MMSC 402 Exam 1 (Body Fluid Analysis)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
QA
Quality Assurance
- preanalytical
-analytical
-post analytical
- internal QC
-external QC
Pre-analytical
Pre testing
-Proper ordering
-Specimen collection
-Patient prep/education
-Accurate procedure
-Adequate personal training
-Documentation of problems
analytical
testing
-Equipment
-Reagent/supplies
-Standardized procedures
-Analytical methods
-Monitor QC
-Lab personnel tech skills
Postanalytical
after testing
-Result communication
-Standard reporting format
-Appropriate documentation
-Reporting of critical values
internal QC
-Monitor analytical errors
-Mimic patient samples
-Commercially obtained
-Results recorded, troubleshoot if necessary
-Monitor analysis of same specimen
External QC (proficiency testing)
-Proficiency testing in multiple labs
-Reports useful for detecting quantitative small changes
-Accredited labs must participate and pass PT
Saftey
-biological + chemical
Biological Saftey
transmission precautions
-contact
-droplet
-airborne
routes of infection
-inhalation
-ingestion
-direct inoculation
Chemical Safety
label, date
always dispose properly in correct container
other hazards
Flammable substances
Compressed gas tanks
Electrical hazards
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
Requires facilities to have chemical hygiene plan
Educate personnel
-Proper labeling
-Lab safety manual
-PPE
-Safety equipment
SDS
Safety Data Sheet
urine formation process + purpose
- filter plasma though glomeruli
-reabsorbed + selective secretion by renal tubules
- get rid of waste from the blood
-Largest Components ogfH2OF
-solutes eliminates (urea, chloride, Na, K, P, sulfate, Creatinine, Uric acid)
- glucose, bicarbonate, albumin completely eliminated
anatomy of kidney
-nephron
-medulla
-renal pelvis
-papilla
-cortex
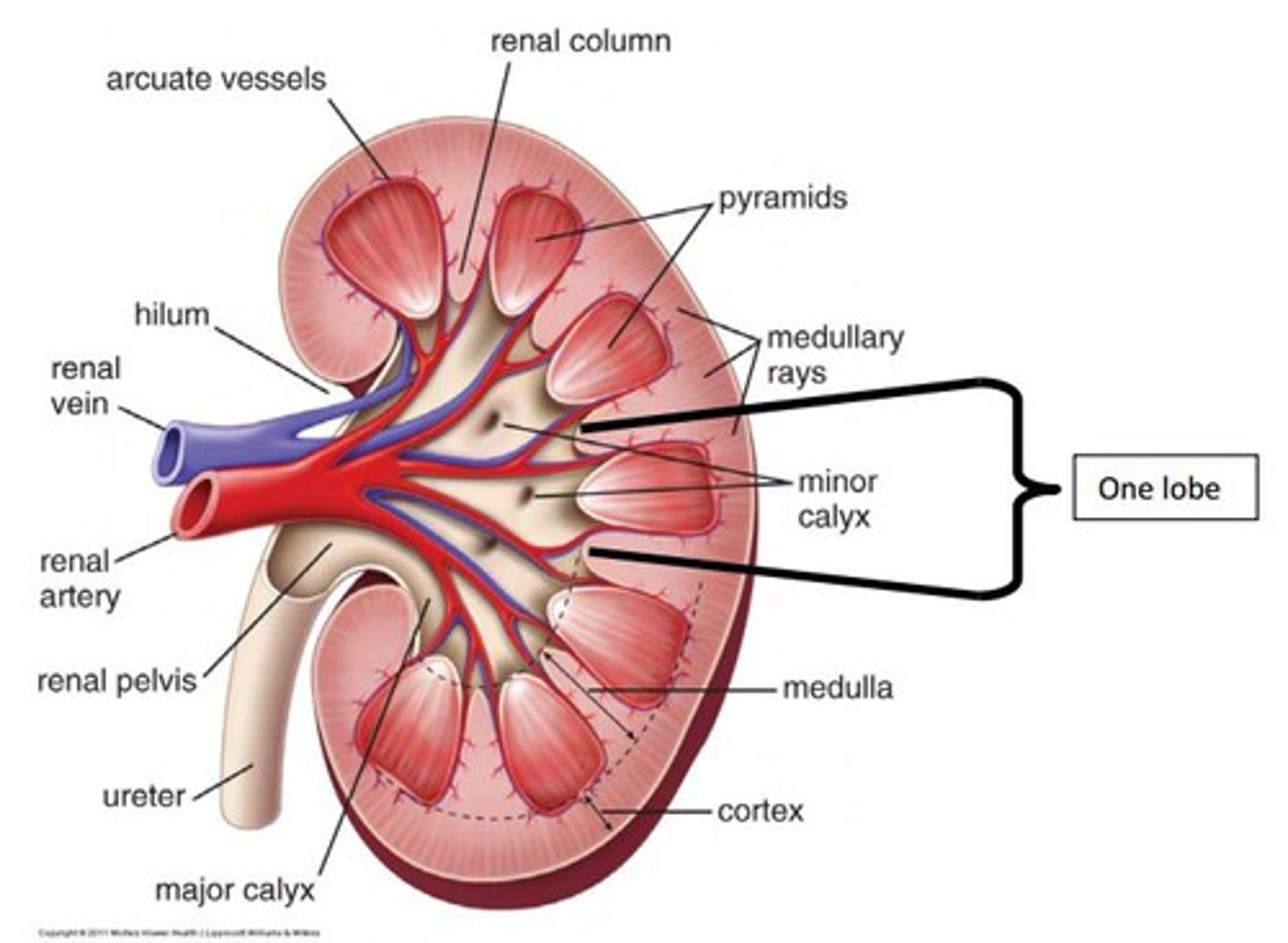
flow of urine through kidney
enters thought ureter
- ureter to bladder
-once 150 ml urine collected signals brain
