Marieb Chapter 15 The Special Senses
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
5 Sensory Receptors
vision, taste, smell, hearing, equilibrium
5 Structures that protect the eye and aid in eye function
1. Eyebrows
2. Eyelids
3. Conjuctiva
4. Lacrimal Apparatus
5. Extrinsic eye muscles
Conjuctiva
Transparent mucous membrane.
that lines eyelid
Lacrimal Apparatus
tear gland and ducts that drain into nasal cavity.
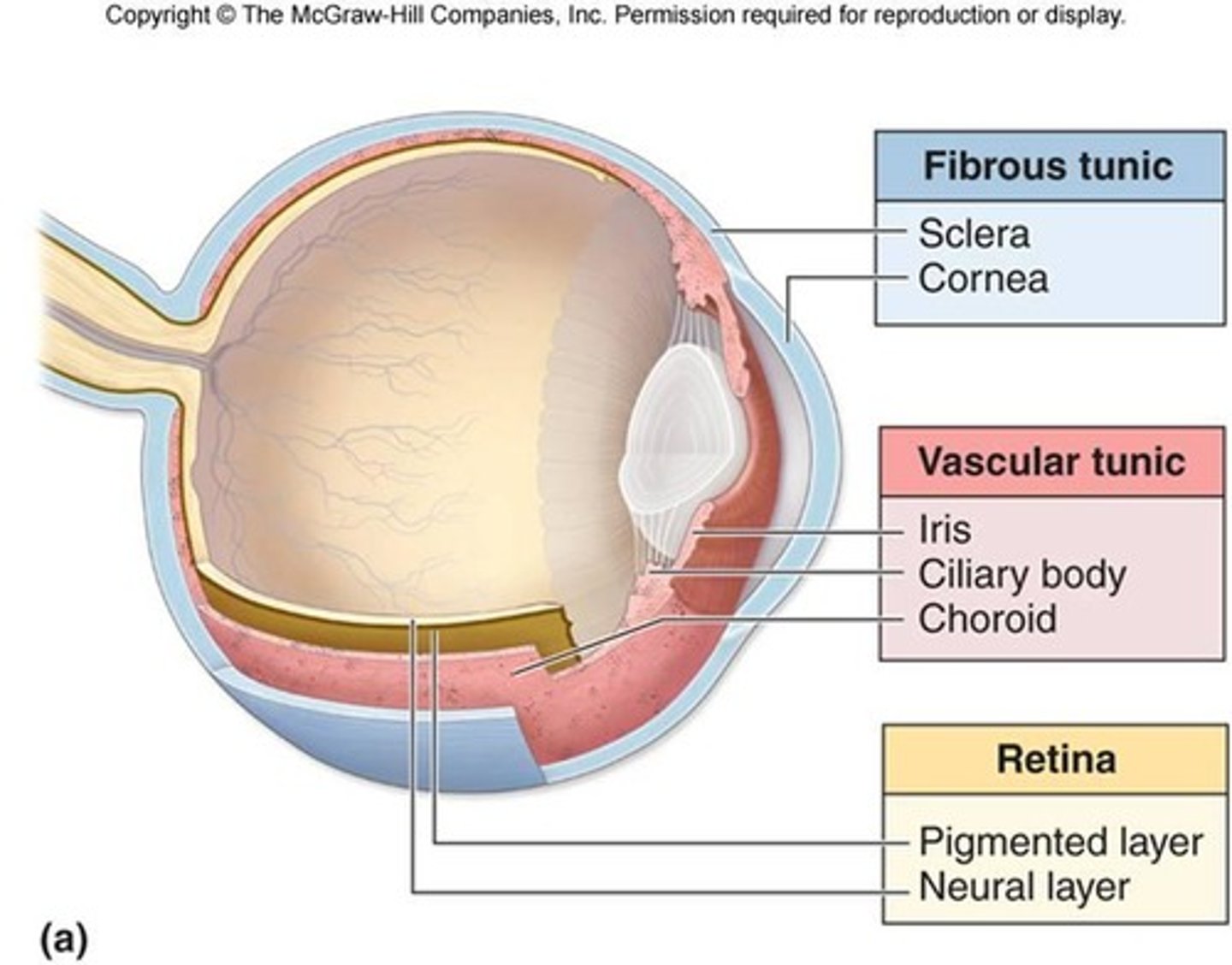
3 Layers of Eyeball Wall
Fibrous, vascular, inner
Internal cavity is filled with fluids called (________)
humors
Lens separates internal cavity into (_______) and (_______) segments
anterior, posterior
Fibrous Layer
Outermost layer; dense avascular connective tissue
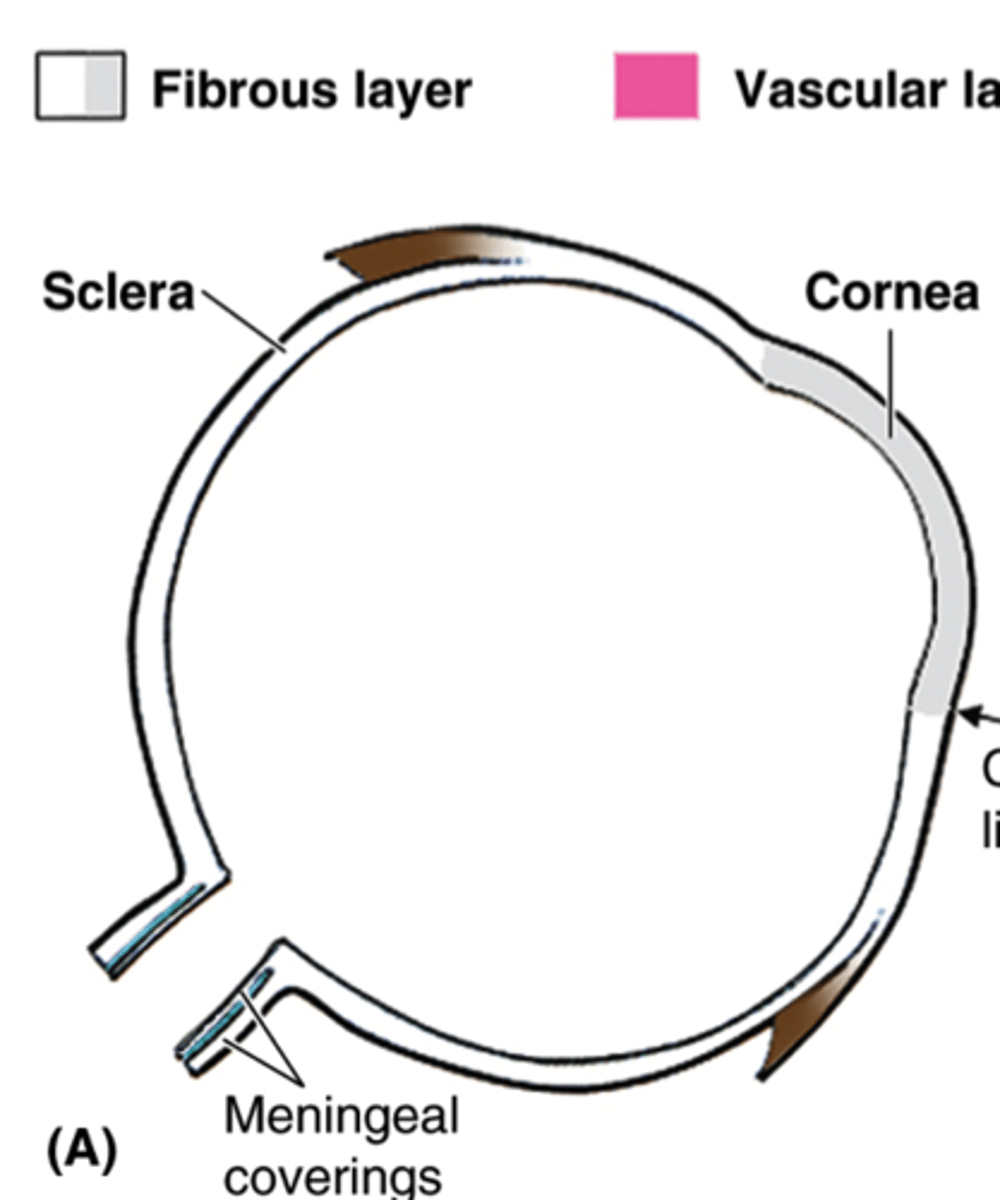
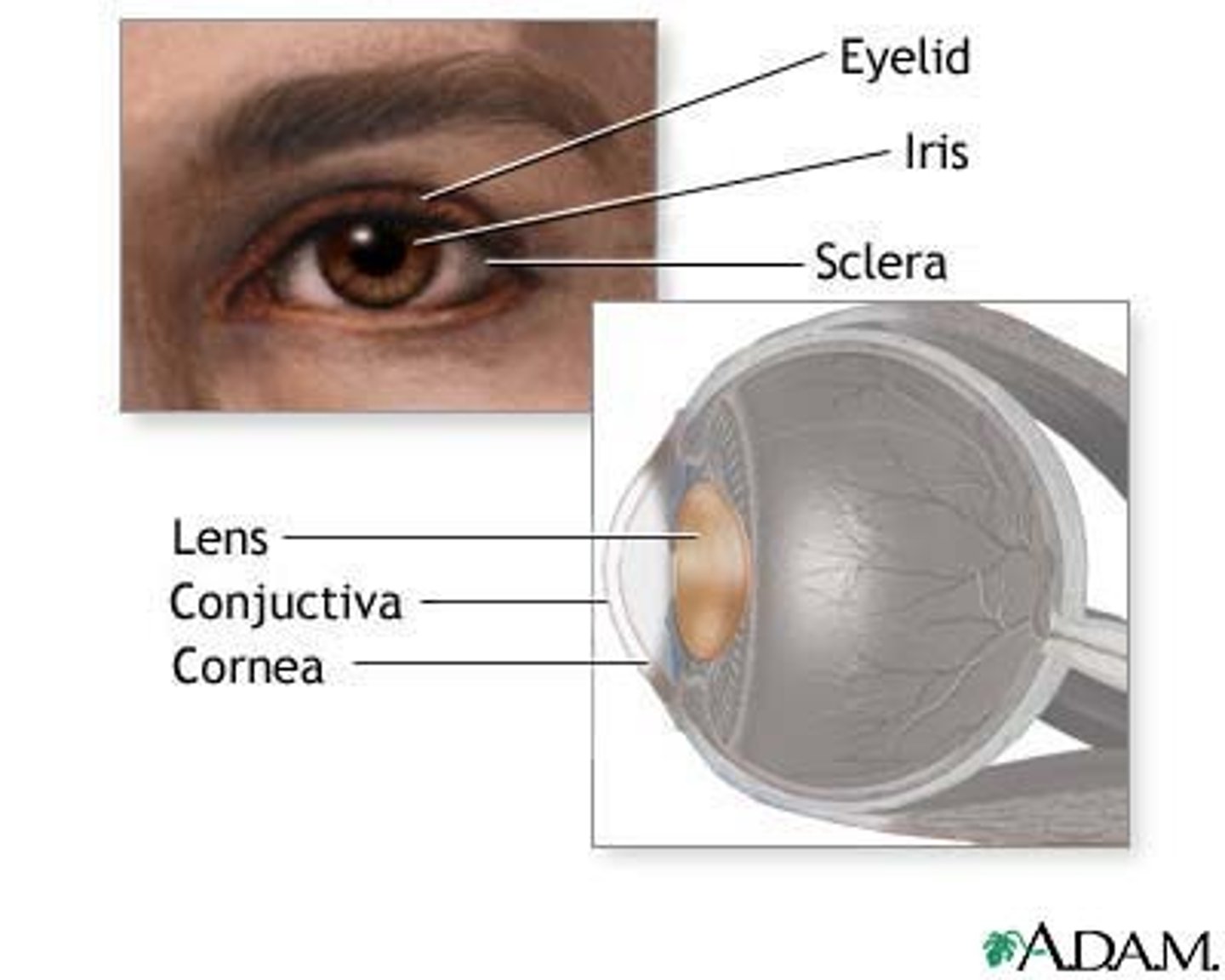
Sclera
Region of fibrous layer. Opaque, posterior. Protects, shapes, anchors extrinsic eye muscles.
