unit 6 humerus and shoulder girdle anatomy
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
what does the humerus and the shoulder girdle compose of?
humerus, shoulder girdle
what does the shoulder girdle compose of?
scapula and clavicle
the scapula is the _________ part of the shoulder girdle
posterior
the clavicle is the _________ part of the shoulder girdle
anterior
humerus anatomy (proximal)
head and anatomic neck
lesser tubercle (anterior)
greater tubercle (lateral)
intertubercular groove
surgical neck
deltoid tuberosity
body (shaft)
the greater tubercle is _______ and its an attachment site for the _________ ______ and _______________ muscles
lateral, pectoralis major, supraspinatus
the intertubercular groove of the humerus is an attachment site for the _______ tendon
biceps
which proximal part of the humerus is a common fracture site?
surgical neck
the surgical neck is ________ to tubercles
inferior
the humerus is classified as what kind of bone?
long
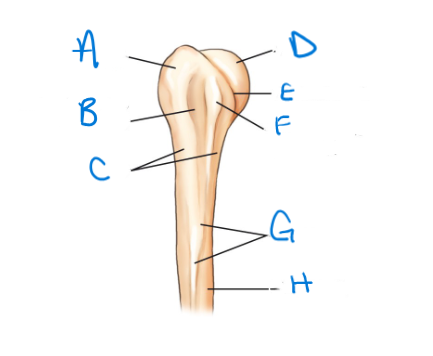
label the diagram in order from A-H
greater tubercle (tuberosity), intertubular groove (bicipital groove), surgical neck, head, anatomic neck, lesser tubercle (tuberosity), deltoid tuberosity, body (shaft)
the clavicle is described as having a _______ curvature with ___ main parts
double, 3
what are the 3 main parts of the clavicle?
acromial extremity (end), sternal extremity (end), body (shaft)
the acromial extremity of the clavicle is ______ and _________ with a __________ curvature
lateral, flattened, downward
the sternal extremity of the clavicle is _____ and _______
medial, triangular
in comparison to males, female clavicles tend to be…
shorter and less curved
in comparison to females, male clavicles tend to be…
thicker and more curved
the clavicle is classified as a ______ bone
long
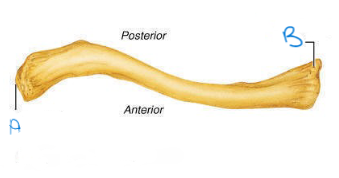
label A and B; which clavicle is this? which view is this?
acromial (lateral) end, sternal (medial) end, right, superior
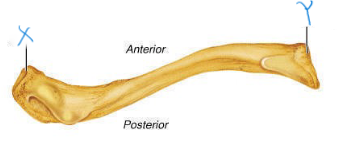
label X and Y; which clavicle is this? which view is this?
acromial end, sternal end, right, inferior
the scapula is relatively _____ and _______ shaped
flat, triangular
how many borders does the scapula have? what are they?
3, superior, lateral (axillary), medial (vertebral)
how many angles does the scapula have? what are they?
3, superior, lateral (head), inferior
the scapula is classified as a ______ bone
flat
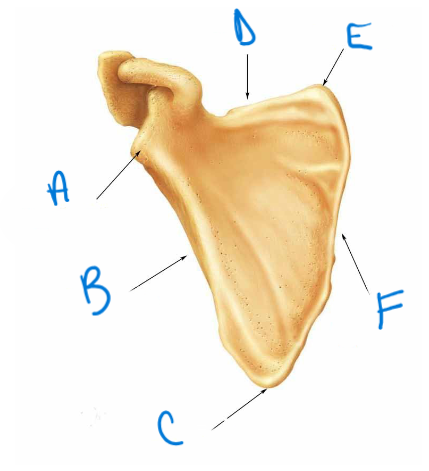
label the diagram A-F
lateral angle (head), lateral (axillary) border, inferior angle, superior border, superior angle, medial (vertebral) border
anterior scapula anatomy
body (blade) portion
anterior (costal) surface
subscapular fossa
neck
coracoid process
scapular notch
acromion
subscapular fossa is a _________ for _______ attachment
depression, muscle
what is the scapular neck between?