- contraction of bladder and relaxation of urinary sphincter push urine into urethra
renal circulation
Afferent arteriole = supply blood to each glomeruli per nephron
efferent arteriole = bring filtered blood from glomerulus to kidney/ into circulation
peritubular capillaries (fine capillary plexus)
vasa recta (long u shaped vessel)
renin a
-enzyme
-when released forms angiotensin
-actively retains NA and passively retains H2O
Glomerlus
-form barrier
-plasma ultrafiltration
-glomerular filtration barrier (permeable to H2O + low molecule weight solutes)
-shield of negativity repels plasma proteins
structural components
-mesangium
-fenestrated endothelia cells
-podocytes
-trilayer basement membrane
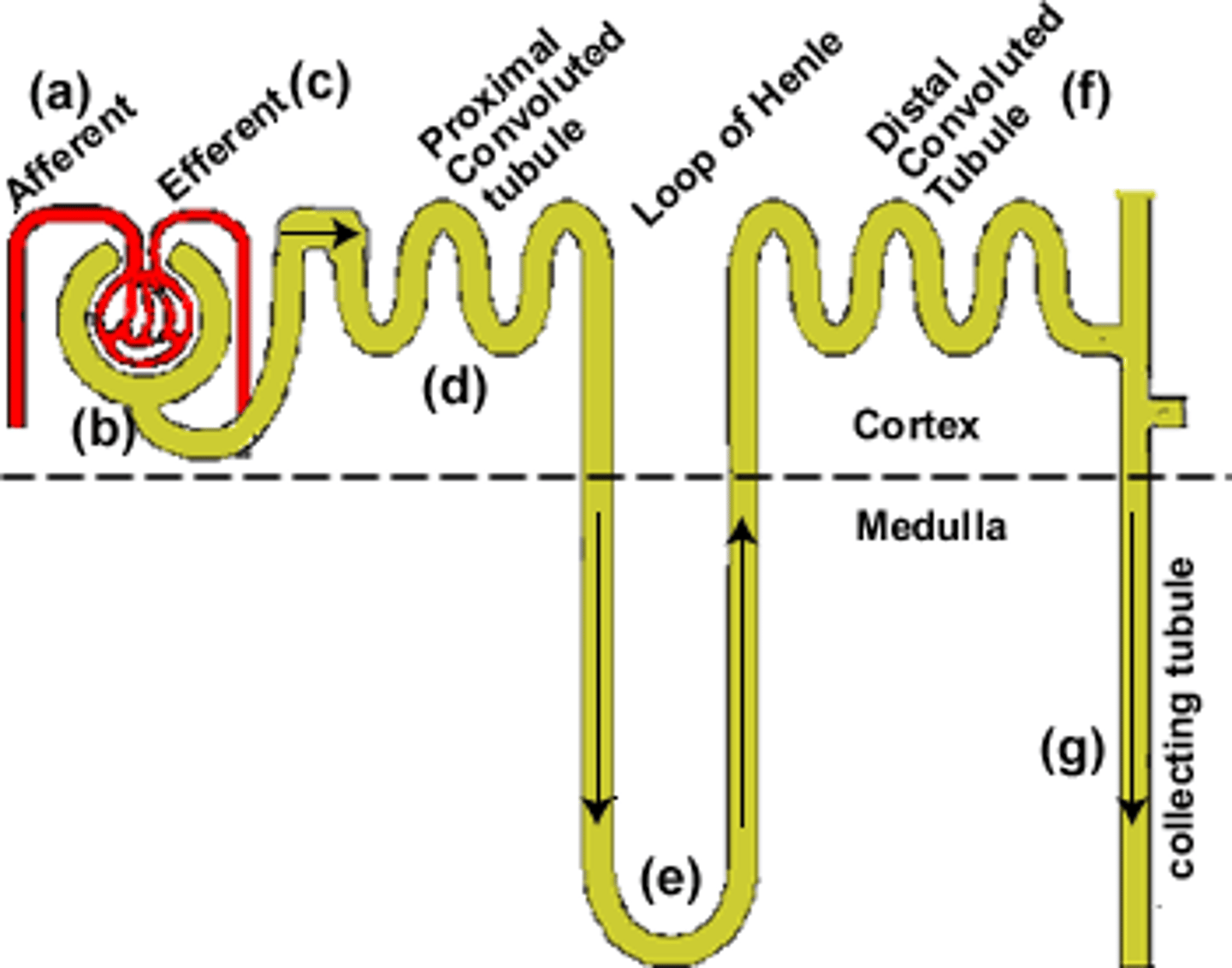
Tubular function / process
parts
-proximal tubes
-macula densa, distal convoluted tubes
-collecting tubes (final urin concentration -, ADH present)
tubular transport
active
- against gradient
-direct requires anergy
-indirect = coupled with another substance
passive
-no energy required
tubular function
reabsorption
- H2O, salts, glucose, AA, proteins
-excrete creatine and metabolic acids
secretion
- eliminates waste
-adjusts acid base equilibrium
acid-base equilibrium
H+ ions secreted into proximal tubular lumen
-->prevent bicarbonate loss
Phosphate acid converts to salts (Titratable acids)
Ammonia secretion, exchange of Na ions for ammonia ions
7.35-7.54 pH
renal threshold level
blood concentration
Antiduretic hormone (ADH)
-vasopressin
-controls H2O reabsorption in colleting tubes
- produced in hypothalamus and released into blood from posttrial pituitary gland
-change in tubule epithelium increases H2O reabsorbtion
- ADH release is controlled by negative feedback w/ arterial blood pressure
and
positive feedback w/ plasma osmolarity
diabetes insipidus
low ADH
diabetes mellitus
insulin is not secreted adequately or tissues are resistant to its effects
alderstone
Hormone produced by renin
- causes kidneys to retain sodium
-BP rises as s result
