Axial Skeleton--Pictures
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
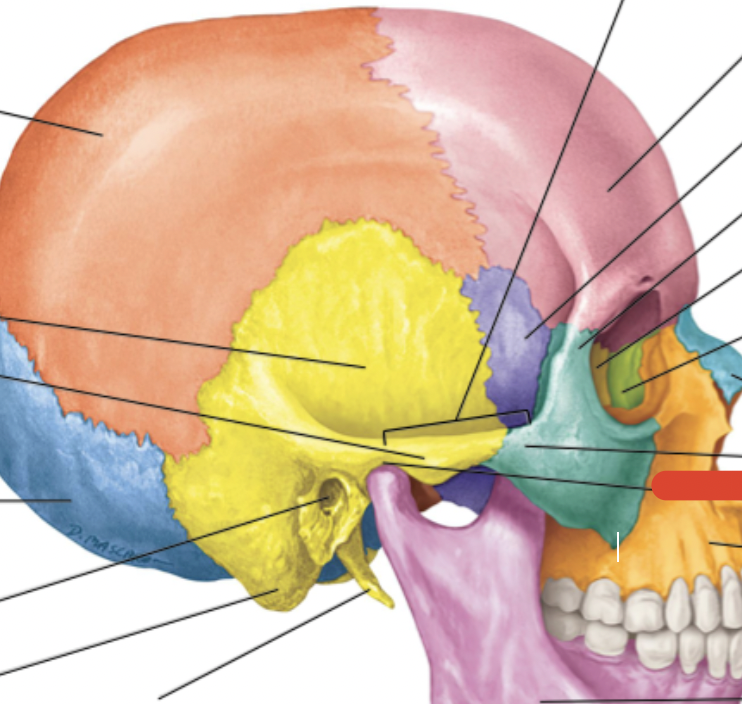
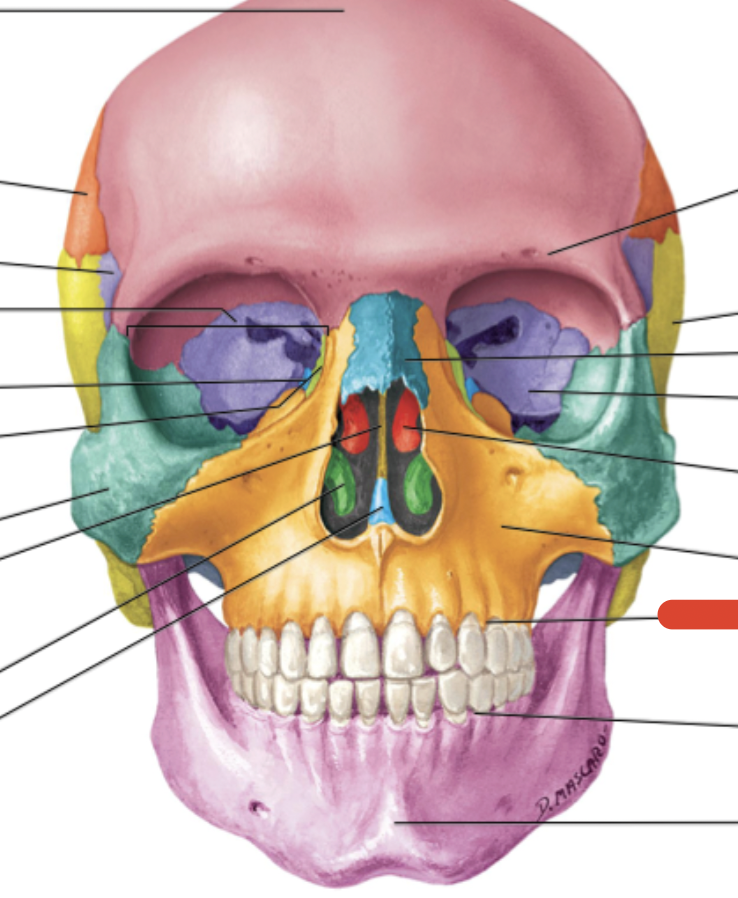
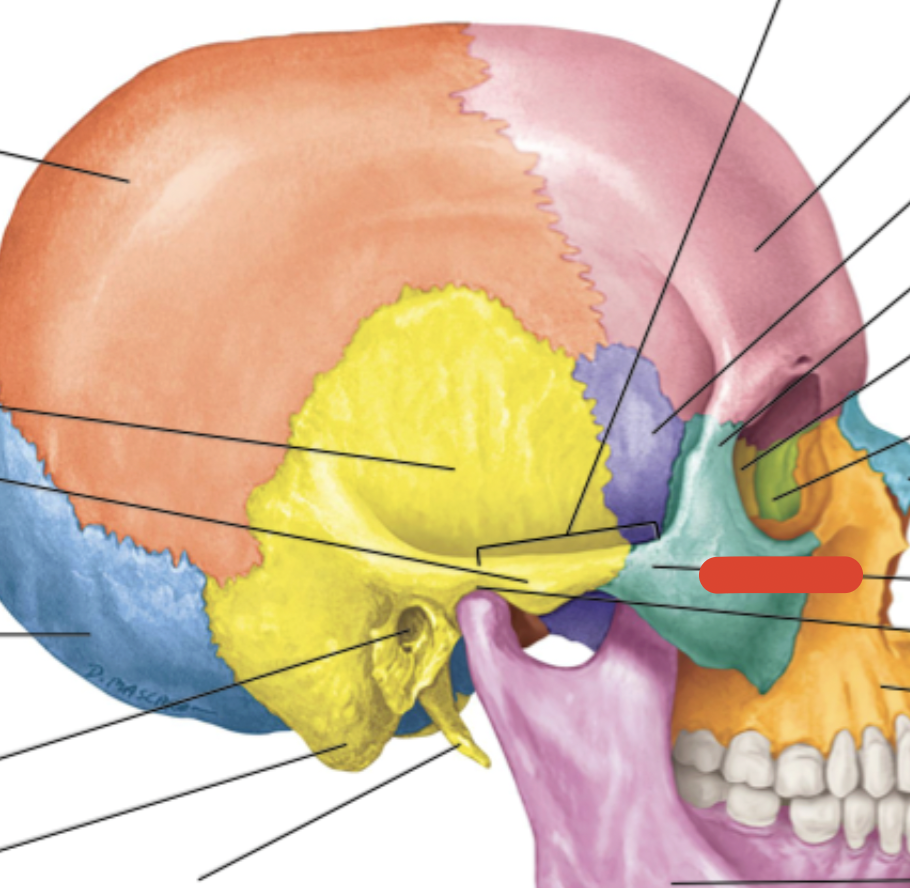
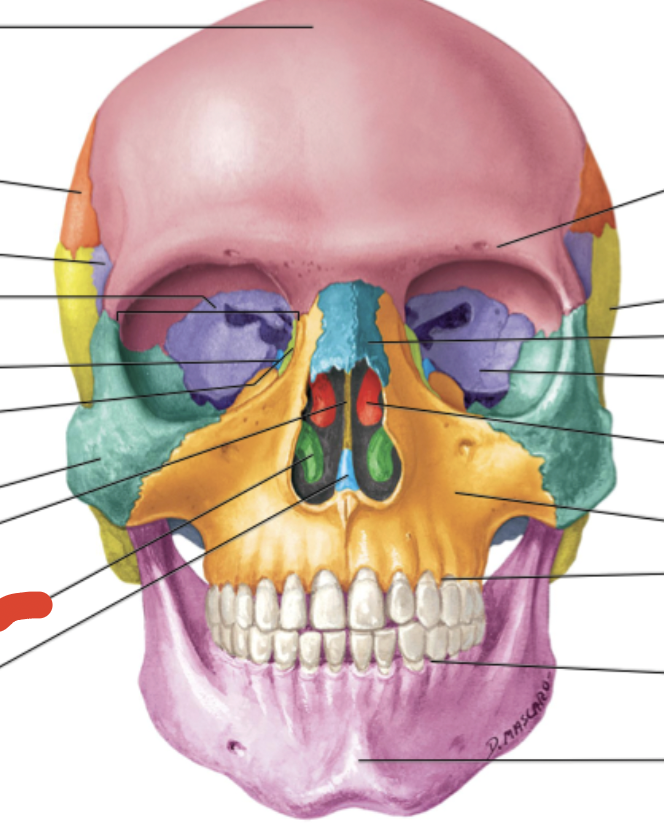
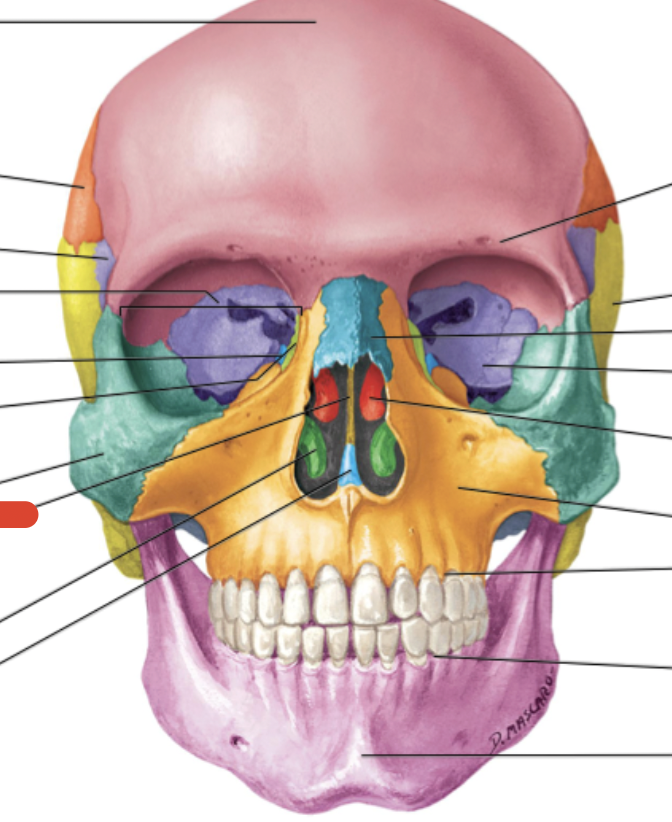
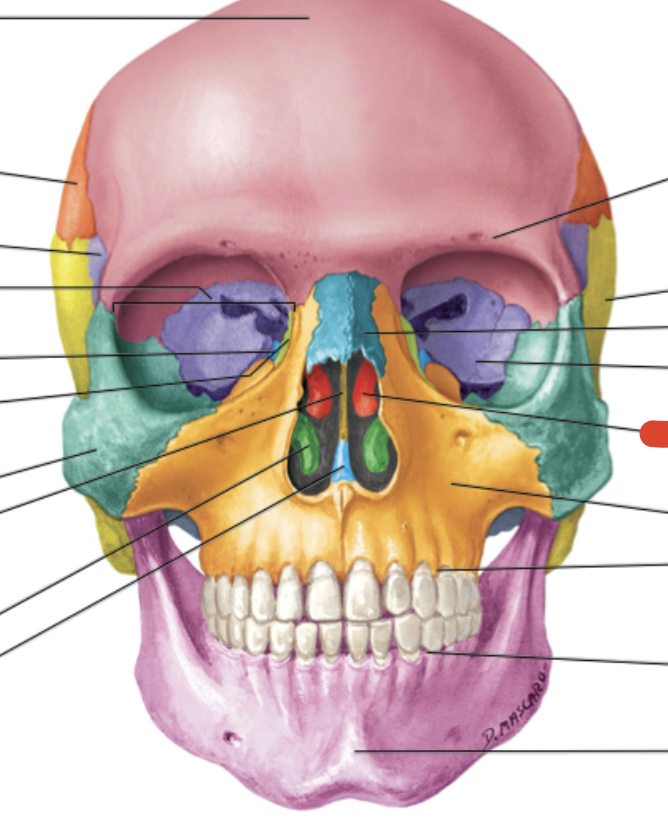
Ethmoid bone
separates nasal & cranial cavities
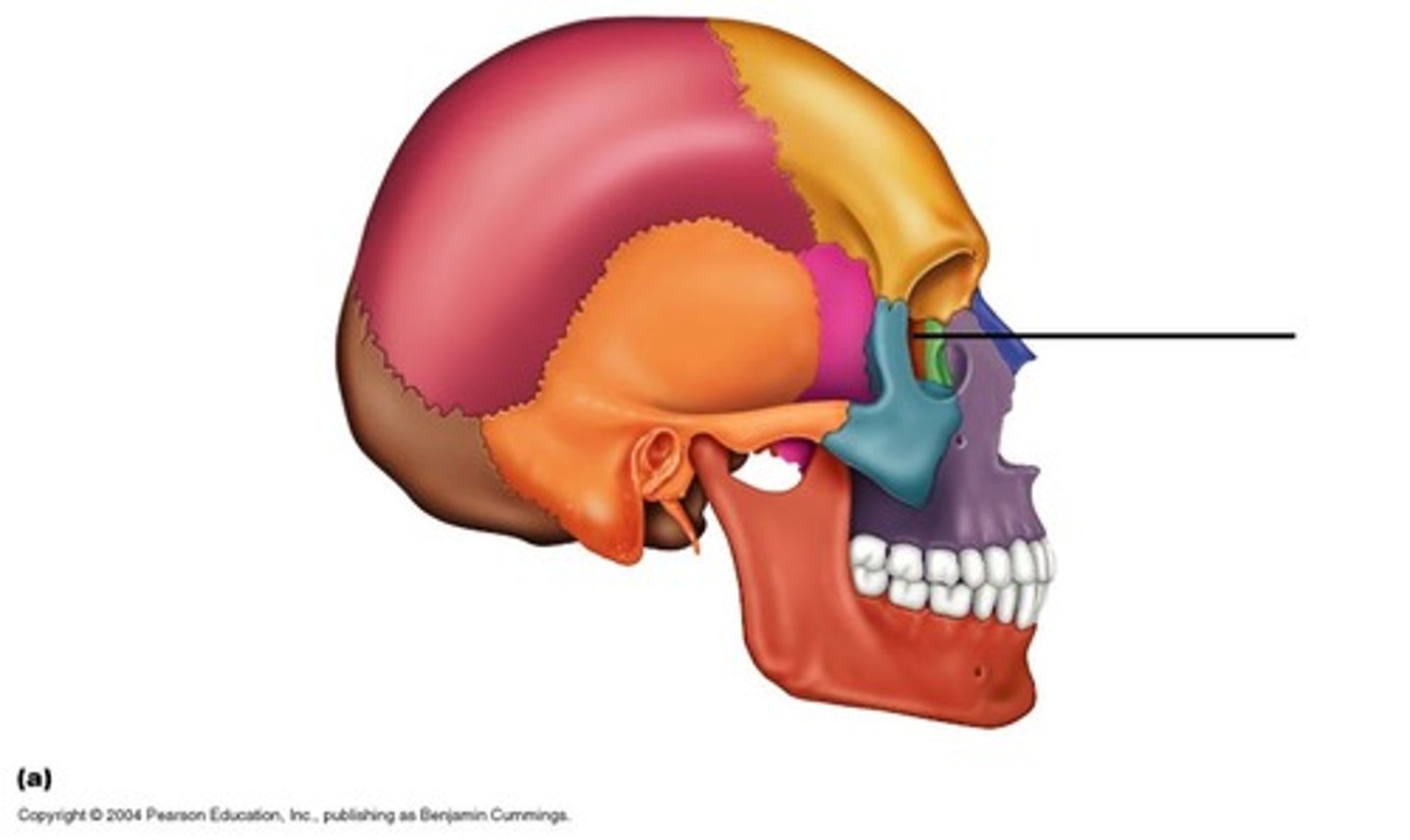

part of axial. 8
cranial bones

part of axial. 14
facial bones
the skull bones
Hyoid Bone
Found below chin under the mandible
attachment point for tongue muscles
Attachment point for neck muscles that elevate larynx during speech & swallowing

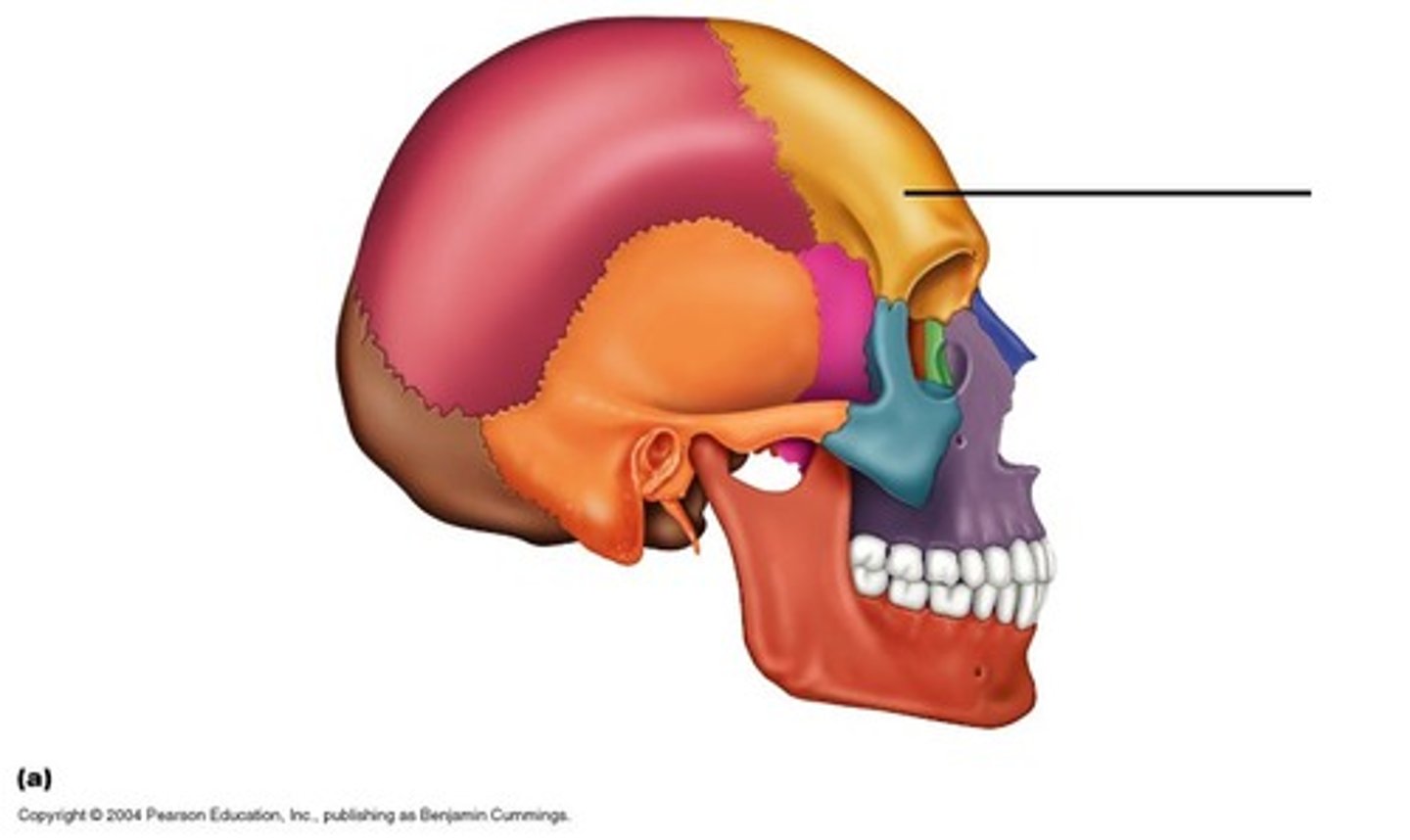
Frontal bone
Sphenoid bone
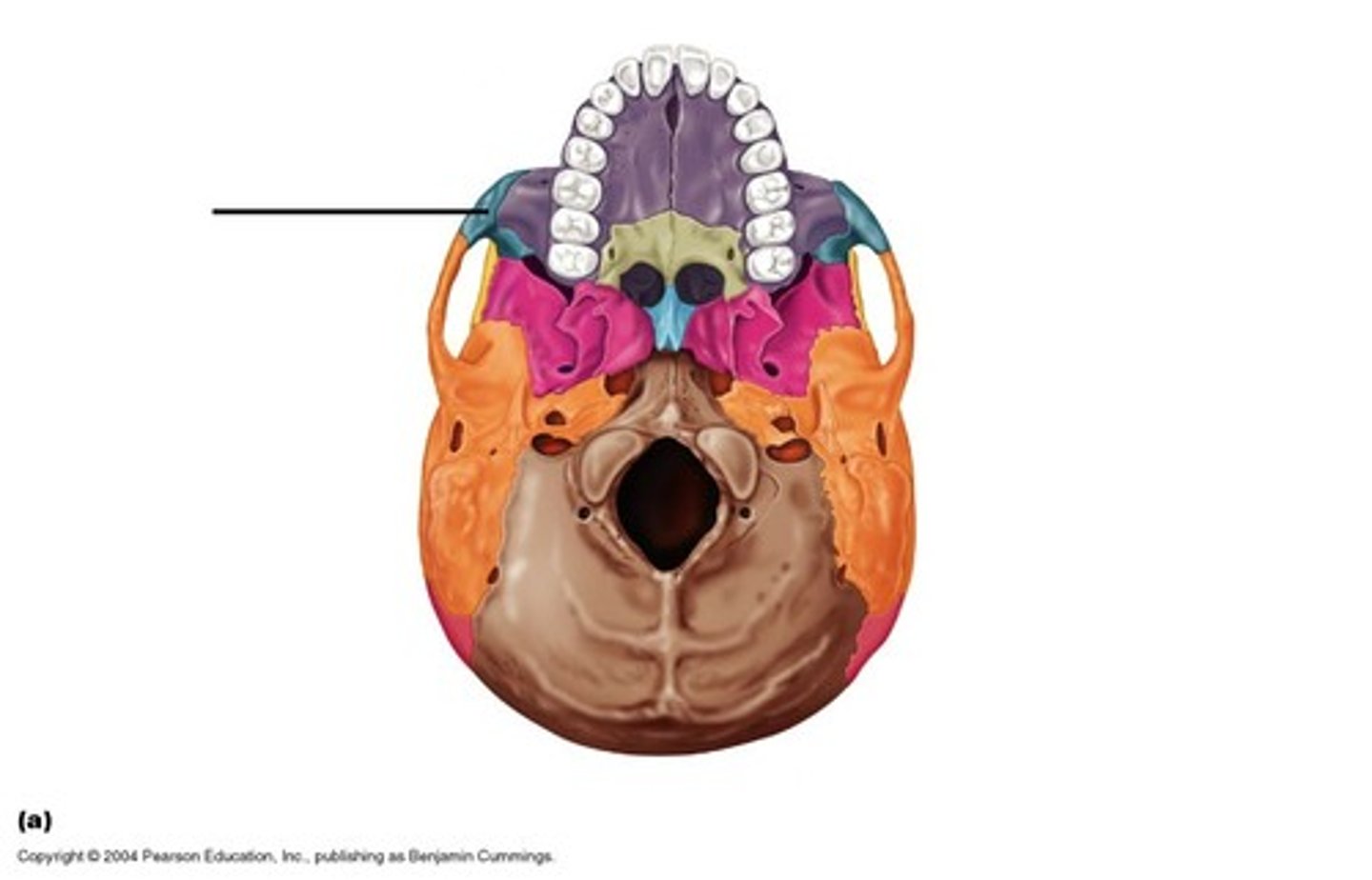
Zygomatic bone
Maxilla bone
Palatine bone
Lacrimal bone
Ethmoid bone
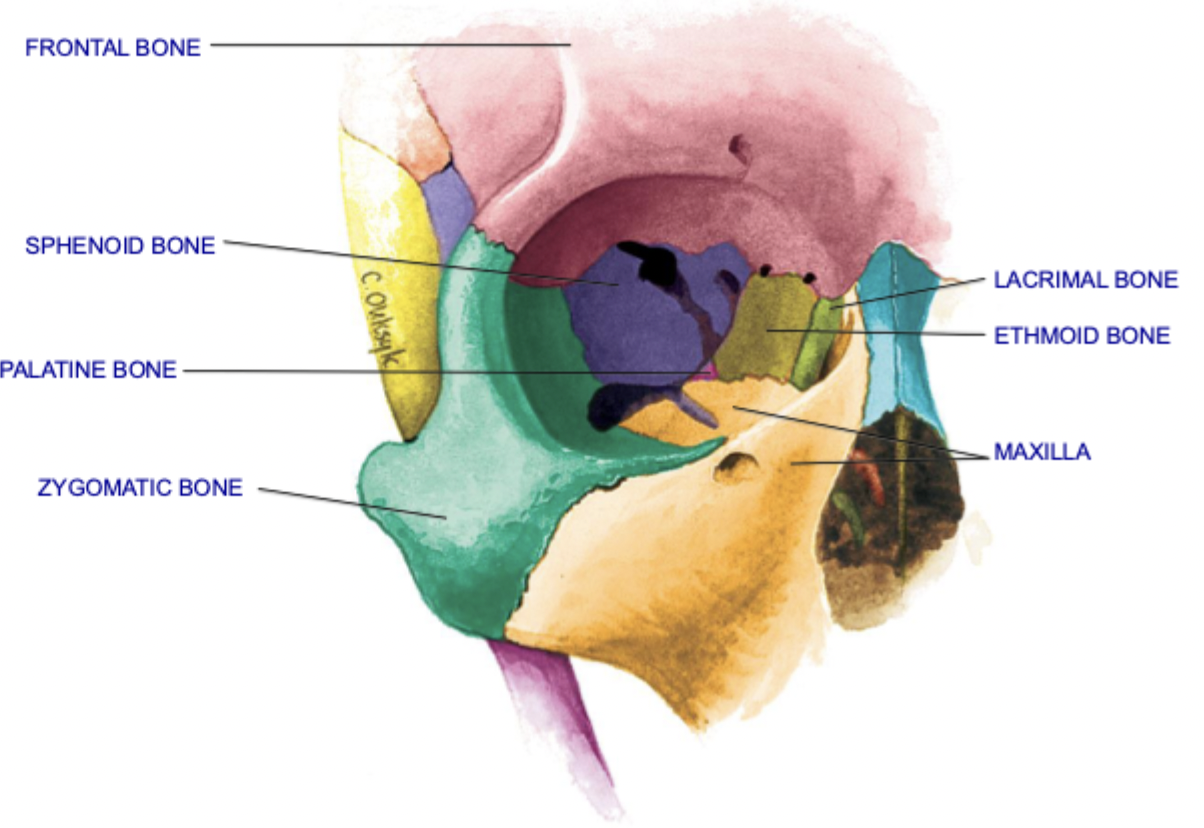
Bones of the Orbit - 7
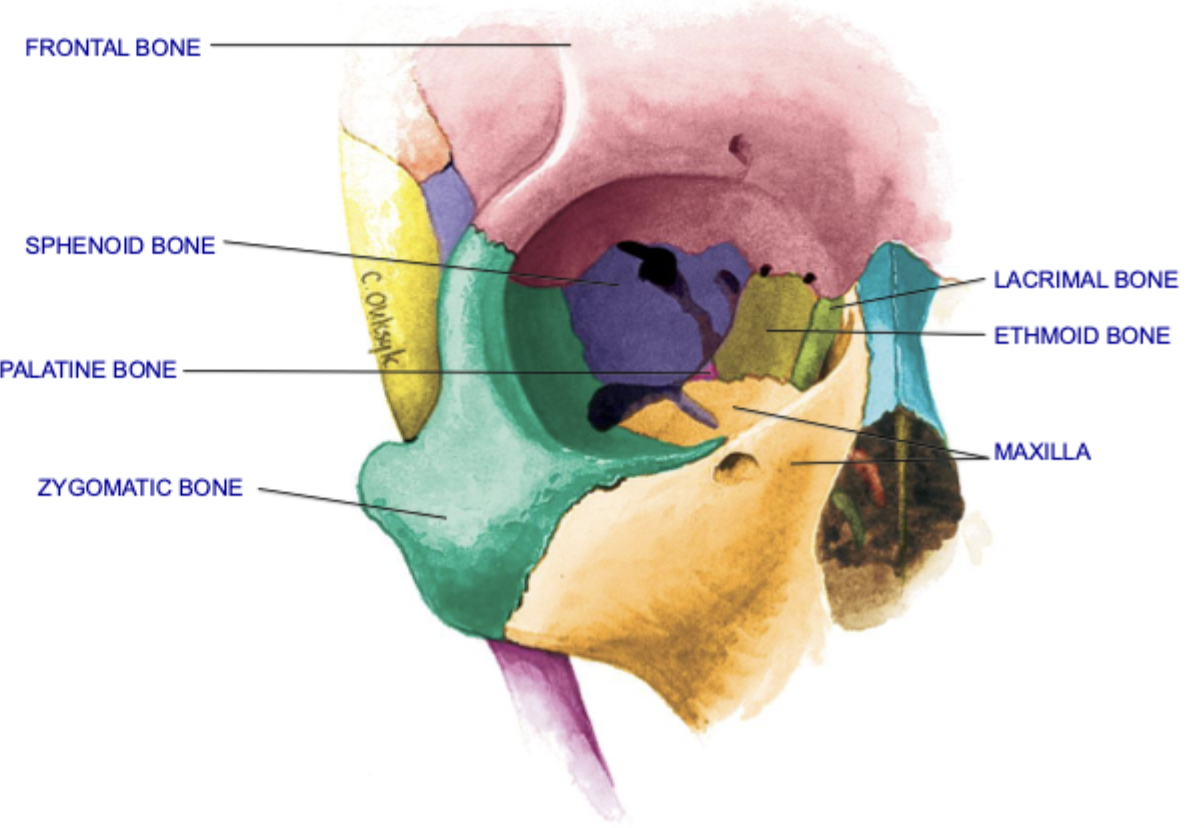
Roof of orbit: frontal, sphenoid