body and head
the coracoid process is a ________ _______ for ______ attachment
beaklike projection, ligament
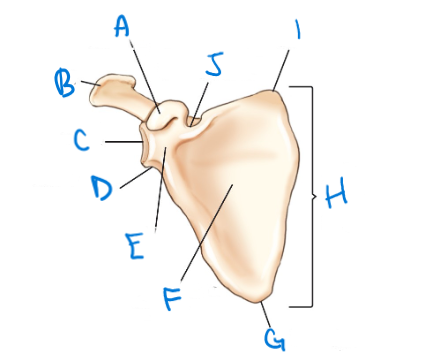
label A-J
coracoid process, acromion, glenoid cavity (fossa), lateral angle (head), neck, costal surface (anterior) subscapular fossa, inferior angle, body (blade, wing, ala), superior angle, scapular notch
posterior anatomy of the scapula includes…
supraspinous fossa, crest of spine, acromion, infraspinous fossa, dorsal surface (posterior)
in the posterior view of the scapula, the infraspinous fossa is a ________ for ________ attachment
depression, muscle
in the posterior view of the scapula, the acromion extends _________ over the ________
laterally, humerus
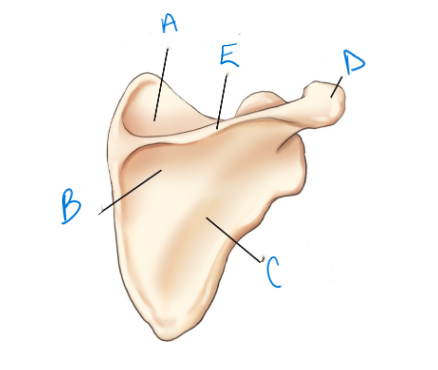
label A-E accordingly
supraspinous fossa, infraspinous fossa, dorsal surface (posterior), acromion, crest of spine
in the lateral view of the scapula, what letter does the scapula look like?
Y
the lateral upper part of the scapula consists of two parts, the….
acromion and coracoid
the lateral lower part of the scapula is known as the …
body
the glenoid cavity (fossa) is a _______ for _______ with the head of the ________
depression, articulation, humerus
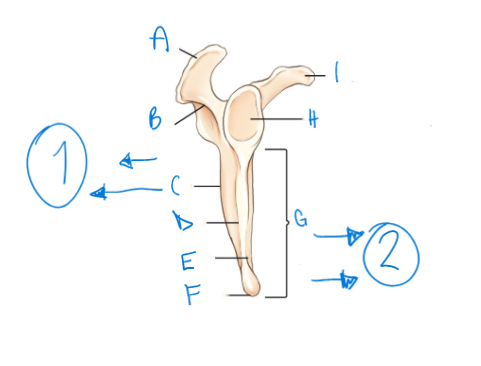
label A-I accordingly. indicate in anatomical terms what numbers 1 and 2 are (front or back of the scapula?)
acromion, spine of scapula, dorsal surface, lateral (axillary) border, ventral (costal) surface, inferior angle, body, glenoid cavity (fossa), coracoid process
posterior, anterior
what are the two clavicle articulations?
sternoclavicular joint, acromioclavicular joint
in terms of medial or lateral, the sternoclavicular joint is ______
medial
in terms of medial or lateral, the acromioclavicular joint is ______
lateral
the sternoclavicular joint is the ______ end of the clavicle and connects to the ______ of the _______
sternal, manubrium, sternum
the acromioclavicular joint is the ________ end of the clavicle and connects to the _____ of the ______
acromial, acromion, scapula
what is the joint of the proximal humerus?
scapulohumeral (glenohumeral)
the scapulohumeral (glenohumeral) joint is also known as the ….
shoulder joint
the scapulohumeral joint is located at the _____ of the _____ and _____ _____ of the ______
head, humerus, glenoid cavity, scapula
all joints of the upper limb are classified as….
diarthrodial
although diarthrodial, the scapulohumeral joint is also classified as….
spheroidal (ball and socket)
although diarthrodial, the acromioclavicular joint is also classified as….
plane (gliding)
although diarthrodial, the sternoclavicular joint is also classified as….