Cornea
Transparent anterior covering in fibrous layer. Bends light as it enters eye. Numerous pain receptors contribute to blinking and tearing reflexes.
Vascular Layer
Middle pigmented layer.
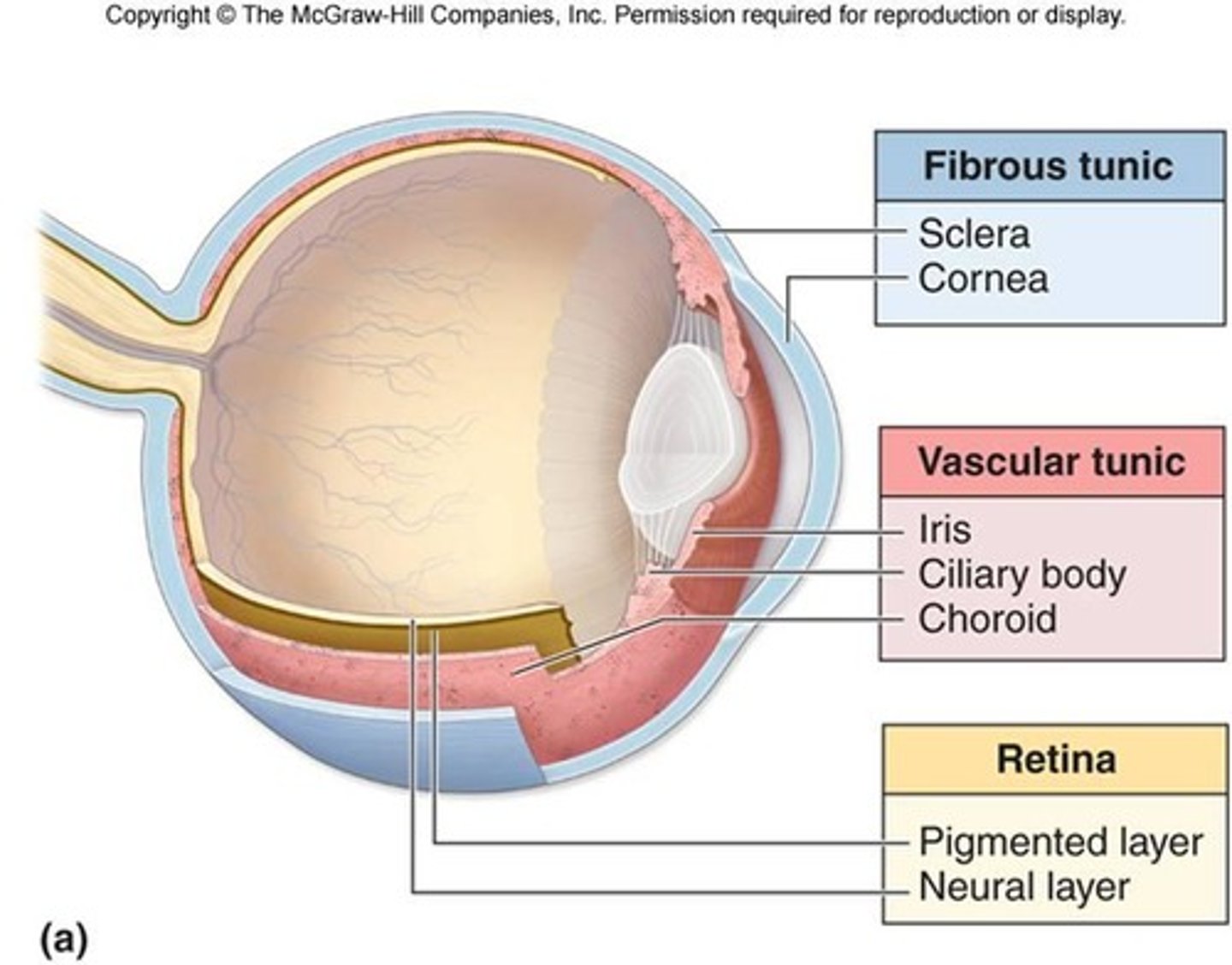
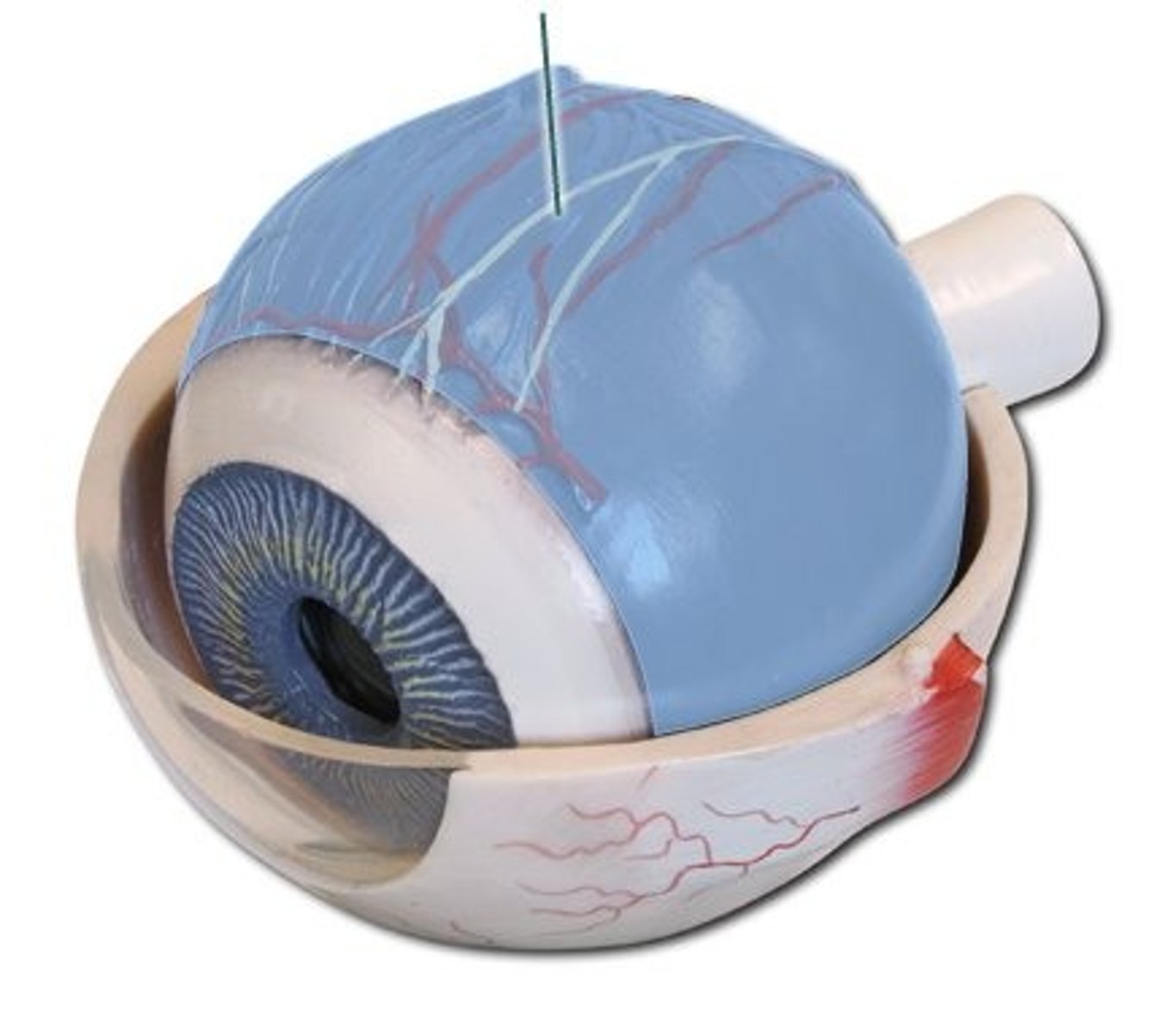
Choroid
Posterior portion of vascular layer, supplies blood to all layers of eye
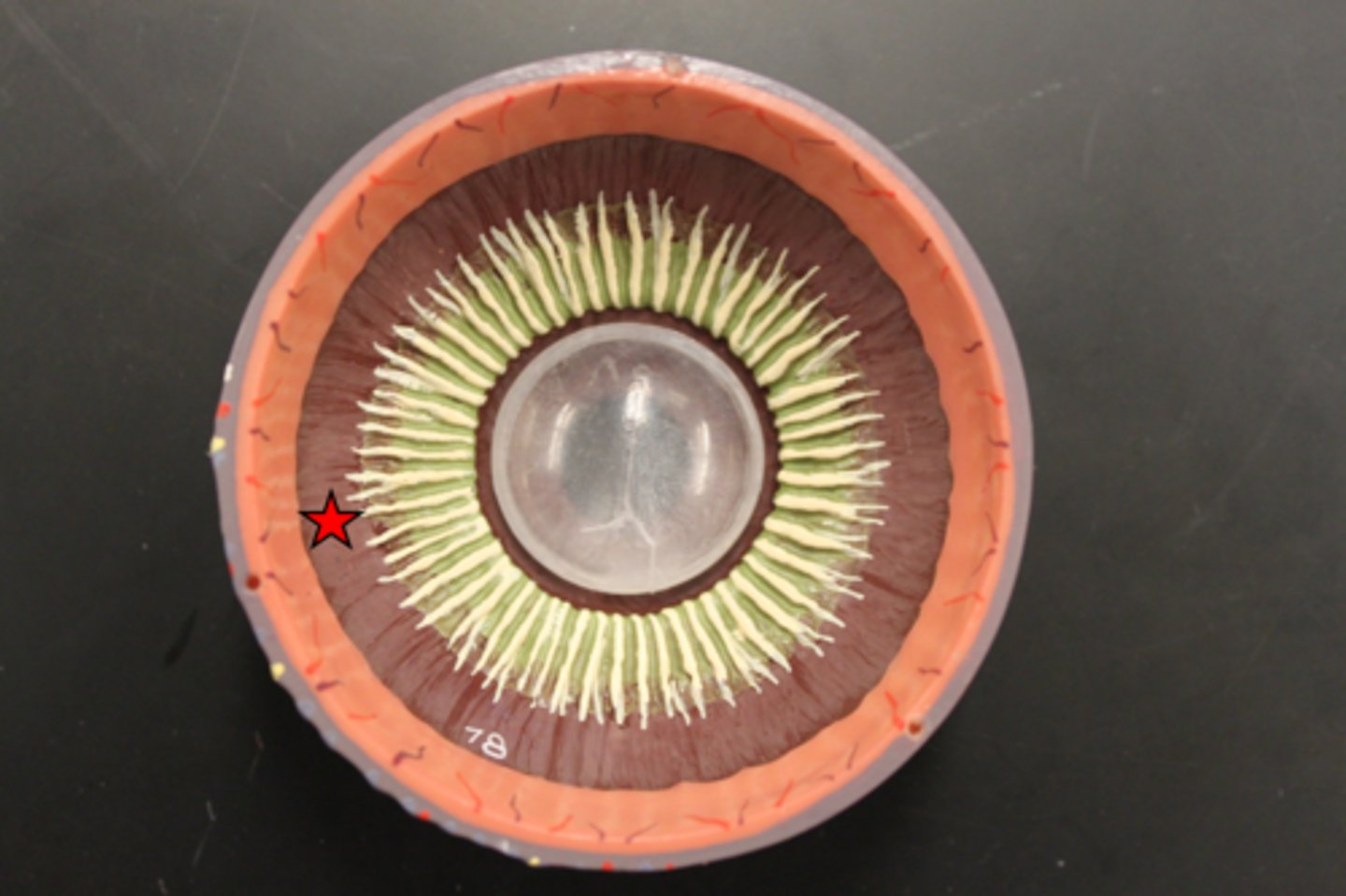
Ciliary Body