Lateral wall of orbit: sphenoid, zygomatic
Floor of orbit: zygomatic, maxilla, palatine
Medial wall of orbit: sphenoid, maxilla, lacrimal, ethmoid
bones of orbit places
- Palatine process & maxilla
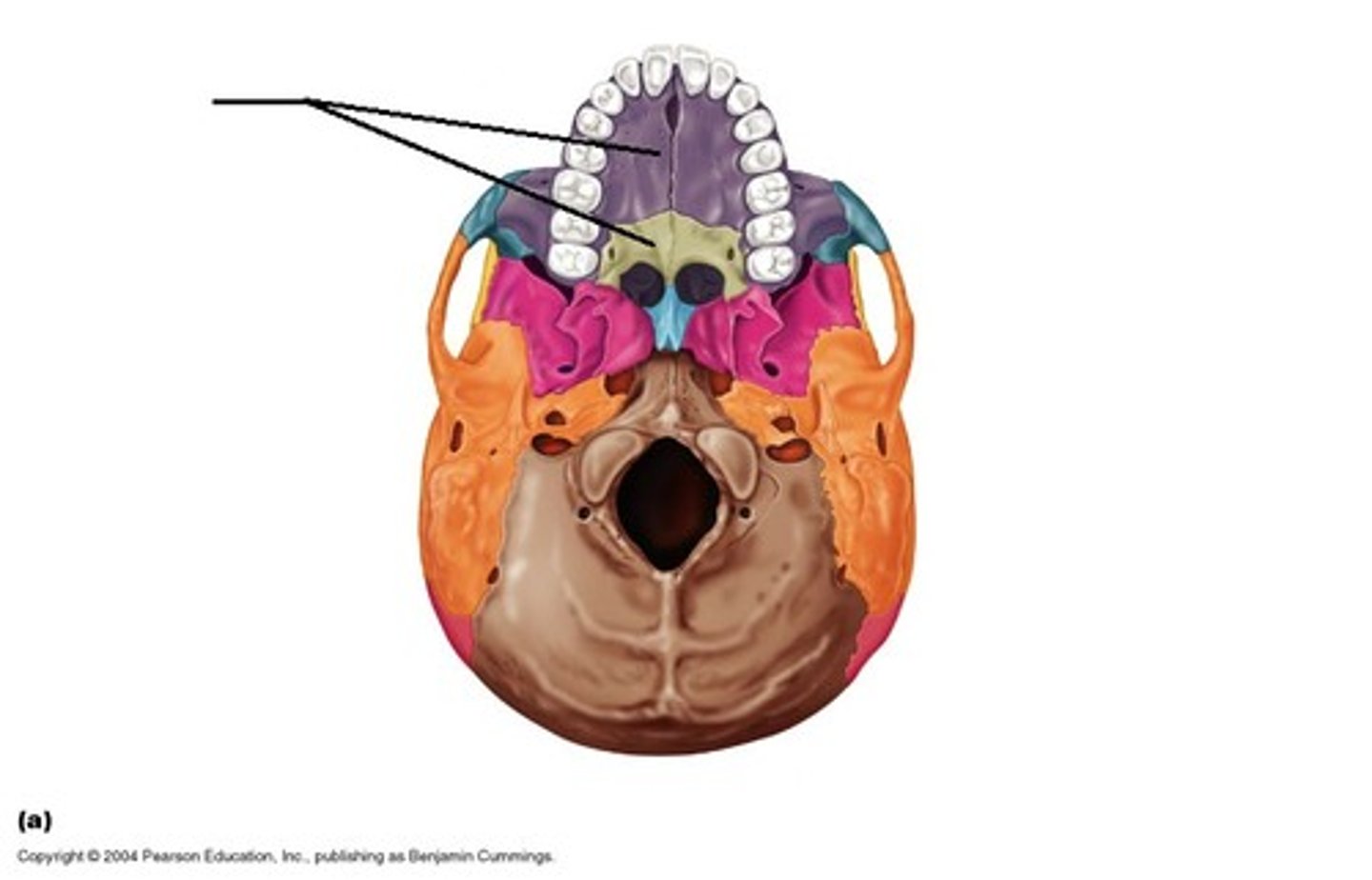
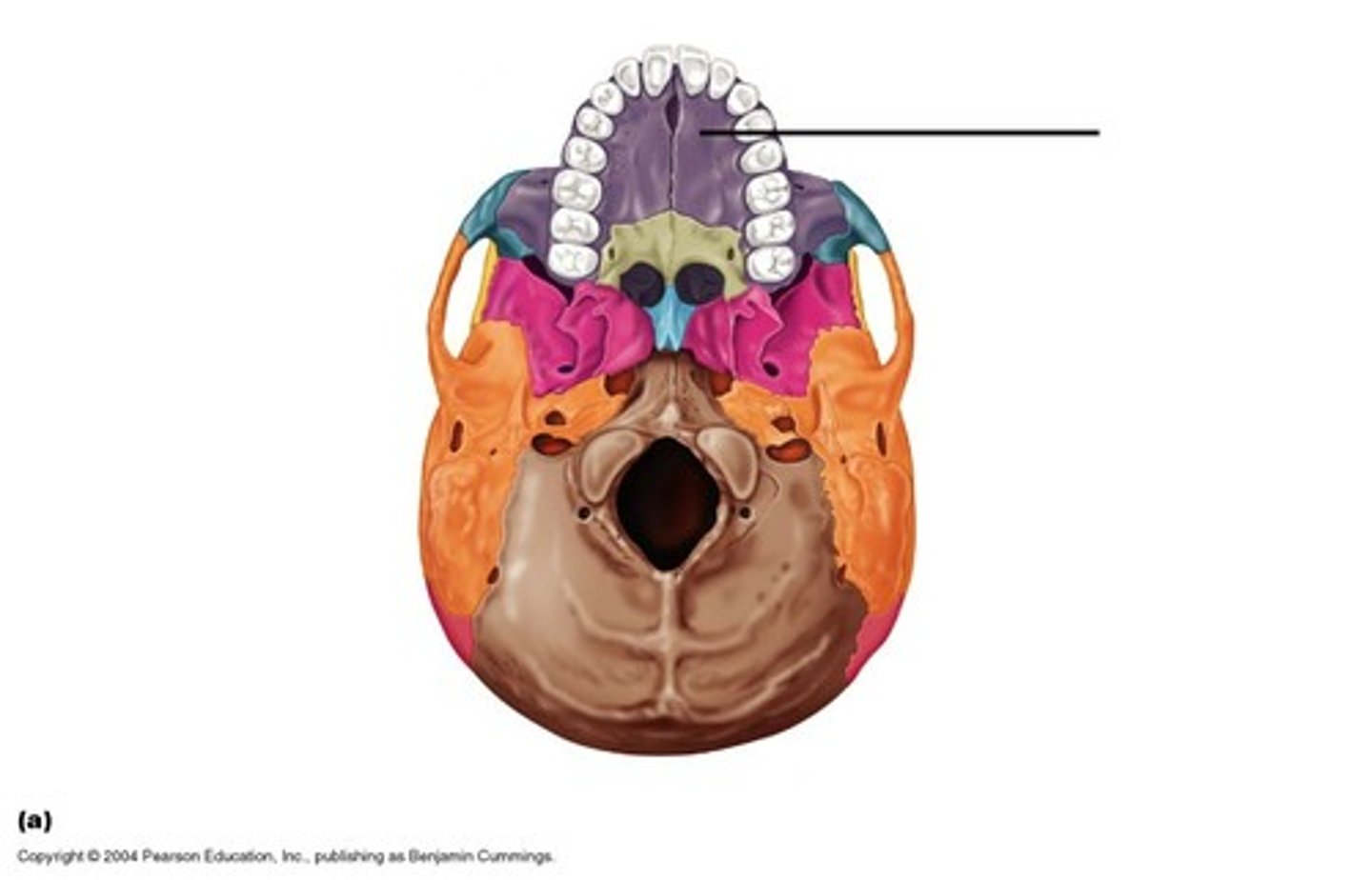
What makes up the “hard palate”?
mandibular fossa
wehre Articulates with temporal bone
Alveolar process of maxilla
creates spaces so teeth fits into upper & lower jaw
temporal process
joins together with zygomatic process of temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch → cheekbone
Supraorbital margin
thickened region of frontal bone that protects region of orbit
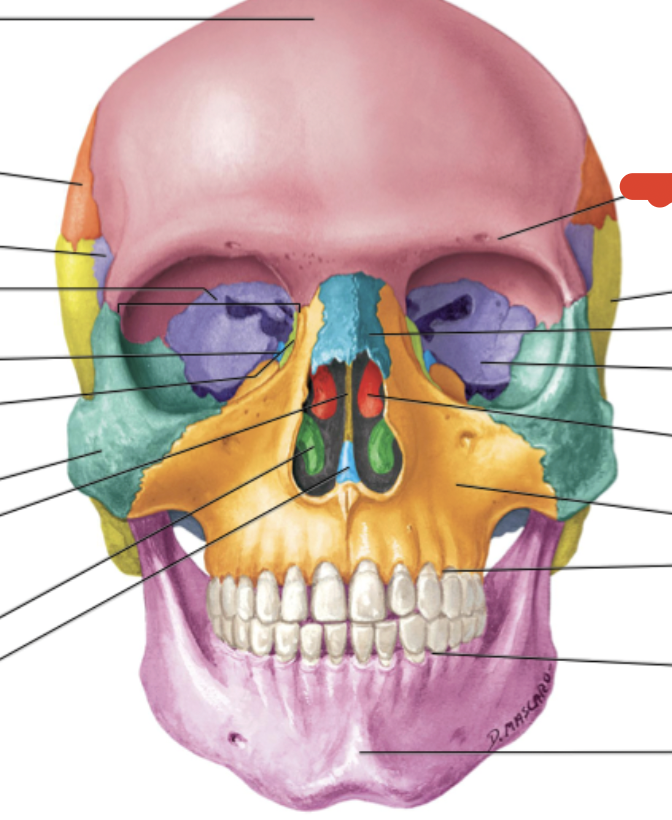
Inferior nasal conchae (2)
ridges - fhelps guide odorants to chemoreceptors & ridges trap air
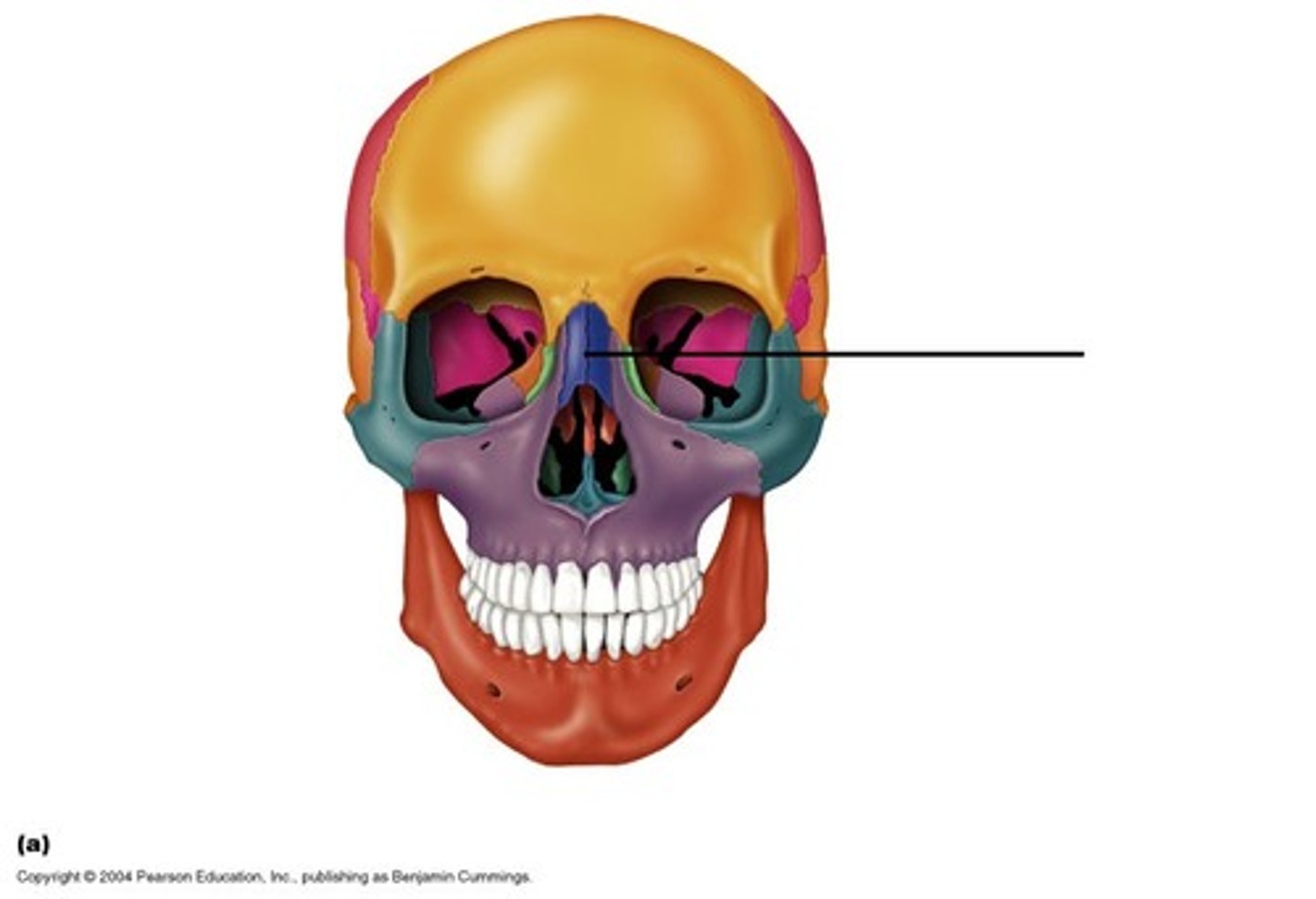
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
Middle nasal conchae & superior nasal conchae of ethmoid bone
Ethmoid bone
separates nasal & cranial cavities
