adv micro exam 2
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
The best way to isolate Listeria from a mixed culture is to use:
Cold enrichment at 4 C followed by subculture
2
New cards
Upon examination, a 7-day-old infant is found to have mucopurulent discharge from his eye. A Giemsa stained smear of his eye scraping shows intracellular inclusions in epithelial cells. The MOST probable organism is which of the following?
Chlamydia trachomatis
3
New cards
An infant was admitted to the hospital with symptoms of meningitis. A lumbar puncture was performed and cultures were ordered. What is the best tube to be sent to Micro for culture and susceptibility testing?
Tube 2 or 3
4
New cards
Clue cells are found on a direct smear of a vaginal specimen. This indicates a possible infection with:
Gardnerella vaginalis
5
New cards
Endemic trachoma and genital infections are caused by:
Chlamydia trachomatis
6
New cards
The most common type of organisms found in the normal intestinal tract is:
Bacteroides and other anaerobic gram negative rods
7
New cards
Which of the following organisms causes hemolytic uremic syndrome in children associated with consumption of under-cooked beef?
E. coli 0157:H7
8
New cards
Hyphae which has become divided into a chain of cells by the formation of transverse walls at regular intervals are described as being:
Septate
9
New cards
Which of the following is a sexual spore?
Ascospore
10
New cards
Listeria may be differentiated from Group B Beta hemolytic Streptococci by the following tests
Gram stain, catalase
11
New cards
A purulent CSF drawn from and 18 year old male reveals the following: WBC: 200/microliter, 98% neutrophils, protein: 80 mg/dl, Glucose: 20 mg/dl. These findings are MOST consistent with
Bacterial meningitis
12
New cards
Non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU) can be caused by certain species of which of the following:
Chlamydia
13
New cards
You have set up biochemical tests on a non-lactose fermenting colony from Hektoen agar on a stool culture. After 4 hours, the urea slant is bright pink. Select the most appropriate action:
Discard the tests, since the NLF is not Shigella or Salmonella
14
New cards
Which genera of the Enterobacteriaceae are known to cause diarrhea and are considered enteric pathogens?
Escherichia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia
15
New cards
In the study of molds it is often necessary to observe the relationship between the reproductive structures and mycelium. This is best accomplished by:
Slide culture technique
16
New cards
The slide culture technique is useful to:
Demonstrate undisturbed sporulating structures
17
New cards
The best procedure to differentiate Listeria monocytogenes from Corynebacterium species is:
Motility
18
New cards
The following statement BEST describes the results of a CSF from a patient with bacterial meningitis:
Decreased glucose, increased protein, increased WBCs with PMNs predominating
19
New cards
Soft chancre or chanchoid is due to infection with
Hemophilus ducreyi
20
New cards
E. coli 0157:H7:
All of the above (produces cytotoxin similar to Shigella, is acquired by heating poorly cooked beef, produces hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) in children, produces bloody diarrhea)
21
New cards
Microscopically, Vibrio appears as a:
Curved gram negative rod
22
New cards
The thick-walled conidia formed from a pre-existing hyphal cell which detaches from the hyphae is a(n):
Arthrospore
23
New cards
Fungus cultures should be incubated at which of the following temperatures for maximum recovery:
30 C
24
New cards
A CSF was received into your microbiology lab. Upon examining the patient information on the request from and comparing it to the information on the specimen itself, a difference in names is noted. The appropriate course of action would be to:
Phone the physician and ask for a confirmation
25
New cards
A colony on blood agar from a vaginal specimen looks like group B Strep. However, the colonies are catalase positive and gram stain reveals a gram positive rod. It has enhanced umbrella motility at room temperature and grows at 4°C. It probably is:
Listeria monocytogenes
26
New cards
"Clue cells" indicating infection with Gardnerella vaginalis may be observed in which of the following?
saline wet preparation or gram stain of vaginal discharge
27
New cards
Normal flora of the female genital tract (of childbearing age) includes heavy amounts of:
Lactobacillus
28
New cards
Which of the following tests best differentiate Shigella species from E. coli?
