Storms 2: Supercells, Rain and Air Upbursts
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Satellite imaging
Satellite
Visible Imaging: show clouds during day time only
IR (infrared) images show clouds during both day and night
What does radar imaging show?
Precipitation inside the storm
in updraft, downdraft, stem of mushroom cloud
dbZ
a disaster intensity scale for radar echo strength
indicator of Rainfall Rate
dbz (radar echo intensity (in decibles)
Scale: 0.1-2 light, above 90 (extreme)!
Mesocyclone
A rotating thunderstorm ( includes supercells)
more info about squall lines
Many thunderstorms in a linear/quasi linear line
forms a cold-front! (front of thunderstorm direction is cold!)
Can cause gust front or gustnados
3 types of supercells and what they do
1) low precipitation- LP supercell, produces lots of hail
2) classic supercell- rainy downdraft, rain-free updraft
3) high precipitation- HP supercell, updraft mostly surrounded by rain
What does a rainfall rate of 90-100 and a Radar Echo intensity of over 50dbZ mean?
extreme rain fall (downpours can cause flash floods!!)
Downburst
What: cold dense air sinking that come down from thunderstorm
Why: thunderstorm can create dense air where rain falls; due to evaporative cooling
Risks: often invisible but a hazard to aircrafts
Gust front
what: leading edge of cold horizontal straight line winds
why: downburst air hit ground & spreads outward in straight lines
visible: haboob (if dry ground); arc cloud (if moist air); gustnado
risk: can blow down large trees and destroy weak structures, hazard to aircraft take off and landing
safety: avoid weak buildings and trees