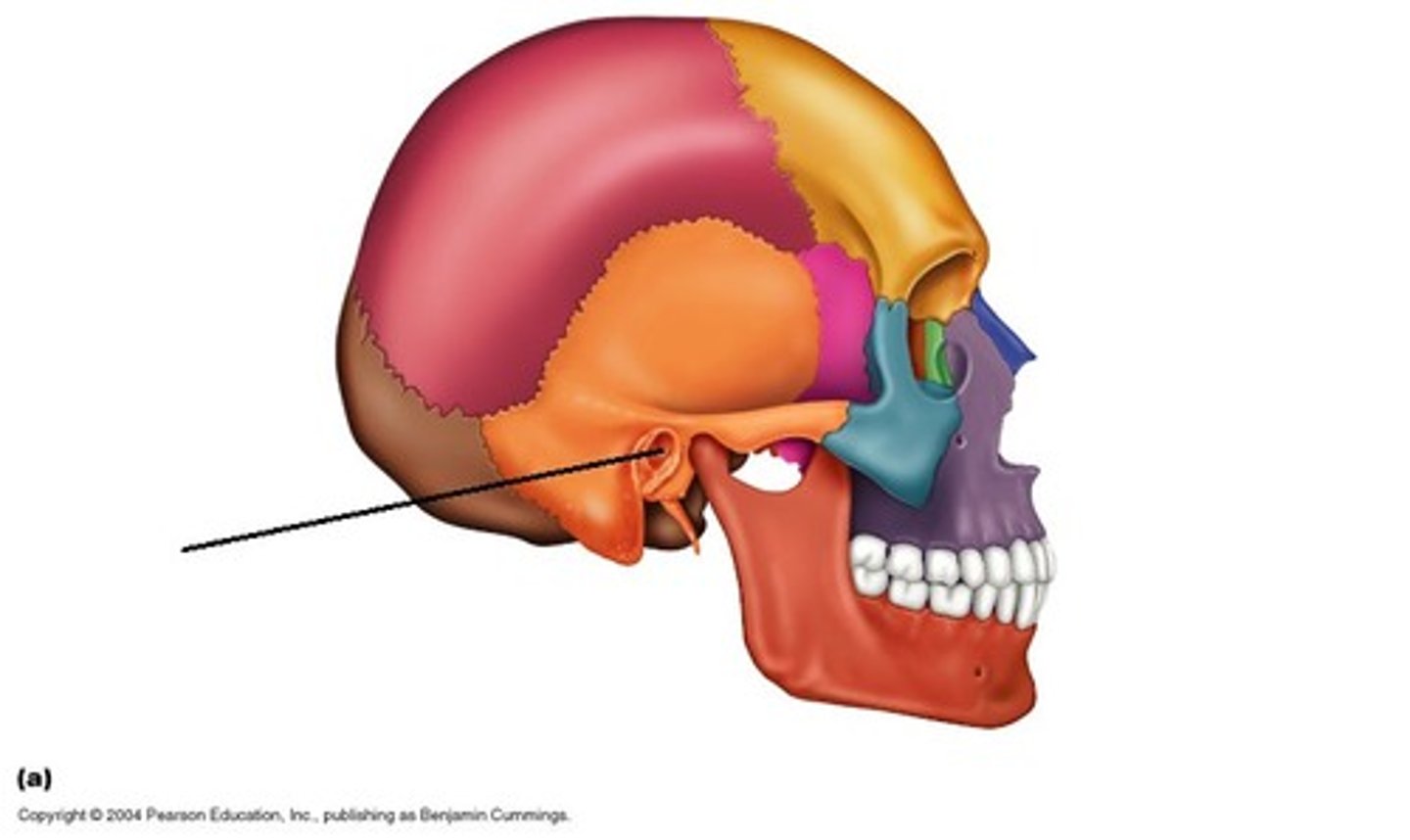
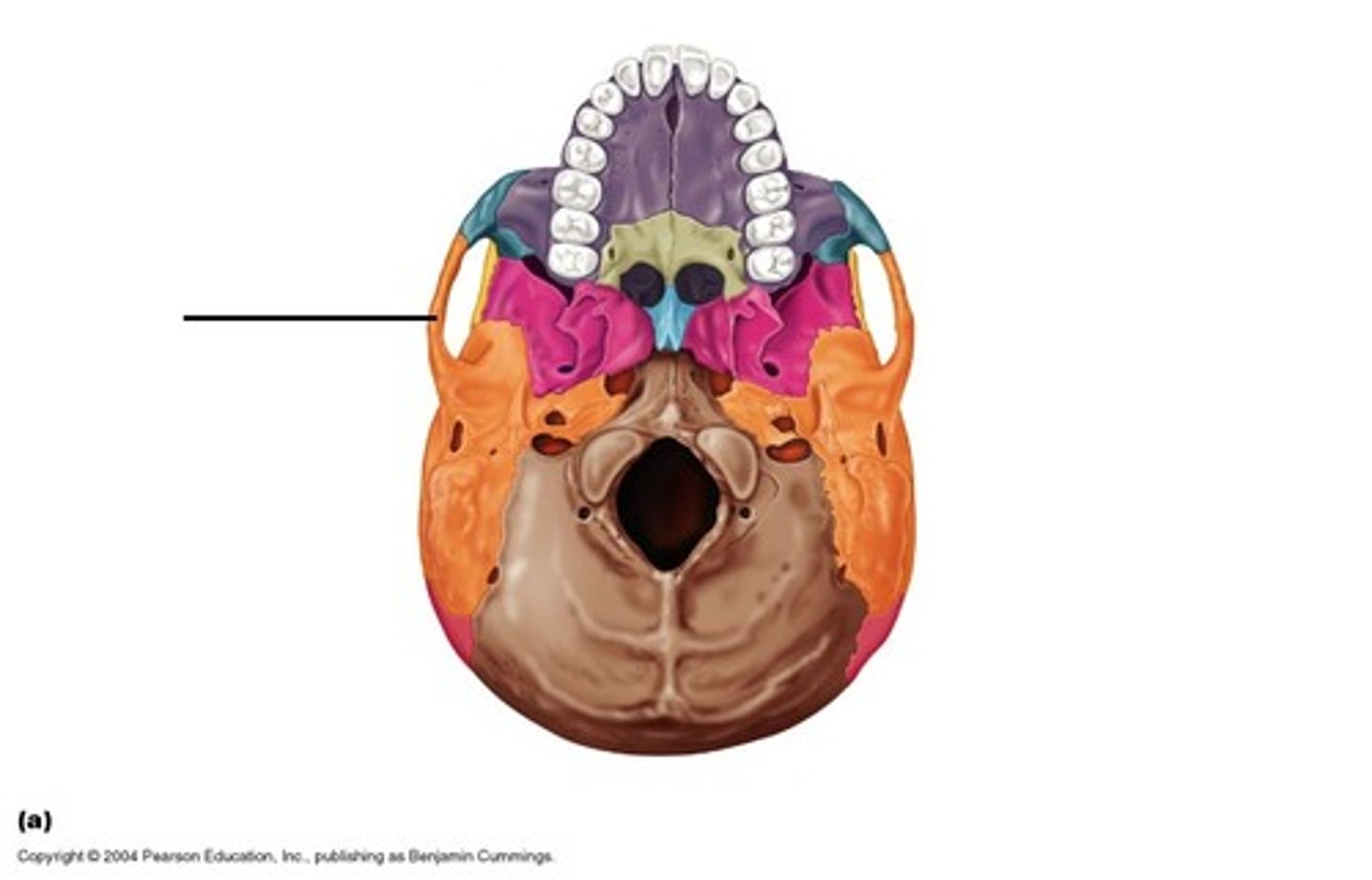
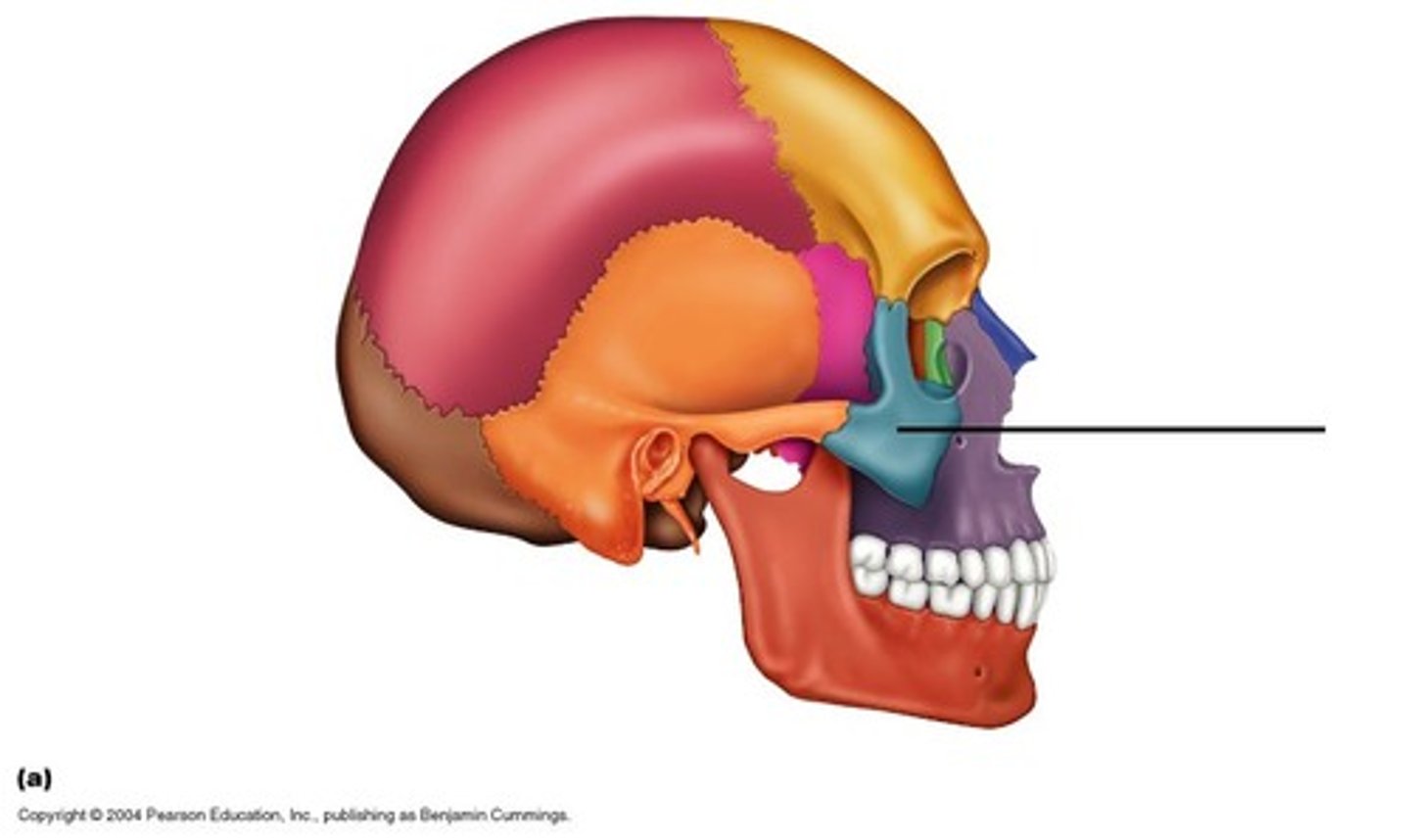
External Auditory Meatus
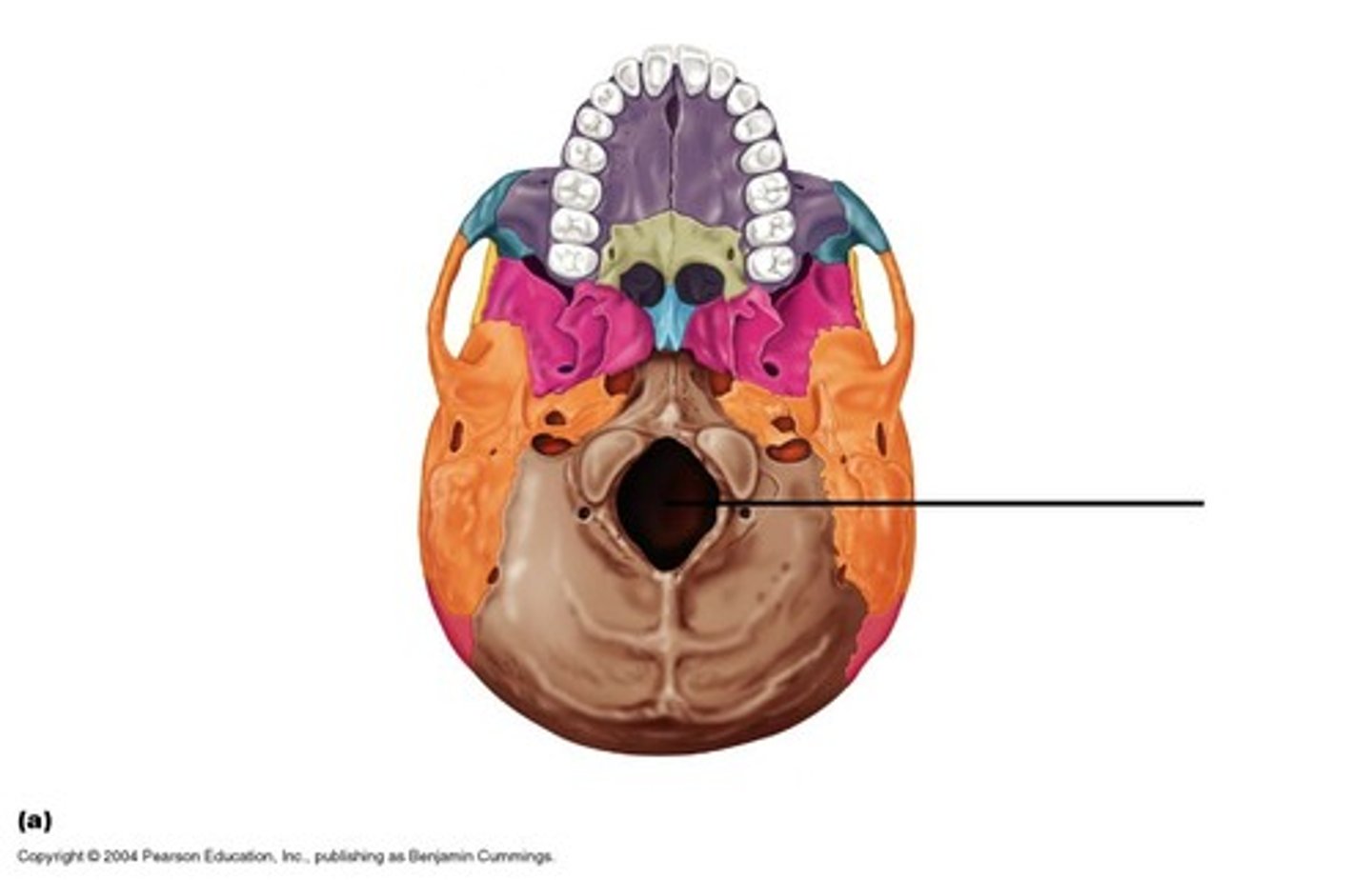
Foramen Magnum
spinal cord connects to brainstem in occipital
Frontal bone
Hard Palate
Lacrimal bone
smallest of facial bones & contain canal with lacrimal sac (eye orbit)
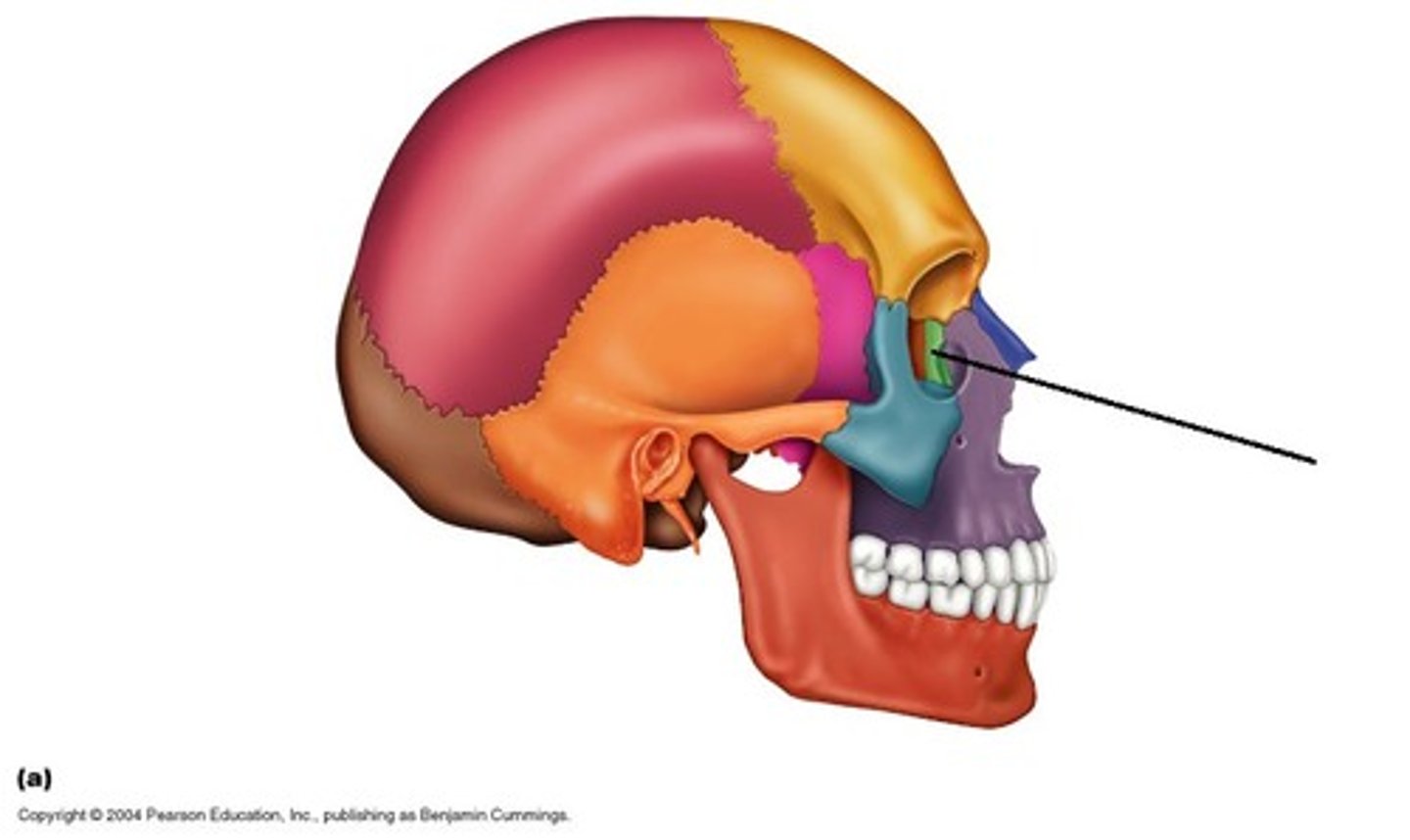
Lacrimal bone
smallest of facial bones & contain canal with lacrimal sac (eye orbit)
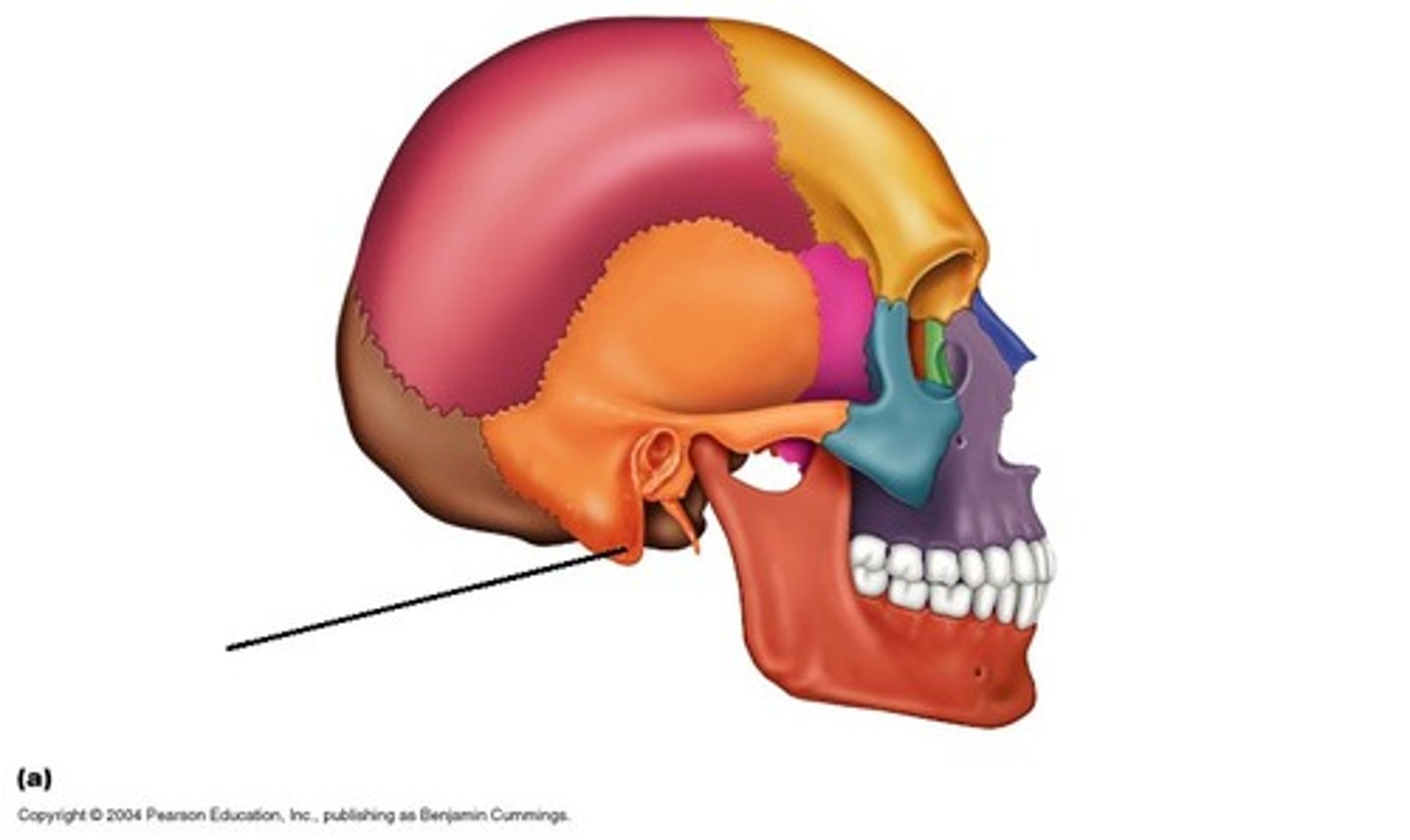
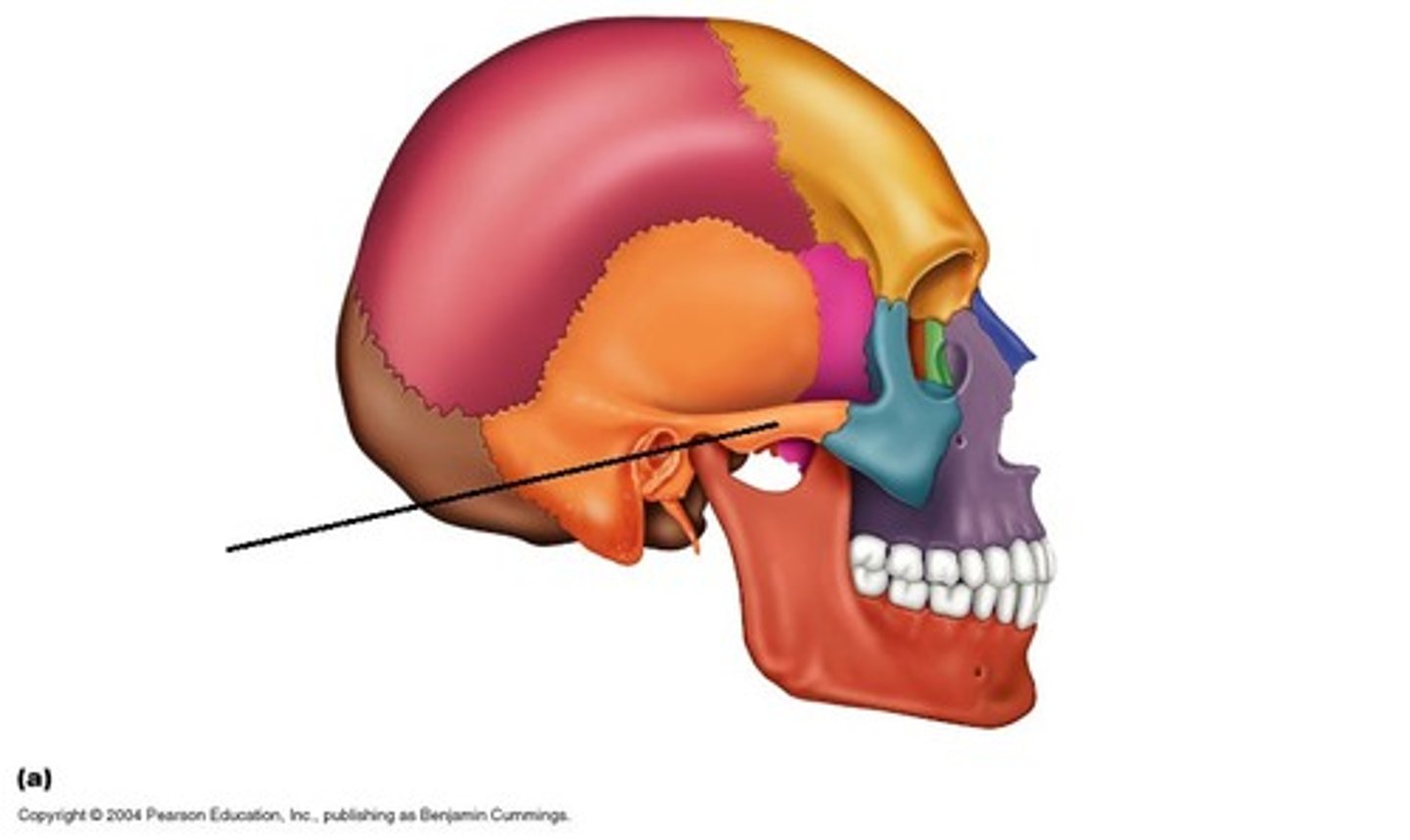
Mastoid process
attachment point for neck muscles
Maxilla
form upper jaw, floors of orbit, nasal cavity & hard palate (mouth roof)
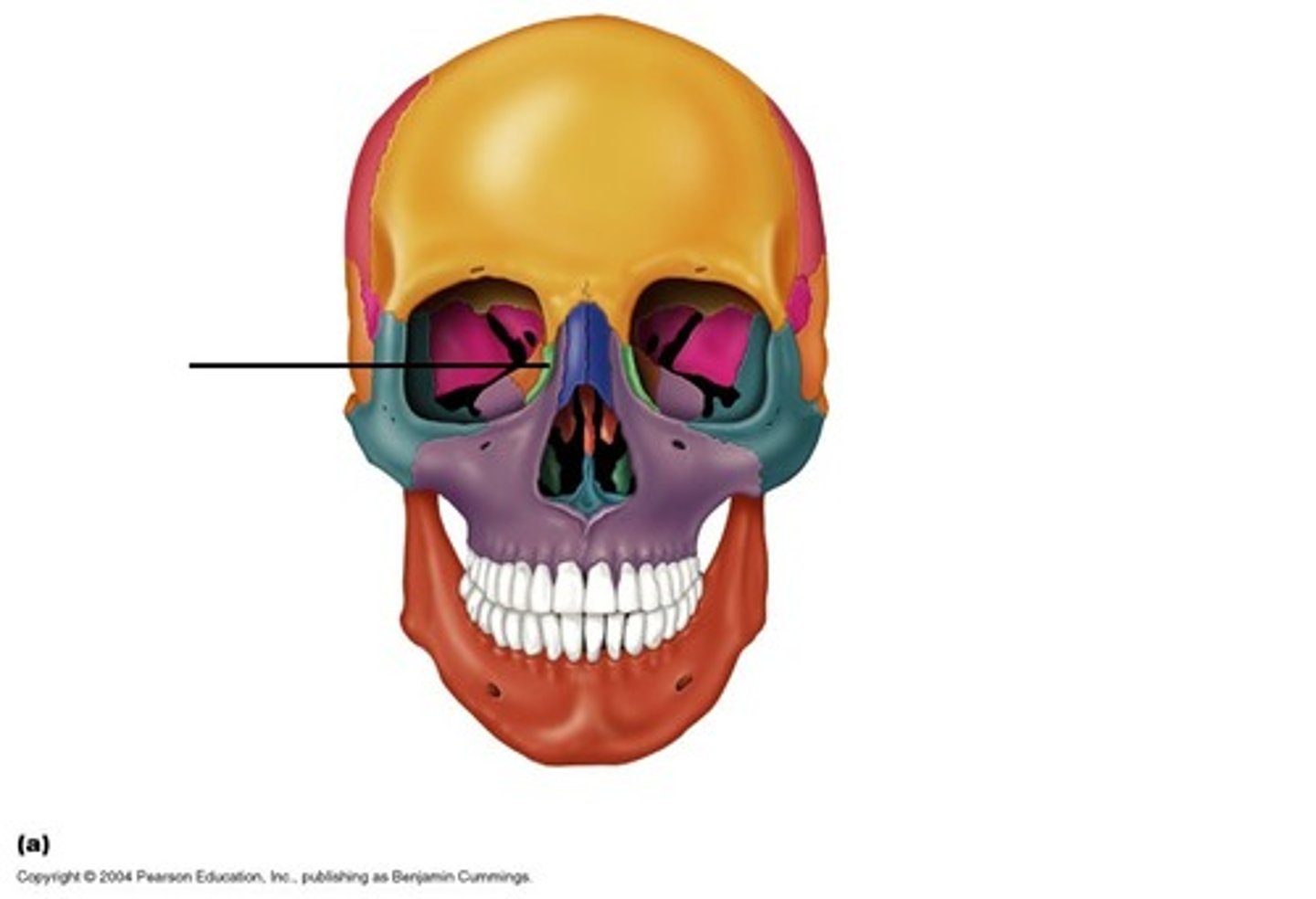
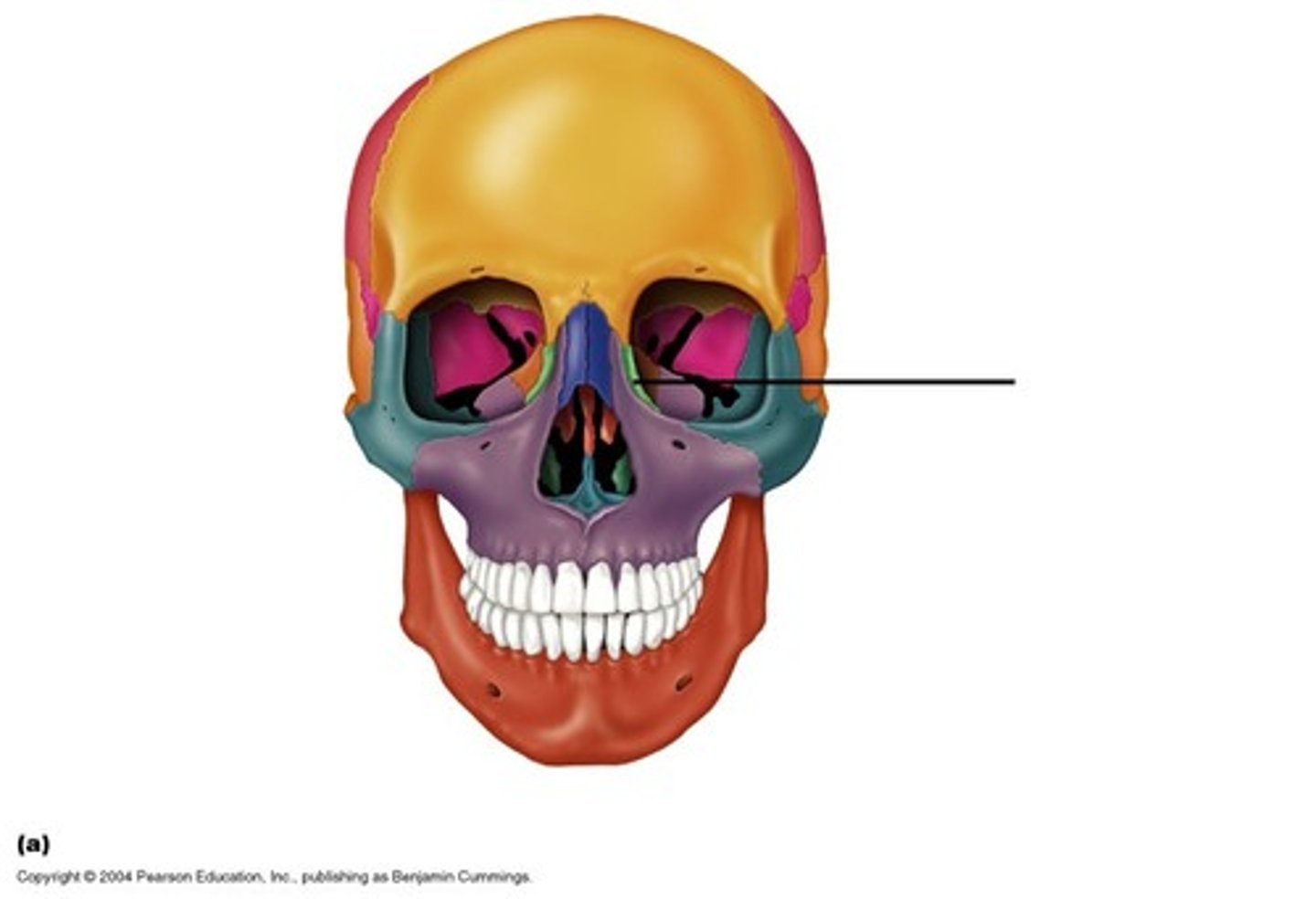
Nasal bone
form the upper portion of bridge of nose & anterior roof of nasal cavity
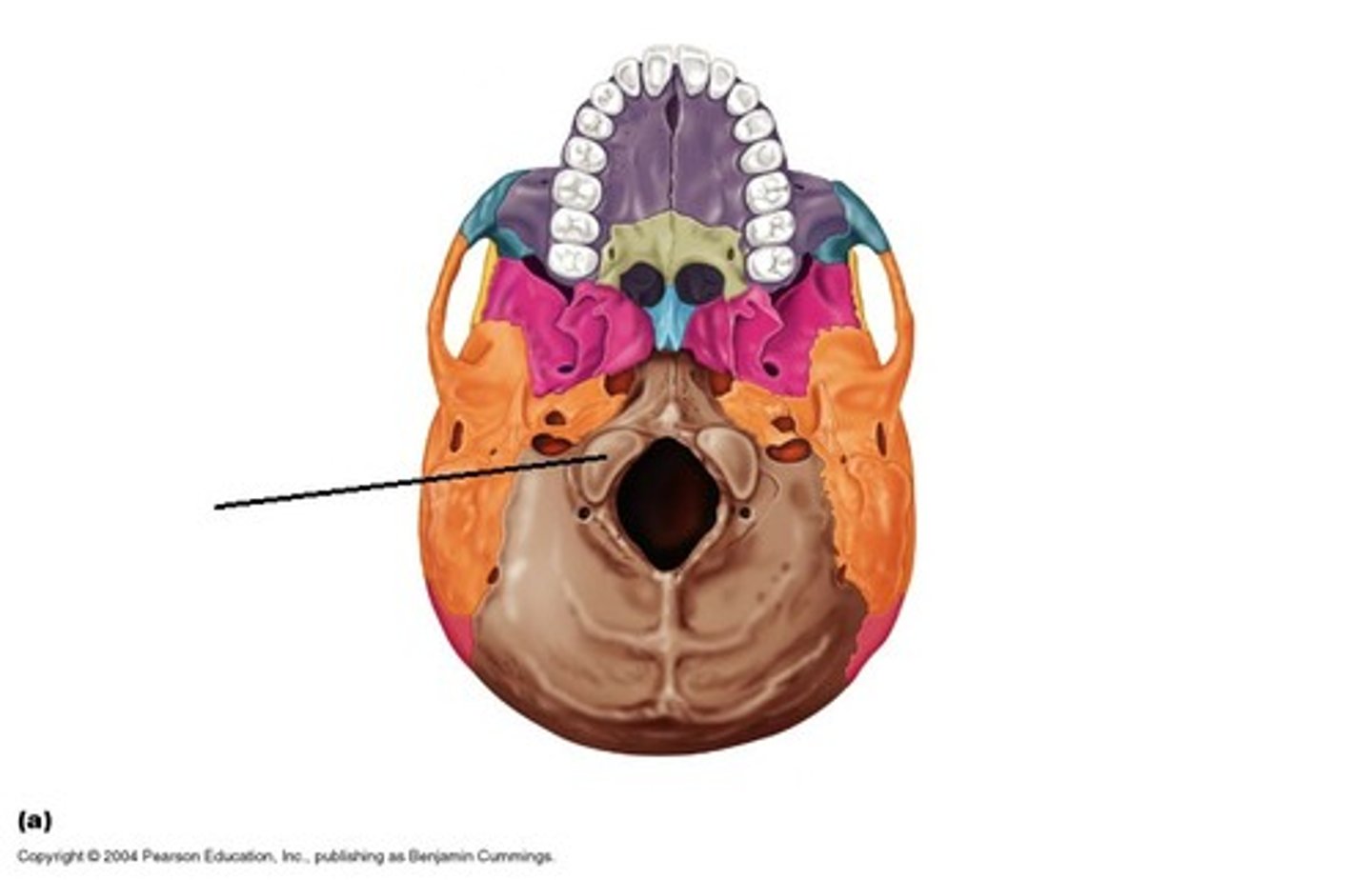
Occipital condyle
two rounded bony features
Articulate with C1 vertebrae
Occipital bone
