Chemistry Autmn2/Spr1Y7
There are 3 states of matter: solids, liquids and gases
Examples of solids include wood and metal
Examples of liquids include water and apple juice
Examples of gases include oxygen and carbon dioxide
Each state of matter has different properties and are represented differently in diagrams.
Drawing of the states of matter:
In a particle diagram a particle/molecule is represented by a circle - the circles are the same size and colour unless to distinguish between different materials. Try not to overlap any particles.
The drawings do say a lot about the particle properties themselves
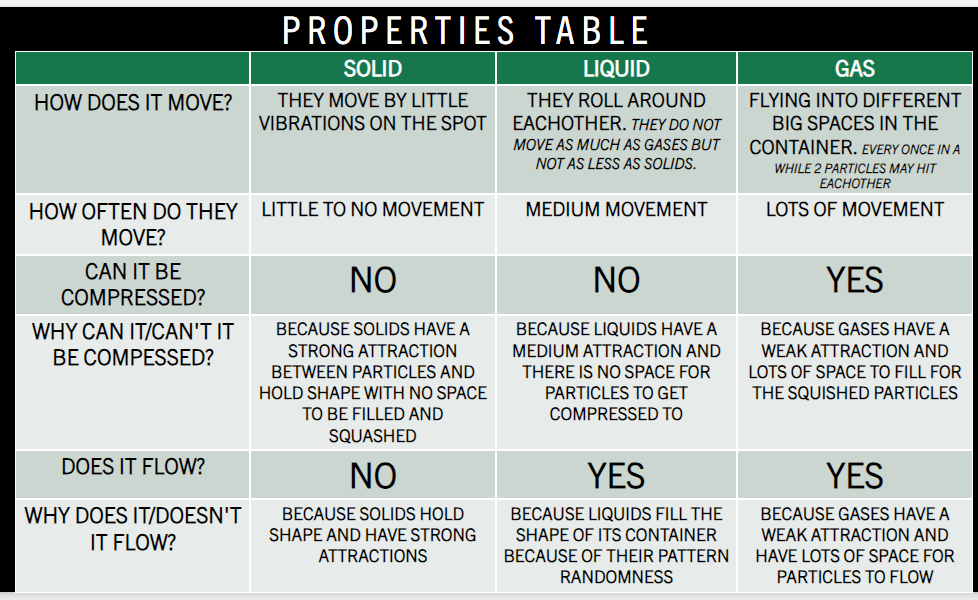
Solids are drawn in arranged rows and columns in a regular pattern with particles being very close and touching.
Liquids are drawn as a random shape as liquids will flow but all the particles must be touching.
Gases are drawn as a random shape with random patterns and will not touch. (there could be one anomaly touching but because the 99% of others are not touching it will be distinguishable as a gas)
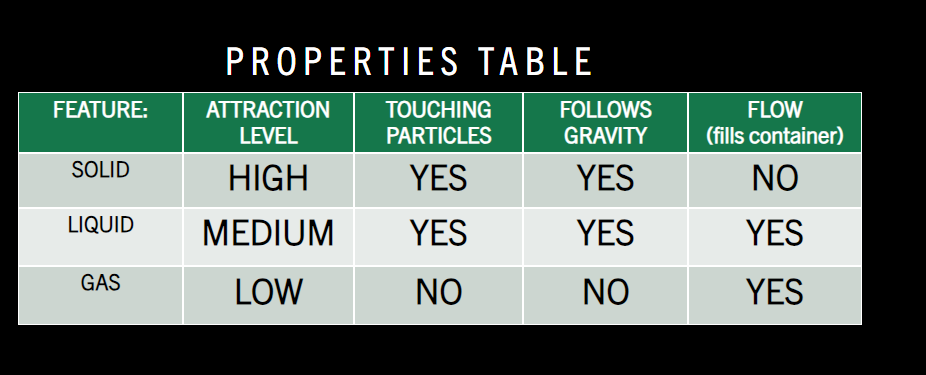
The particles for a solid have a strong attraction are touching and in organised rows and columns in a regular pattern and holds shape (which means there will be limited space in between particles and the container) and does not flow and fill said container.