Ring of smooth muscle surrounding lens in uvea; controls lens shape
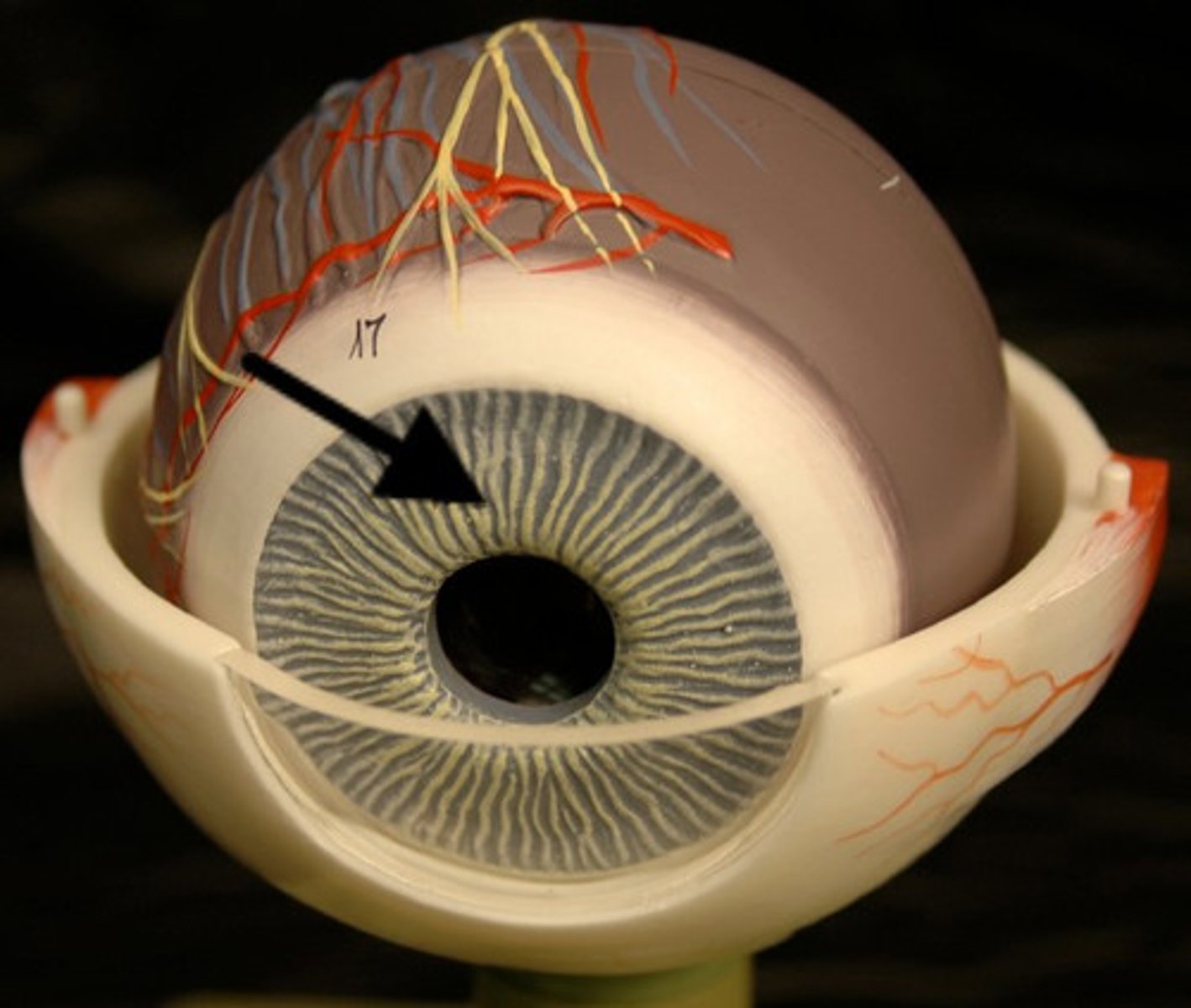
Iris
Colored part of eye & vascular layer that controls the size and shape of the pupil
Inner Layer
Retina is the sensory portion of the eye and contains a quarter billion photoreceptors of rods & cones
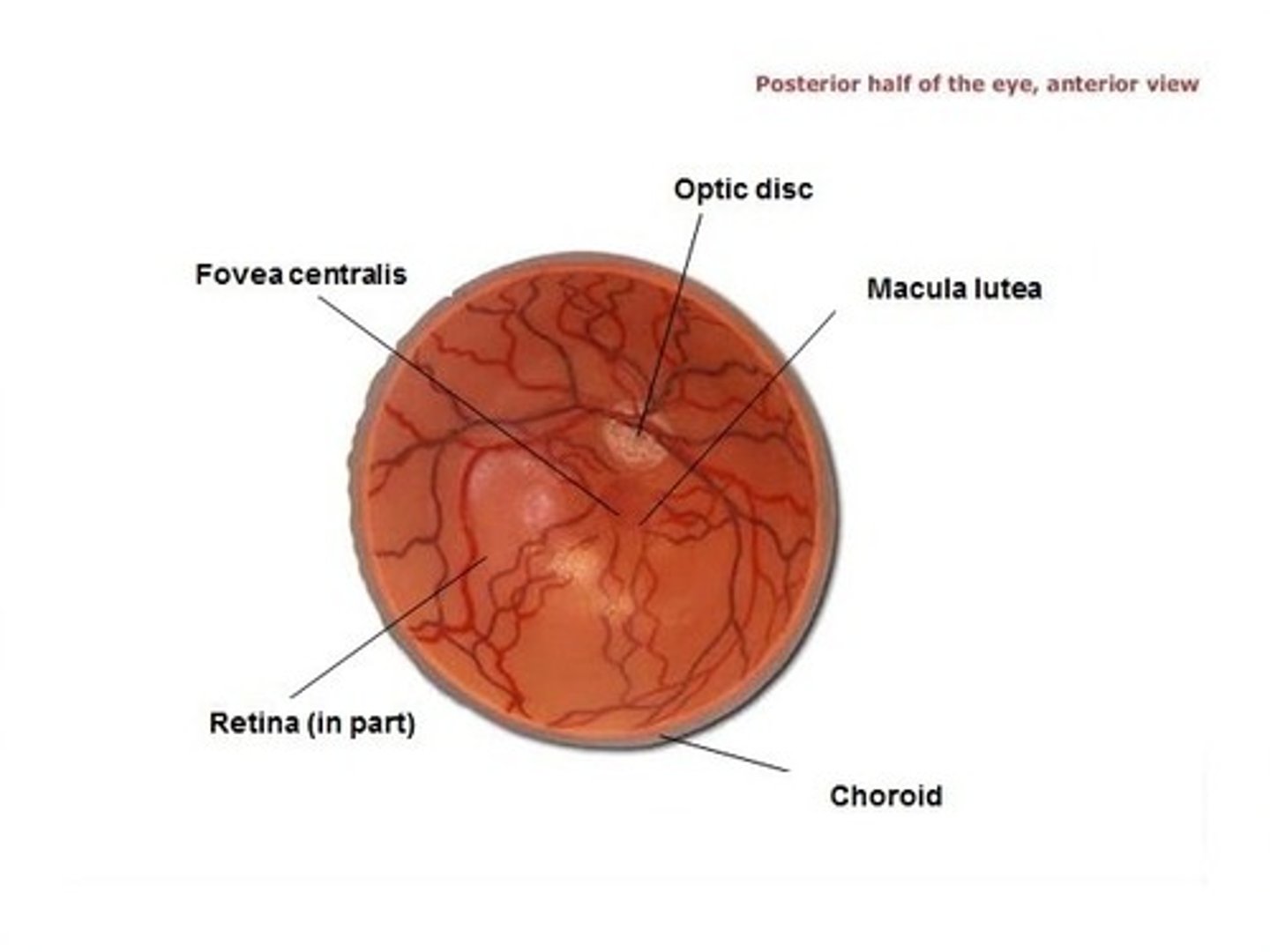
Optic disc
(blind spot): site where optic nerve leaves eye, lacks photoreceptors.
