Exam 1: Pathology of the Oral Cavity
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
How is cleft palate defined
palatoschisis
failure of maxillary bones to fuse
variably sized defect in hard palate
may interfere with nursing, feeding, chronic nasal infections, aspiration pneumonia
may also have cheiloschisis (hare lip)
what is odontodystrophy
developmental enamel hypoplasia
secondary to canine distemper virus in dogs
fluorine toxicity, malnutrition, vitamin A deficiency, tetracycline
what oral lesions can present themselves with viral stomatitis
vesicular stomatitides
erosive and ulcerative stomatitides
papular stomatitides
what vesicular diseases affect ruminants
foot and mouth disease
vesicular stomatitis
what vesicular diseases affect affect horses
vesicular stomatitis
what vesicular diseases affect pigs
seneca valley virus
swine vestibular disease
vesicular exanthema of swine
foot and mouth disease
vesicular stomatitis
what vesicular diseases are zoonotic
Vesicular Stomatitis
what are vesicular stomatitides
small circumscribed elevation of the epidermis/mucous membrane containing serous liquid
oral cavity, feet, teats
cannot be differentiated grossly, call state or federal vet immediately
all but vesicular exanthema of swine and seneca valley virus are reportable
how is foot and mouth disease generally described
genus aphthovirus, family Piconavviridae
highly contageous viral infection of all cloven hoof animals, horses not affected
low mortality but large economic impact due to production loss, vaccination, mass culling, serious trade restriction
what are the lesions of foot and mouth disease
vesicles on oral cavity, tongue, interdigital cleft, teats
malignant form usually in young animals <6m, myocarditis without vesicles (uncommonO
how is vesicular dermatitis generally described
genus vesiculovirus, family Rhabdoviridae
affects horses, cattle, pugs
zoonosis
biting insects such as black flies and midges
generally self limiting- skin/oral cavity lesions, drooling, fever
only in american continents
present in US
what are the major Porcine specific vesicular stomatitides
swine vesicular disease virus
Seneca Valley virus (present in US)
Vesicular exanthema of swine virus (historical only, likely from SMSL virus)
what is the difference between erosion and ulceration
loss of superficial layers of epidermis or mucosal membrane
loss of all layers of the epidermis or mucosal membrane, penetrates the basement membranes
what are the major erosive and ulcerative viral stomatitides
bovine viral diarrhea
riderpest
Pest des petits ruminants
malignant catarrhal fever
bluetongue
infectious bovine rhinotracheitis
feline calcivirus
how is bovine viral diarrhea generally described
genus pestivirus, family Flaviviridae
BVDV-1 and 2, each with cytopathic and non-cytopathic strain
subclinical or mild disease (no or mild signs, but immunosuppression)
mucosal disease
severe acute BVD
fetal infection
describe the process of BVD mucosal disease infection in a pregnant cow
infection during first 4 months with non-cytopathic strain (fetus becomes immunocompetent around 150-200 days)
may cause fetal death
if fetus survives, PI calf super infected with cytopathic strain causing mucosal disease
what are the lesions of BVD mucosal disease
low morbidity but high mortality
anorexia, bloody diarrhea, fever, mucoid nasal damage
erosion/ulceration in the GI tract: mouth, esophagus, forestomachs, over Peyer’s patches, small and large intestines
lymphocytolysis in Peyer’s patches
most PI calves succumb to mucosal disease 6m-2y
how is severe acute BVD (BVD type 2) described
high morbidity and mortality in all age groups
associated with virulent strain of virus but not al cause severe disease
lesions similar to BVD MD (GIT ulceration and lymphocytolysis) + hemorrhage
how are persistently infected BVDV calves described
infected during first 4 months of gestation with NCP strain
immunotolerant to homologous NCP BVDV
viremic for life and sheds virus in all vody secretion
most important source of infection in the population
clinically normal or weak
mostly succumb to disease 6m-2y
how is malignant catarrhal fever described
caused by several different ruminant gammaherpesviruses (10 viruses, 6 cause disease)
caused by cross-species infection
cattle, deer, most other even toed ungulates
-Ovine Herpesvirus 2 in north america
-Alcelaphine herpesvirus-1 in African wildebeest in Africahigh mortality in susceptible species
dead end host, not contagious among cattle
what are the clinical signs of malignant catarrhal fever
sudden death
fever
lymphadomegaly
hemorrhagic diarrhea
corneal opacity
mucopurulent exudate from upper respiratory and oral cavity
neurologic signs
what are the gross and microscopic lesions of malignant catarrhal fever
gross
ulceration of mucosal surfaces (digestive, respiratory, urinary tract that are similar to BVD and rinderpest)
Edema, mucopurulent nasal discharge
lymphadenomegaly
Microscopic
-lymphoproliferation (CD8 T cells)
-vasculitis