Lysine, indole, ONPG, and motility
29
New cards
A mass of threadlike filaments, branched or composing a network, which constitute the vegetative structure of a fungus is:
Mycelia
30
New cards
In the study of molds it is often necessary to observe the relationship between the reproductive structures and mycelium. This is best accomplished by:
slide culture technique
31
New cards
A woman who had recently returned from a vacation in Mexico was admitted to the hospital. She was febrile and complained of flu-like symptoms. Her case history revealed that she had eaten cheese that had been made from unpasteurized milk while on vacation. The most likely etiologic agent in this case would be:
Listeria monocytogenes
32
New cards
The MOST common cause of bacterial meningitis in newborns is:
Gp B strep and E. coli
33
New cards
Bacterial pathogens for newborns, which are always looked for on a routine genital culture from the mother, are:
Group B Beta hemolytic Strep, Listeria
34
New cards
When examining stool cultures for Enterohemorrhagic E. coli 0:157 H7, select the media used and colony characteristics of this organism:
MAC Sorbitol: negative– colorless colony
35
New cards
A lactophenol cotton blue tease prep is prepared on a fungal colony. Upon examination no intact sporulating structures can be found. Select the most appropriate technique which will easily show intact sporulating structures.
Modified slide culture
36
New cards
The most appropriate step to visualize intact sporulating structures on a fungus would be:
Prepare a slide culture with PDA
37
New cards
Small, milky white, beta hemolytic colonies that are catalase negative grow from the CSF of a one-week-old baby. Select the most appropriate work-up:
Camp test or hippurate test
38
New cards
Which virus is associated with genital warts and produce lesions of skin and mucous membranes?
Human Papillomavirus
39
New cards
A small, beta-hemolytic, catalase positive colony has been isolated from a vaginal culture. Gram stain shows gram positive rods and umbrella motility in semi-solid agar. This is most descriptive of:
Listeria monocytogenes
40
New cards
Safety practices in Mycology include
using a biological safety hood
41
New cards
The MOST common pathogens causing meningitis in older children and adults are:
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis
42
New cards
Which of the following are characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes:
causes septicemia and meningitis primarily in neonates and the immunocompromised, umbrella motility at 25°C
43
New cards
Corn meal agar is most useful in:
Stimulating sporulation for identification
44
New cards
Select the method used to screen for E. coli 0157:H7 in stool specimens:
MacConkey containing sorbitol
45
New cards
Which of the following is/are characteristic of Chlamydia trachomatis
Produces inclusion bodies in the cytoplasm of infected cells
46
New cards
A fecal specimen is inoculated with Hektoen enteric agar. Blue-green colonies are isolated. Biochemical screening produces the following key characteristics.
TSI: K/A no gas
Motility: Non motile
Lysine Decarboxylase: Negative
Urease: Negative
The isolate MOST probably belongs to which of the following genera?
TSI: K/A no gas
Motility: Non motile
Lysine Decarboxylase: Negative
Urease: Negative
The isolate MOST probably belongs to which of the following genera?
Shigella
47
New cards
In working up a stool culture you carefully pick up four different suspicious colony types and inoculate them to TSI, LIA, and urea. The next day the following results are noted. Which should be worked up further as a possible Salmonella or Shigella?