Rods
Dim light, peripheral vision receptors. More numerous, more sensitive to light than cones. No color vision or sharp images.
Cones
vision receptors for bright light. High-res color vision
Posterior cavity
Contains vitreous humor:
-transmits light
-holds neural layer of retina firmly against pigmented layer
-contributes to intraocular pressure
Anterior cavity
contains aqueous humor that is frequently drained and replaced as it supplies nutrients and oxygen mainly to lens and cornea but also to retina & removes waste.
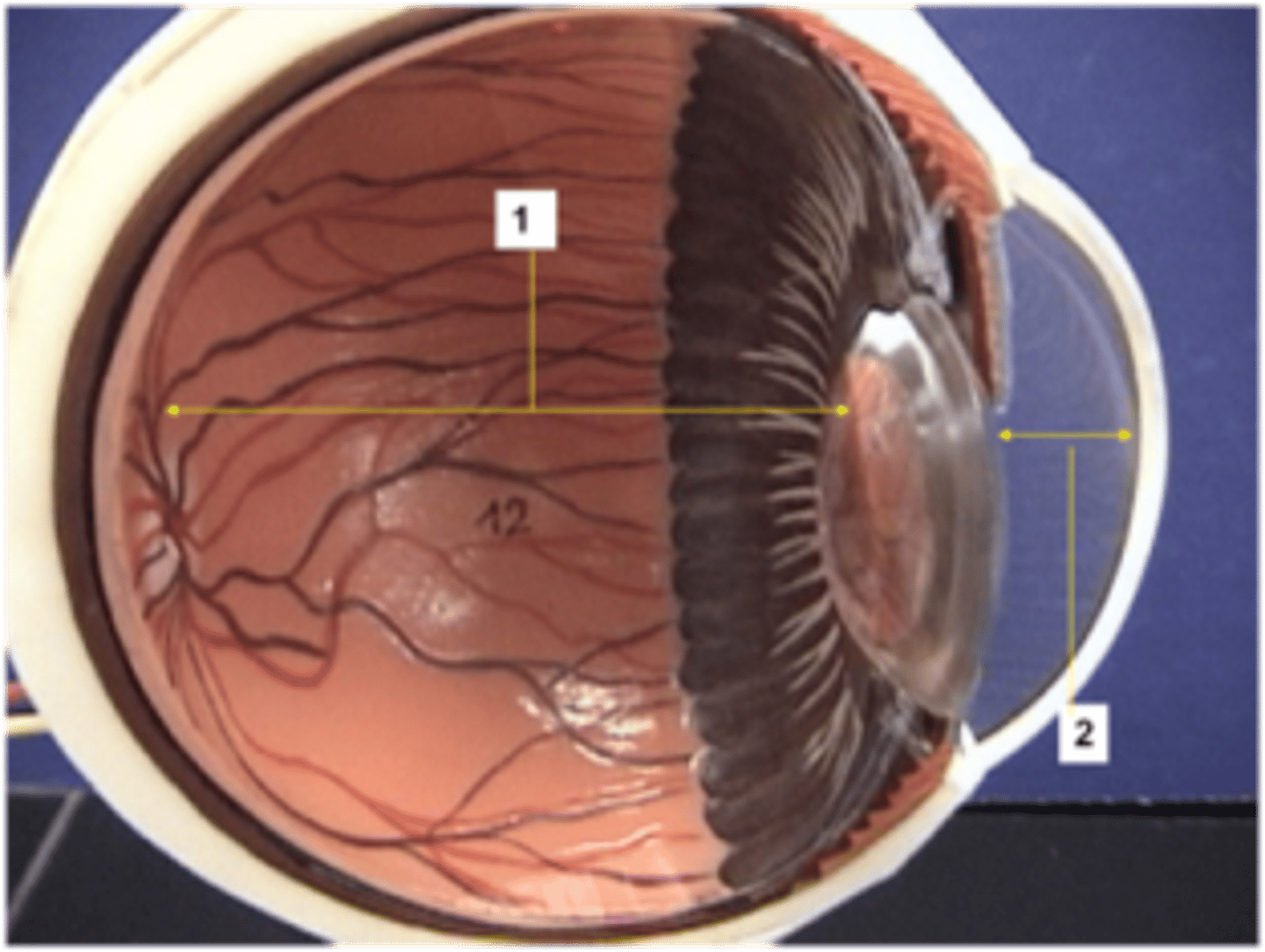
Lens
Biconvex, transparent, flexible and avascular. Changes shape to precisely focus light on retina
Focusing Light on the Retina
Pathway of light entering eye: cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, entire neural layer of retina, photoreceptors.
Focusing for Distant Vision
Ciliary muscles relaxed, lens stretched flat by tension in ciliary zonule
Accommodation
Changing lens shape to increase refraction. Near point of vision.
Visual Pathway to the Brain
Axons of retinal ganglion cells form optic nerve. Medial fibers of optic nerve decussate at optic chiasma. Most fibers of optic tracts continue to thalamus. Then to occipital lobes.