posterior inferior portion – most base of cranium
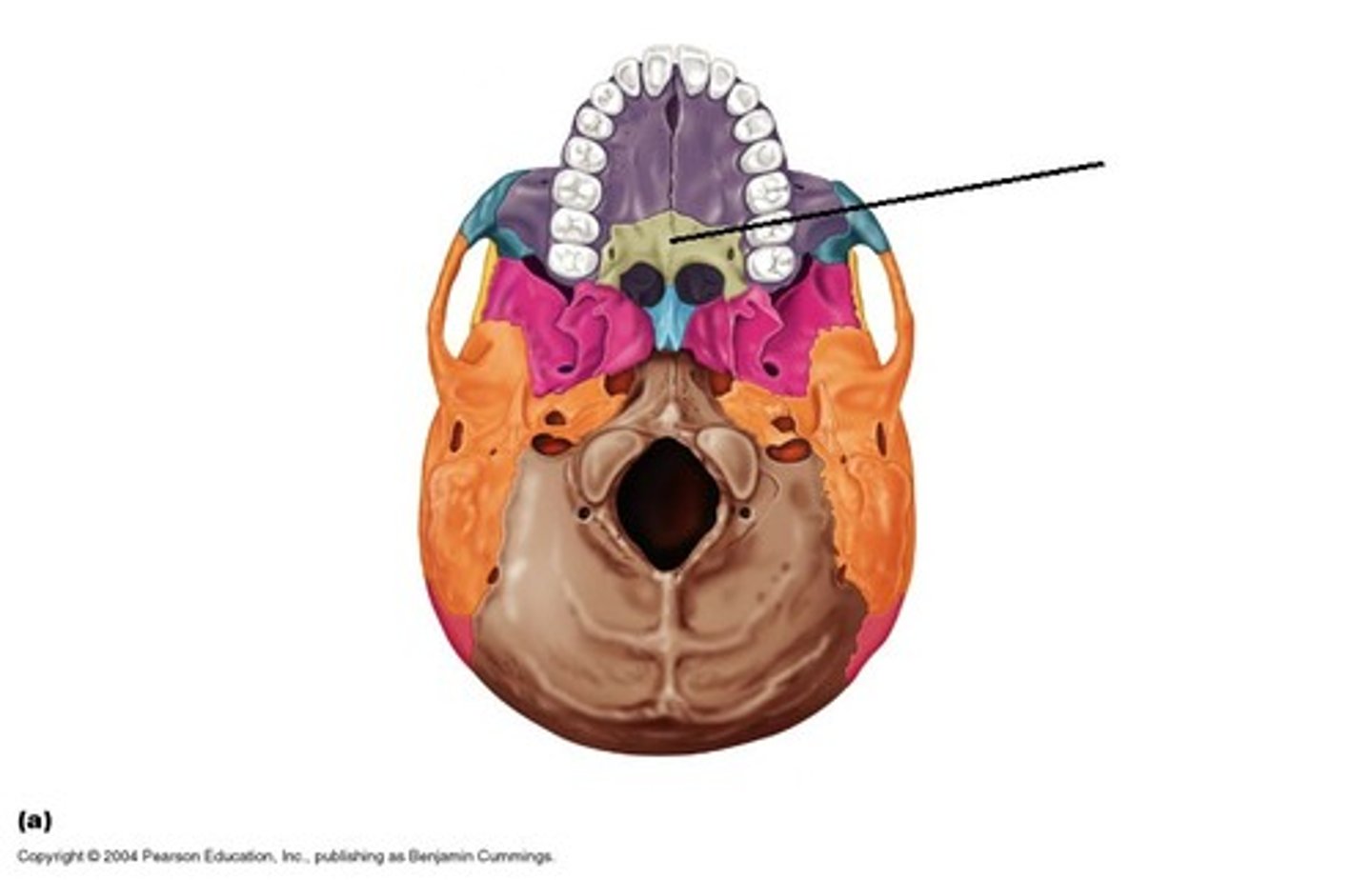
Palatine bone
forms posterior portion of hard palate, floor of nasal cavity
L-shaped
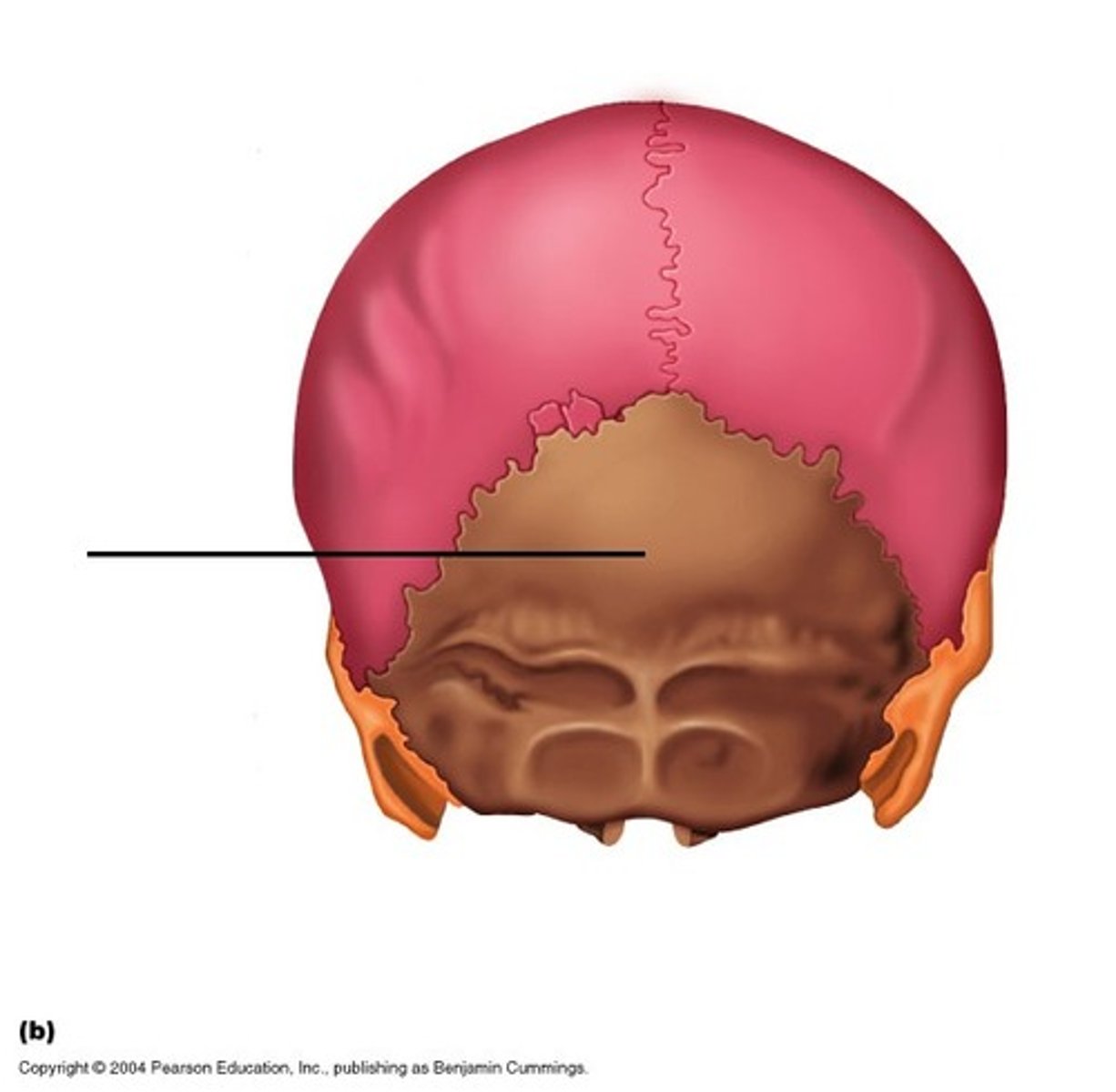
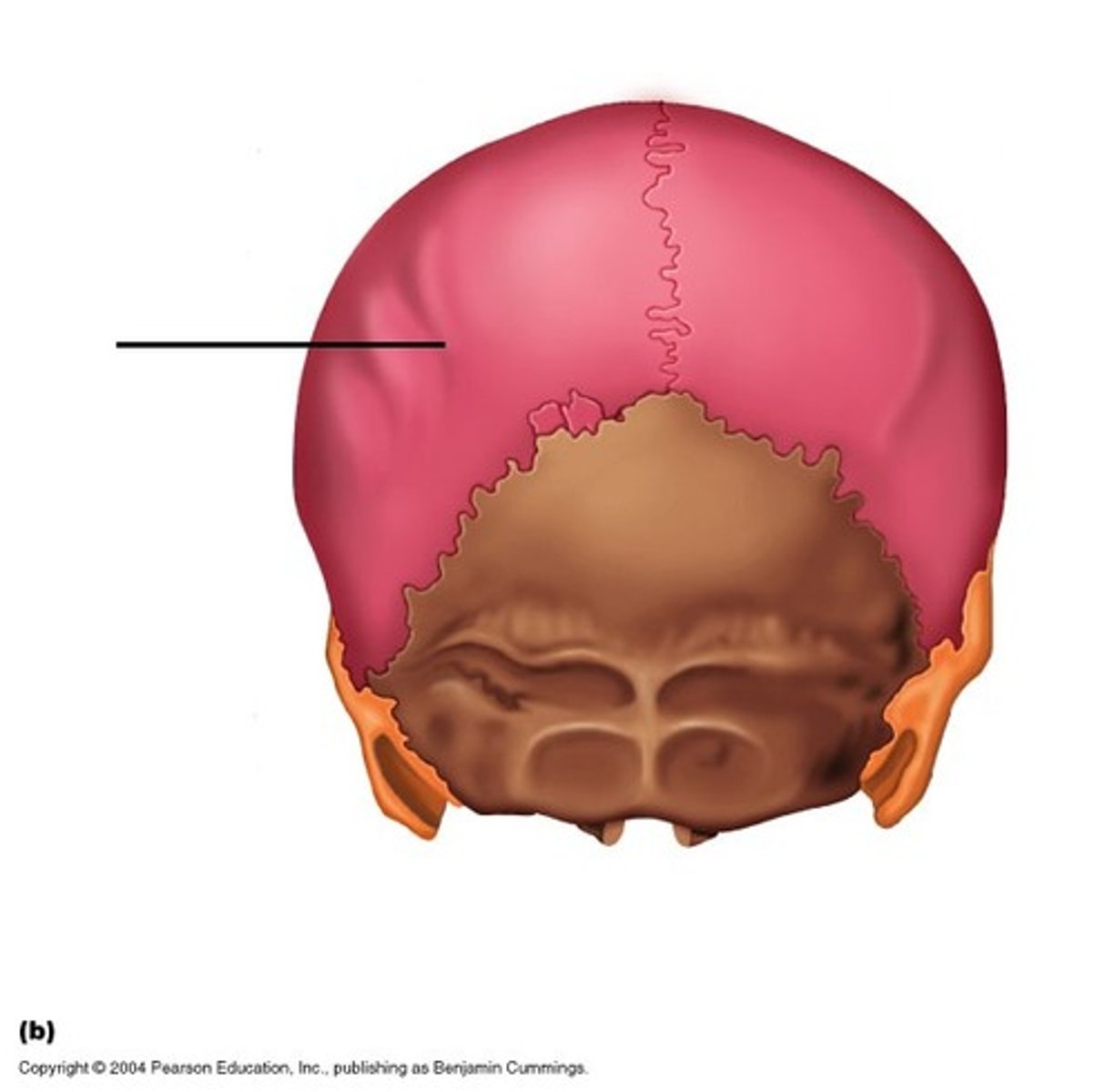
Parietal bone
most of sides & roof of cranial cavity
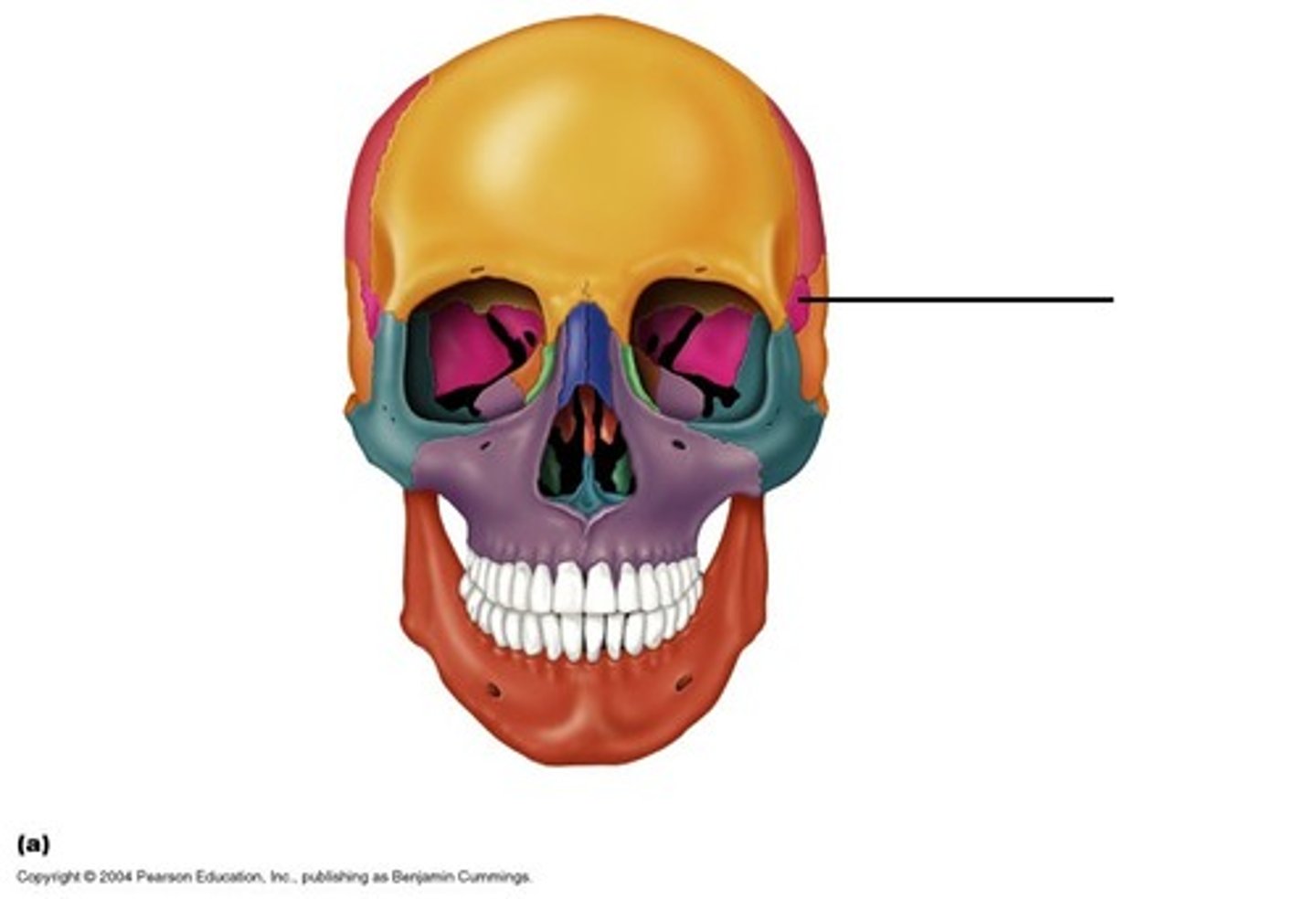
Sphenoid bone
portion of lateral skull & cranial floor & portion of orbit
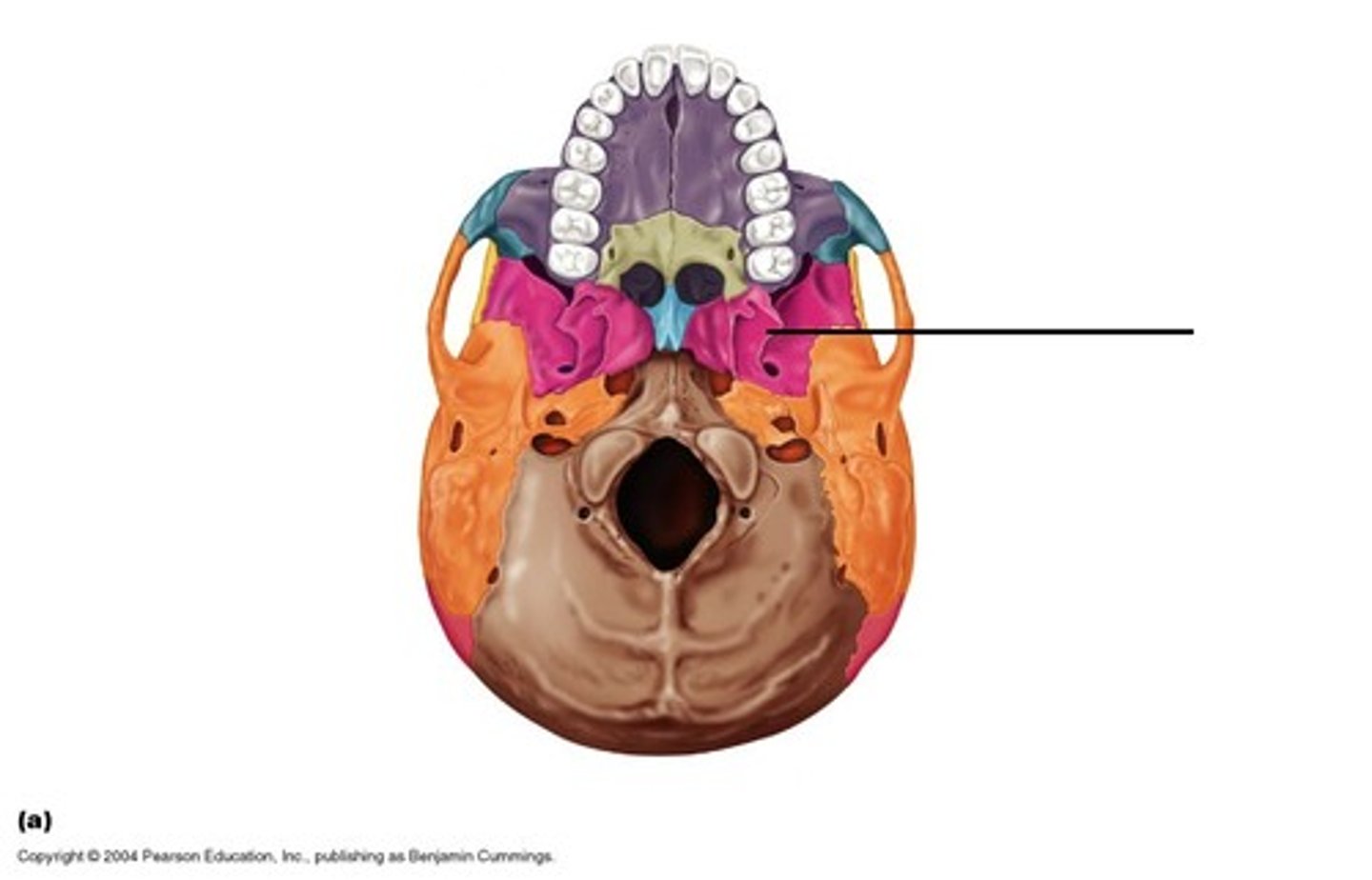
Sphenoid bone
portion of lateral skull & cranial floor & portion of orbit
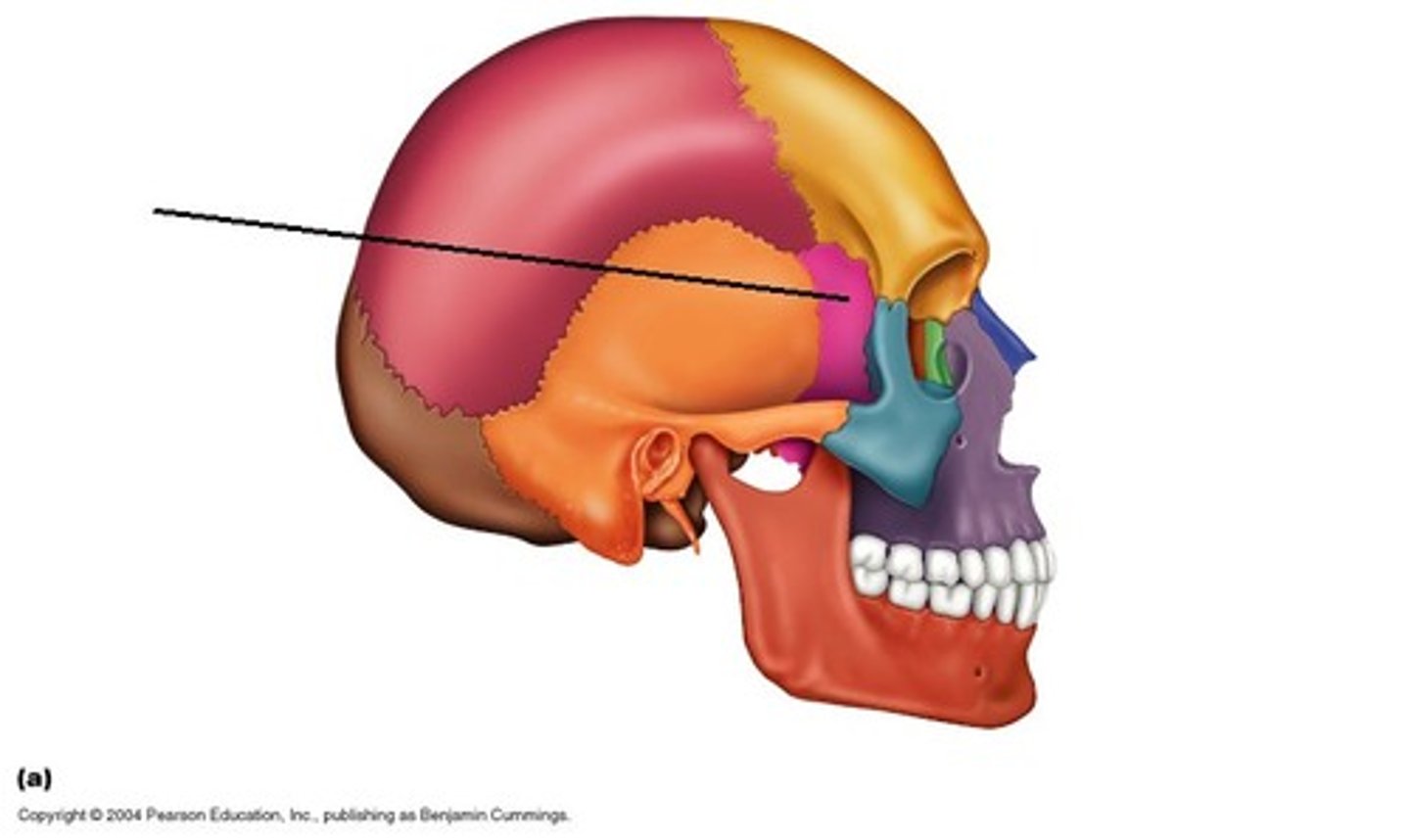
Sphenoid bone
portion of lateral skull & cranial floor & portion of orbit
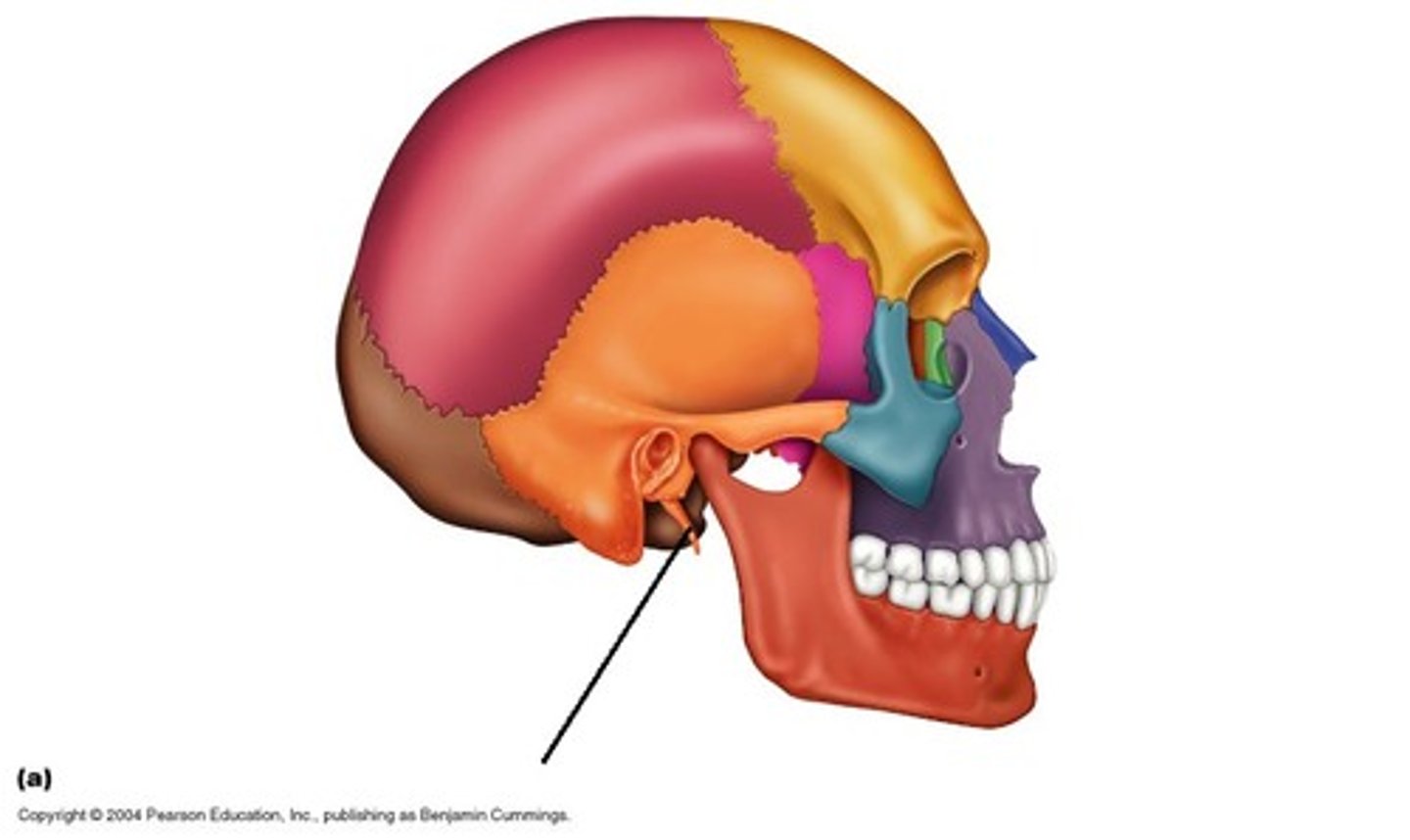
Styloid process
attachment point for neck & tongue muscles
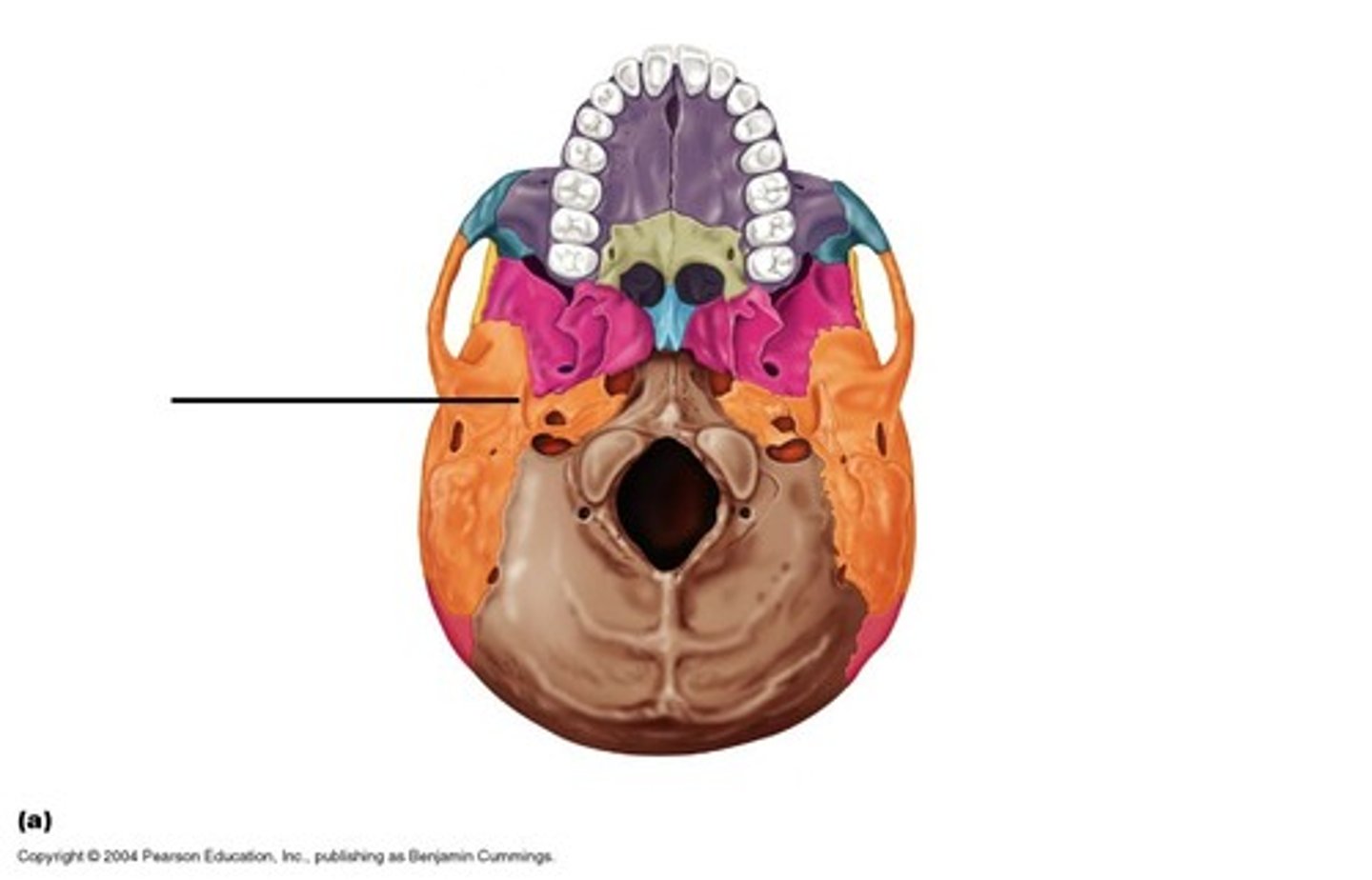
Styloid process
attachment point for neck & tongue muscles
Temporal bone
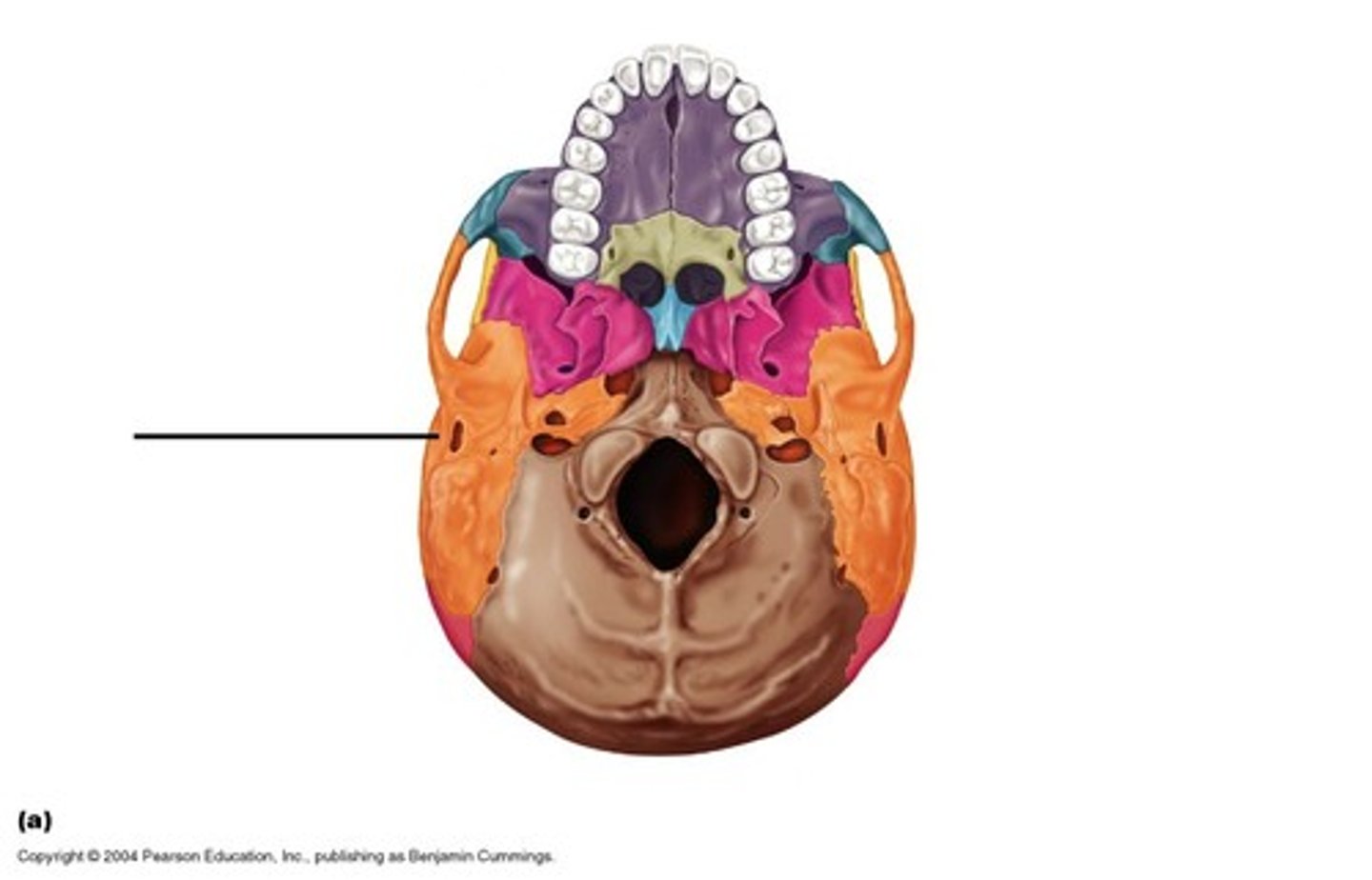
Temporal bone

Vomer
forms inferior posterior region of nasal septum