TSI: K/A/H2S LIA: K/ K H2S Urea: =
48
New cards
Treatment of Vibrio cholera is imperative because of:
Rapid and intensive loss of fluids and electrolytes
49
New cards
A stool pathogen, which requires a media with increased salt such as TCBS, is:
Vibrio
50
New cards
Streptococcus agalactiae is most noted as a cause of:
Neonatal disease
51
New cards
A stool specimen was received in the lab and the clinical history of the patient indicated possible infection with Vibrio. Which additional medium should be inoculated
TCBS (thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose) agar
52
New cards
A purulent CSF drawn from and 18 year old male reveals the following:WBC:200/μl, 98% neutrophils
Protein: 80 mg/dl
Glucose:20 mg/dl
These findings are MOST consistent with:
Protein: 80 mg/dl
Glucose:20 mg/dl
These findings are MOST consistent with:
Bacterial meningitis
53
New cards
The organism, which may be confused with Corynebacterium species (diphtheroids) on a Gram stain smear, is:
Listeria monocytogenes
54
New cards
An opportunistic yeast, which never forms mycelia or pseudohyphae, does not have a capsule, and assimilates only glucose and trehalose is most likely
Candida glabrata
55
New cards
The specific type of conidium produced by asexually reproducing yeast is the:
Blastospore
56
New cards
Serious infection by yeast may occur in diabetics, young children, or infants and the immunosuppressed host. What is the most probable causative agent?
Candida albicans
57
New cards
A white, powdery mold with brown reverse pigment is isolated on Mycosel agar in 5 days. Microscopic morphology demonstrates septate hyphae, globose microconidia in grape-like clusters and smooth pencil shaped multi celled macroconidia. Select the most appropriate techniques for definitive identification:
Hair penetration testing, urease
58
New cards
The hair penetration test is utilized primarily to differentiate the following organisms:
T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes
59
New cards
The Dermatophytes infect which of the following:
Hair, skin, nails
60
New cards
Sporothrix schenckii has the following characteristic
Dimorphic
61
New cards
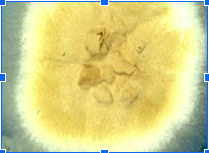
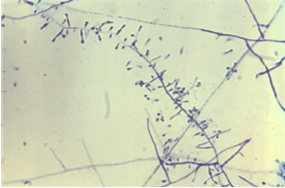
This organism was isolated from an inflammatory lesion of the skin from the scalp of a young male athlete. Pictured below is the organism on sab dex agar and a lactophenol blue mount. Based on these observations, what is the presumptive identification of the fungus?
T. tonsurans
62
New cards
Which of the following causes Chromomycosis:
Cladosporium species
63
New cards
Which of the following morphological features would correspond to Phialophora sp.?
Urn or vase-shaped phialides
64
New cards
Which of the following on direct exam can differentiate Eumycotic mycetoma from actinomycotic mycetoma:
Microscopic width of the hyphae compared to the width of the branching rods
65
New cards
The slide culture technique is useful to:
Demonstrate undisturbed sporulating structures
66
New cards
A definitive method to fully identify a yeast is:
Carbohydrate assimilation
67
New cards
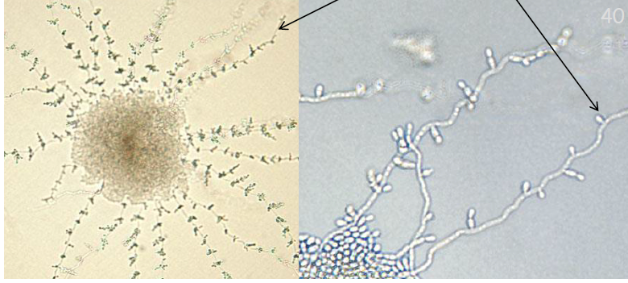
This organism was collected from an immunocompromised patient with prolonged antibiotic use. The images below are from the cornmeal slide culture of this organism. What is the identification of this organism?
Candida tropicalis
68
New cards
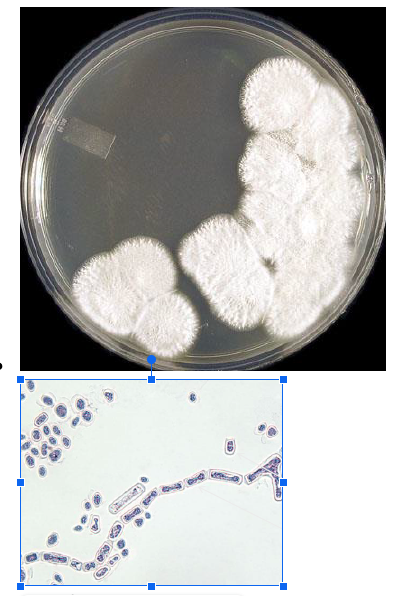
Pictured below is an organism isolated from a lesion of the mouth. What is the presumptive identification of this organism?