Olfactory Epithelium
In roof of nasal cavity, covers superior nasal conchae. Contains bipolar neurons.
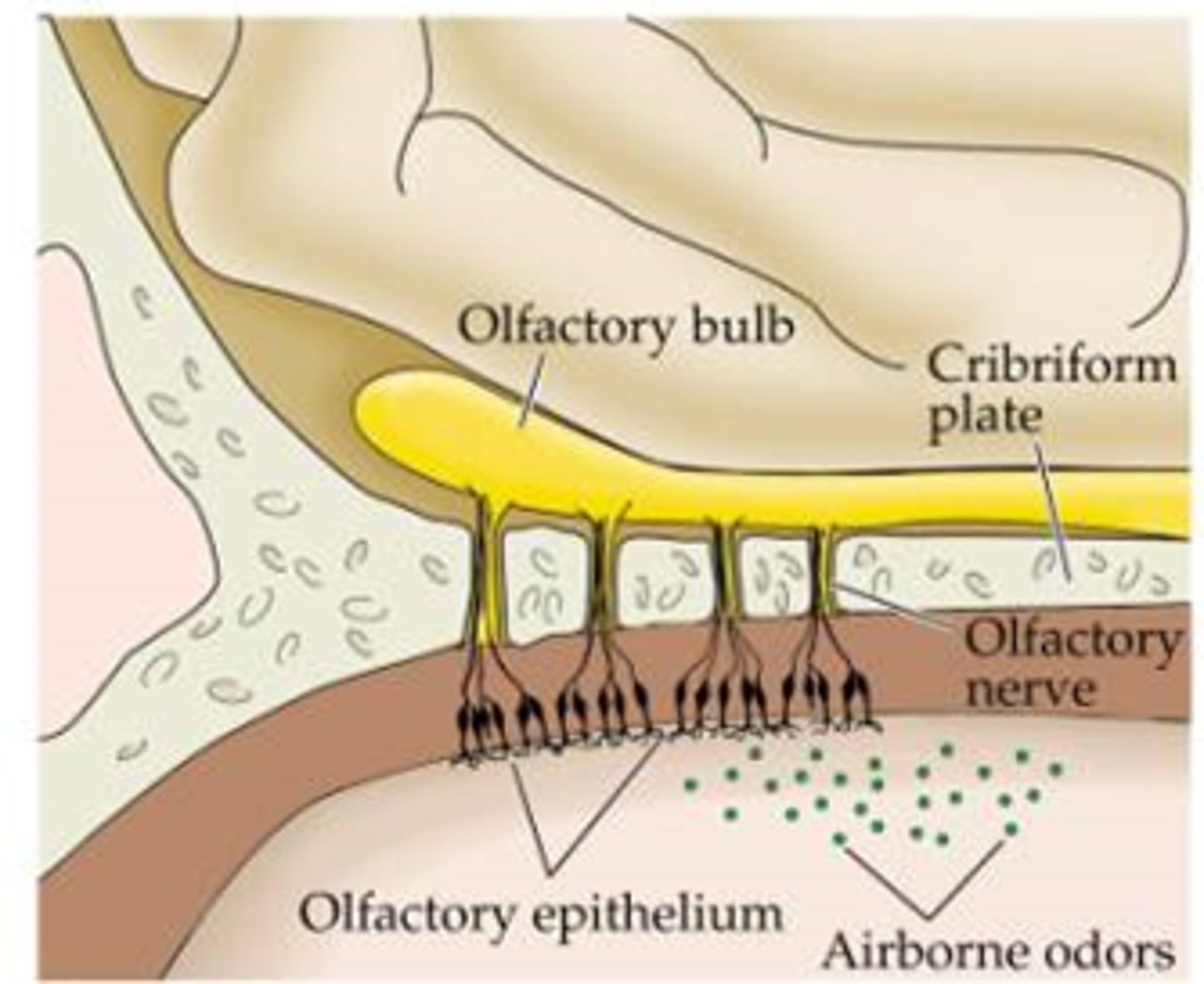
Gaseous odorant must (________) in fluid of olfactory epithelium to activate olfactory sensory neurons
dissolve
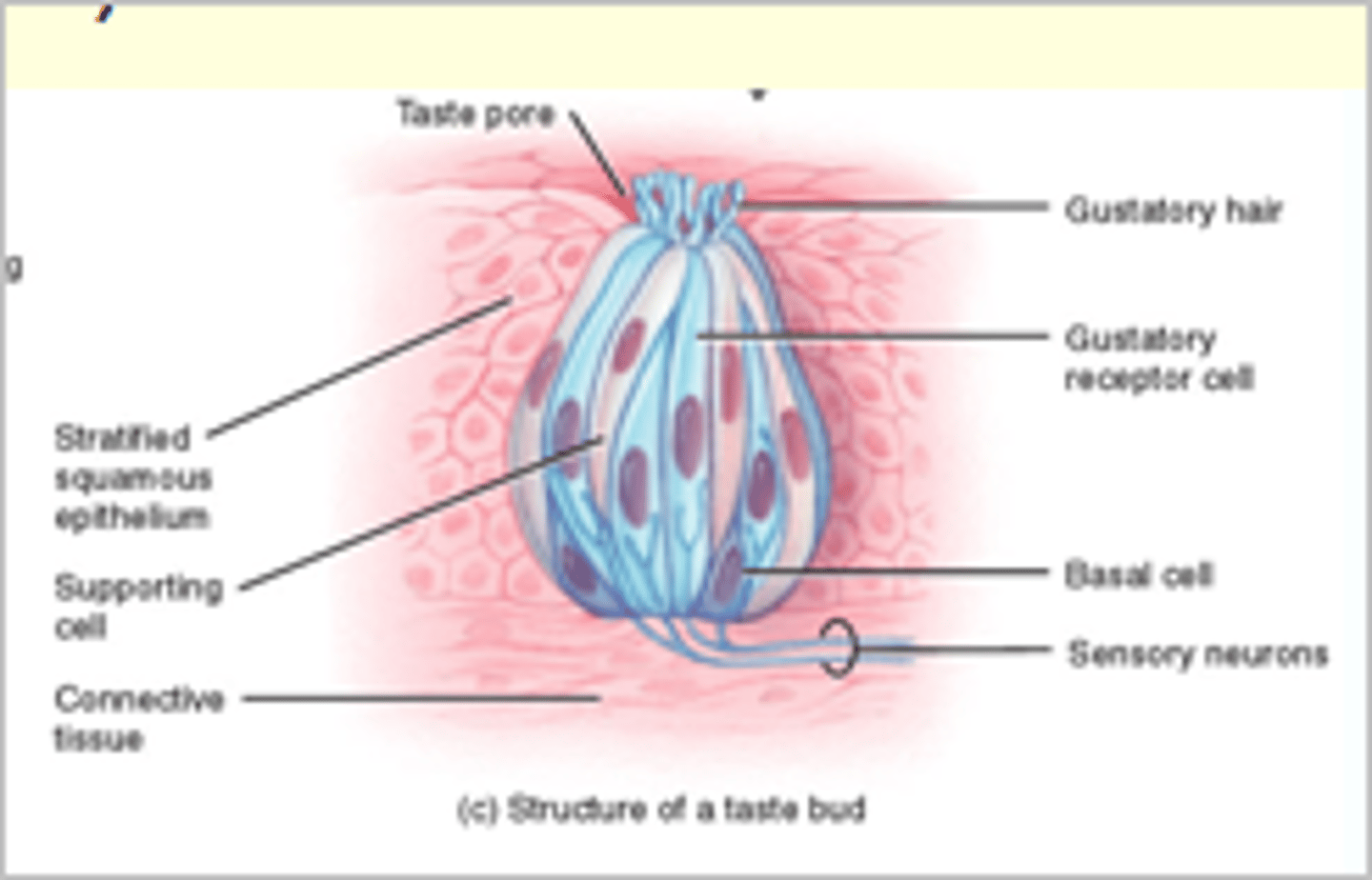
Taste Buds
Most of 10,000 are on tongue papillae.
-Gustatory Epithelial Cells: taste cells
5 Basic Taste Sensations
1. Sweet: sugars, alcohol, some amino acids, some lead salts
2. Sour: hydrogen ions in solution
3. Salty: metal ions
4. Bitter: alkaloids just as quinine and nicotine
5. Umami: amino acids glutamate and aspartate
To taste, chemicals must
Be dissolved in saliva, diffuse into taste pore, contact gustatory hairs
Binding of food chemical depolarizes taste cell membrane >>
neurotransmitter release >> different thresholds for activation (bitter most sensitive)
3 Major Areas of Ear
1. External Ear - hearing only
2. Middle Ear (tympanic cavity) - hearing only
3. Inner ear - hearing and equilibrium
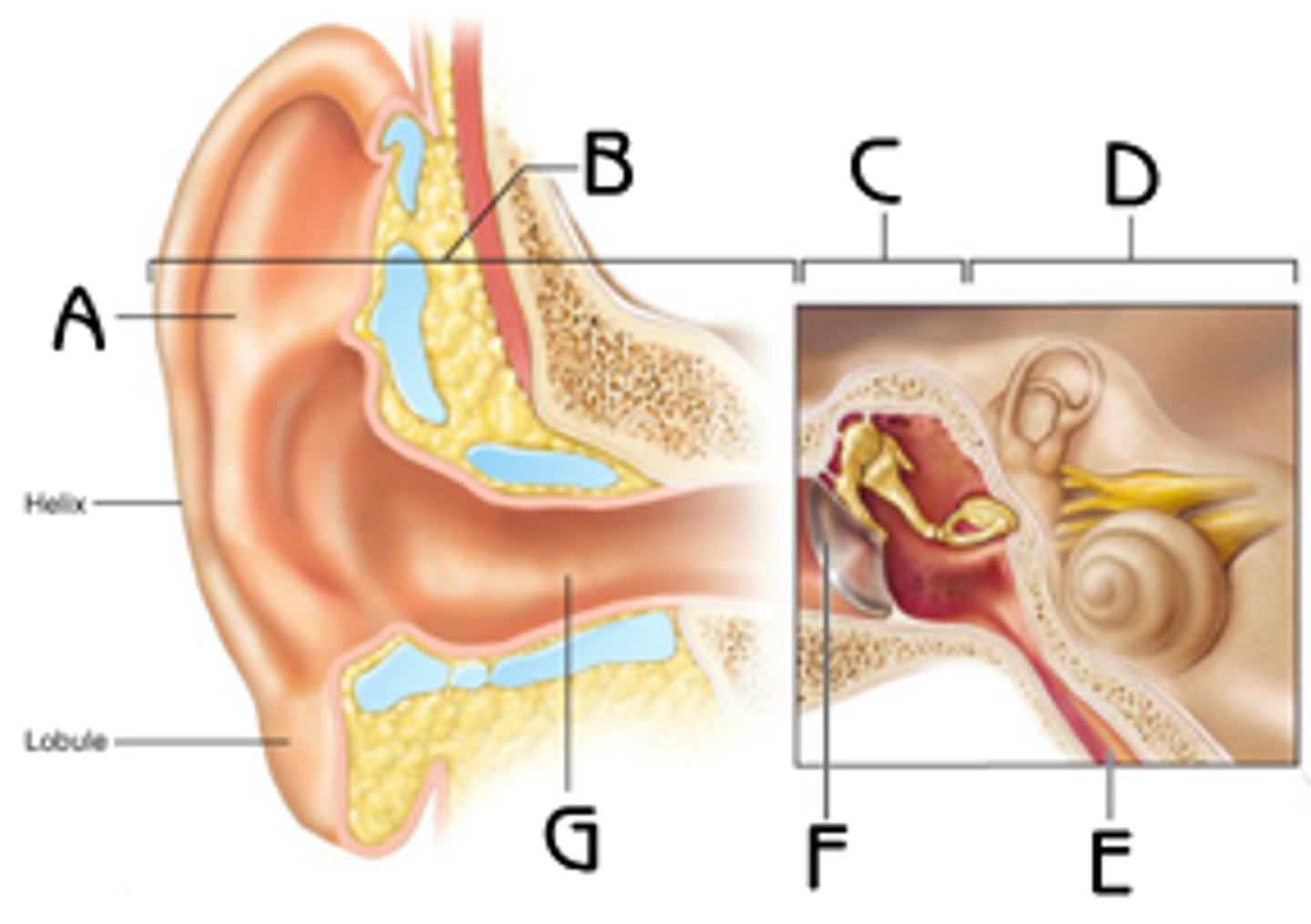
Auricle (Pinna)
External ear, funnels sound waves into auditory canal.