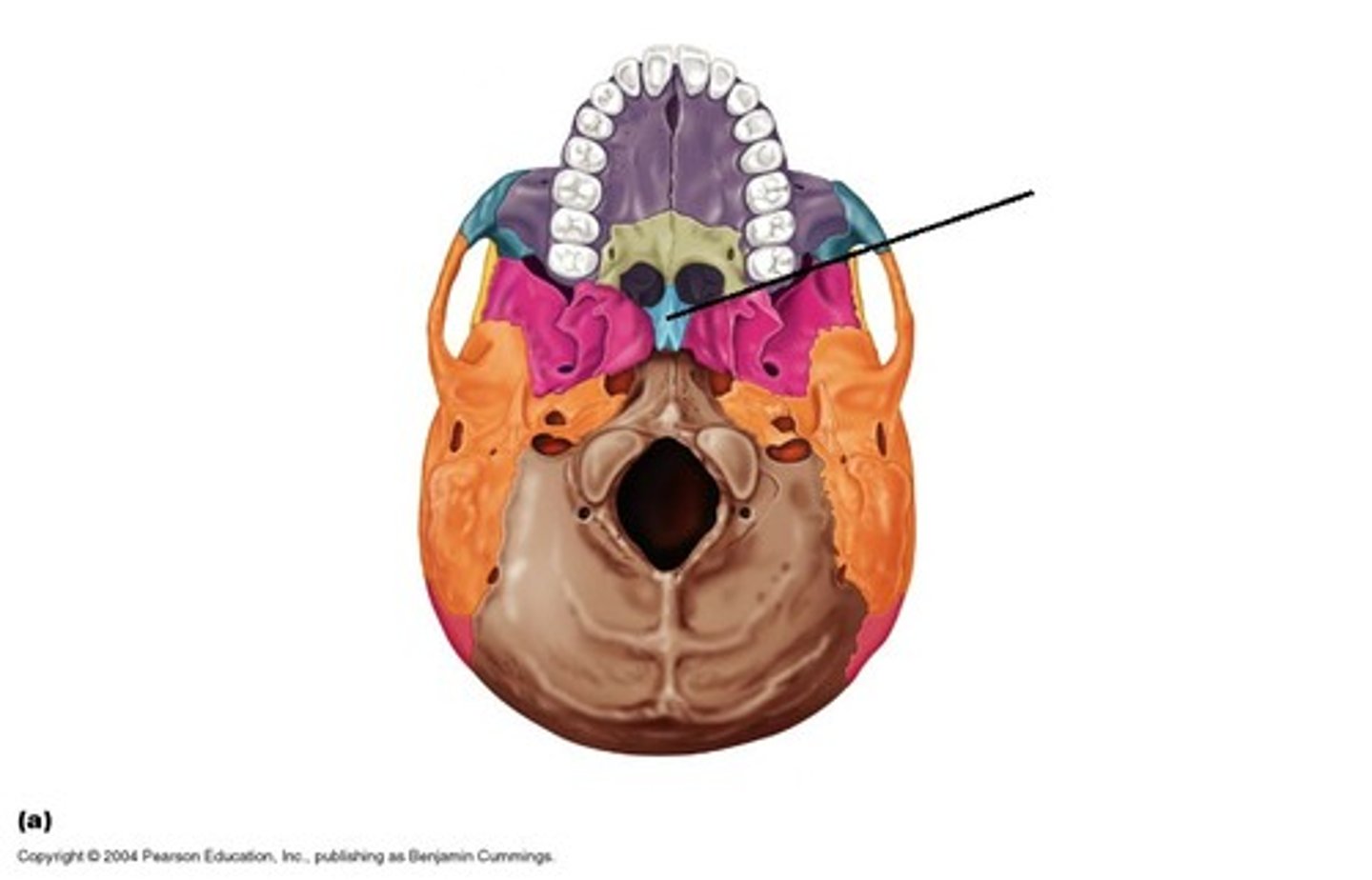
Zygomatic process
makes up region of cheek bone
Zygomatic process
makes up region of cheek bone
Zygomatic bone
Zygomatic bone
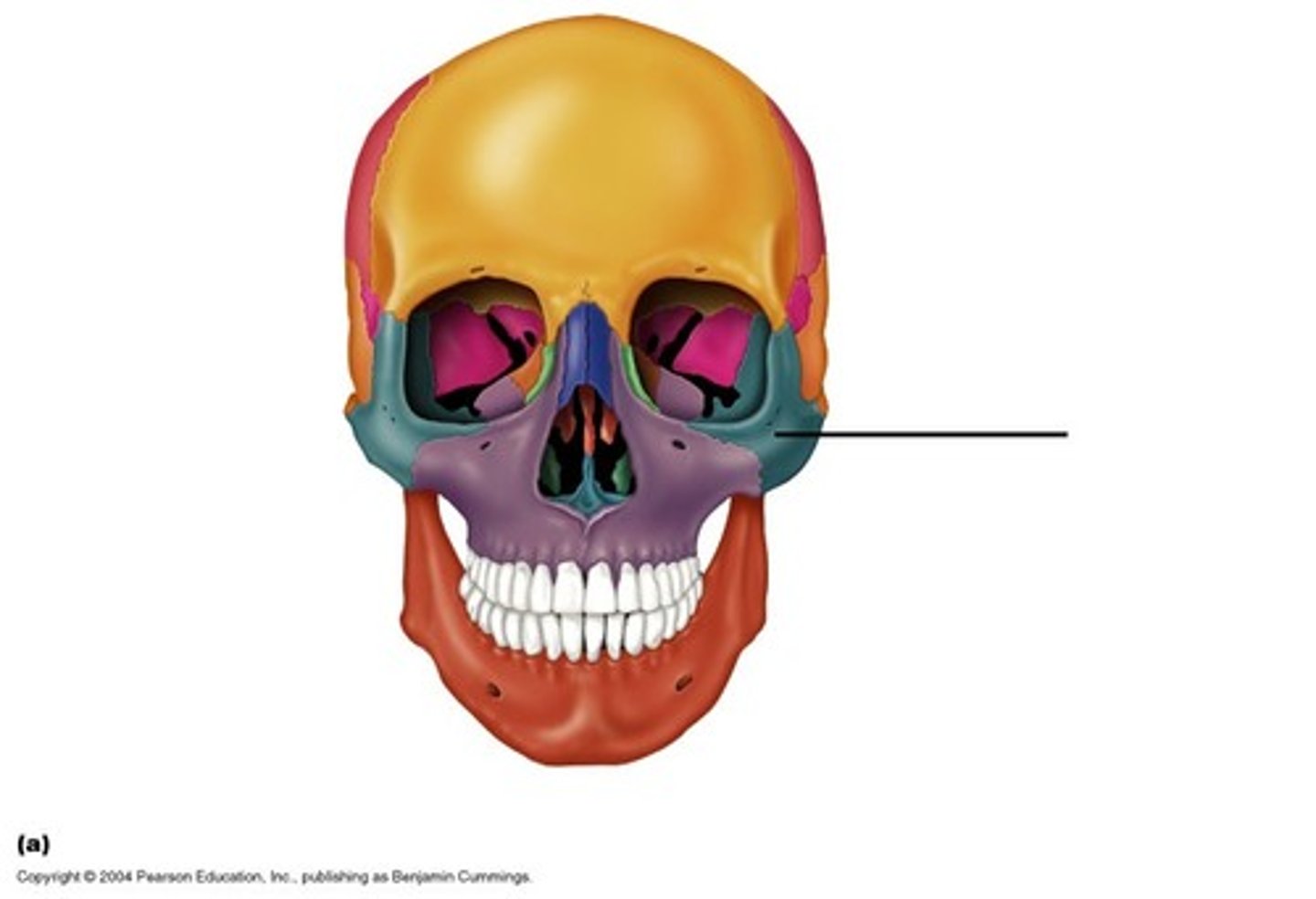
Zygomatic bone
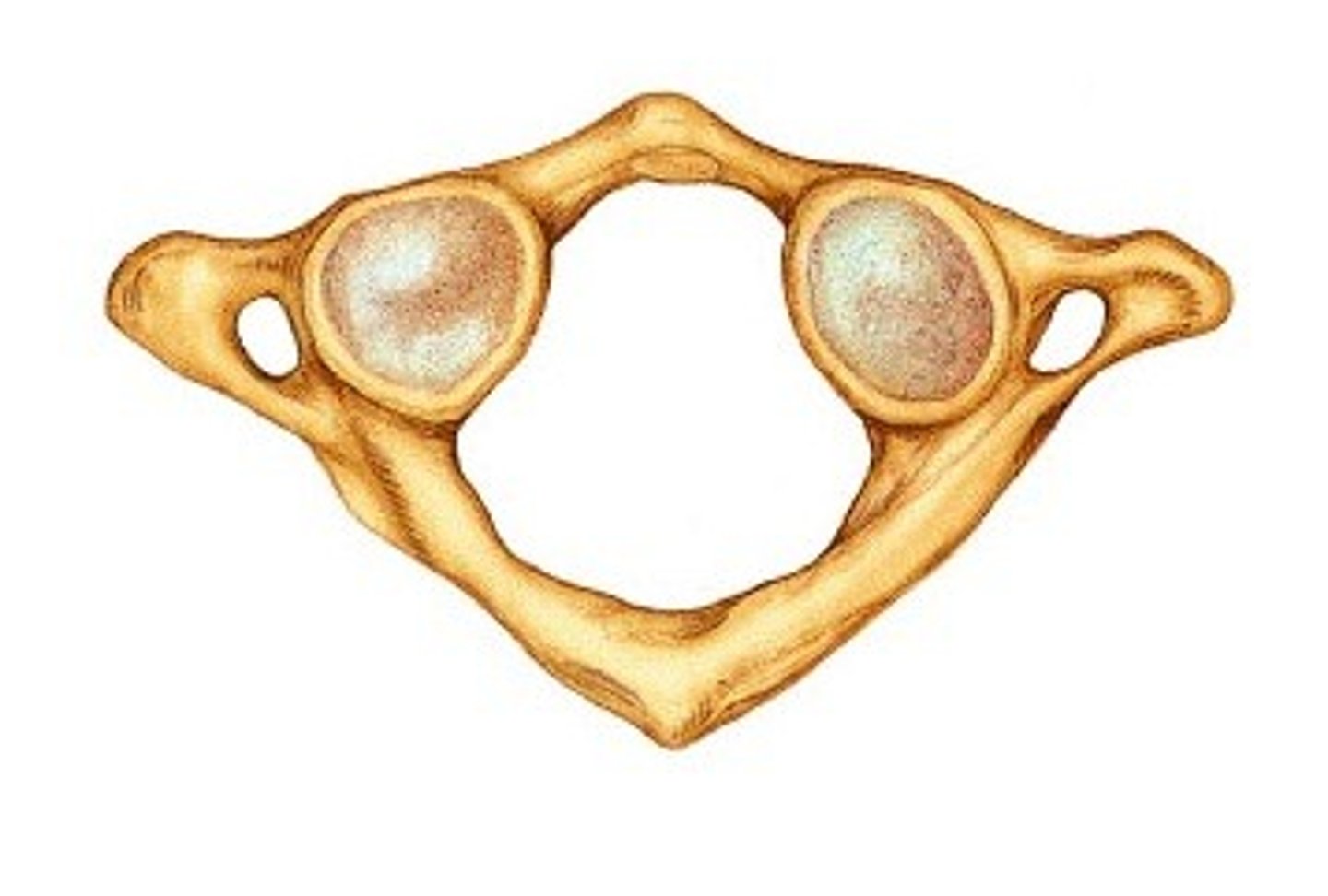
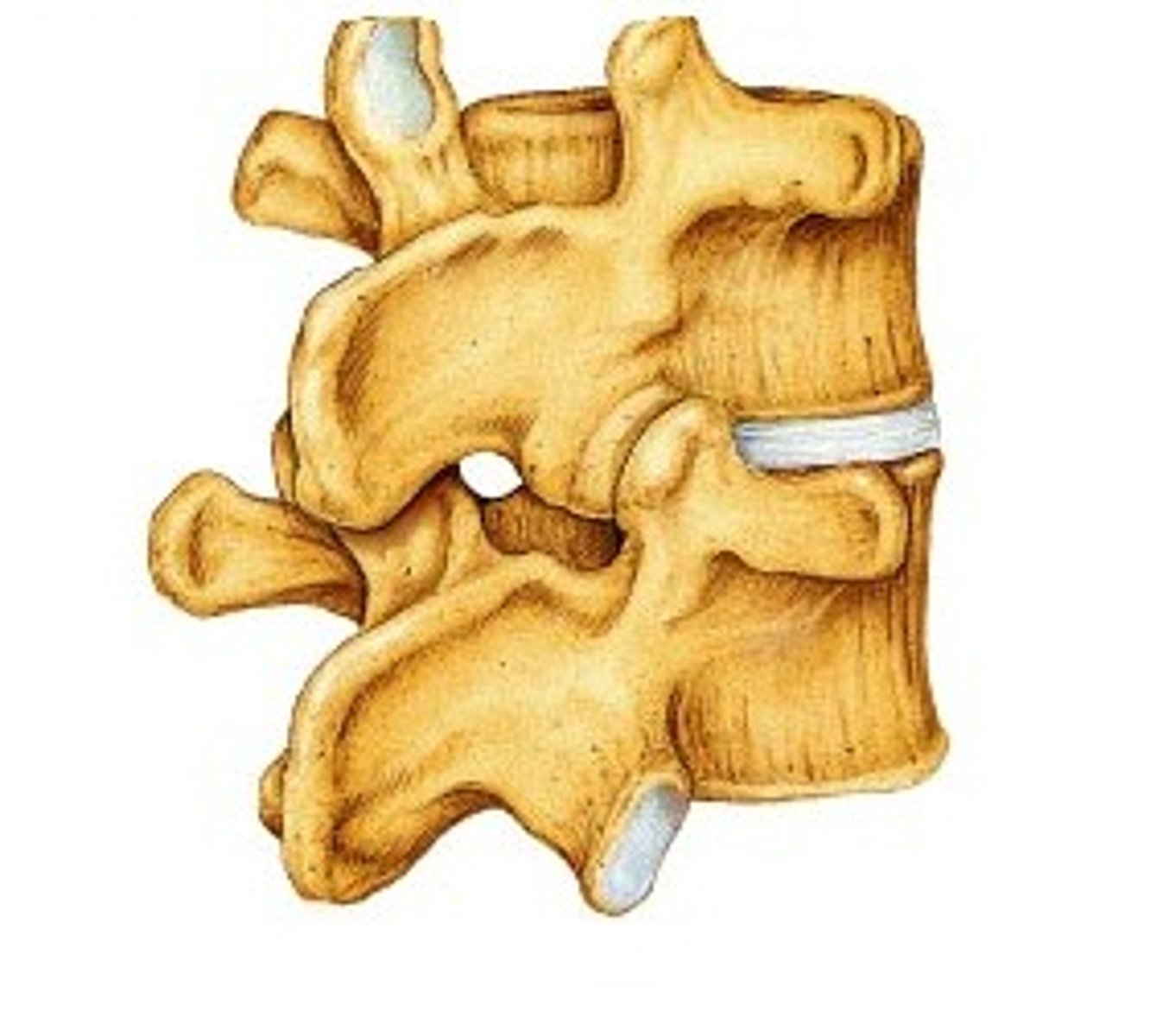
Axis vertebrae
second
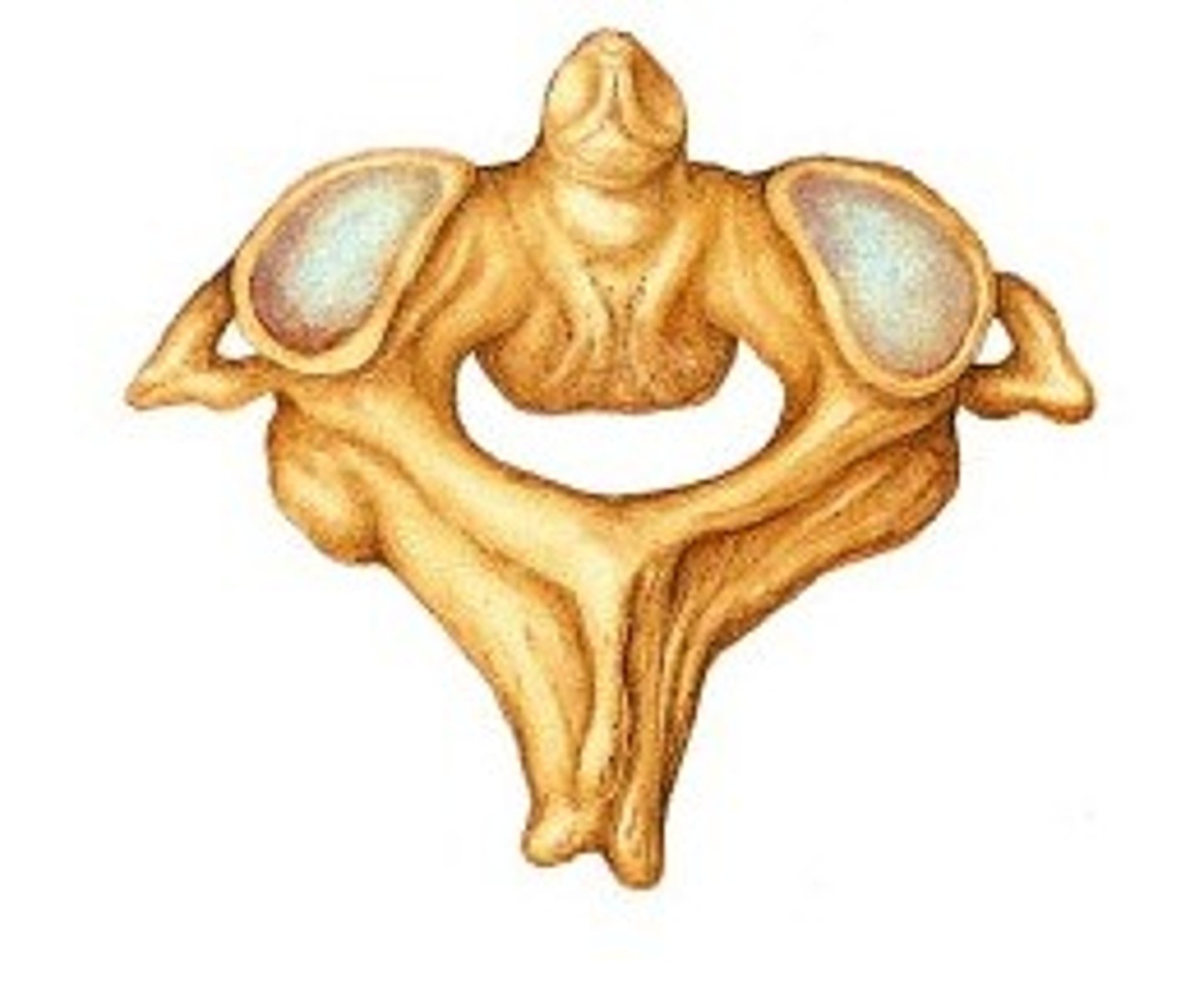
Atlas vertebrae
first cervical vertebra
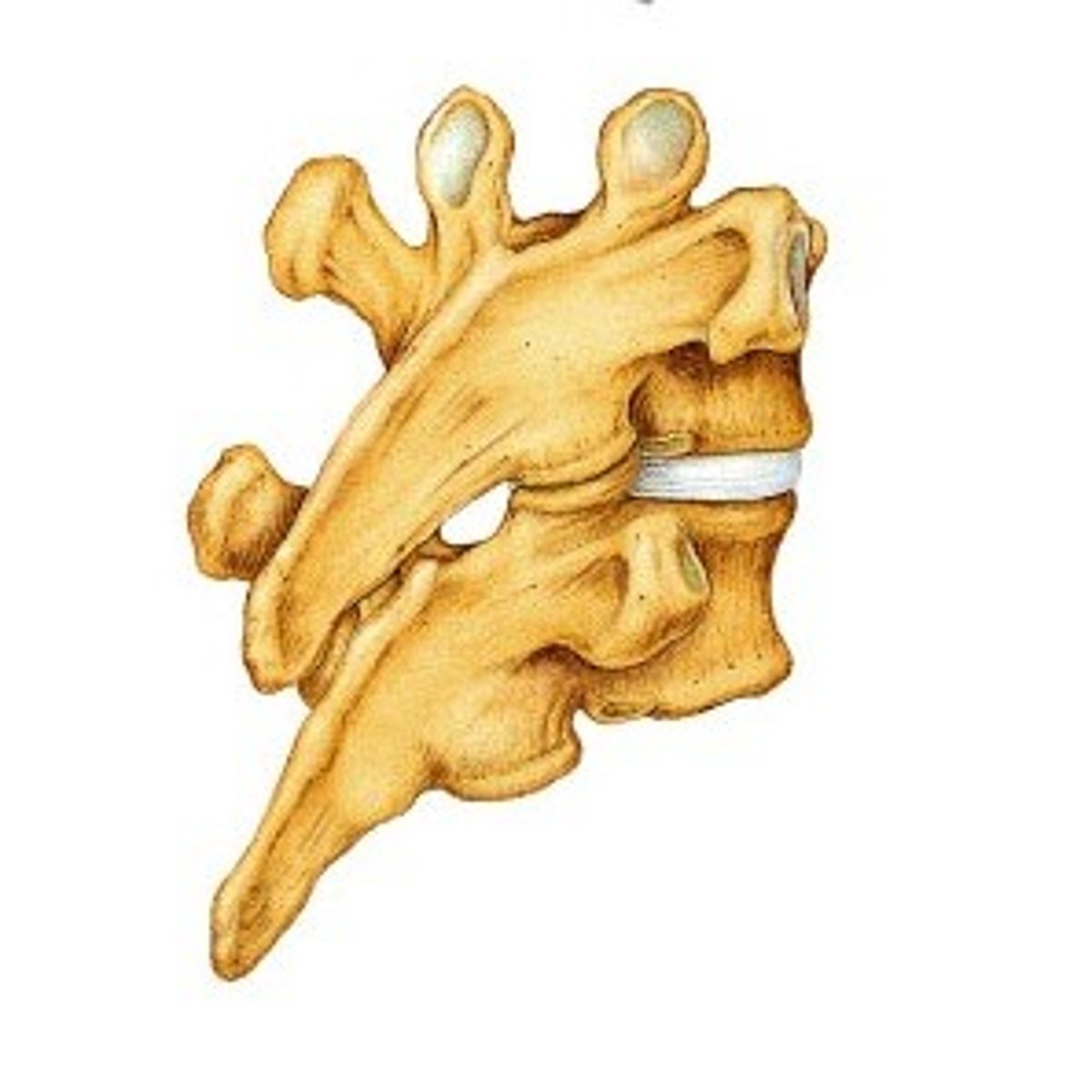
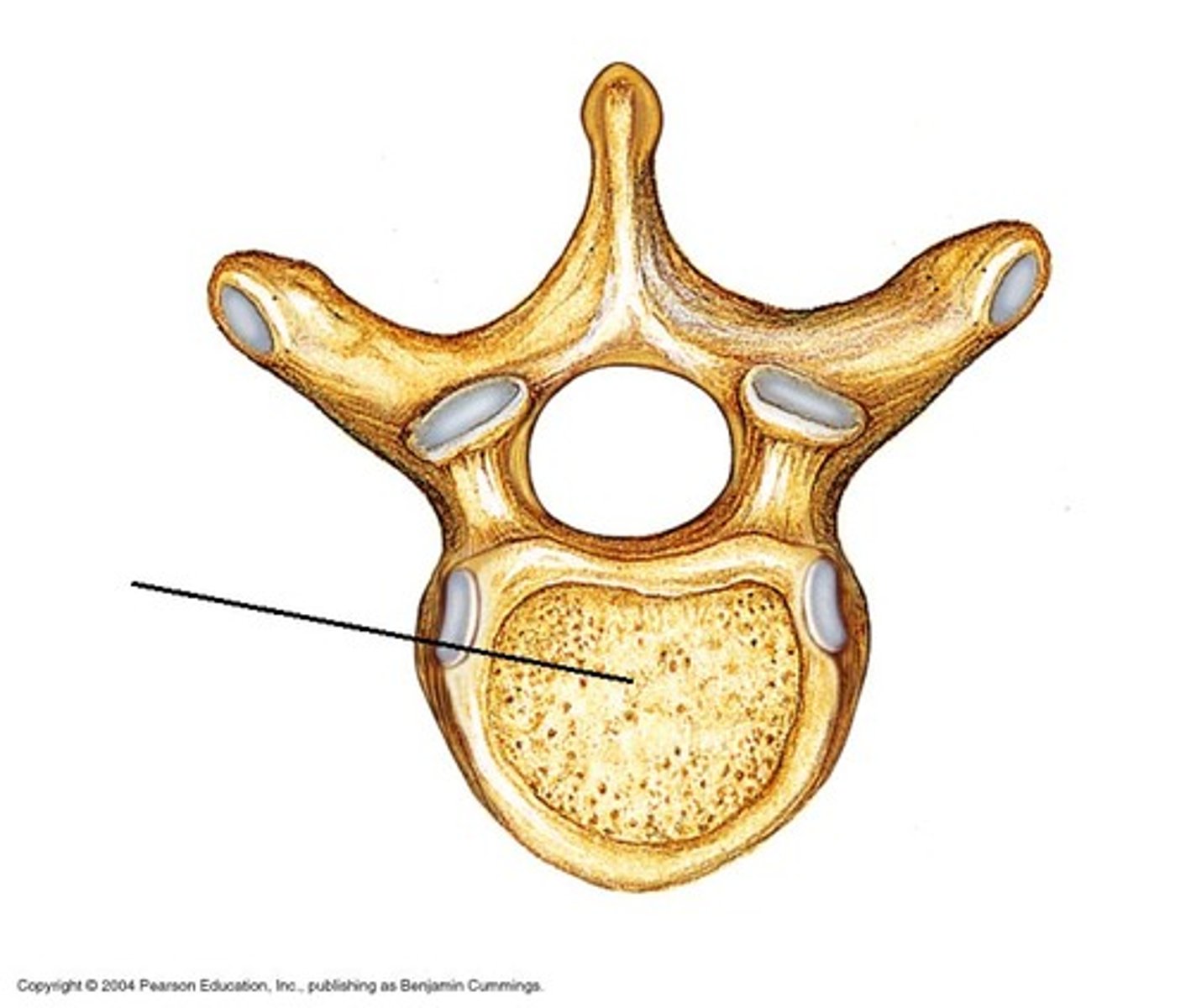
Thoracic vertebrae
Lumbar vertebrae
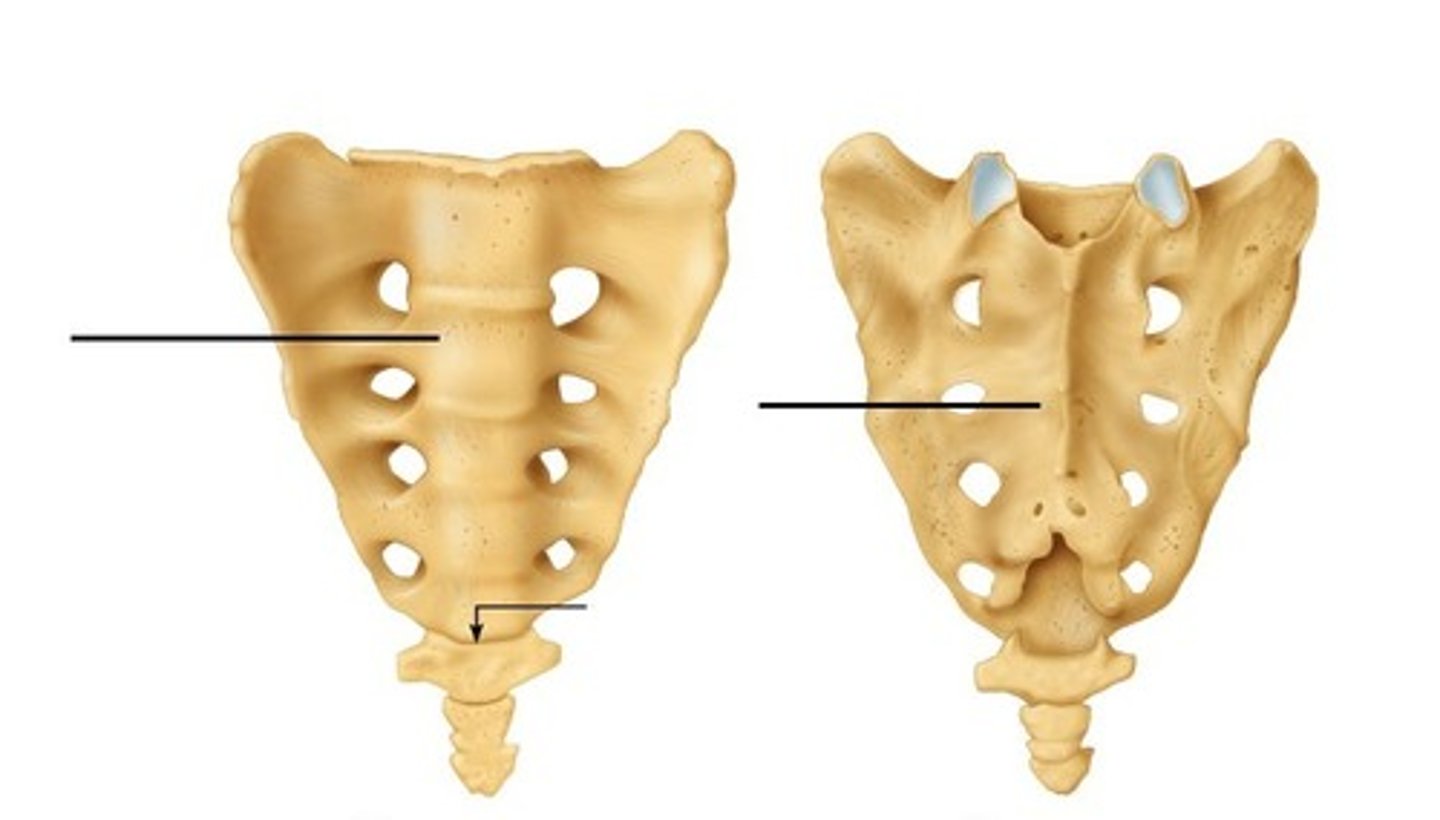
Sacrum
fusion of 4-5 by age 16-18
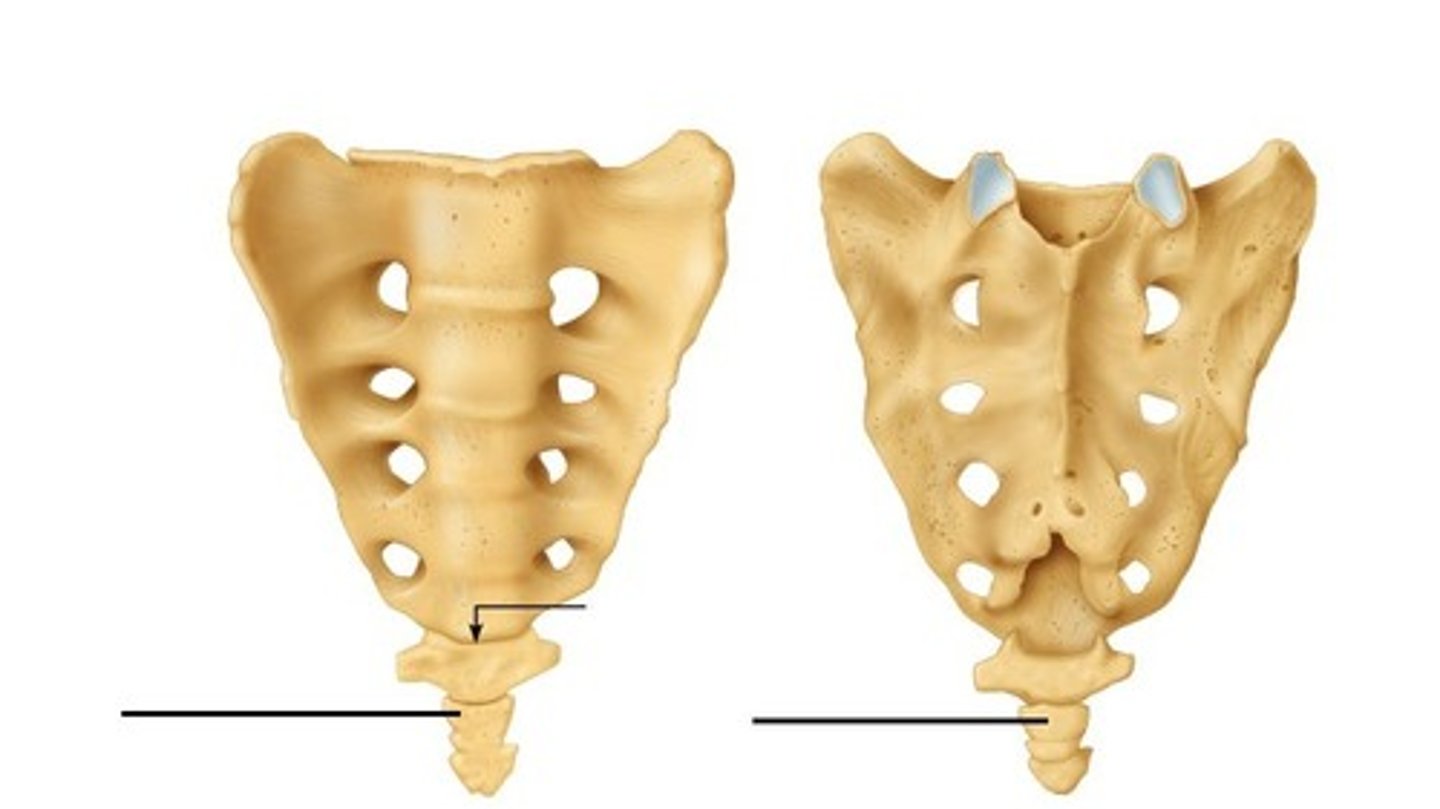
Coccyx
bones fused together. complete by age 20-30
attachement for filum terminale
Lamina
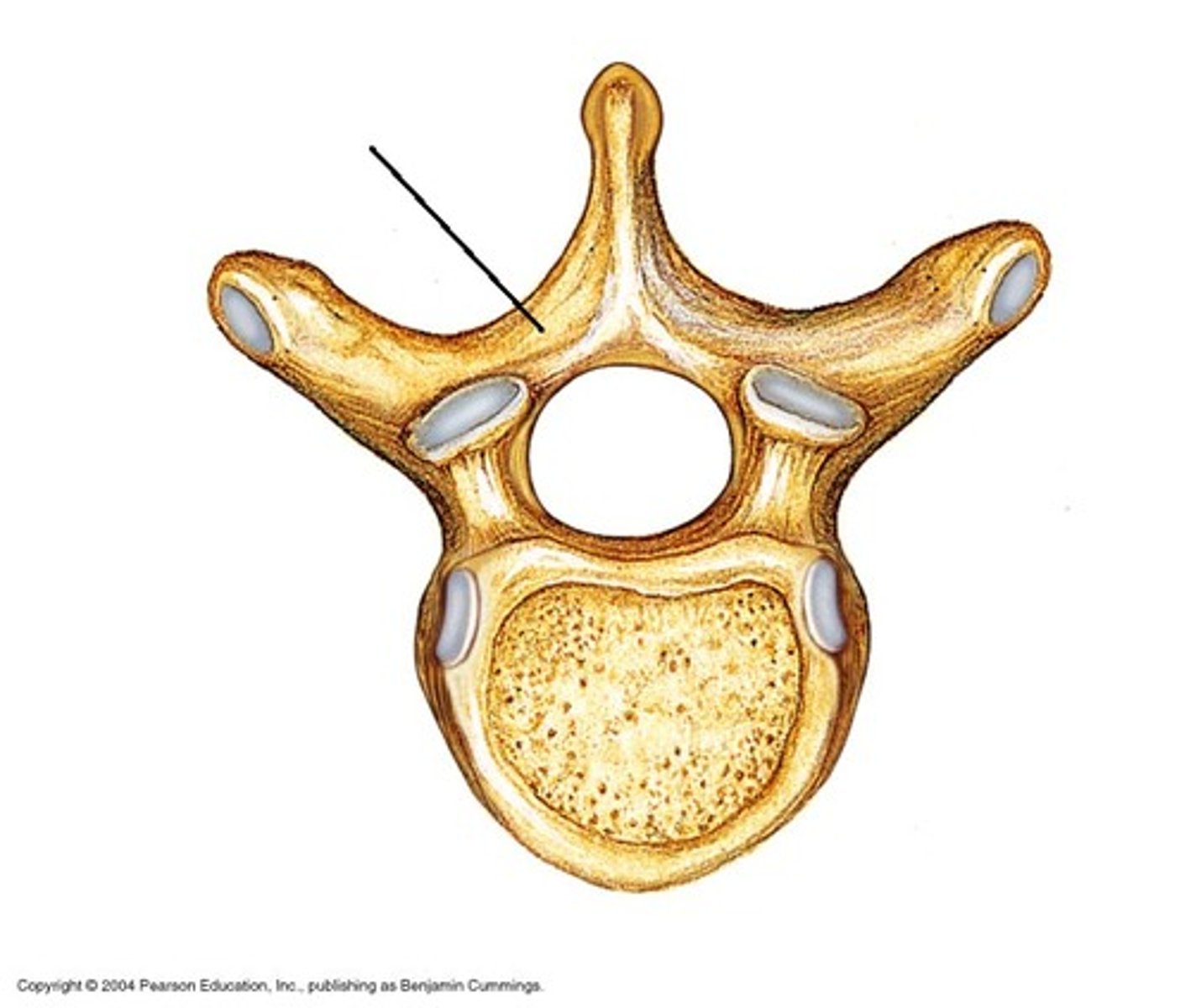
Spinous process

Superior Articular Cartilage
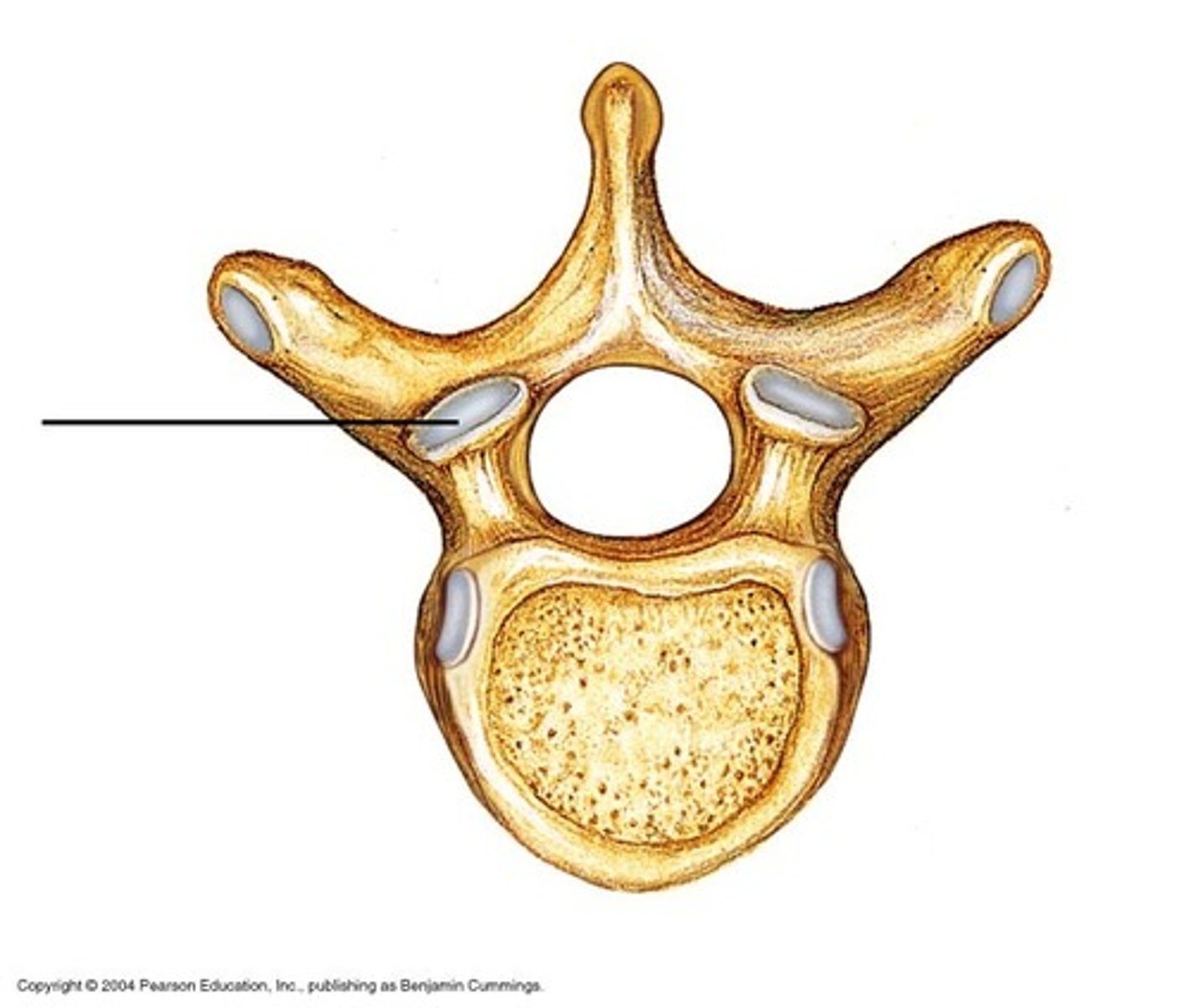
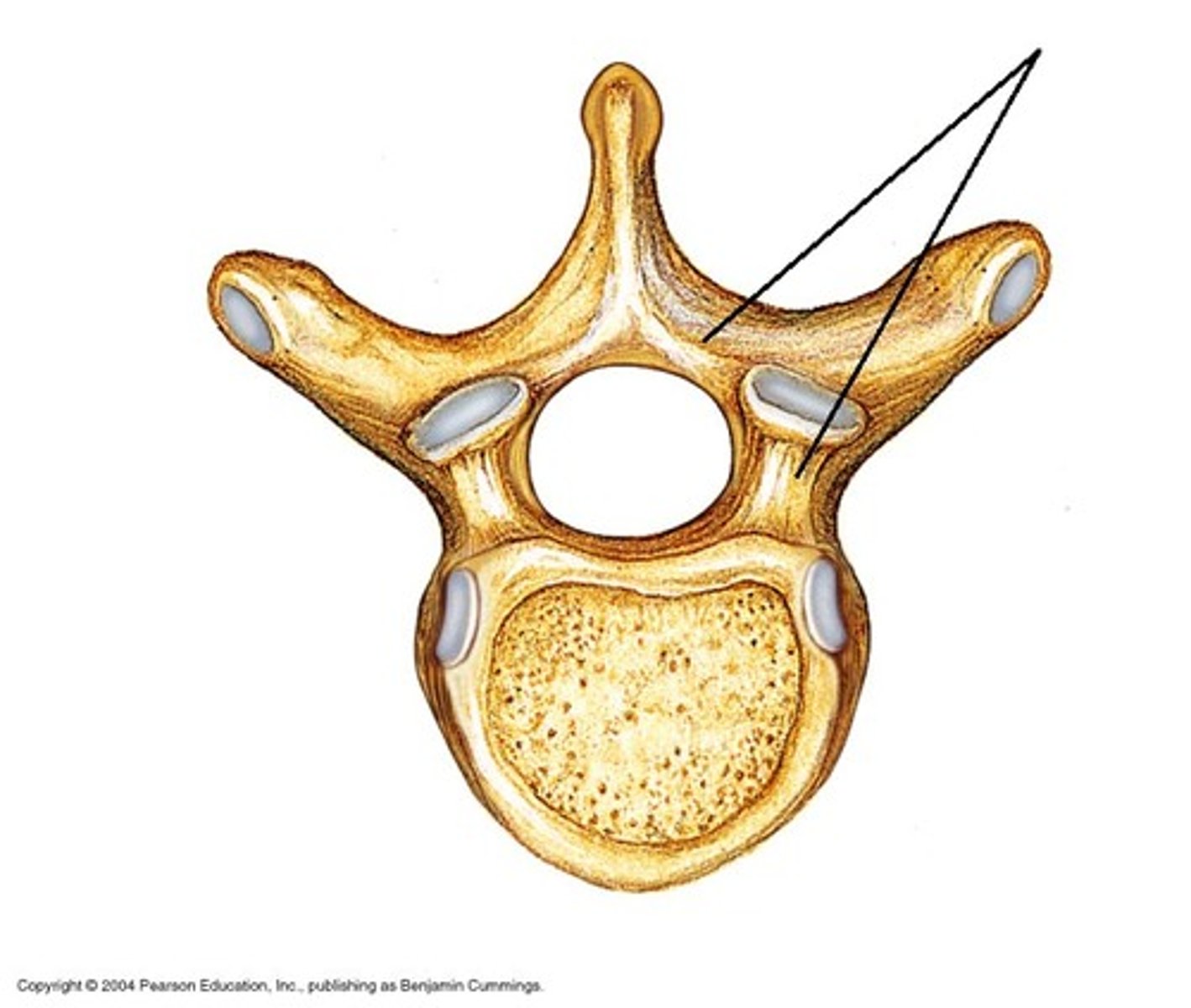
Transverse process
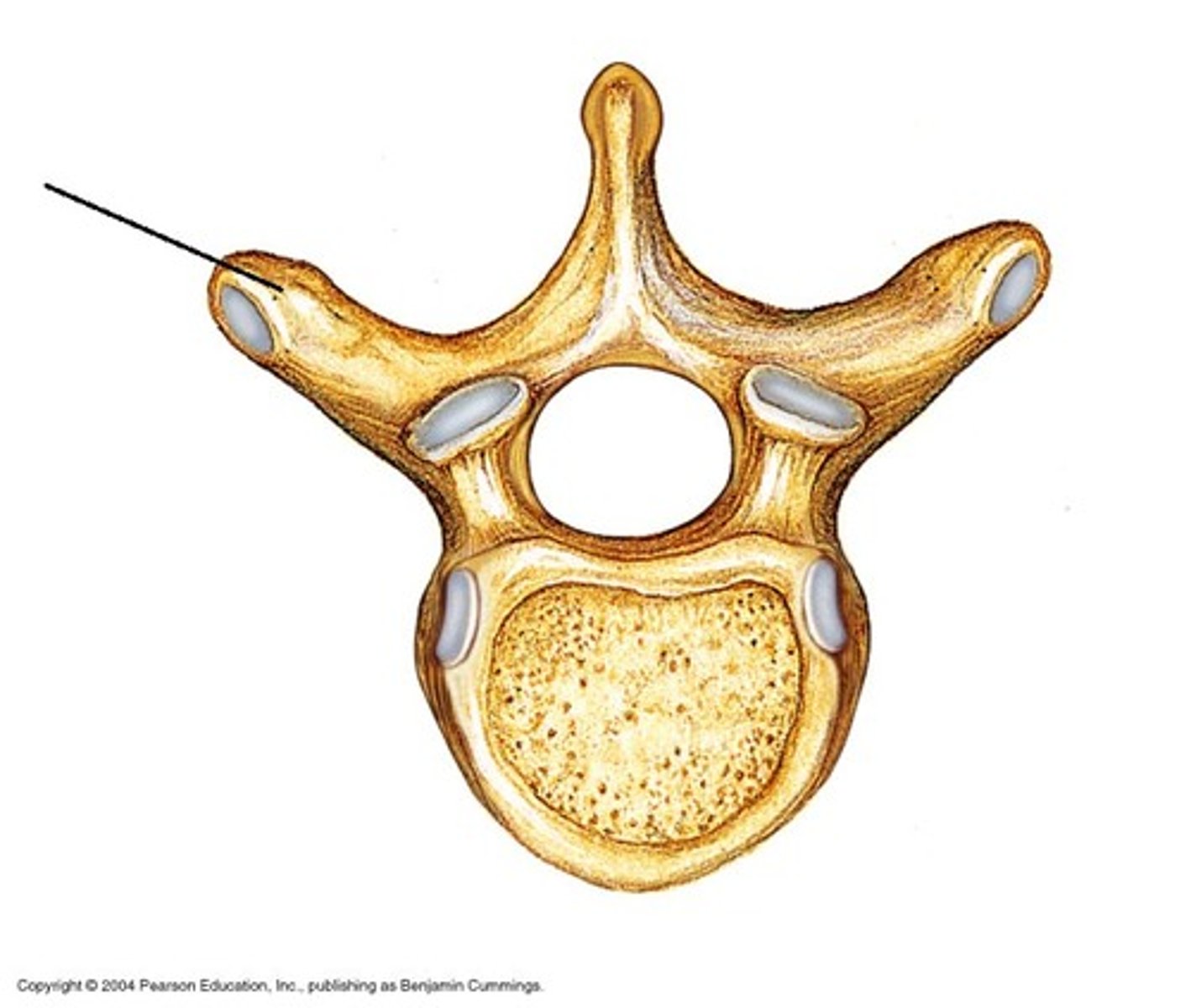
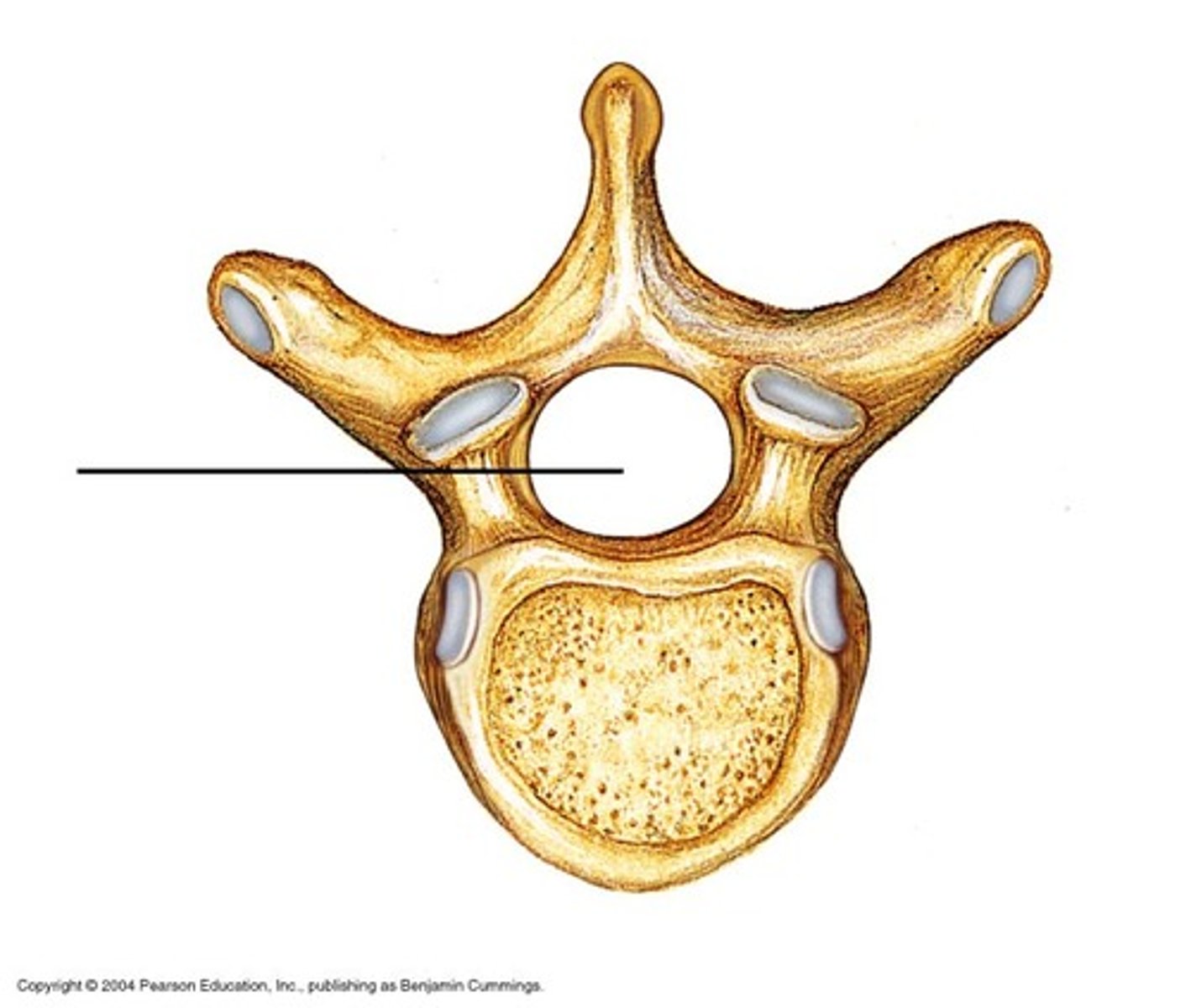
