Ortho Review
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
NSAID side effects
1. GI: ulcers
2. Kidney probs
cant take if on anticoagulants
arthroscopy vs arthroplasty
Scopy: holes made to clean out debris/do surgery/look into the joint
Plasty: replacement
Planks are an example of what type of exercise
Isometric (contraction without movement)o
Bench press and squats are and example of what type of exercise
Isotonic (mechanical resistance applied as muscle moves through ROM)
Muscle contraction at a constant rate of speed
Isokinetic
DVT risk
Virchows triad
-stasis
-hypercoaguable
-endothelial injury
DVT presentation
-unilateral leg swelling
-leg pain
-low grade fever
-positive homans sign
MRI vs CT uses
MRI: soft tissue
CT: bone
General anesthesia vs nerve block
general anesthesia: major surgeries, prolonged sedation and recovery
Nerve block: UE and LE, just blocks the sensory nerve pain
Aspiration: Clear to pale yellow with <200 WBC
Normal
Aspiration: deeper yellow, transparent with <2000 WBC
OA
Aspiration: dark yellow, cloudy with <80,000 WBC
Inflammatory
Aspiration: purulent, dense, opaque, with >50,000 WBC
Septic
Aspiratoin: red, blood tinged, opaque
Hemarthrosis
Most common bone affected in child abuse
Long bone shaft
(Then metaphysis)
Child abuse fracture presentation
-long bones
-posterior/lateral ribs
-vertebral compression fx
-multiple sites
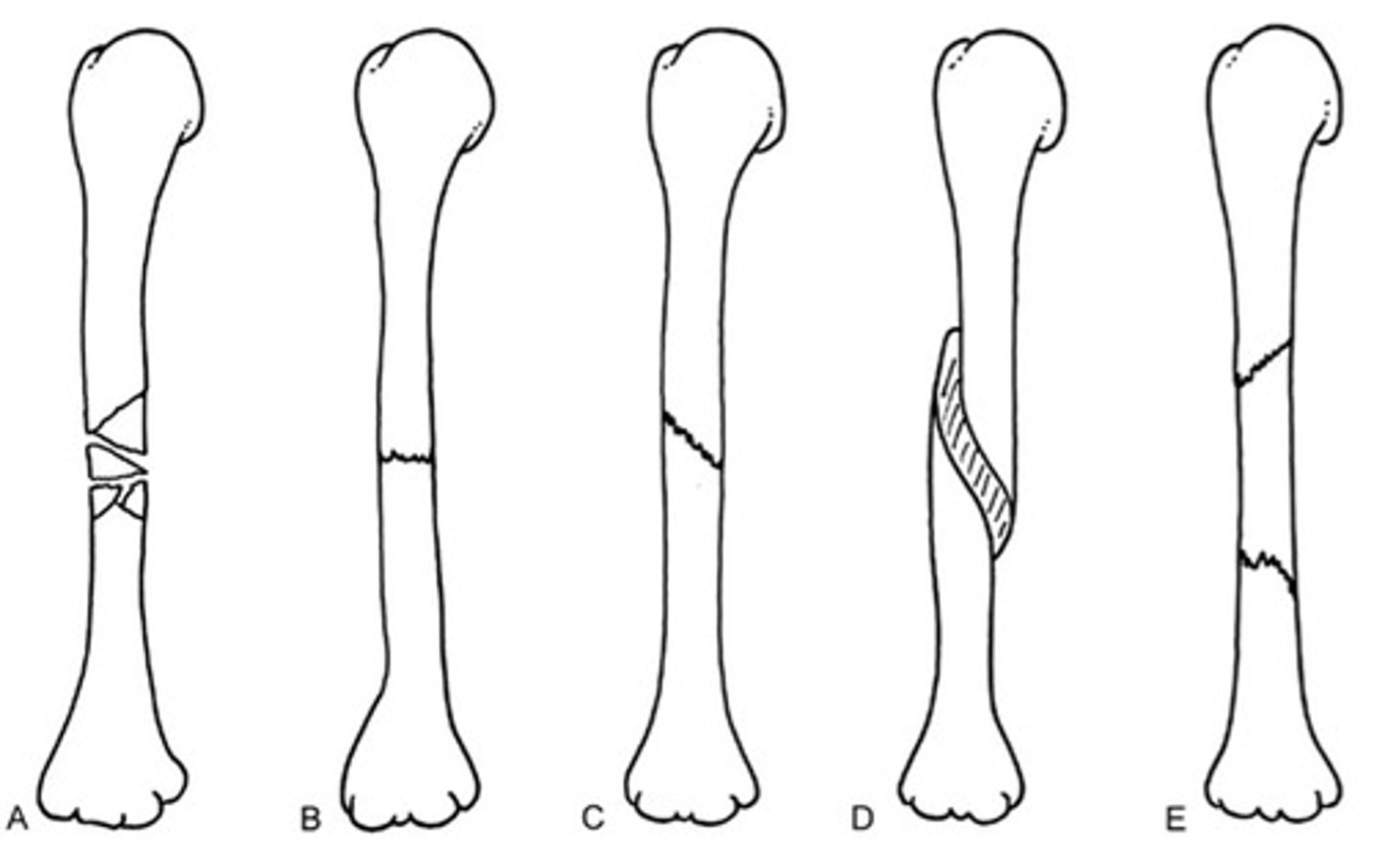
What type of Fx:
A: comminuted
B: transverse
C: oblique
D: spiral
E: segmental
Fracture through physis plate
Salter Harris I
Fracture through physis and metaphysis
Salter Harris II
Fracture through physis and epiphysis
Salter Harris III
Fracture through distal metaphysis, physis, and epiphysis
Salter Harris IV
Crush injury involving the physis
Salter Harris V
Reduction of a fracture with instrumentation through the skin
Open reduction external fixation
Reduction of a fracture reinforced with instrumentation inside the patient
ORIF
Closed reduction
Manual reduction of a fracture
3 most common primary bone tumors
Osteosarcoma (sunburst)
Ewings (onion)
Chondrosarcoma (cartilage)
where do enchondromas occur? What age group?