plane (gliding)
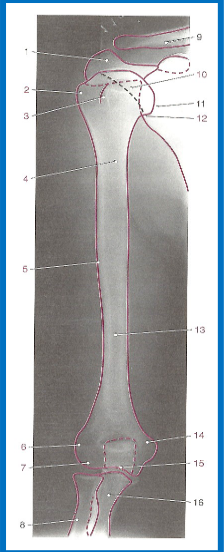
label 1-16 accordingly
1. Acromion process
2. Greater tubercule
3. Intertubercular groove
4. Surgical neck
5. Deltoid tubercule
6. Lateral epicondyle
7. Capitulum
8. Radius
9. Clavicle
10. Humeral head
11. Glenoid cavity
12. Anatomical neck
13. Body (shaft)
14. Medial epicondyle
15. Trochlea
16. Ulna
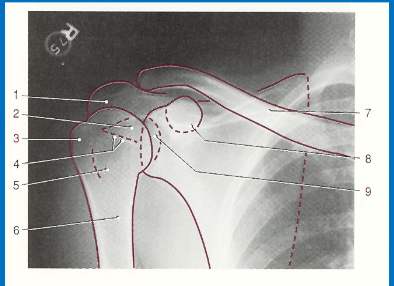
without labeling, this is the anatomy of what kind of x-ray? (projection and body part)
AP shoulder
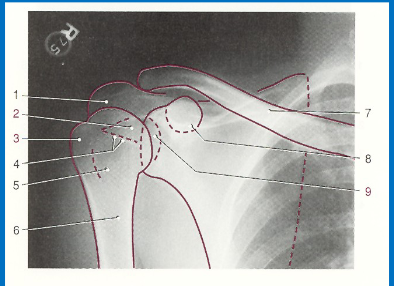
label 1-9 accordingly
1. Acromion
2. Humeral head
3. Greater tubercule
4. Anatomical neck
5. Lesser tubercule
6. Surgical neck
7. Clavicle
8. Coracoid process
9. Glenoid cavity
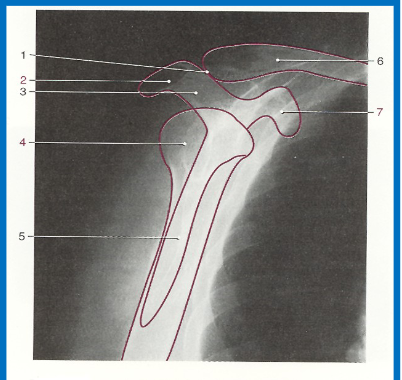
without labeling, this is the anatomy of what kind of x-ray? (projection and body part)
scapular Y lateral
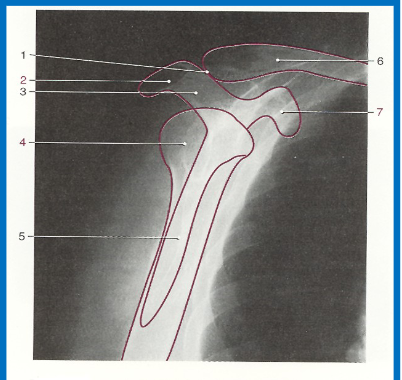
label 1-7 accordingly
1. AC joint
2. Acromion
3. Scapular spine
4. Humeral head
5. Body of scapula (superimposed over
humerus)
6. Clavicle
7. Coracoid process
external rotation of the hand and arm
hand supinated (anatomical position)
neutral rotation of the hand and arm
palm facing thigh with arm down by side
internal rotation of the hand and arm
hand pronated until back of hand against thigh

label the rotation accordingly
proximal humerus rotation (external)
label the rotation accordingly
proximal humerus rotation (external)
proximal humerus rotation (external) characteristics
hand supinated
epicondyles parallel to IR
humerus in “true” AP
greater tubercle lateral (in profile)
lesser tubercle anterior
when the proximal humerus is rotated externally, the hand is
supinated
when the proximal humerus is rotated externally, the epicondyles are ______ to the IR
parallel
when the proximal humerus is rotated externally, the humerus is said to be in ______ __
true AP
when the proximal humerus is rotated externally, the greater tubercle is ______ ___ _______
lateral in profile
when the proximal humerus is rotated externally, the lesser tubercle is ________
anterior
label the rotation accordingly
proximal humerus rotation (internal)
label the rotation accordingly
proximal humerus rotation (internal)
characteristics of a proximal humerus rotation (internal)
back of hand against thigh
epicondyles perpendicular to IR
humerus in “true” lateral
greater tubercle anterior
lesser tubercle medial in profile
when the proximal humerus is rotated internally, the back of the hand should be against…
the thigh
when the proximal humerus is rotated internally, the epicondyles are to be ________ to the __
perpendicular, IR
when the proximal humerus is rotated internally, humerus is said to be in _____ _______
true lateral
when the proximal humerus is rotated internally, the greater tubercle is ________
anterior
when the proximal humerus is rotated internally, the lesser tubercle is ____ ____ _____
medial in profile

label the rotation accordingly
proximal humerus rotation (neutral)
label the rotation accordingly
proximal humerus rotation (neutral)
characteristics of a proximal humerus rotation (neutral)
Palm against thigh
Epicondyles 45° to IR
Humerus in oblique
Greater tubercle (not in profile)
Lesser tubercle (not in profile)
when the proximal humerus is rotated neutrally, the palm is against…
the thigh
when the proximal humerus is rotated neutrally, the epicondyles are ___ to the IR
45 degrees
when the proximal humerus is rotated neutrally, the humerus is in ________
oblique
when the proximal humerus is rotated neutrally, the greater tubercle is….