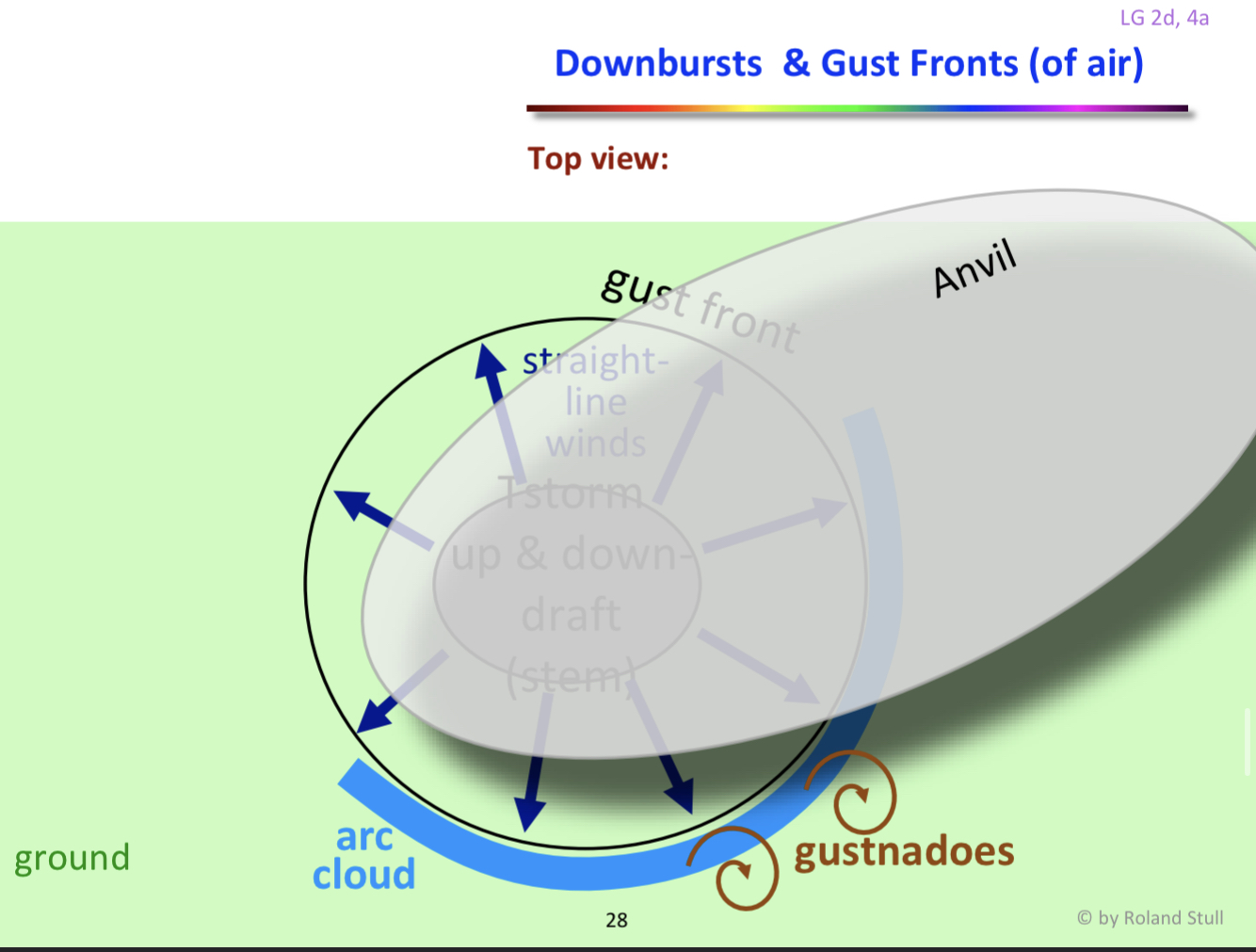
What is a haboob?
A sand storm caused by gust front
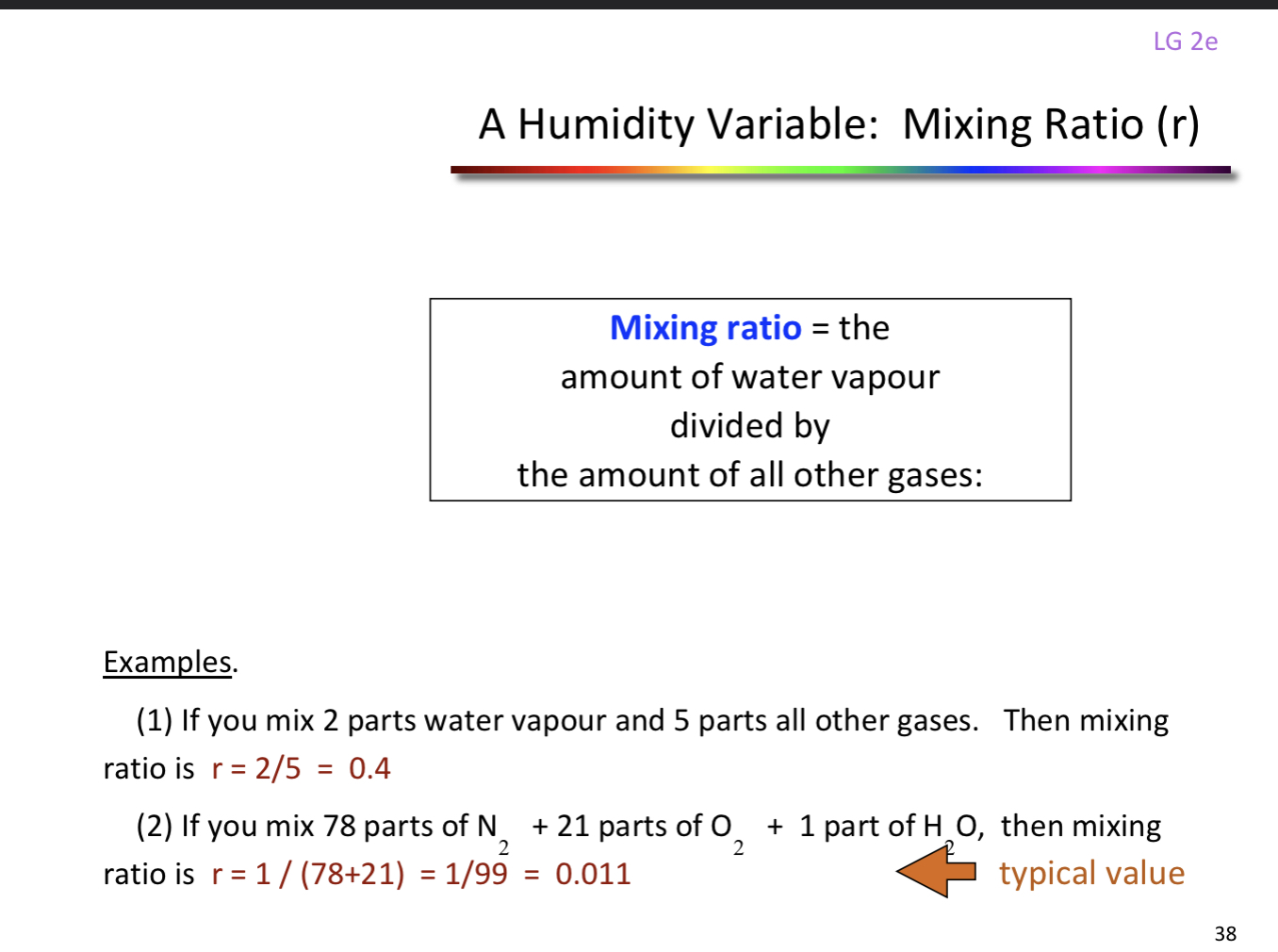
Mixing ratio
The amount of water vapour divided by amount of all other gases
ex. 2 parts water vapor with 5 parts all other gases 2/5=0.4
Saturation
When Mixing ratio—> equillibrium:
condensation rate = evaporation rate
What is saturation value important for?
is important in controlling atmospheric humidity
warmer air can hold more water vapour at equilibrium than cold air!
air that contains max water vapour = saturated (cloudy//foggy). air with less is unsaturated!
What is the relationship between Saturation mixing ratio and temperature?
Its exponential. As temperature goes up, so does the mixing ratio (so it gets more saturated)
Advection
movement of air by the wind. water vapor can be advected into a thunderstorm by the wind
How do storms strengthen (heat wise)?
when latent heat—> sensible heat
When does condensation occur?
When the saturation humidity value becomes smaller than actual humidity value
condensation does what 3 things?
1) releases latent heat back into sensible heat—> makes storms warmer
2) reduces the humidity down to equilibrium (saturation) value
3) produces or increases liquid cloud drops—> become rain drops
What the difference between a mesocylones and supercell?
They are both rotating thunderstorms
however:
Mesocyclone are ANY rotating thunderstorms
Super cells are very large and single-cells (and cause the most violent weather!)
Explain a LP supercell
It can produce lots of hail
Explain a classic supercell
rainy downdraft & rain-free updraft