Vertebral foramen
Vertebral arch
Body
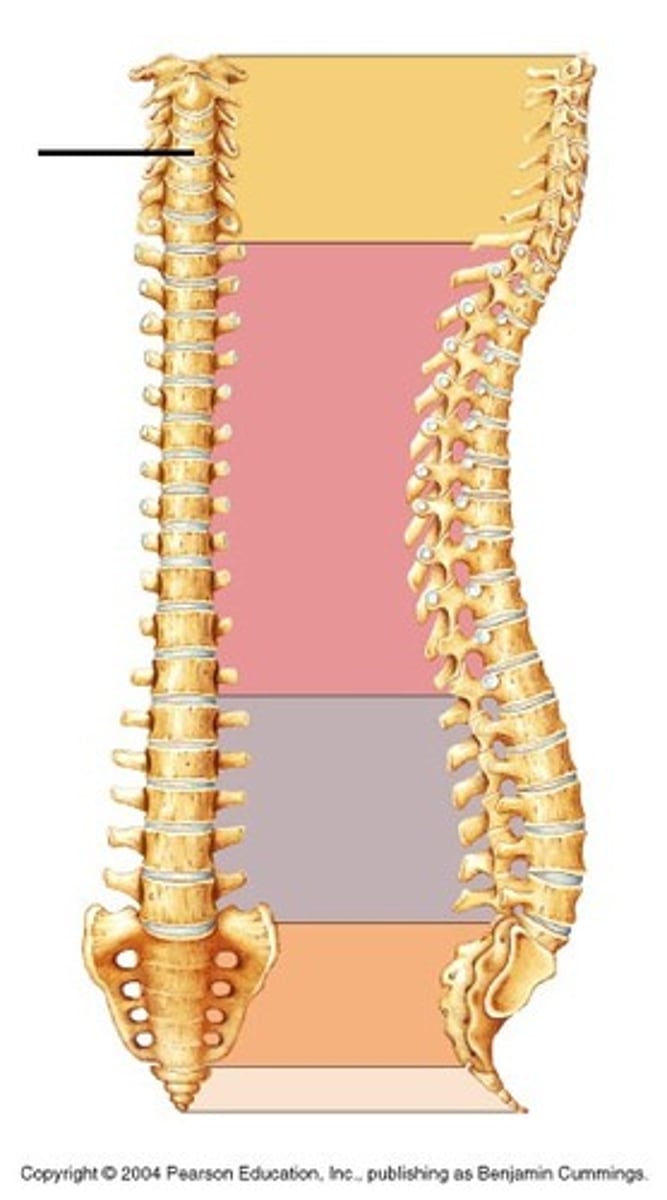
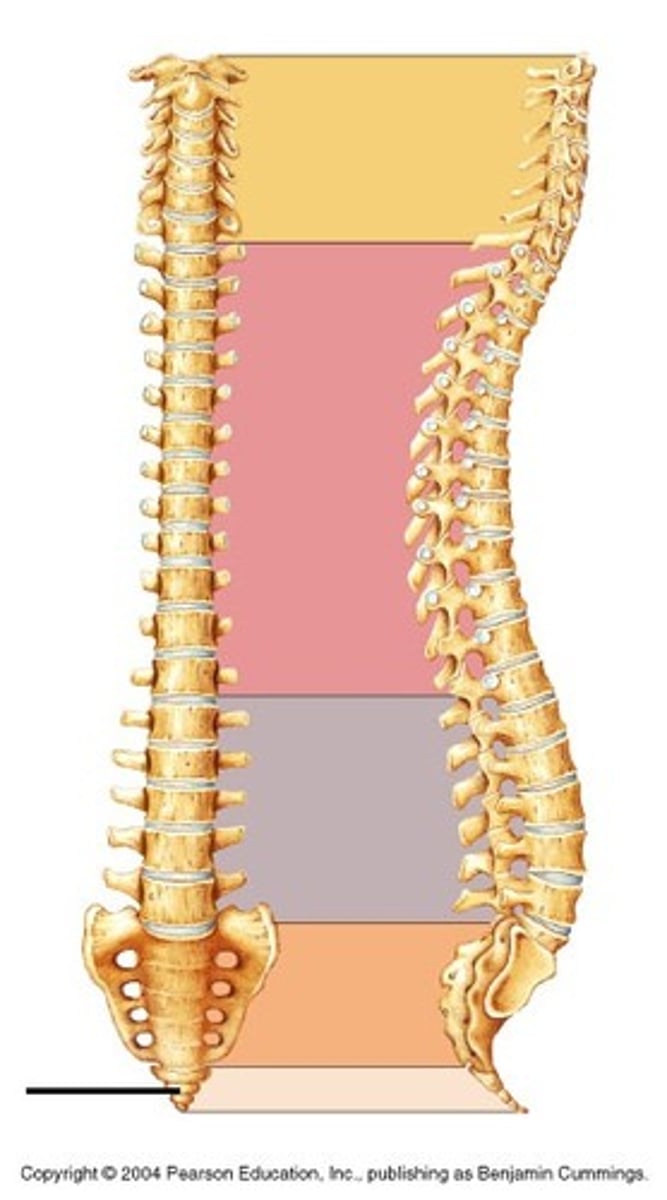
Cervical vertebrate (curvature)
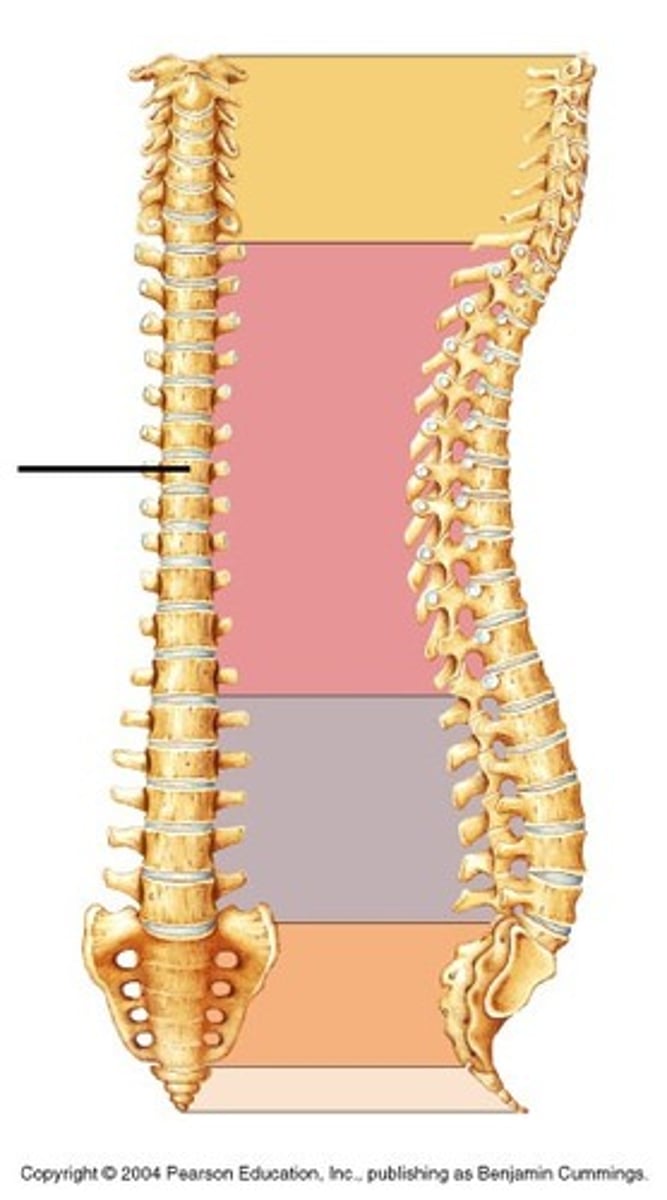
Thoracic vertebrae (curvature)
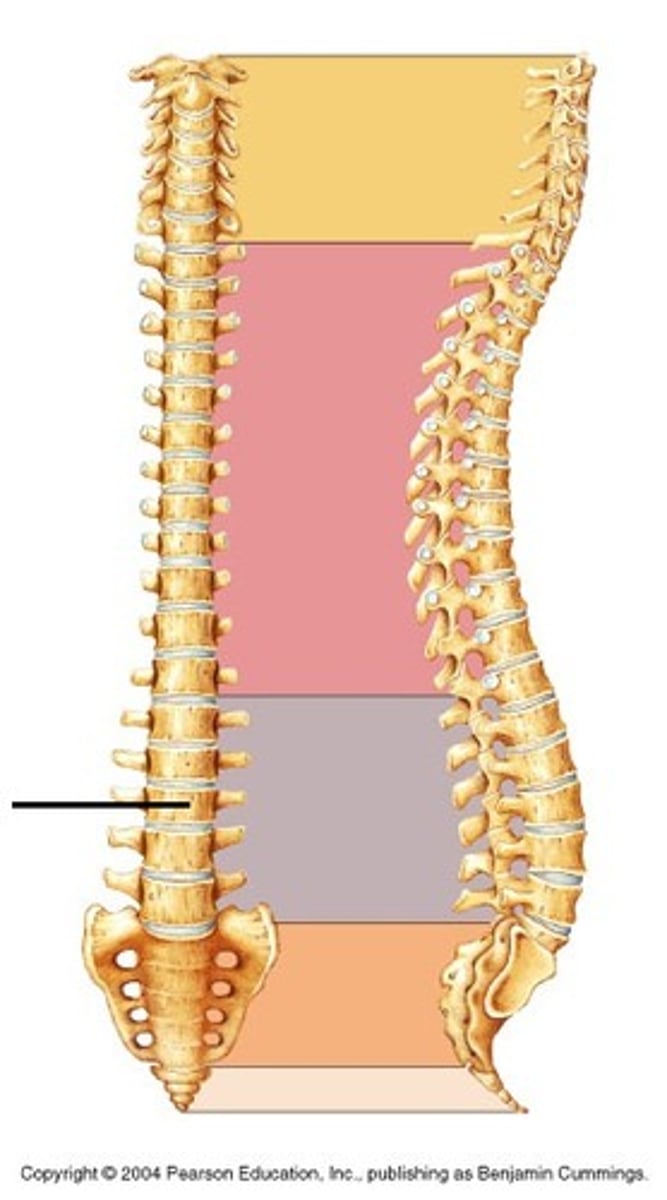
Lumbar vertebrae (curvature)
Sacrum (sacral curvature)
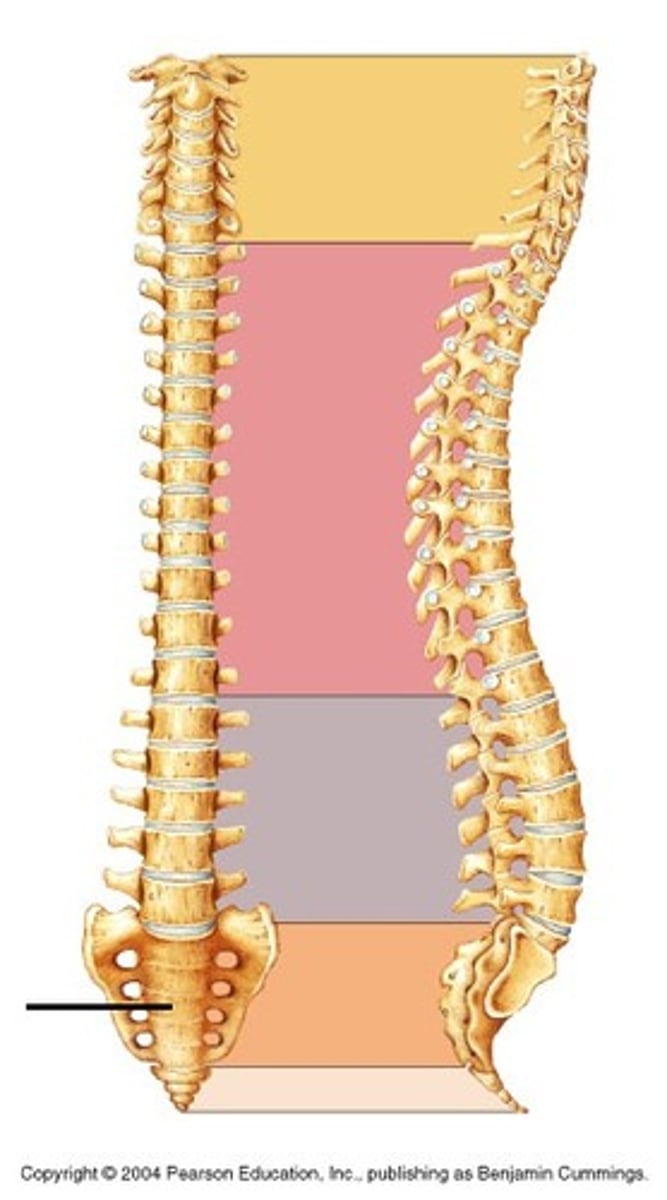
Coccyx
Superior articular
facet (articulates
with occipital condyle)
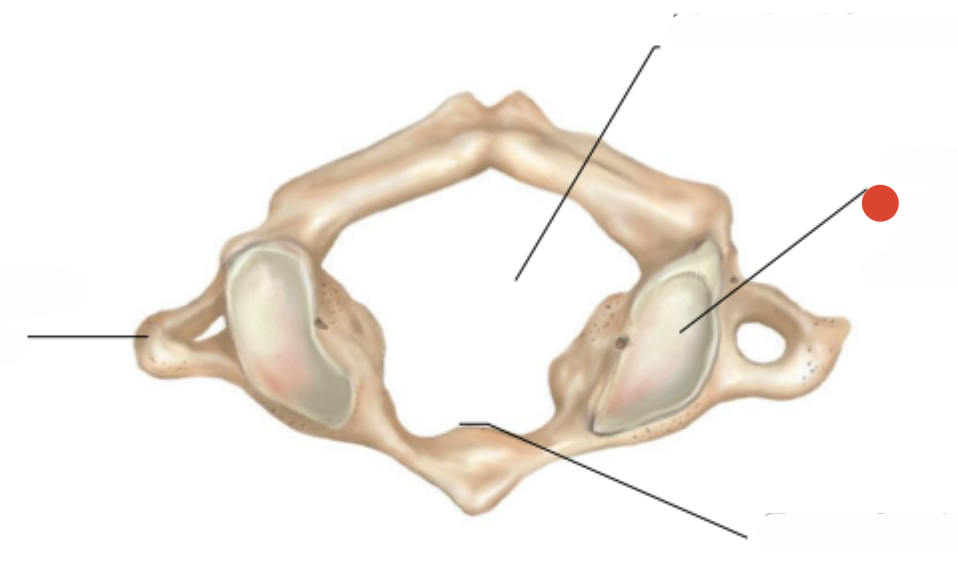
transverse of atlas
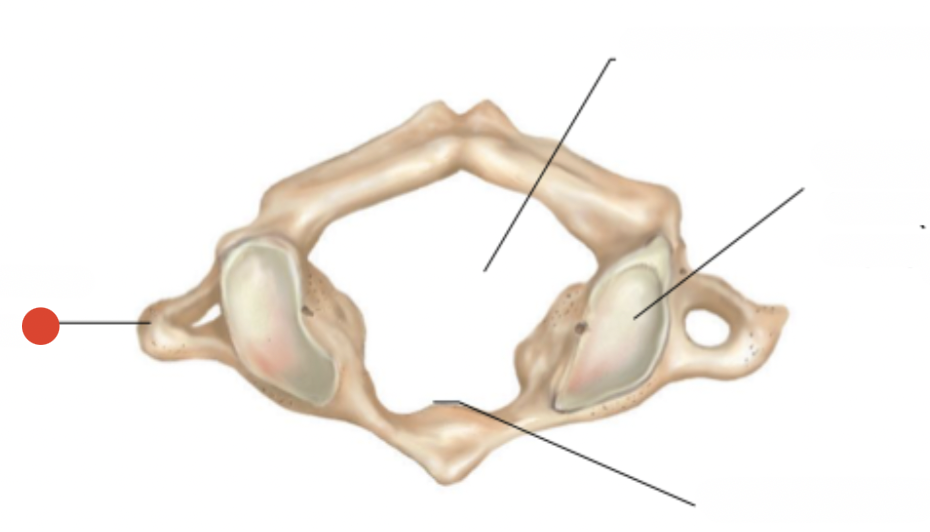
Vertebral foramen of atlas
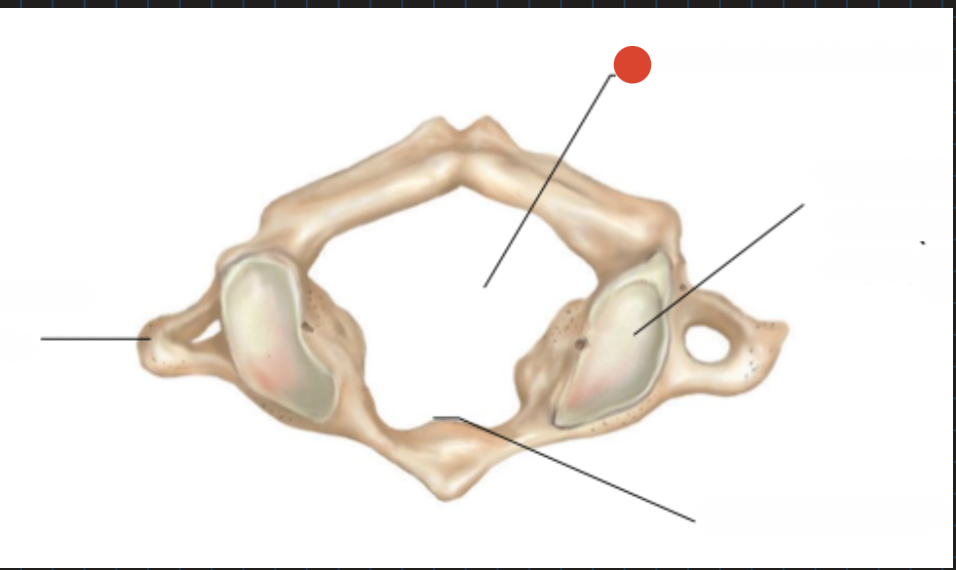
atlas facet for dens
forms joint with 2nd cervical vertebra

superior articular facet and under inferior
point directly up and down
flat because sit on top of each other
allows for large degree of movement
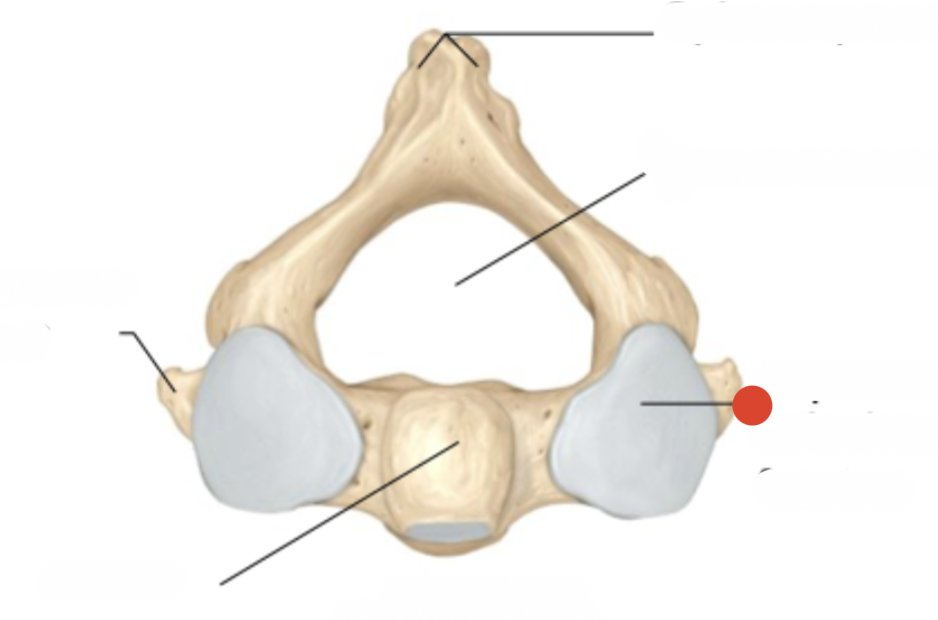
dens'
what atlas is connected to
so it can swivel
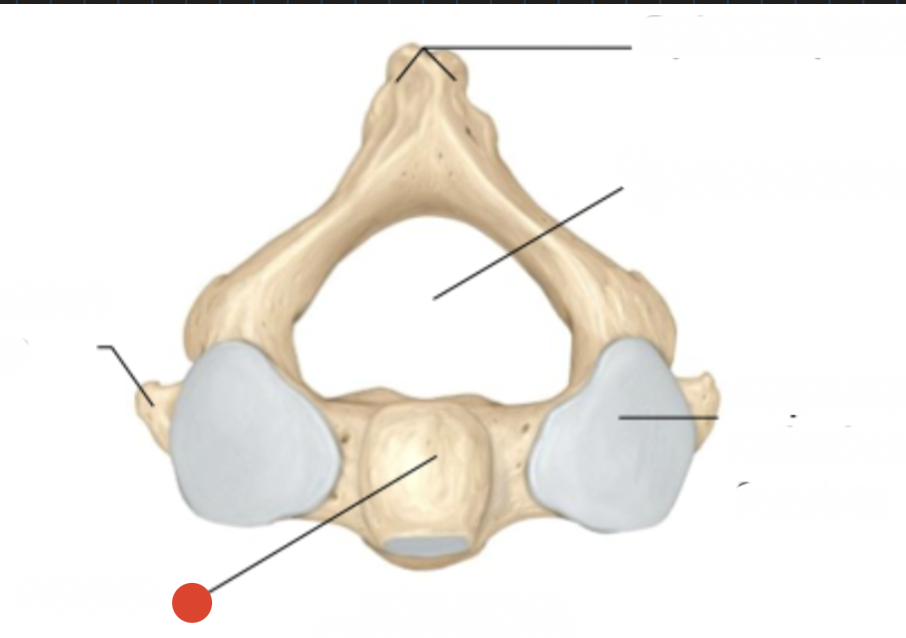
spinous process - bifid
unique to cervical