Geotrichum candidum
69
New cards
The morphologic structures which identify Candida albicans and distinguish it from other Candida species are:
chlamydospores
70
New cards
The species of fungus causing epidemic ringworm infection in children in the US is:
Microsporum audouinii
71
New cards
A fungus presumptively identified as a Trichophyton is inoculated to T agars. T1 and T2 show scant growth. T3 and T4 show good growth. The organism is:
Trichophyton tonsurans
72
New cards
Species of Cladosporium, Phialophora, and Fonsecaea can be differentiated from each other by:
Pattern of conidial formation seen in microscopic exam from culture
73
New cards
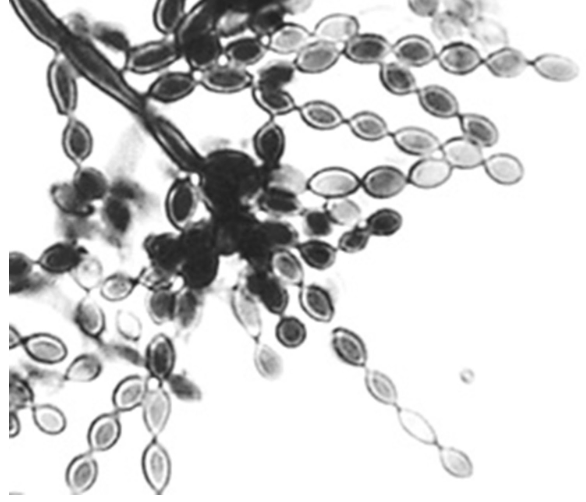
Illustrated in this image is the fruiting head of one of the fungal agents of chromomycosis. Which of the following represents the type of sporulation illustrated here?
Cladosporium sporulation
74
New cards
The thick-walled conidia formed from a pre-existing hyphal cell which detaches from the hyphae is a(n):
Arthrospore
75
New cards
The yeast characterized by "giant hyphae" on cornmeal is:
Candida parapsilosis
76
New cards
The genus of Dermatophytes characterized by the thick-walled, echinulate, spindle shaped macroconidia is:
Microsporum
77
New cards
An organism, which usually causes a lymphatic infection after an initial prick with a rose thorn, is which of the following:
Sporothrix schenckii
78
New cards
A carnation grower in Colorado developed an ulcerated lesion on his hand. With time the infection spread up the lymphatics resulting in several lesions along his arm. The fungus most likely to be responsible for this disease is:
Sporothrix schenckii
79
New cards
A mass of threadlike filaments, branched or composing a network, which constitute the vegetative structure of a fungus is:
Mycelia
80
New cards
A yeast, which produces pink to red colonies, is:
Rhodotoruia
81
New cards
A yeast-like organism has been isolated from a blood culture. No mycelium was produced on corn meal agar, inositol was assimilated, and urease was produced at 35°C. This organism is:
Crytococcus neoformans
82
New cards
If a single budding, yeast surrounded by a wide gelatinous capsule is found in an India ink preparation of the spinal fluid, or is + by Cryptococcal Antigen EIA, the organism is most likely:
Crytococcus neoformans
83
New cards
A dermatophyte, which produces smooth, thin-walled macroconidia singly or in clusters and which does not produce microconidia is:
Epidermophyton floccosum
84
New cards
From a skin scraping culture of tinea pedis, a colony with a very white and powdery surface and patchy reddish-brown reverse pigment has grown. Microscopically, numerous microconidia (en grappe) and spiral hyphae are seen. Hair penetration test is positive. The most likely identification is:
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
85
New cards
The tissue form of chromomycosis is:
Sclerotic bodies
86
New cards
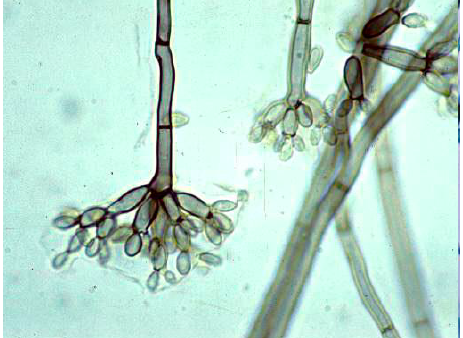
Given the image below, what is the presumptive identification of this organism?