Explain a HP supercell
supercell updraft mostly surrounded by rain
Explain a Hybrid or “mix-mode storm”
They are in between or contain 2 more types of HP, Classic, or LP supercells
What is a key safety measure to remember during flash floods if you are in a car?
Do not attempt enter flood water (or drive through it) if you dont know the height of the water before you. Even if it looks shallow.
What are 2 big hazards for aircraft?
Downbursts and Gustfronts
Haboobs (dry ground) , arc clouds (moist air) , gustnados are all examples of?
Gust fronts
What is the composition of Air
0-4% water vapor
78% nitrogen
21% oxygen
the rest trace gases
Humidity formal definition
the amount of water vapor in the air
Mixing Ratio Question: if you mix 2 parts water vapor with 5 parts other gases, what is the mixing ratio?
r=2/5= 0.4
Mixing Ratio Question 2: if you mix 78 parts (nitrogen) + 21 parts (oxygen) + 1 part (water), what is the mixing ration?
r= 1/ (78+21)= 1/99 = 0.011
SATURATION VALUE
Maximum humidity that air can hold
If air is cloudy or foggy, what does it mean?
The air is saturated / high saturation value
When a thermal of unsaturated air rises adiabatically, what happens?
the thermal cools roughly 10º celcius/ km rise
cooler air hold less water as water vapour
so some vapour must condense into liquid droplets
condensation releases latent heat
What type of energy does conensation release?
Latent heat!
Adbiatic Cooling
Changes in temperature caused by the expansion (cooling) or compression (warming) of a body of air as it rises or decents in the atmosphere
with no exchange of heat with the surronding air