External Acoustic Meatus
External ear, auditory canal. Transmits sound waves to the eardrum
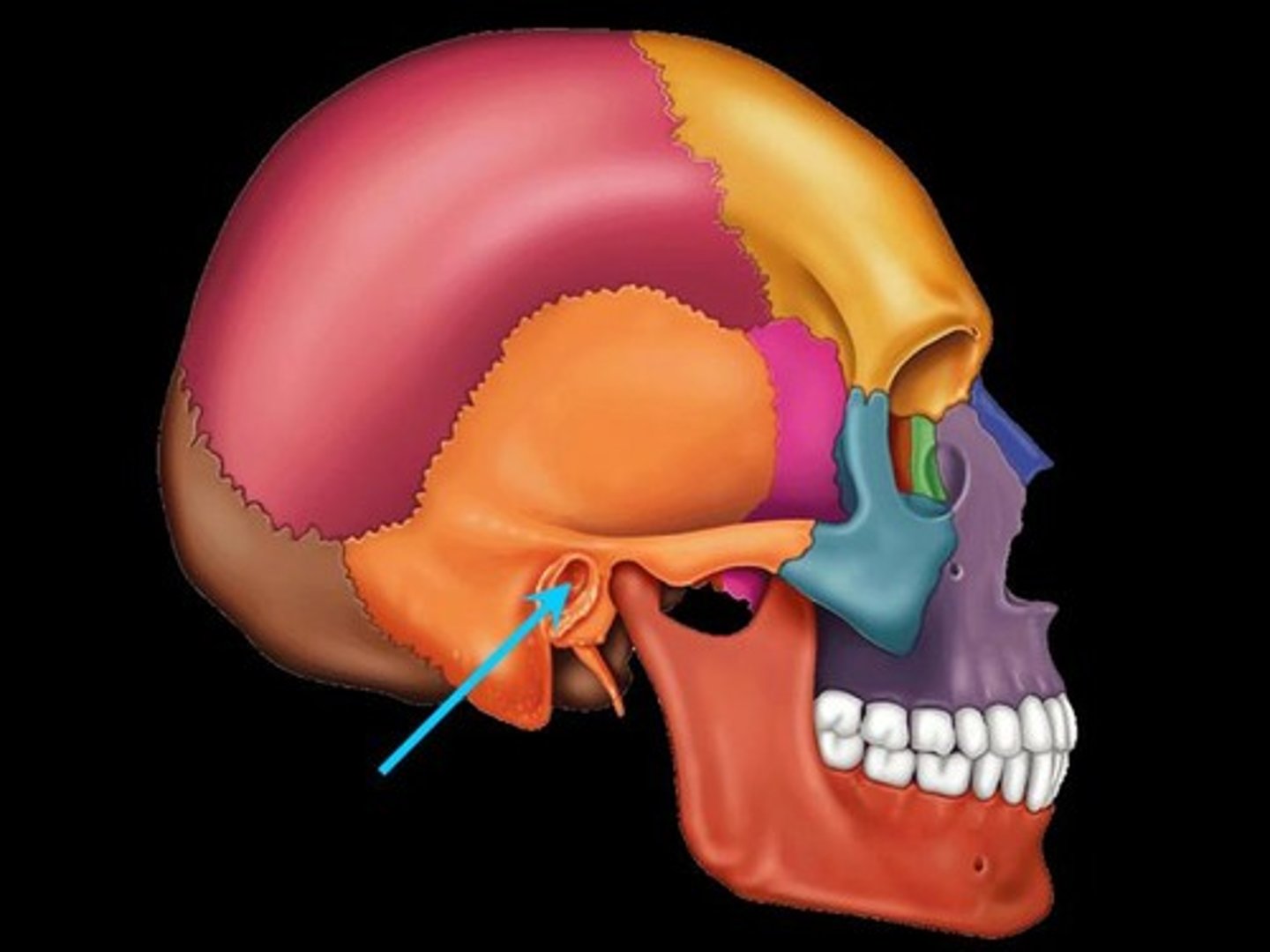
Tympanic Membrane
Eardrum - external ear
Boundary b/w external and middle ears. Transfers sound energy to bones of middle ear.
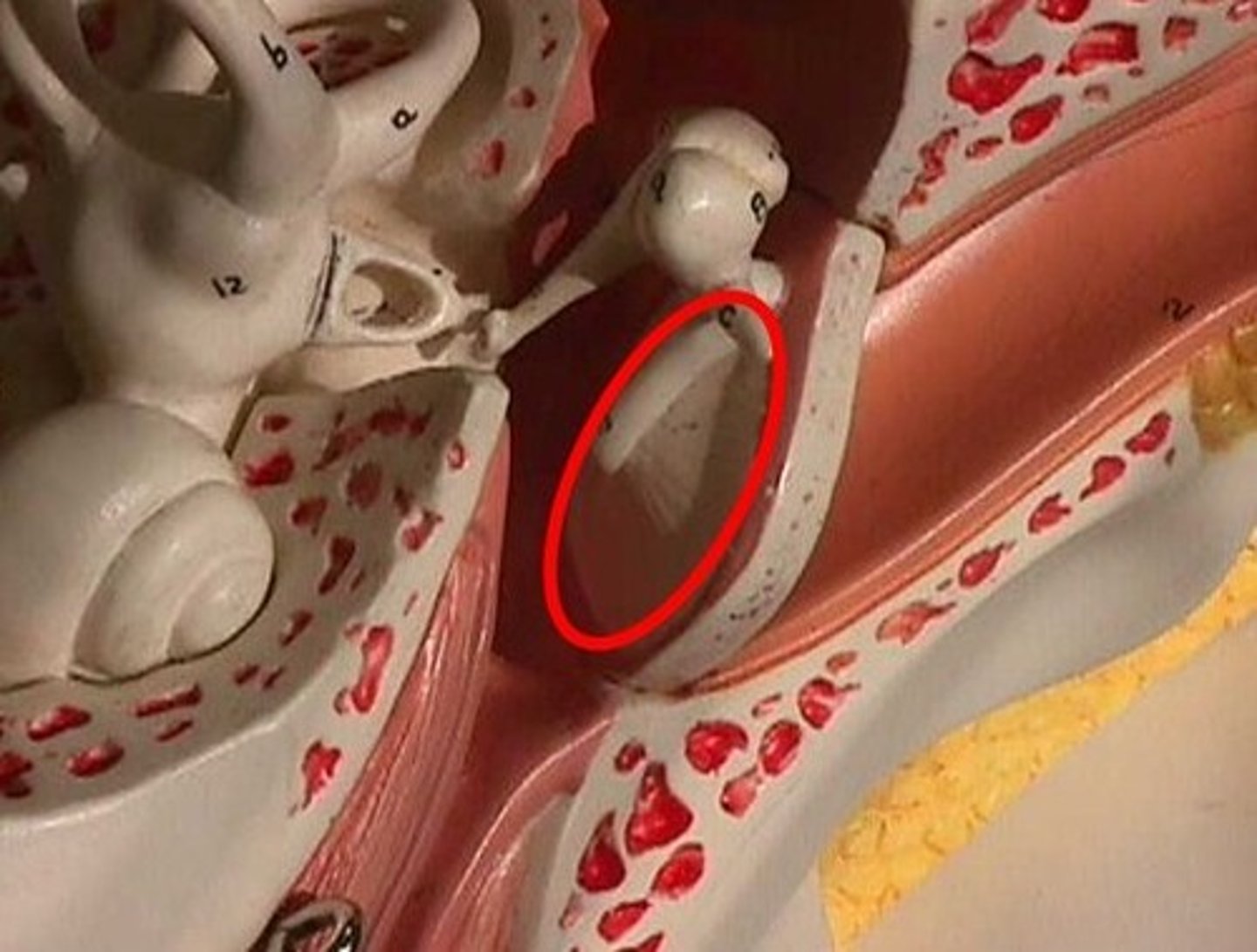
Middle Ear
Tympanic Cavity - a small, air-filled mucosa-lined cavity in temporal bone.
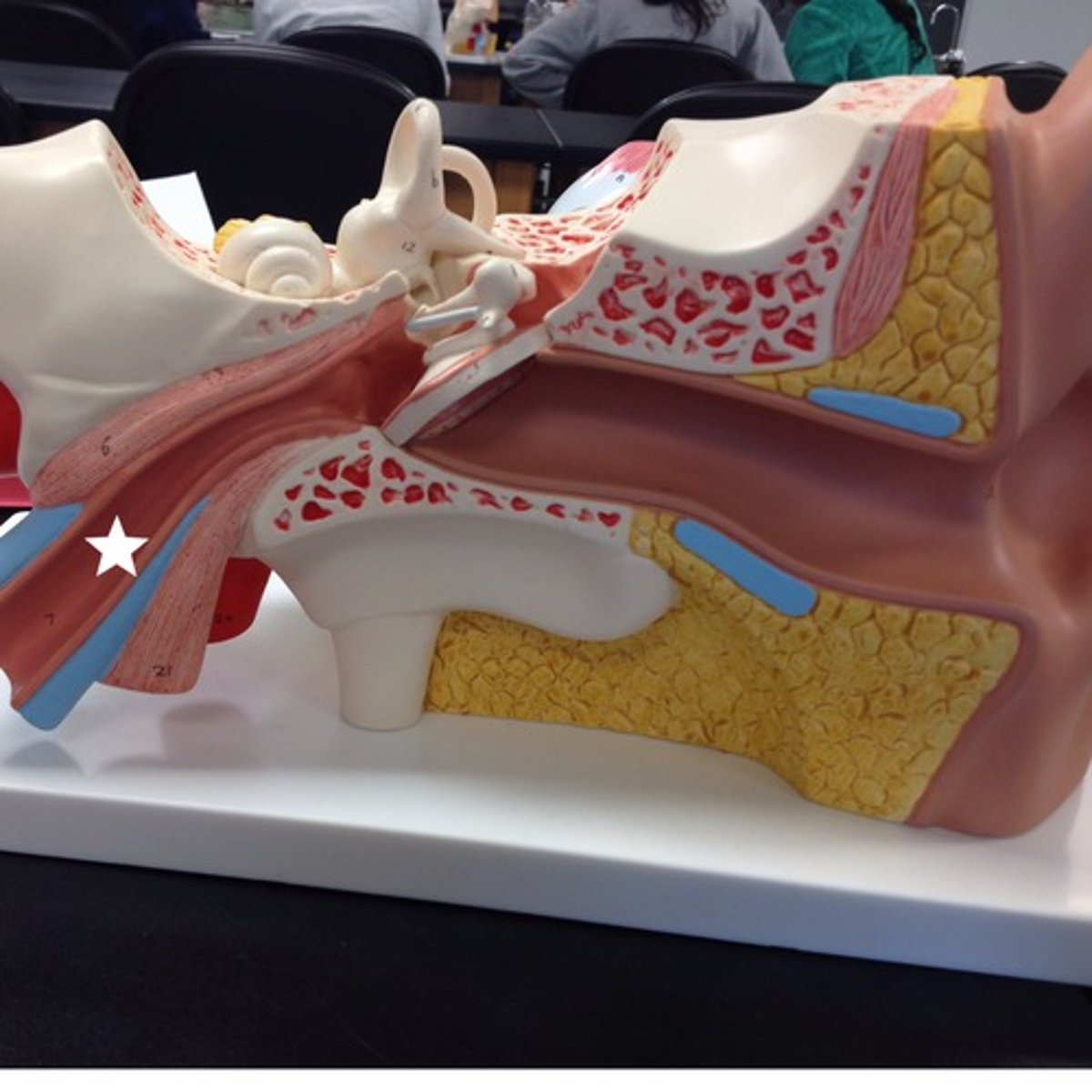
Pharyngotympanic Tube
Auditory tube, connects middle ear to nasopharynx. Equalizes pressure in middle ear cavity with external air pressure
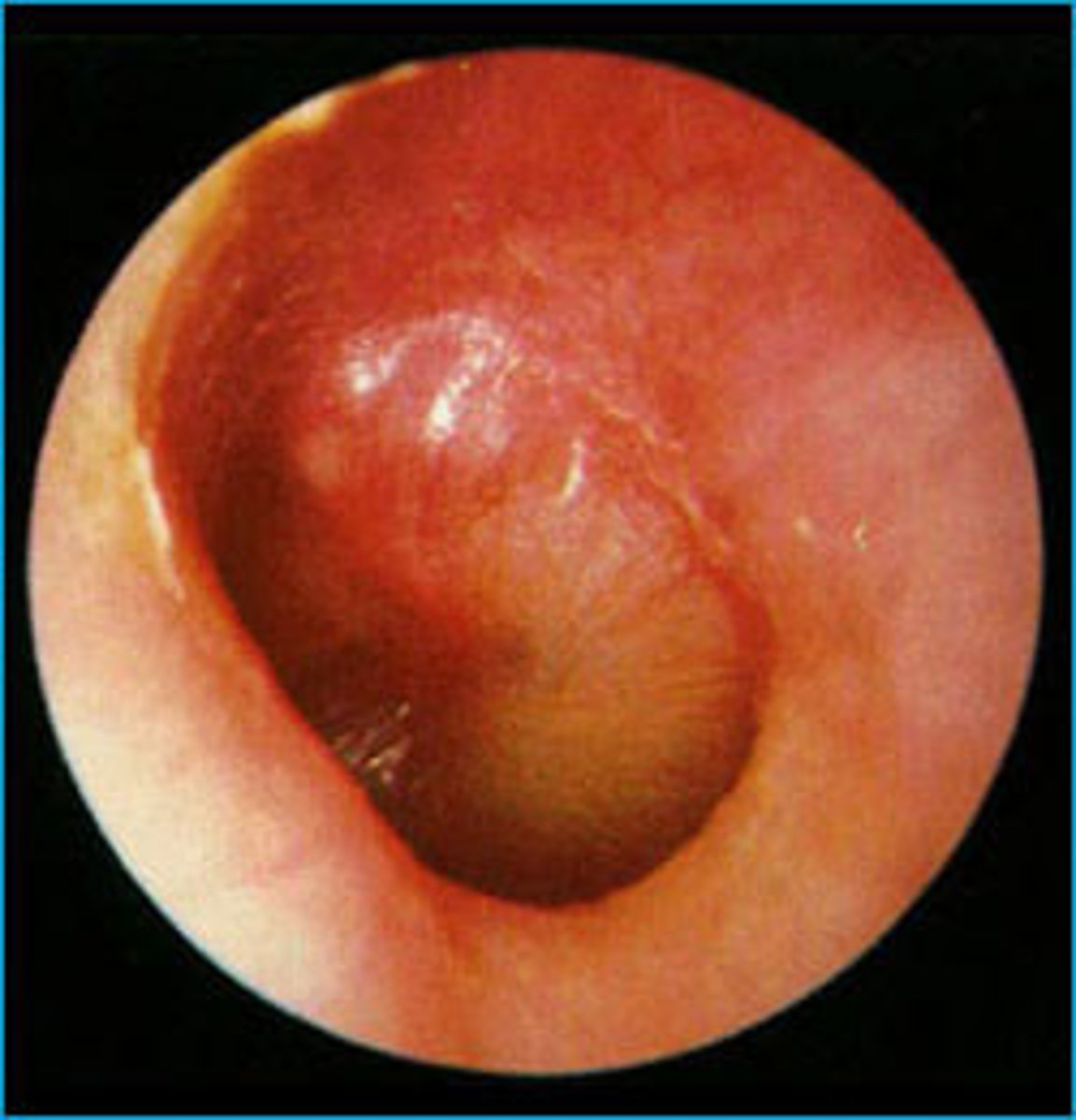
Otitis Media
Middle ear inflammation - especially in children. Most frequent cause of hearing loss in children
