found primarily in the _____
urinary bladder
what is the ground substance in blood called?
plasma
the predominate cell type in areolar tissue is______
fibroblast
where can elastic cartilage be found?
the ear
what is the formed element in blood that is the red blood cell?
erythrocyte
_____ epithelial tissue can be found where you have a callus.
stratified squamous keratinized
epithelial tissue is said to be polar because...
it has two distinct surfaces, basal and apical
match the neurolemma with the type of channel: contains voltage gated calcium channels
transmissive
match the neurolemma with the type of channel: the axon hillock that contains sodium and potassium voltage gated channels
initial
match the neurolemma with the type of channel: the area where there are no voltage gated channels, only chemically gated channels
receptive
match the neurolemma with the type of channel: the axon where there are sodium and potassium voltage gated channels
conducting
in the plasma membrane of a neuron, which segment produces only graded potentials?
receptive
what event stimulates the release of the synaptic vesicle?
voltage gated Ca+ channels opening up to allow Ca+ into the transmissive segment
what is a graded potential?
a small, localized change in the resting membrane potential
what does the neurotransmitter bind to?
post synaptic membrane
which type of neuron would you find in the retina of the eye?
bipolar
sensory/afferent neurons mostly what type of neuron?
unipolar
what event must happen before an action potential can be generated?
threshold must be met
free amino acids are dependent upon ____ for absorption into the endothelial cells.
Sodium