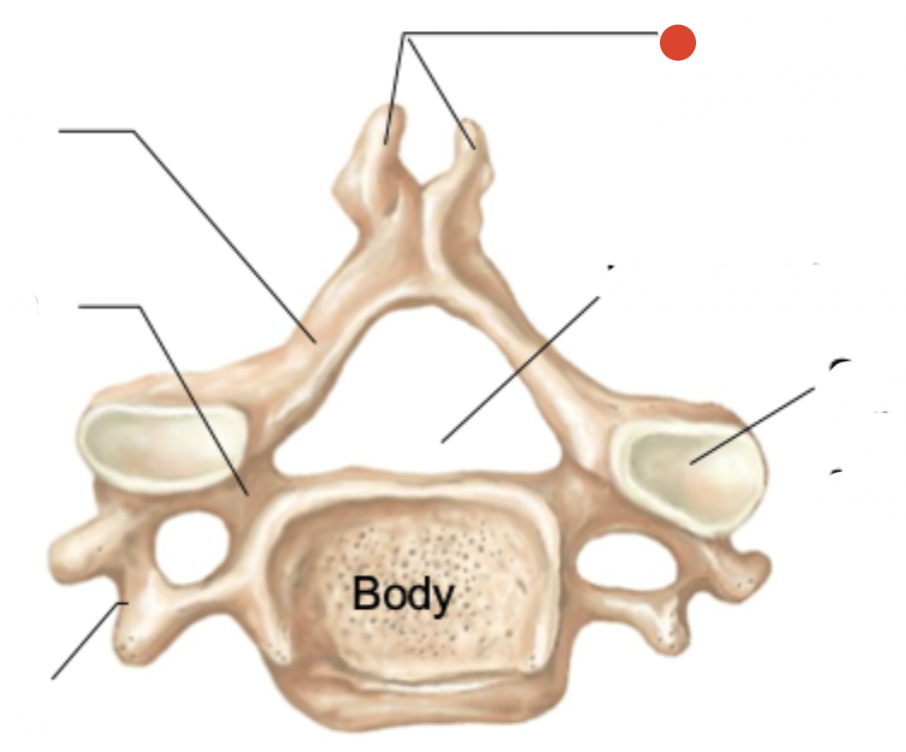
positioned at oblique angles to
lock together when stacked & provide greater stability
superior & inferior articular facet of thoracic
superior oriented medially
post laterally
movement limited
superior & inferior articular facet of lumbar
sacral canal
initially the vertebral foramen of the original 4-5 bones that make sacrum
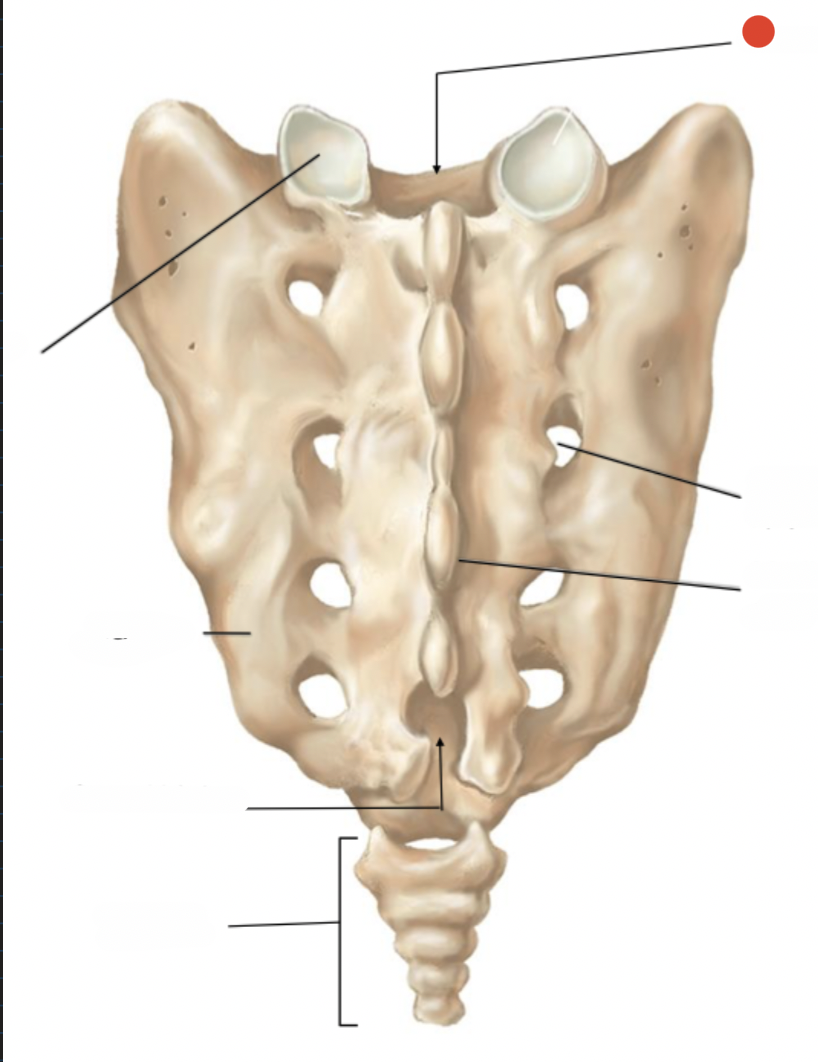
median sacral crest
orignally spinous processes
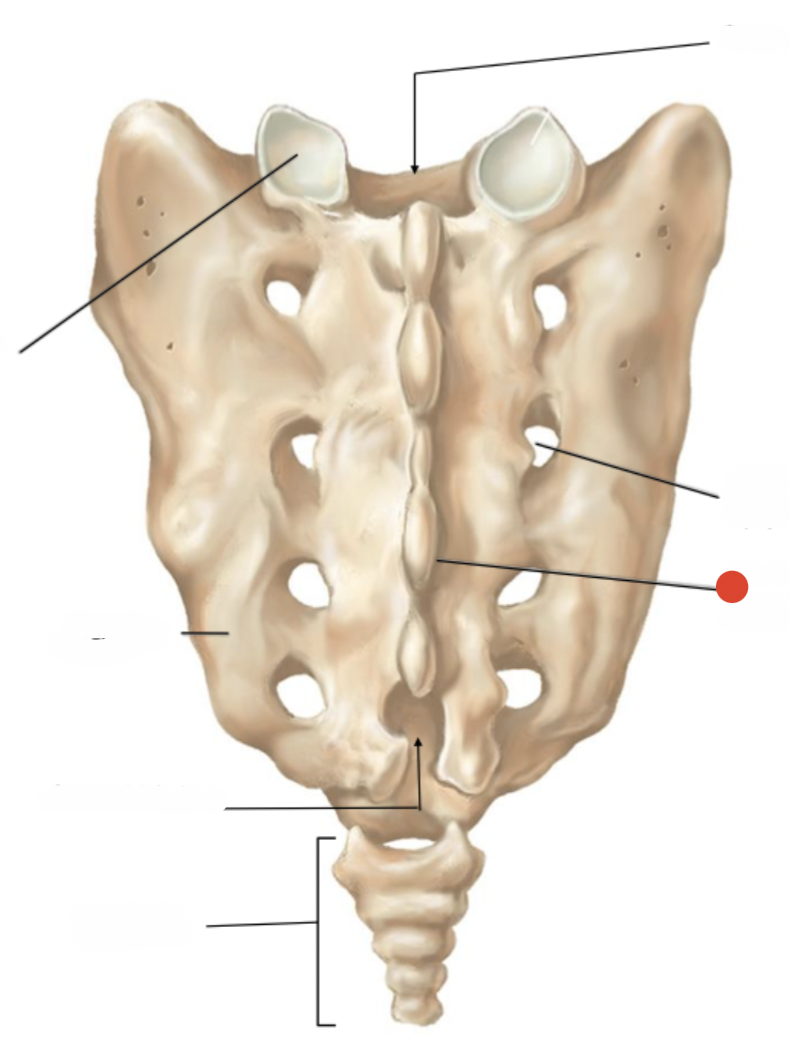
posterior sacral foramen
openenings to allow for exit of spinal nerves
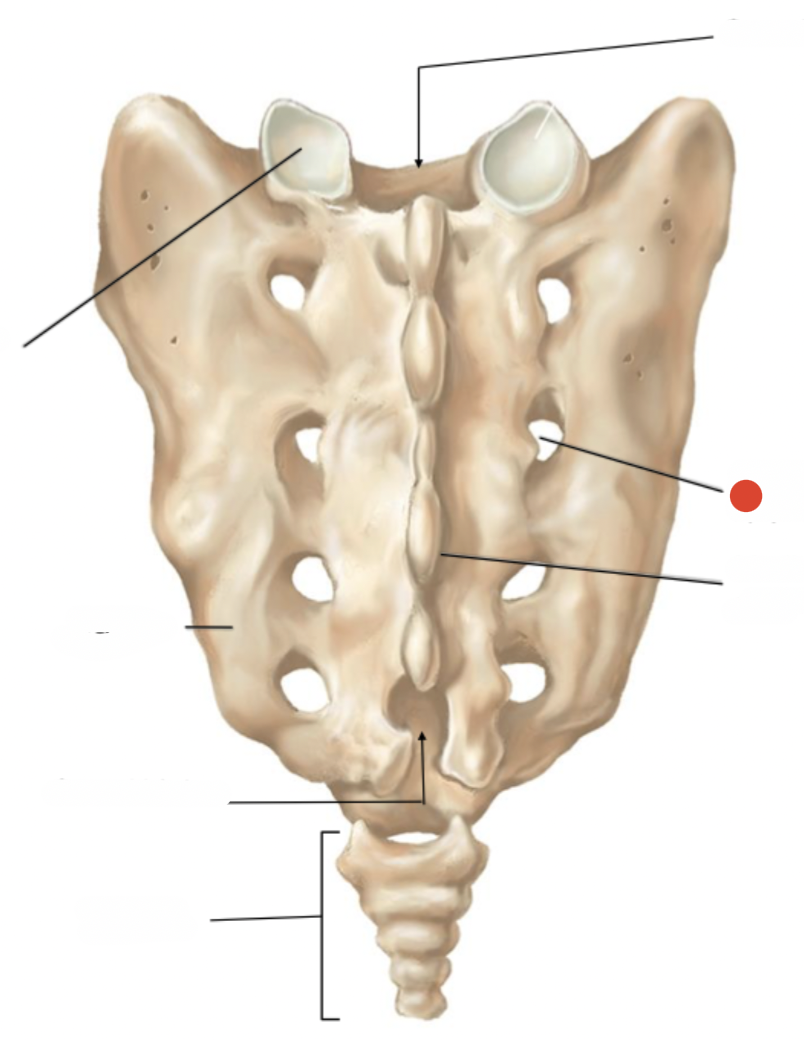
sacral hiatus
last bone has no spinous process
exit for last of spinal nerves
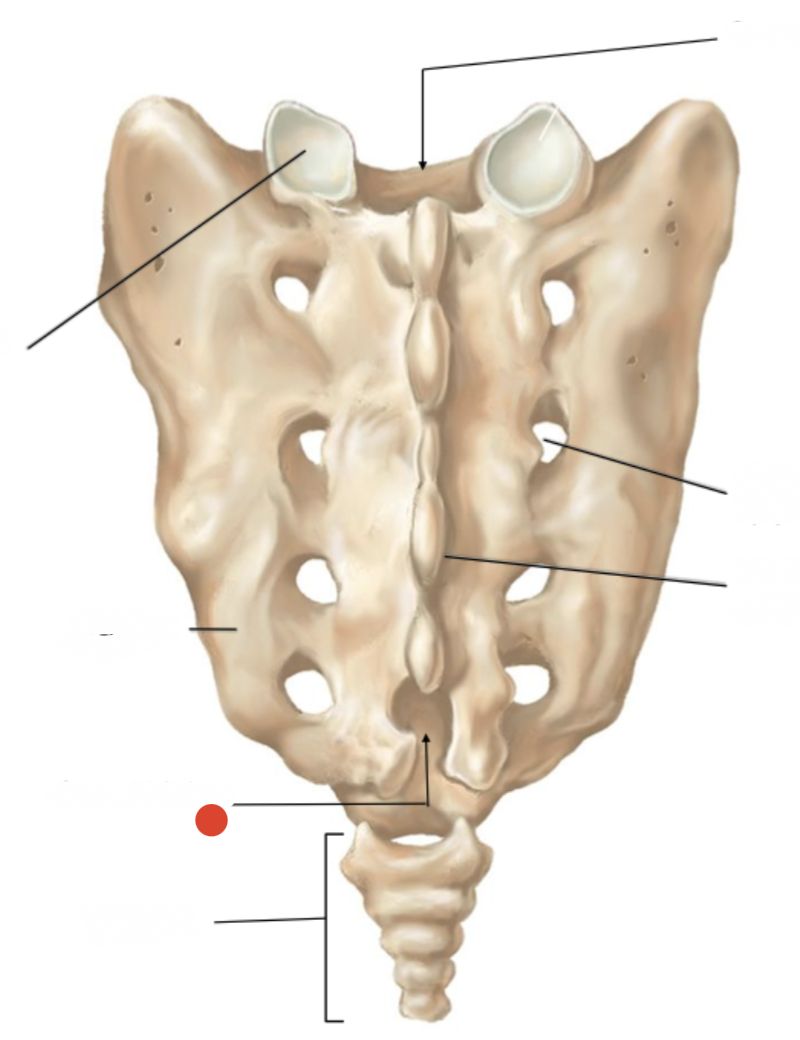
intervertebral foramen
space between bones
where spinal nerves exit
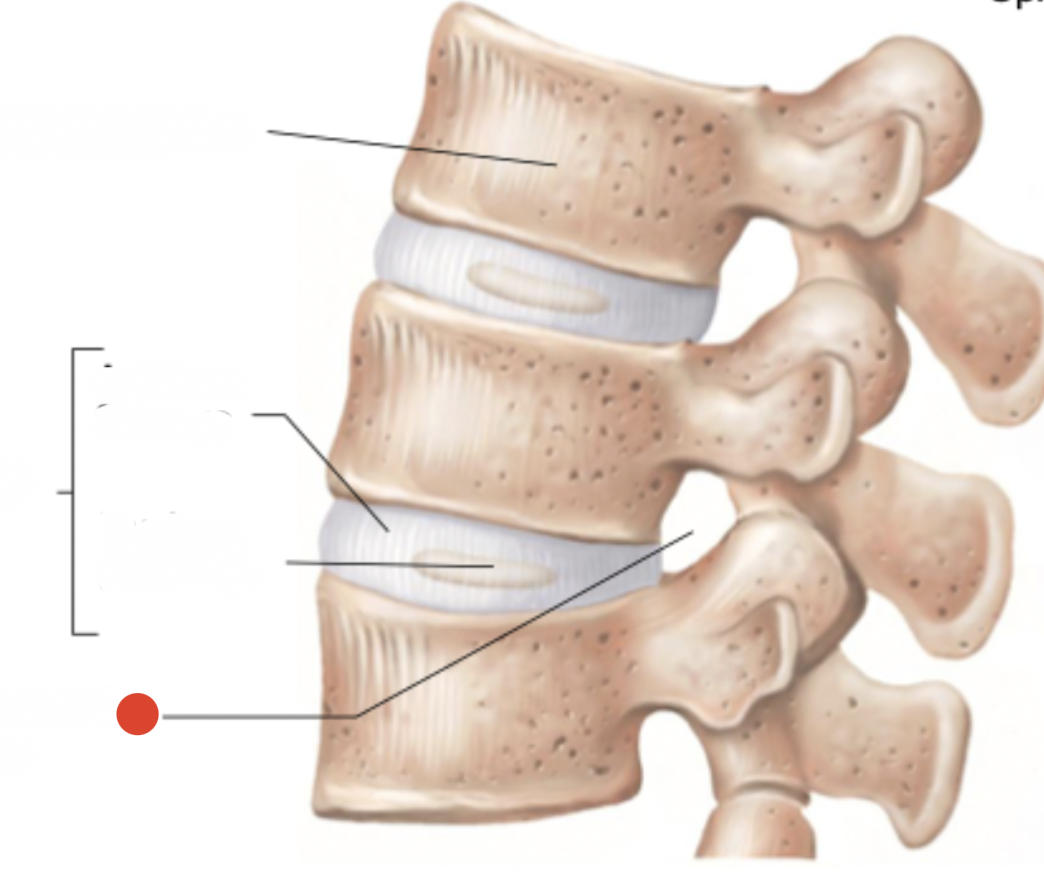
annulus fibrosus
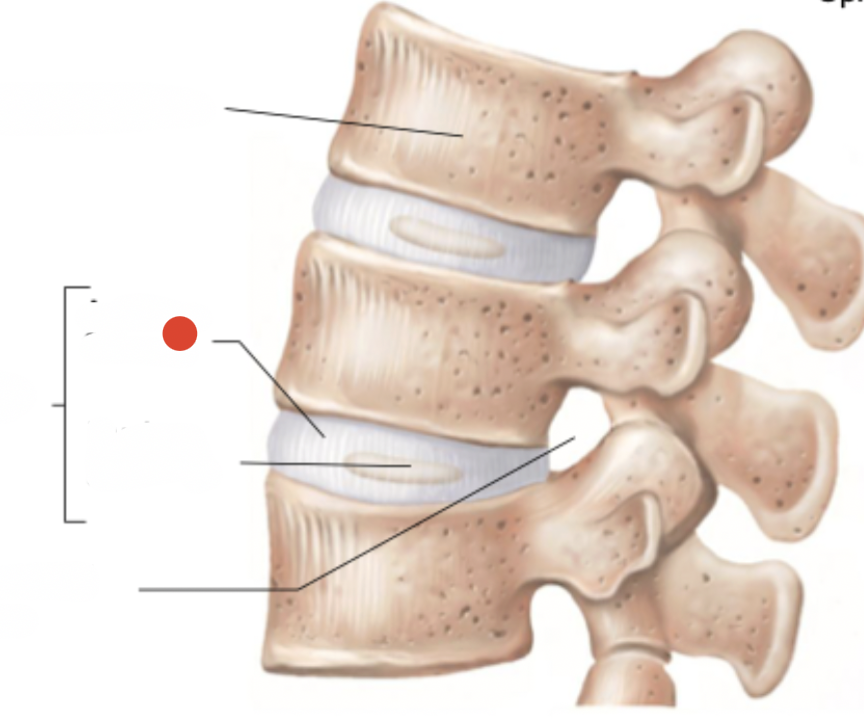
interverebral foramen
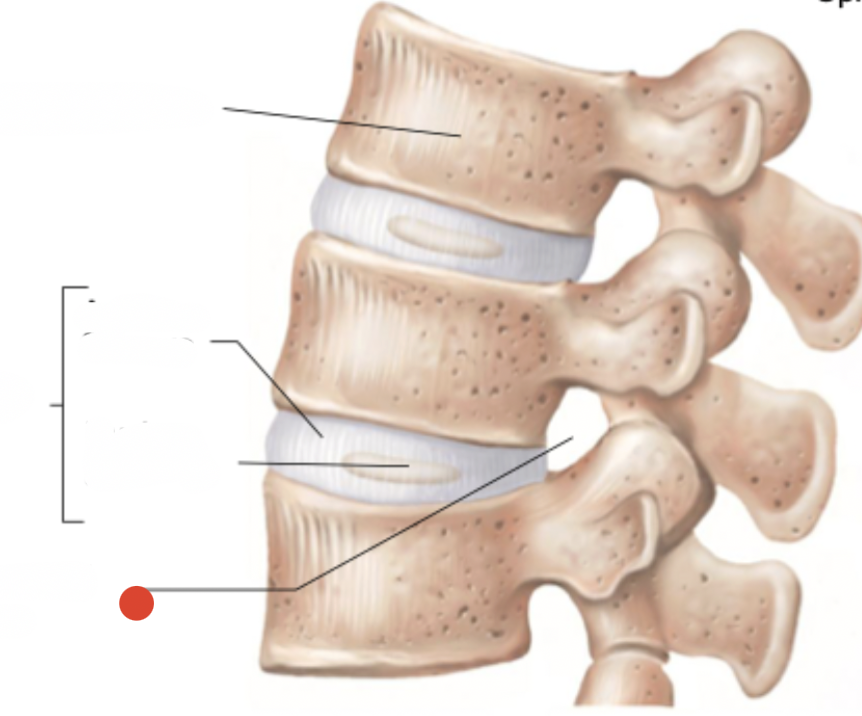
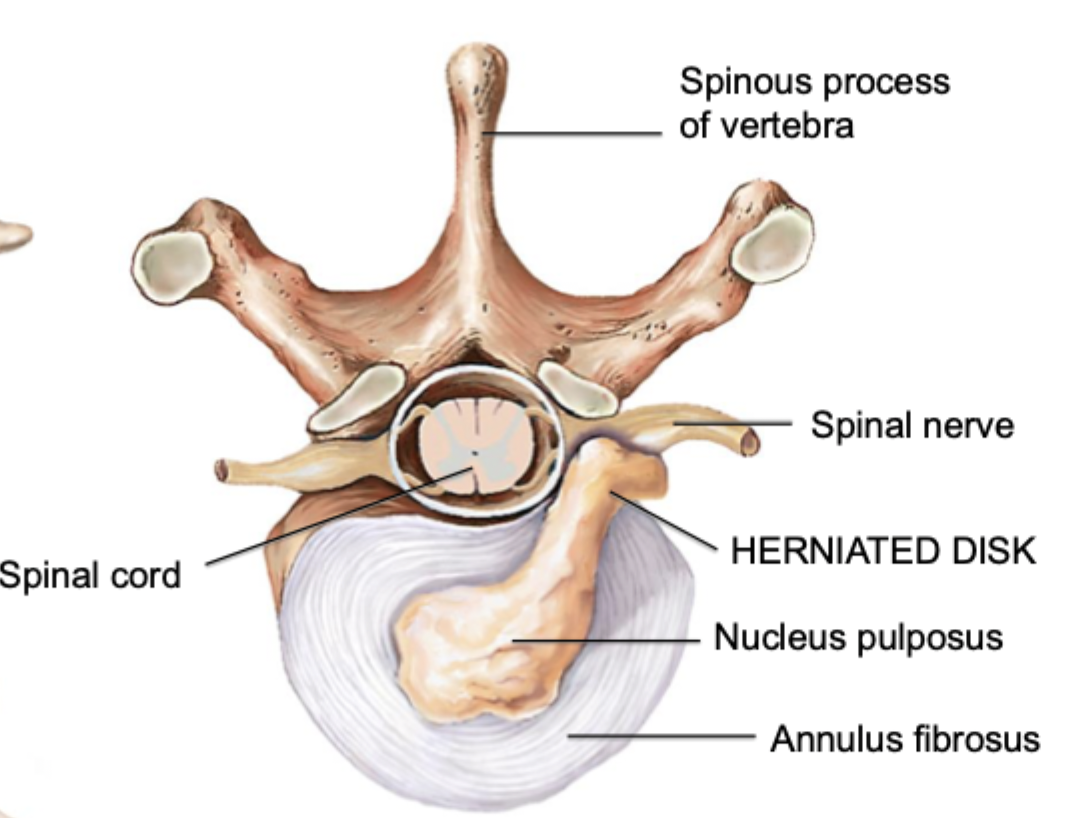