organic constituents of urine
urea, uric acid, creatinine
Inorganic constituents of urine
ammonia, sodium, chloride, traces of iron, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, and calcium
oliguria
Decreased urine output
less than 400ml per day
anuria
No urine
renal frailer
polyuria
excessive urination
greater than 3 L per day
conditions w/ H2O and Solute diuresis
labeling urine specimens
-label on side not cap
so caps can be switched
reason for lab to reject specimen
1. mislabeled
2.. improper collection method
3. improper preserved
4. viable contaminated
5. insufficient volume (need 10-15 ml)
changed that happen to urine after two hours
- pH will become alkaline
-color ill become darker
-false neg glucose
-false neg ketones
-increased nitrate and pH
midstream clean catch
Routine screening
Bacterial culture
catheterized (urethral) sample
bacteria fungi culters or kidney infection
Suprapubic aspiration
the passing of a sterile needle through the abdominal wall into the bladder to remove urine
pediatric collection bag
plastic used for babies to get quantitative assays
routine void
collected by having patient void into container; sterile specimen NOT required
specimen types
-first mornings --> most concentrated
-random --> most common
-times --> intervals
test used to evaluate glomerular filtration rate
-blood test
-based on serum creatinine levels
-greater then 60ml/min = normal
- specify if under 60
test to evaluate tubular reabsorption
creatinine clearance test
-renal clearance = (urine concentration x volume urine)/ plasma concentration
creatinine clearance test
Measures the rate at which creatinine is cleared from the blood by the kidney.
-renal clearance = (urine concentration x volume urine)/ plasma concentration
use of calculated glomeruli filtration rate
measure kidney function
Osmolarity
Concentration of solution expressed in osmoles of solute particles per kg of solvent
urine to serum = 1:3
SG
1.002-1.035
Density of urine to density of equal volume pure H2O