-hands/fingers and metaphysis of long bones
-15-40 yr old
Most common primary bone tumor
Osteosarcoma
How does an enchondroma appear on XR
Ground glass appearance
Where does osteosarcomas typically occur? In who?
Femur, tibia and humerus in teenagers (adolescents)
Appearance os osteosarcoma on XR
Sunburst
"Pain out of proportion"
CRPS/RDS
Where does CRPS occur
Distal to injury/trauma
pencil in cup deformity on XR
psoriatic arthritis
How is psoriatic arthritis differentiated from RA
DIP joint involvement, absence of nodules
How to treat psoriatic arthritis
Methotrexate
Benign bone tumor that presents in 10-30 y/o on long bones and posterior spine
Osteoid Osteoma
Osteoid Osteoma presentation
Pain at night relieved by NSAIDs
How does osteoid osteoma appears on XR
Sclerotic with small lucent nidus
Most common site of osteomyelitis
Metaphyseal end of a long bone near knee joint
Gold standard to diagnose osteomyelitis
Open biopsy and aspiration
(Need positive patho and bx)
MC pathogen causing osteomyelitis
Staph
How to treat osteomyelitis
Abx: cefazolin, clinda, vanco
MC type of arthritis
OA
MC joints affected by OA
Knees, then hips
How does OA present on XR
-Loss of joint space
-sclerosis
-subchondral cysts
-osteophytes at joint
Autoimmune disorder with inflammation of synovium causing proliferative and erosive joint changes
RA
What joints does RA affect?
-hands, wrists, knees, feet, ankles
Presentation of RA
-pain, stiffness, swelling
-DIP joints are spared
-nodules
How to diagnose RA
-Lab tests: anti-CCP, RF factor
-XR: bone erosion
Know how to differentiate OA and RA
:)
Reiter Syndrome Triad
Conjunctivitis, urethritis, arthritis
-cant see, cant pee, cant climb a tree
What is reactive arthritis triggered by?
-GI/GU infection, STD
-common in young males
Gout vs Pseudogout diagnostic features
Gout: hyperuricemia, negative birefringent urate crystals
Pseudogout: positive birefringent rhomboid crystals
Gout treatment
Indomethacin
Colchicine
Allopurinol
Types of osteoporosis
Type 1: postmenopausal
Type 2: senile (age)
What type of injury is more common in type 2 osteoporosis
Hip/Pelvic fractures
What needs to be present in a cervical XR
All 7 vertebrae
Pt presents post MVA c/o neck pain...how to differentiate herniation vs cervical sprain/strain
Herniation: neck pain with radiculopathy/paresthesias
Sprain/strain: non radicular, non focal neck pain
How to diagnose an odontoid fracture (C2)
XR: open mouth Fuchs view
How does an odontoid fracture present
Injury from forceful flexion, extension, or rotational injury
How does torticollis present?
-Tilting of head with chin rotated to opposite side
-SCM contracture causes pain/dizziness
-may or may not lump in the neck
Cervical spondylosis
DJD of cervical spine causing cervical stenosis
Caused by: bone spurs, herniations, protruding ligaments
Where are cervical degenerative changes most commonly seen
C5-6 and C6-7 disc spacing
How to manage a cervical trauma
-immobilization
-cross table lateral XR
saddle anesthesia is seen with
Cause equina syndrome
Where does the cauda equina begin?
L1-L2
How does cauda equina syndrome present?
-low back pain
-bowel/bladder incontinence
-LE weakness
-gait probs
-saddle anesthesia
How does Scheuremanns kyphosis present?
-kyphosis >40 degrees
-schmorls nodes
At what degree do you need to brace with scoliosis? Kyphosis?