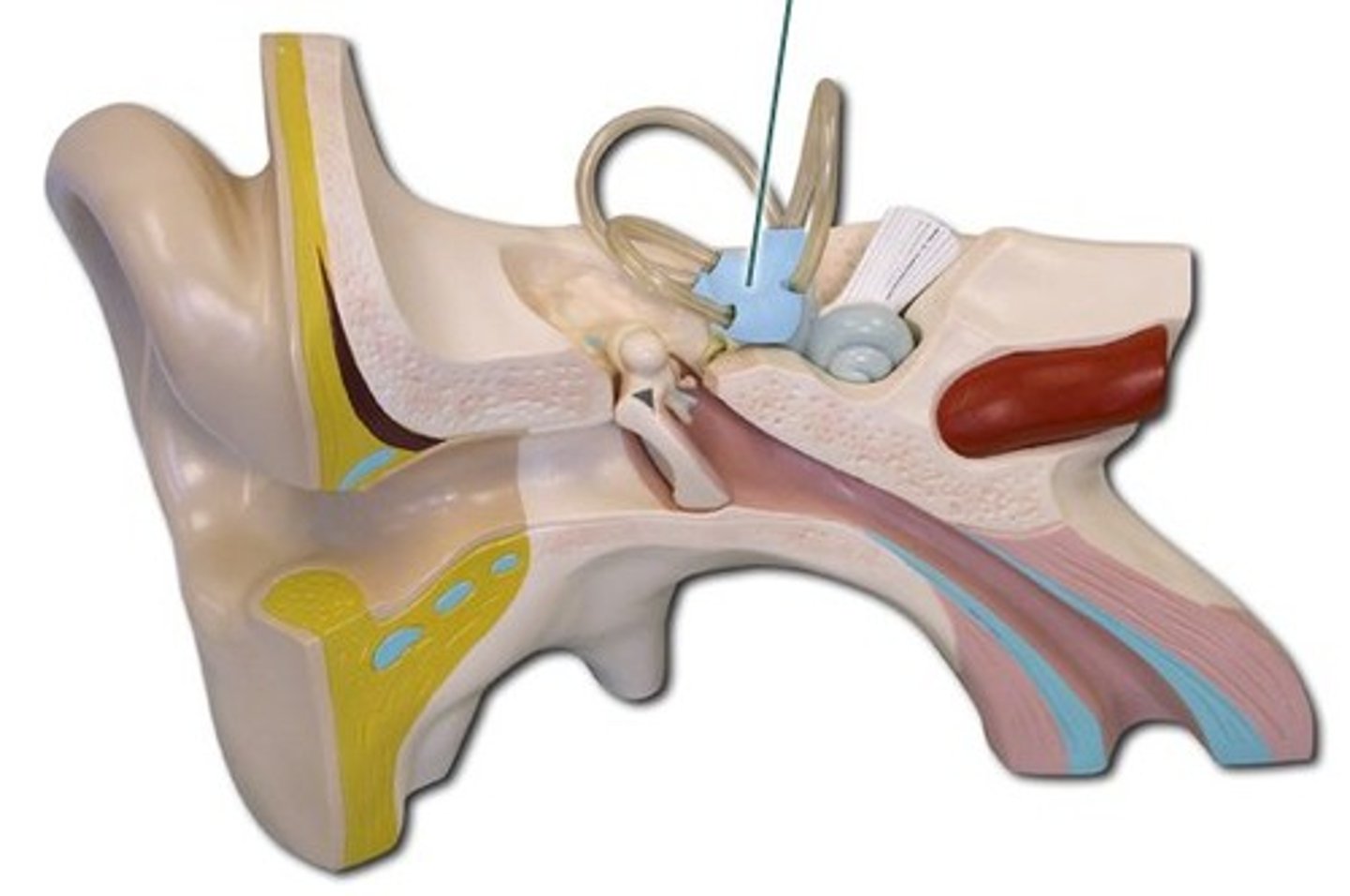
Ear Ossicles
Three small bones in tympanic cavity: malleus, incus, stapes
-Transmit vibratory motion of eardrum to oval window
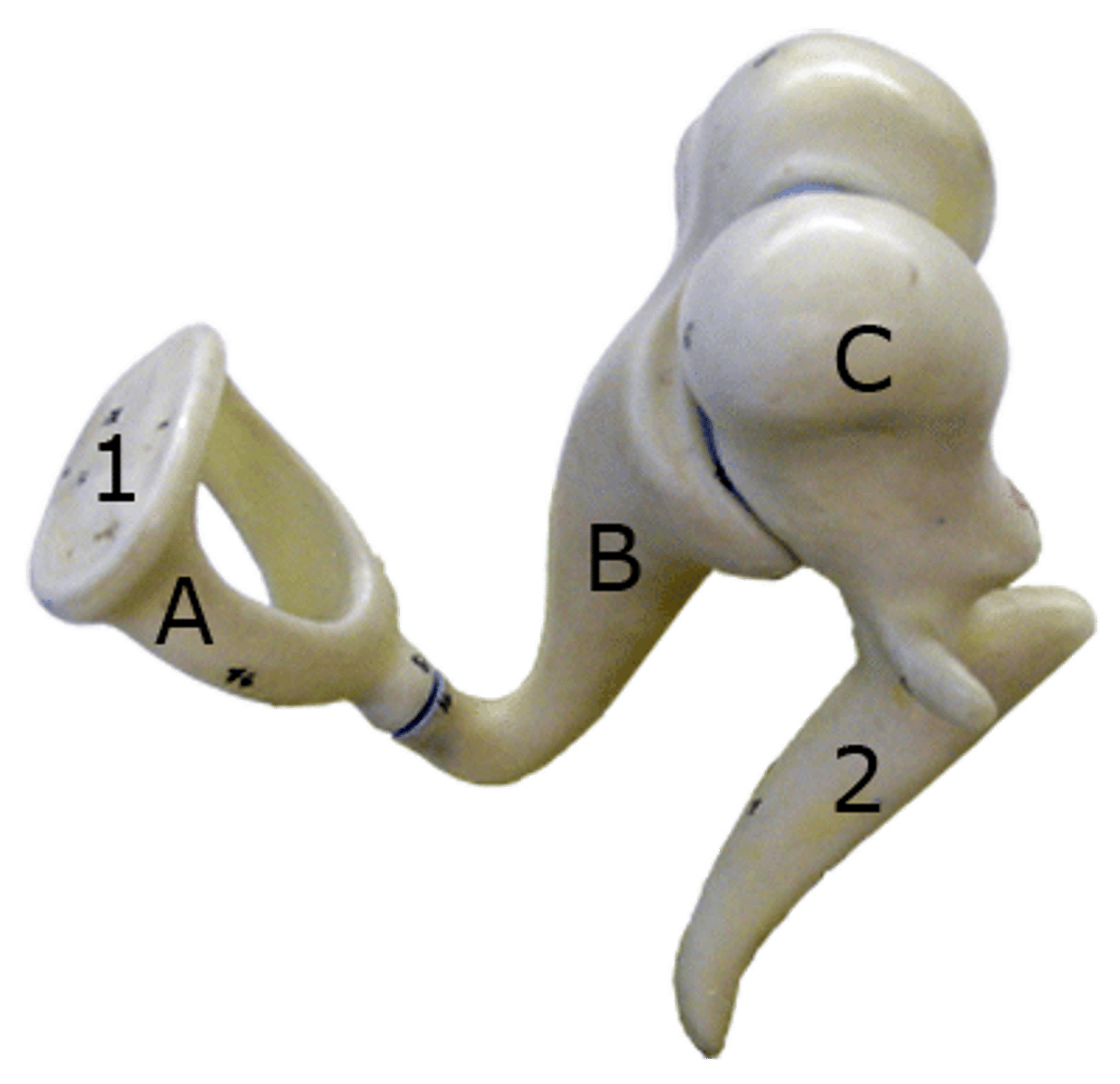
Vestibule
Contains 2 membranous sacs that house equilibrium receptor regions and respond to gravity changes in position of head
Semicircular Canals
Membranous semicircular ducts line that contain Crista Ampullaris (ampulara) which are equilibrium receptors for rotational motion
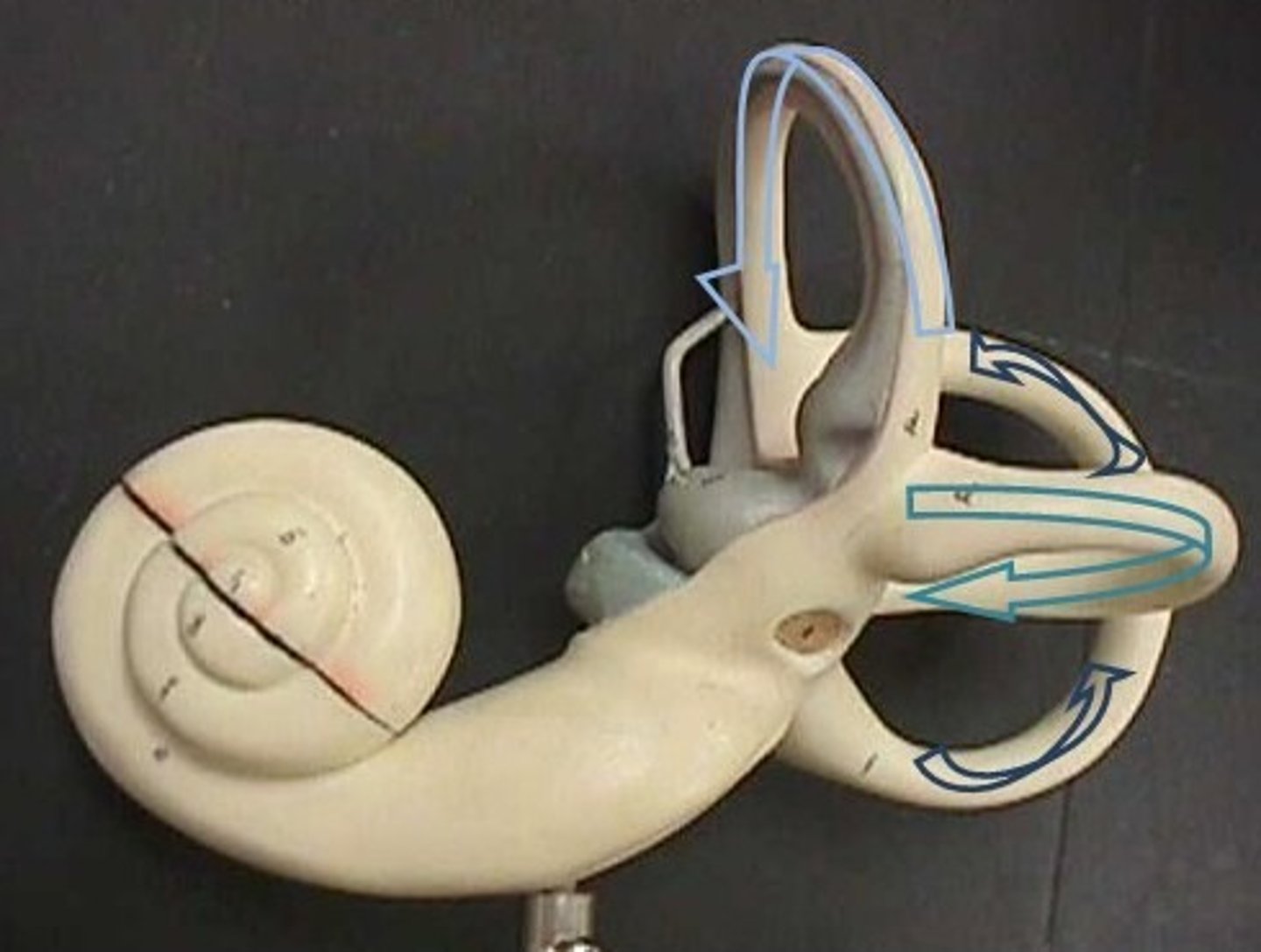
Cochlea
the snail-shaped tube (in the inner ear coiled around the modiolus) where sound vibrations are converted into nerve impulses by the Organ of Corti
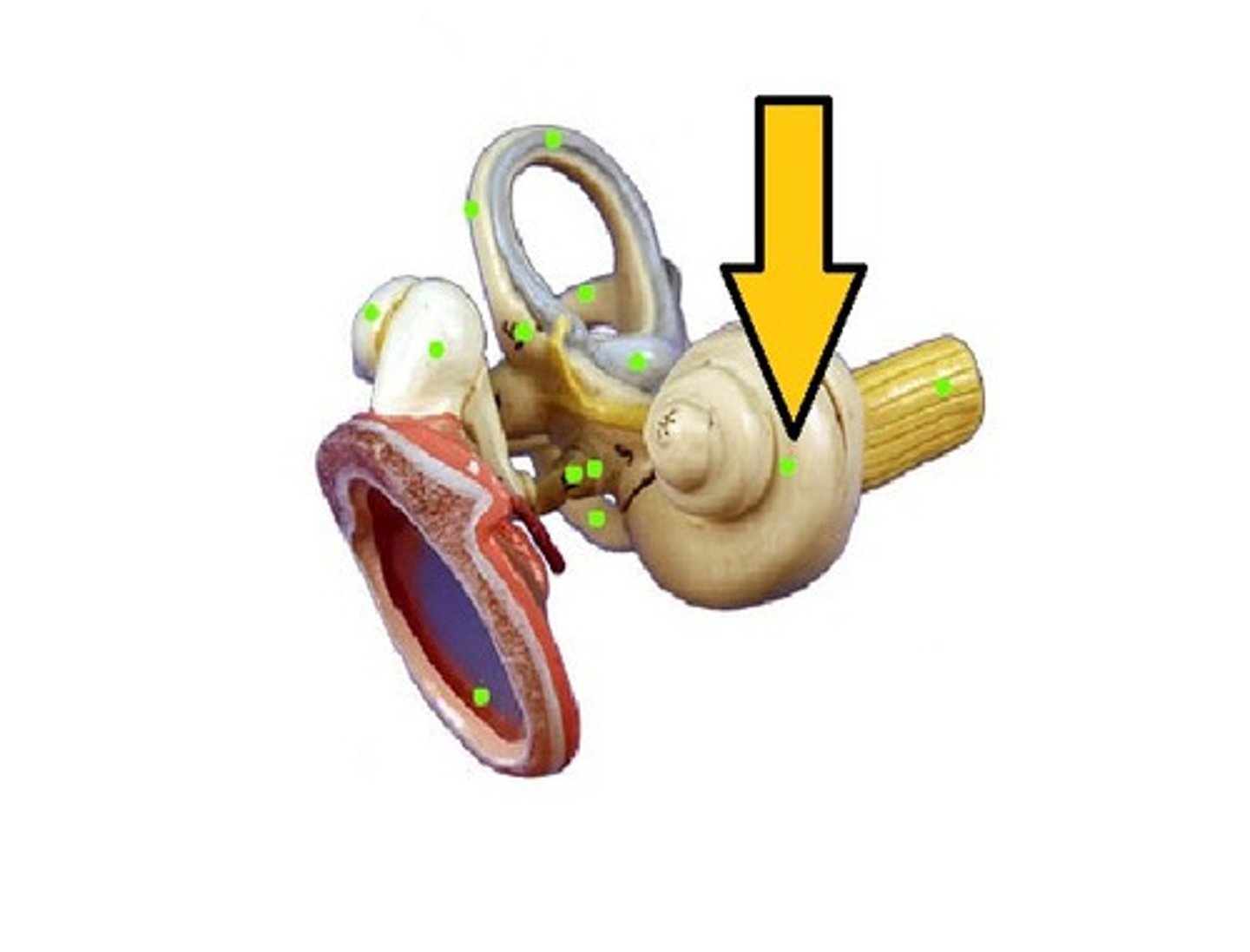
Transmission of Sound to the Inner Ear
Vibrate tympanic membrane > ossicles vibrate & amplify pressure at oval window > cochlear fluid set into wave motion > pressure waves move through perilymph > waves w/ frequencies below threshold of hearing travel to round window > sounds in hearing range go through cochlear duct, vibrating basilar membrane at specific location according to frequency of sound
Resonance of Basilar Membrane
Fibers near oval window short and stiff (high frequency), fibers near cochlea longer, more floppy (low frequency)
Vestibular Apparatus
Equilibrium receptors in semicircular canals and vestibule, monitor static equilibrium, semicircular canal receptors monitor dynamic equilibrium