not in profile
when the proximal humerus is rotated neutrally, the lesser tubercle is….
not in profile
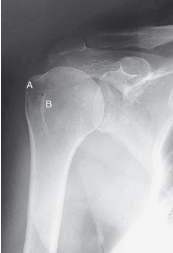
label the rotation accordingly (including projection)
AP external rotation
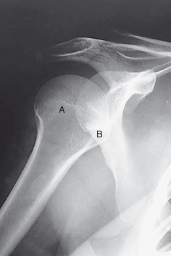
label the rotation accordingly (including projection)
AP internal rotation
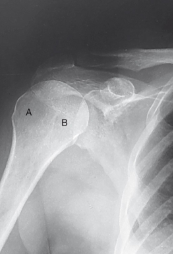
label the rotation accordingly (including projection)
AP neutral rotation
which joint has the greatest freedom of movement of any joint in the body?
scapulohumeral
in which ways can the scapulohumeral joint move?
flexion
extension
abduction
adduction
circumduction
medial/lateral rotation
because the _____ _____ is very _____, the joint requires strong ligaments, tendons, and muscles to provide stability
glenoid cavity, shallow
the shoulder joint is relatively _____ and prone to injuries such as _______ and _____ ____ _____
weak, dislocations, rotator cuff tears
what are the four muscles and associated tendons with the rotator cuff?
subscapularis
teres minor
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
_____ ___ ____ are usually evaluated through MRI after initial x-rays done
rotator cuff injuries
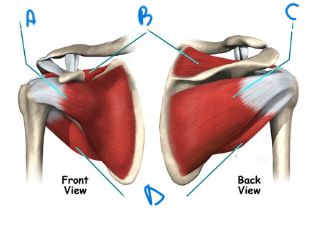
label A-D accordingly
subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor
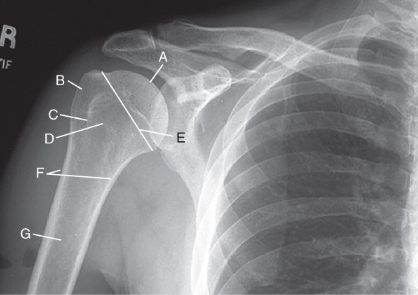
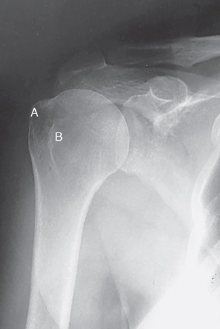
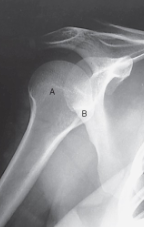
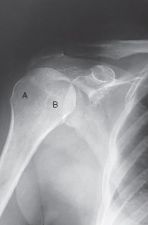
label the anatomy accordingly A-G, the projection/part, and rotation if applicable
head of humerus, greater tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, lesser tubercle, anatomic neck, surgical neck, body
AP shoulder — external rotation
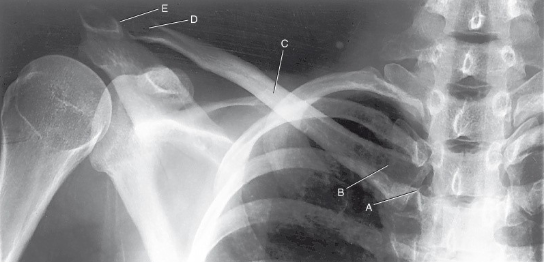
label the anatomy accordingly A-E, the projection/part, and rotation if applicable
sternoclavicular joint, sternal extremity, body, acromial extremity, acromioclavicular joint
AP clavicle
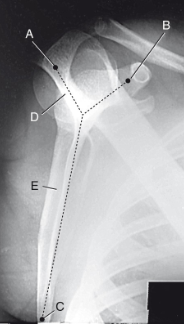
label the anatomy accordingly A-E, the projection/part, and rotation if applicable
acromion, coracoid process, inferior angle, spine of scapula, body of scapula
PA oblique