Scoliosis:
25-45: brace and PT
>45: surgery
Kyphosis:
50-70 degrees: Milwaukee brace
>70: surgery
Slipping of vertebrae
Spondylolisthesis
Loosening of vertebrae
Spondylolysis
Degenerative disease of vertebrae and discs
Spondylosis
Lumbar herniated disc vs sprain stain
Same as cervical :)
Brown sequard syndrome
Hemisection of the spinal cord d/t trauma that causes:
-Loss of Ipsilateral motor function, proprioception, and light touch sensation
-loss of contralateral pain and temp
Anterior hip dislocation presentation
abducted, externally rotated, flexed
XR: femur head is larger
Posterior hip dislocation presentation
adducted, internal rotation, flexed
XR: femoral head is smaller
MOST COMMON
Know these hip fractures:
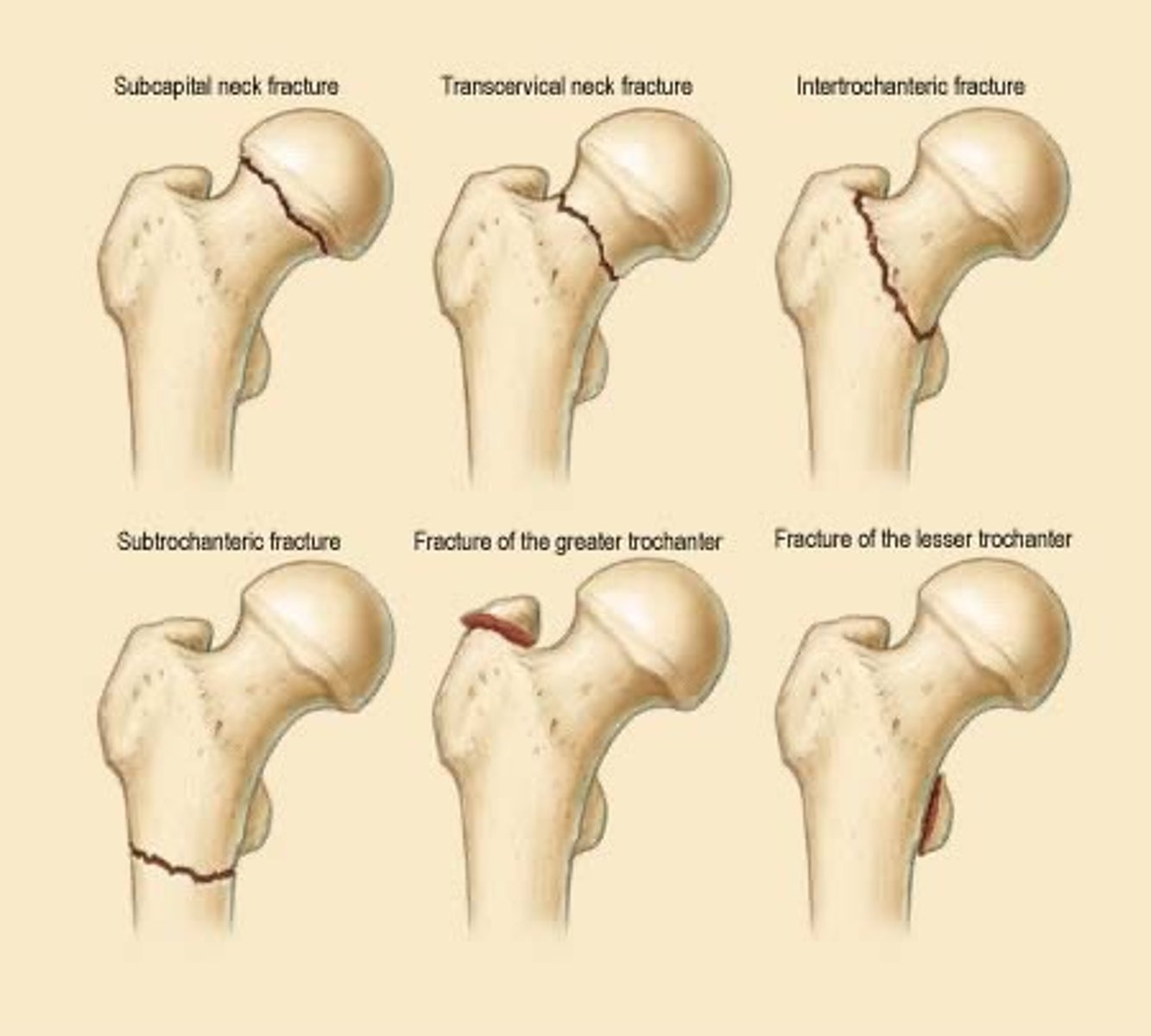
intracapsular vs extracapsular hip fractures
Intracapsular = femoral neck
Extracapsular = intertrochanteric
Causes of avascular necrosis
-trauma/fracture
-etoh
-steroids
Progressive displacement of upper femur in relation to capital femoral epiphysis
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
How does SCFE present on XR
"Ice cream fall of cone"
Klines lines (no epiphyseal intersection)
Pistol grip (chronic)
How does SCFE present?
-groin pain
-Dec internal rotation
- POS trendelenburg
-antalgic gait
Legg calve perthes disease involves a complete block of what?
Capital femoral epiphysis blood supply
How does legg calve perthes disease present?
-limp
-POS trendelenburg
-atrophy of thigh, calf, butt
-leg length inequality
Diagnostic testing for legg calve perthes disease
XR: frog view
MRI