-erosive-ulcerative mucosal lesions
how is Rinderpest or cattle plaque generally described
genus morbillivirus in the family paramyxoviridae
eradicated from planet in 2011
mainly affect cattle, buffalo, but can infect all cloven hoofed animals
high morbidity and mortality
lesions include erosive and hemorrhagic lesions of MM in the GI tract, necrosis of lymphoid tissue (Peyer’s patch)
-similar to BVD-MD
-sycytia and viral inclusion bodies
what is Peste des petits ruminants
genus morbillivrius in family paramyxoviridae
goats and sheep
FAD
clinical signs and lesions similar to rinderpest
interstitial pneumonia similar to canine distemper
syncytia and viral inclusion bodies
what is bluetongue
Orbivirus, Reoviridae
sheep are highly susceptible
goats and cattle usually inapparent or mild clinical signs
vecor borne disease- Culicoides (midges)
endothelial damage → ischemic necrosis of many tissue, edema, hemorrhage
oral cavity, tongue, GI tract, skin, heart, base of the pulmonary artery
what is Epixootic hemorrhagic disease (EHD)
genus Orbivirus, family Reoviridae
Pathogenesis and lesions similar to Bluetongue
White tailed deer extremely susceptible
How is feline calcivirus described
genus vesivirus, family Calciviridaw
RNA virus with high rates of mutation and variable virulence
persistent infections have minimal clinical signs and virus sheds in saliva, nasal secretions, feces
what are the clinical signs of feline calcivirus
ulcers on tongue/oral cavity, upper resp disease
similar to feline herpesvirus infection
what are papular stomatitides
small, circumscribed, superficial, solid elevation of skin or mucus membranes
Bovine papular stomatitis, Orf
How is Bovine Papule Stomatitis generally described
genus parapoxvirus, family poxviridae
young cattle 1-2m
generally little clinical significance
epidermal proliferation
papules, nodues, macules on tongue, gingiva, palate, esophagus, rumen, omasum
zoonotic
how is contagious Ecthyma aka Orf, soremouth, contagious pustular dermatitis
genus parapoxvirus, family poxviridae
sheep and lambs, goats, rarely humans
epidermal proliferation and crusts on the lips, mouth, teats
more exudative and proliferative compared to bovine papular stomatitis
weight loss/poor growth due to pain, self limiting but can cause death in suckling animals
zoonotic
what are bacterial stomatitides associated with
trauma (feeding, iatrogenic, foreign body
opportunistic normal bacterial inhabitant
-Actinobacillus, Actinomyces, Fusobacterium spp
what is necrotizing stomatitis
oral necrobacillosis aka akf diphtheria
caysed by Fusobacterium necrophorum
oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, tongue
foul breath, anorexia, fever
secondary infection following damage to mucosa
coagulative necrosis with necrotic membrane
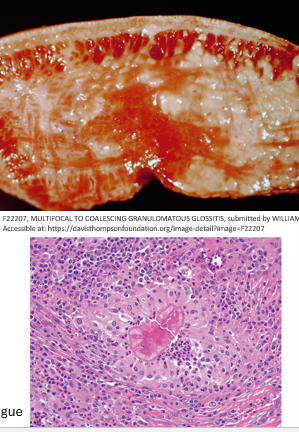
what is wooden tongue
Actinobacilus lignieresii, gram - aerobic caccobacilli
mainly cattle, sheep and pigs
affects soft tissue vs lumpy jaw
how is chronic infection of wooden tongue described
pyogranulomatous glossitis/stomatitis with severe fibrosis
coccobaculli surrounded by Splendore-Hoeppi material (club colonies or sulfur granules)
how is candidiasis or thrush described
Candida albicans
fungal
normal inhabitant of GIt tract
opportunistic following immunosuppression, alterations in oral microbiota, young sick or dehibiliated animals
most common in foals, pigs, dogs
what is pemphigus vulgaris
dermatologic autoimmune disease frequently affecting muco-cutaneous junctions an oral cavity
severe, acute or chronic vesicular/bullous disease of humans dogs and cats
auto Ab against desmoglein 3
flaccid bullae and erosions of muco-cutaneous junctions, oral mucosa, skin
what are the clinical signs and histology of pemphigus vulgaris
salivation, halitosis, mucosal erosion/ulceration
suprabasilar cleft- basal cells remain attached to basement membrane
what is bullous pemphigoid
grossly impossible to tell from pemphigus vulgaris
auto AB against collagen 17 or BPAG1e (component of hemidesmosome)
subepidermal blister formation with no acantholysis
reported in humans, dogs, horses, sometimes cats
what is Feline plasma cell or lymphoplasmacytic gingivitis/stomatitis
raised, erythematous, proliferative lesion
-glossopalatine arch
-periodontal gingivaidiopathic- hypothosis is inappropriate immune reactions
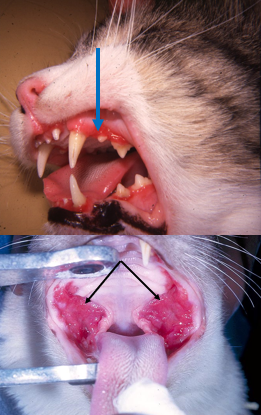
what are eosinophilic ulcers aka rodent ulcer or oral eosinophilic granuloma
cats and sporadically dogs
in cats, belongs to eosinophilic granuloma complex
chronic superficial ulcerative disease of mucosa and mucocutaneous junction
frequently upper lip of cats
affected area is thickened, red, ulcerated
eosinophils and histiocytes
idiopathic
what is uremic glossitis
relatively common lesion associated with renal failure in dogs and less commonly in cats
cyanotic buccal mucosa, fetid ulceration of tongue, margins pf ulcer are swollen
ischemic vascular lesion ith pathogenesis poorly understood
oor correlation between blood ammonia levels and lesion development