herniated disc
cartilage breaks and nucleus pulposus comes out of intervertebral foramen
towards back side
pushes on spinal nerve
protect heart and lungs
semi rigid bcs bones in it are semi moveable
bcs they form joints with other bones
have cartilage
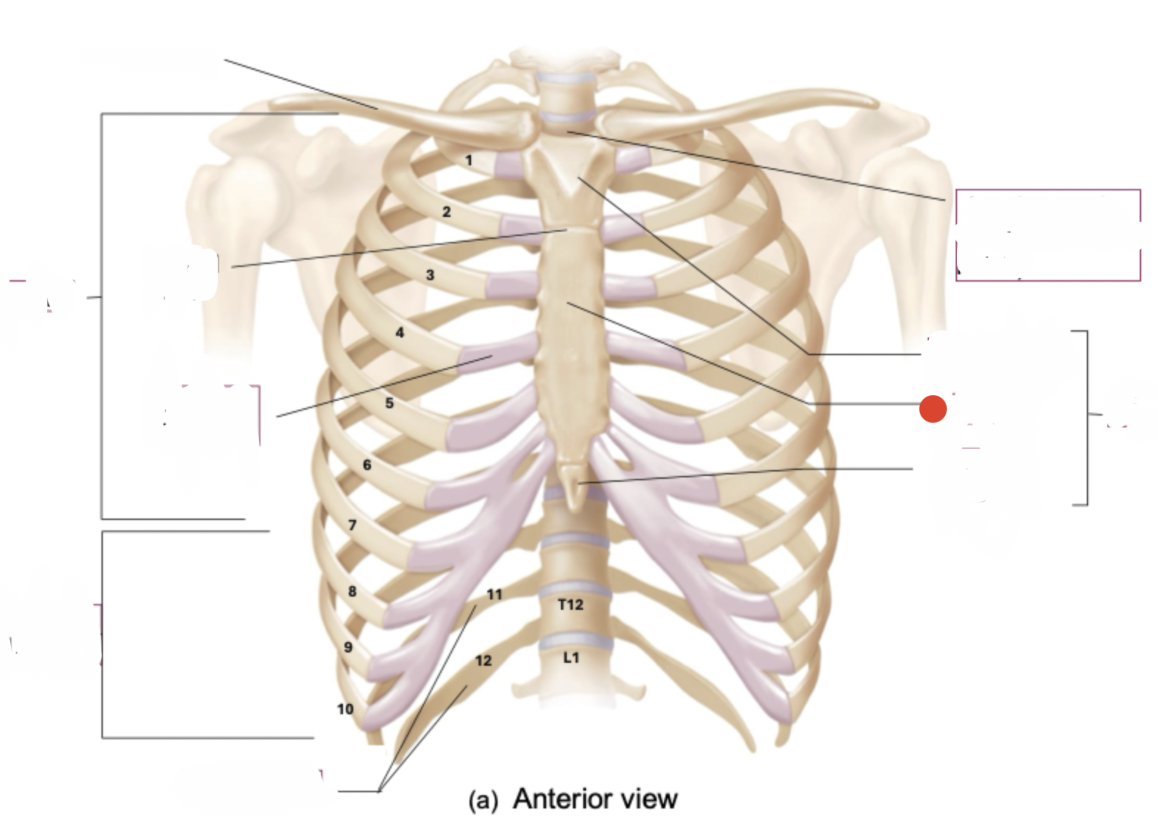
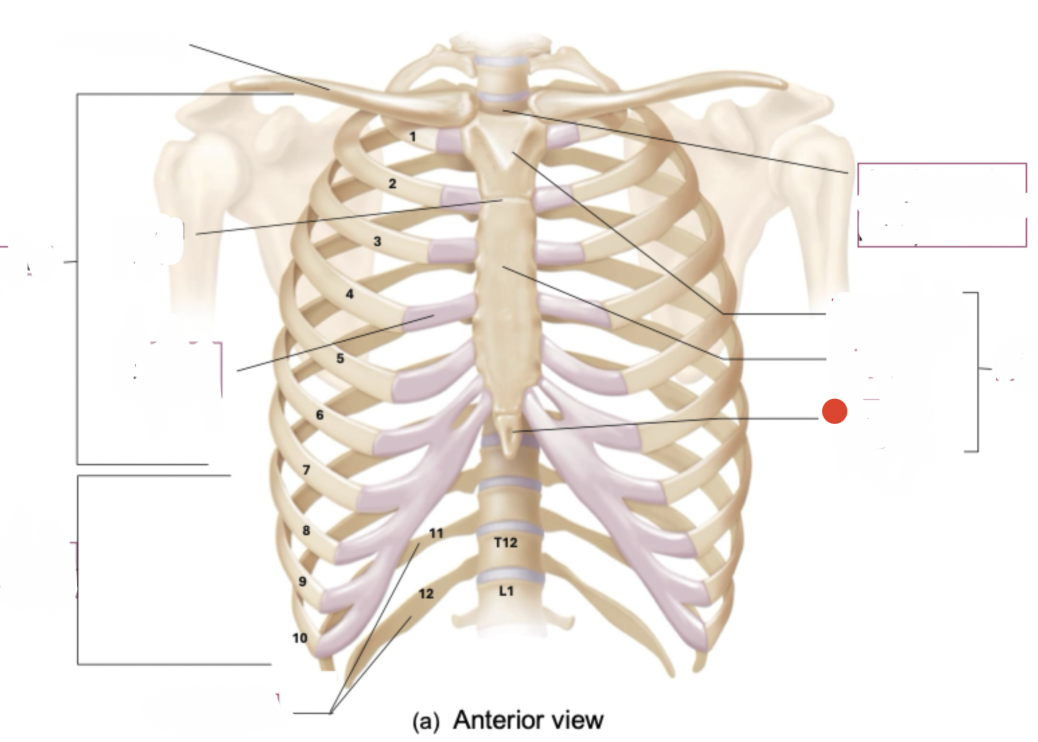
Thoracic vertebrae, ribs and costal cartilages, and sternum
thoracic cage
12 pairs
7 pairs true ribs
ribs
7 pairs are true ribs - vertebrosternal ribs
vertebrae to sternum
true ribs
5 pairs - “false ribs”
3 pair are vertebrochondral ribs (connect to sternum indirectly by connecting to costal cartilage of rib 7)
2 pair are “floating” or vertebral ribs
false ribs
manubrium and sternal angle (angled towards from front as move from top to bottom)
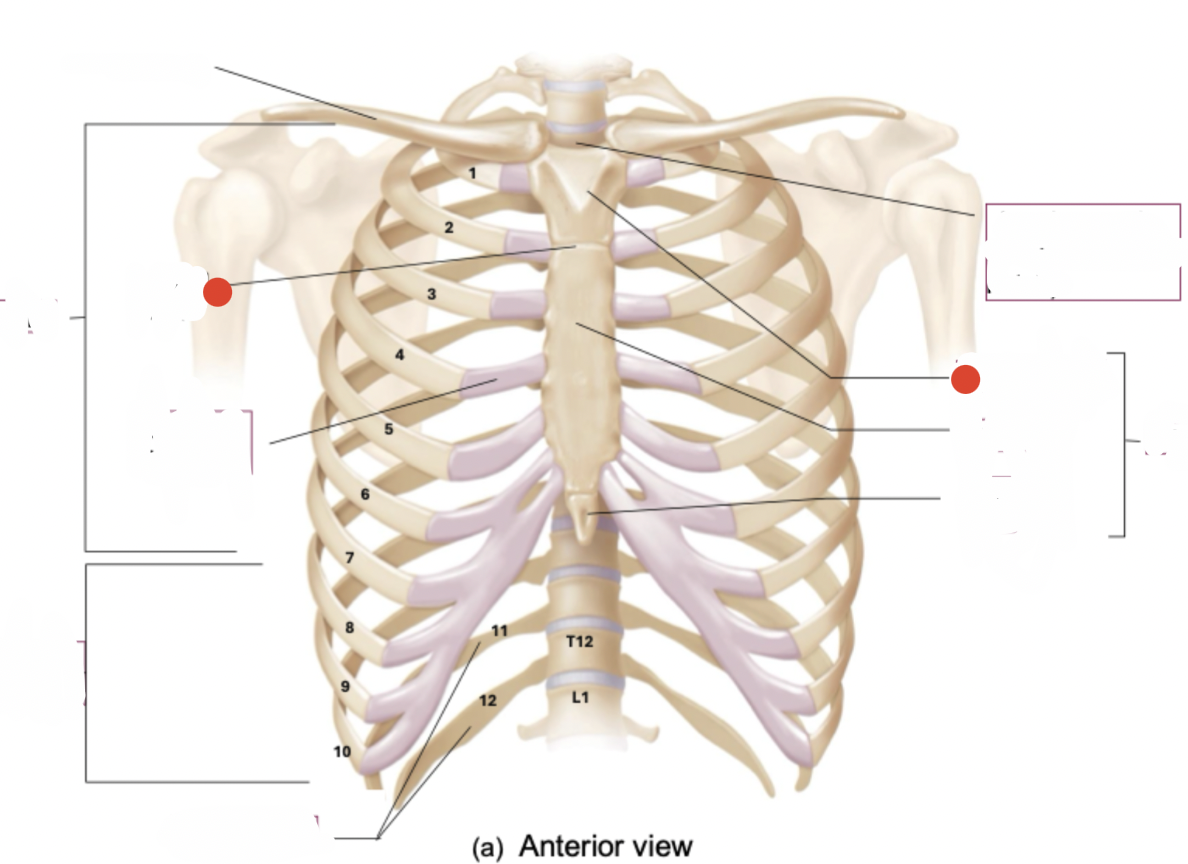
body
xiphoid process
made of cartilage until youre 40
bump on back of your skull that joins to ligaments which hold your head upright
External occipital protuberance