The particles for a liquid have a medium attraction are touching but in a random form and follows gravity. It also takes the shape of its container which means it does flow!
The particles for a gas do not touch are random and do not follow gravity but it does flow and they are high energy and move around a lot. They have a weak attraction between particles as nothing holds them in the model. It is not showed in the model but occasionally two particles will hit each other.
The characteristics of the states of matter can lead to how their properties are formed:
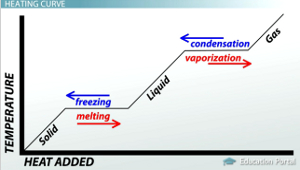
CHANGES OF STATE:
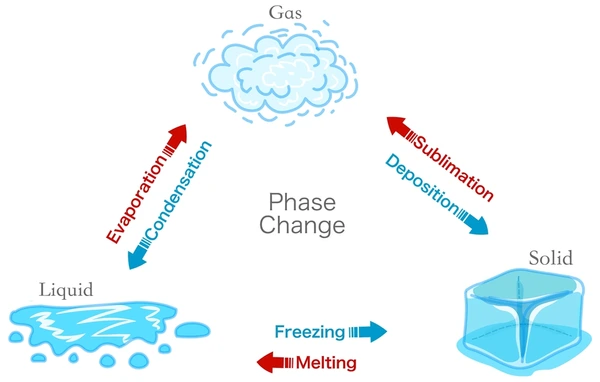
Change of state is when one state of matter turns into another by different processes.
The process that changes solids to liquids is called melting
The process that changes liquids to solids is called freezing
The process that changes liquids to gases is called boiling/evaporating
The process that changes gases to liquids is called condensation
The process that changes solids to gases is called sublimation
The process that changes gases to solids is called deposition
An example of melting would be ice cubes left over the melting point
An example of freezing would be putting water in the freezer to turn into ice
An example of boiling would be putting water into a kettle for it to turn to steam
An example of condensation would be shower windows
An example of sublimation is dry ice
An example of deposition is the chemical Iodine
The difference between boiling and evaporating is that BOILING is turning ALL the liquid into gas; EVERY PARTICLE. It MUST happen at BOILING POINT (water = 100’C) but EVAPORATING is ONLY turning the SURFACE of the liquid into gas and it can happen BELOW the BOILING POINT.
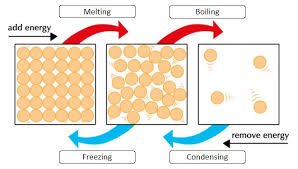
Energy levels rise with heat and energy levels go down when it turns colder as shown by the diagram above.
Helpful diagram to understand boiling points and melting points

DEFINITIONS:
MELTING POINT - The temperature at which a solid turns to a liquid (Every substance has a different melting point). The forces between the particles get weakened.
BOILING POINT - The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas (Every substance has a different boiling point). The forces between the particles get weakened.
Heating curves:
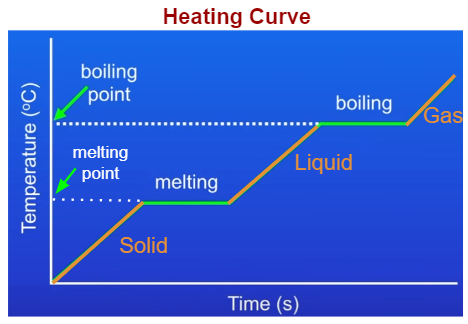
When a substance is in the process of changing state over time it will stay at the same temperature for a while and then rising/dropping temperature again because the heat is used as kinetic energy to break the bonds or strongen the bonds of particles.
DIFFUSION
Diffusion is the RANDOM movement of particles from an area of HIGH CONCETRATION to an area of LOW CONCENTRATION.