Fonsecaea pedrosoi
87
New cards
Which of the following best describes the size and staining characteristics of yeast cells on a gram stain?
About the same size as a red blood cell and stains purplish-blue
88
New cards
Tinea versicolor is caused by which of the following fungi:
Malassezia furfur
89
New cards
A fungus cultured from a case of tinea corporis produces thick-walled, spindle-shaped macroconidia, with 4-6 cells. The colony is tan colored and powdery with a neutral reverse. Which of the following is it most likely to be:
Microsporum gypseum
90
New cards
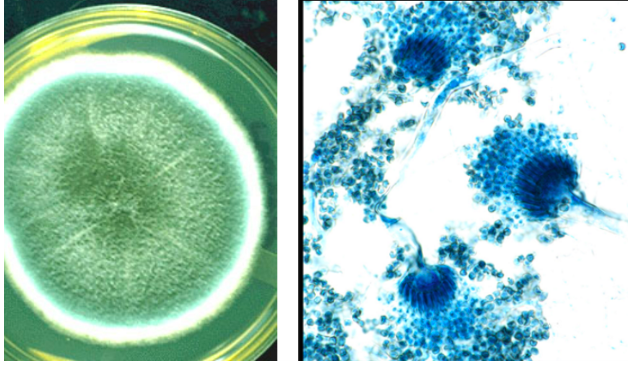
This colony was obtained from a sputum fungal culture from a construction worked with a lung abscess. What is the identification of this organism?
Aspergillus fumigatus
91
New cards
A black mold is isolated from a tissue specimen. Microscopic morphology is simple conidiophores containing long chains of small oval conidia. The identification of this organism is:
Cladosporium sp.
92
New cards
Candida albicans is responsible for a wide variety of diseases and one fourth of all deaths caused by fungi in the US. A factor contributing to this situation is the fact that:
C. albicans is present as normal flora and is readily available to invade when host defenses are lowered
93
New cards
Fungal skin infections may be due to:
Candida albicans, Dermatophytes
94
New cards
Agents of chromomycosis are:
Fonsecaea, Phialolophora, Cladosporium
95
New cards
Yeast recovered from the urine of a catheterized patient receiving chemotherapy for cancer gave the following results:
Germ tube +
Blastospores +
Pseudohyphae +
Arthospores 0
Chlamydospores +
What further testing is necessary?
Germ tube +
Blastospores +
Pseudohyphae +
Arthospores 0
Chlamydospores +
What further testing is necessary?
No further testing is needed for identification
96
New cards
The species of Trichophyton which produces pencil shaped macroconidia, a deep red reverse pigment and tear dropped microconidia in thyrses is:
T. rubrum
97
New cards
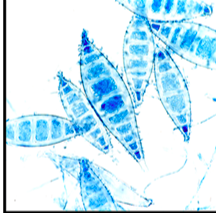
This is an image from a 4-day old culture form a "ringworm" cutaneous infection. With this lactophenol cotton blue stain, what is the identification of this organism?
Microsporum canis
98
New cards
A fungus isolated from a case of "Athlete's Foot" is found to produce urease and is hair penetration positive. The most likely identification is:
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
99
New cards
The following tests are utilized to distinguish Cryptococcus neoformans from other cryptococccus species:
Caffeic acid disc, nitrate
100
New cards
A yeast-like organism has been isolated from a blood culture. No mycelium was produced on corn meal agar, inositol was assimilated, and urease was produced at 35°C. This organism is:
Cryptococcus neoformans