DIAGRAMS THAT REPRESENT DIFFUSION:
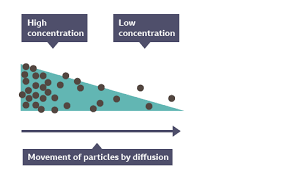
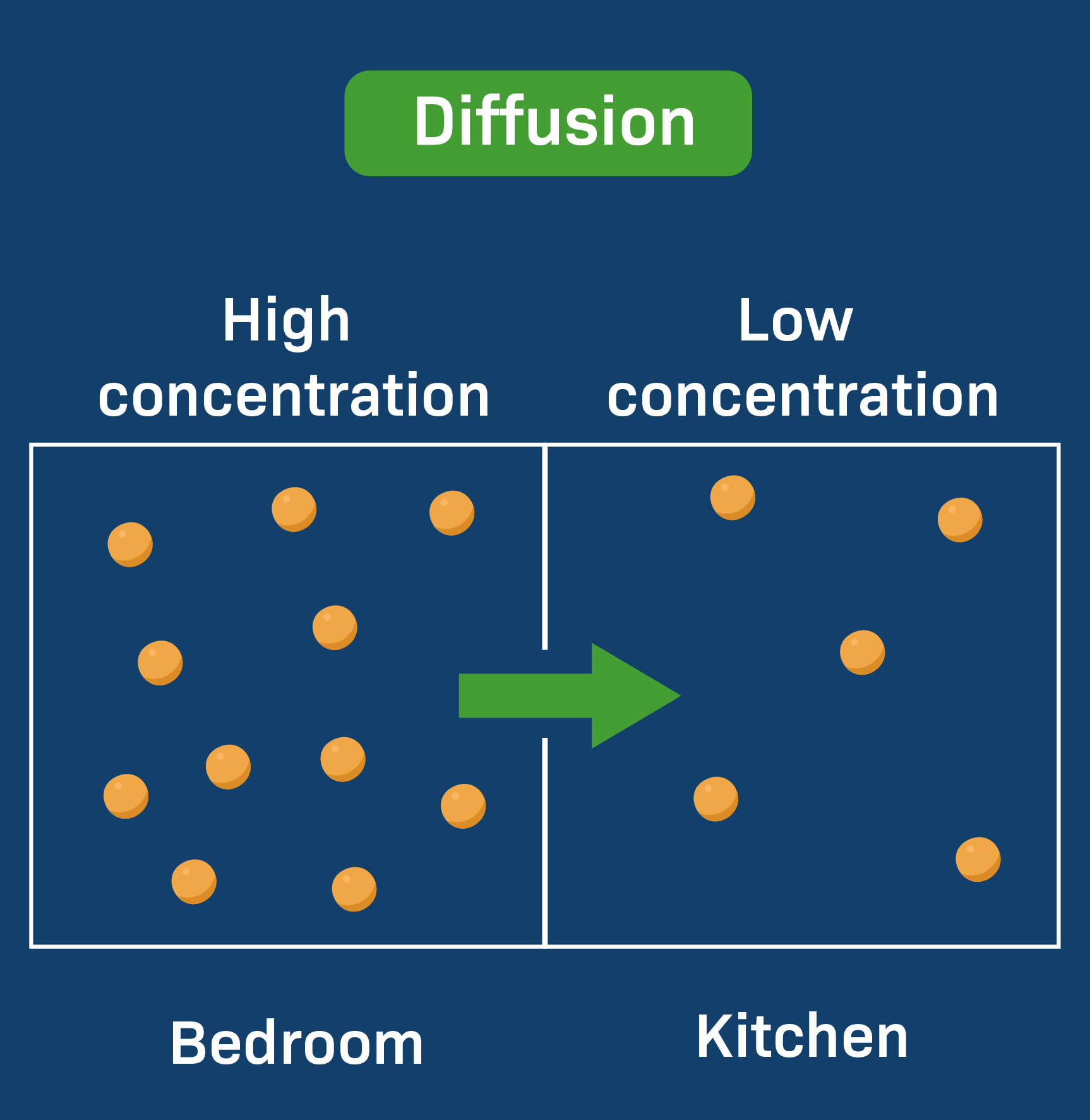
Diffusion happens in only liquids and gases as they can flow.
Gases have quicker diffusion than liquids because:
They have more energy
Gases are free and not joined together which gives more space and speed unlike liquids whom are joined with limited speed and space
Gases are already spread out after being sprayed and they do not have to follow gravity