Upper GI Disorders & Drugs - unit 7
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Mastication
Chewing of food
Pharynx
Aids in swallowing
Esophagus
Long collapsible tube that transports food to stomach
Gastroesophageal sphincter
Prevents reflux of gastric contents
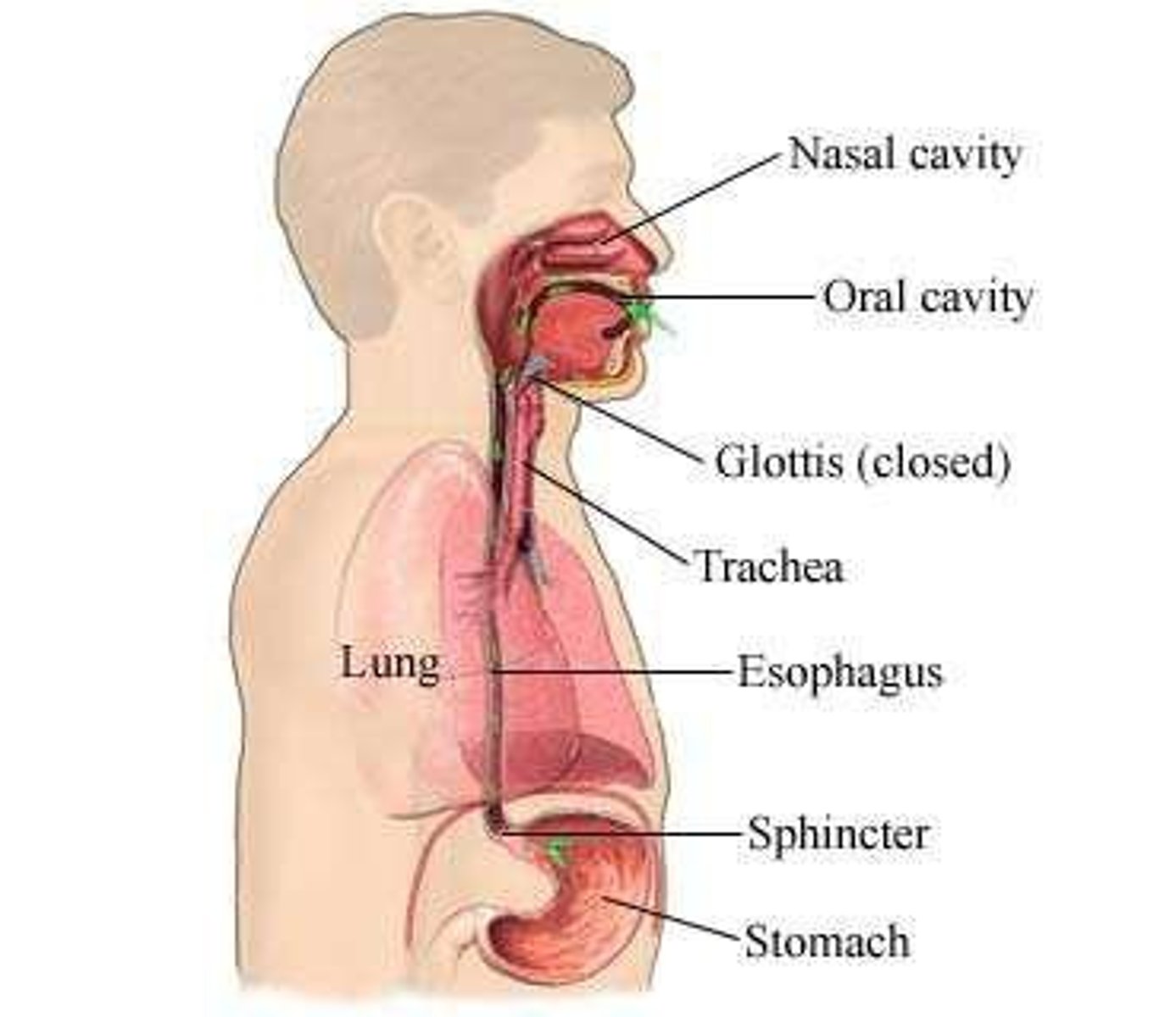
Stomach
Food reservoir where chemical breakdown of food begins
Pyloric sphincter
Controls how much food is emptied into duodenum
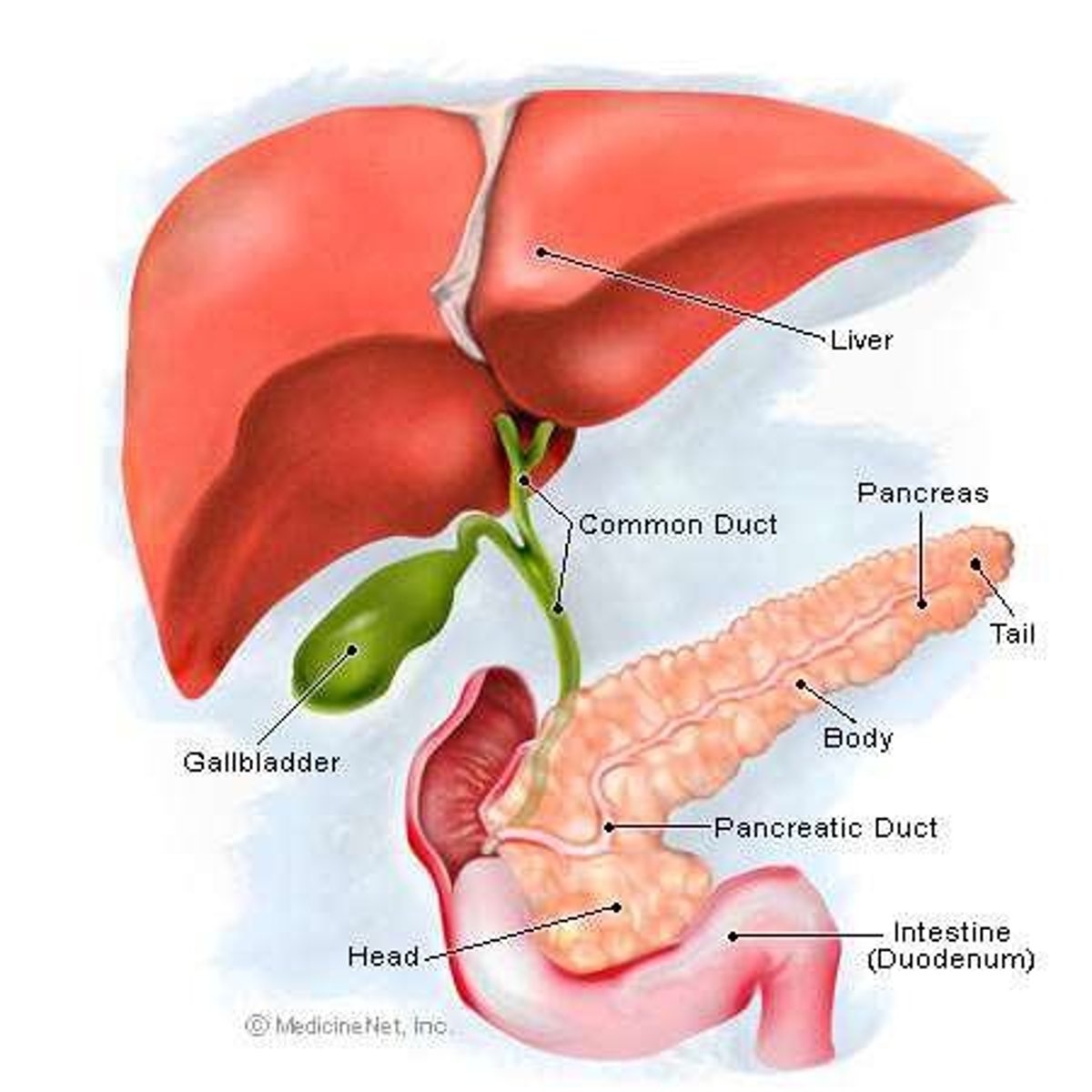
Liver
detoxes blood
Metabolizes carbohydrates, proteins, fats
produces bile
Pancreas
Produces enzymes, electrolytes, and water for digestion
regulates bg
Gall Bladder
Stores and secretes bile
-itis
Inflammation
-oscopy
Scope
-ostomy
Artificial opening
-ectomy
Surgical removal
-phagia
Eating, swallowing
-phasia
Speaking
-oma
Tumor
Cholecystectomy
Surgical removal of gall bladder
hepat
liver
gastr
stomach
cholecyst
gall bladder
colo
large intestine
recta
rectum
dys
difficulty
carcin
cancer
-lith
stone
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing
Dysphasia
Difficulty speaking
Carcinoma
Cancer tumor
Hepatitis
Inflammation of liver
Gastritis
Inflammation of stomach
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of gall bladder
Colitis
Inflammation of colon
Cholelithiasis
Gall stones
Colonoscopy
Scope of colon
Colostomy
Surgical opening of colon
Anorexia
Loss of appetite
causes of anorexia
smell
emotional factors
drugs and diseases
what is the forerunner of nausea
anorexia
Dysphagia Causes
Stroke, Brain Injury,
Esophageal Strictures or Stenosis, Esophageal tumors
Clinical Presentation of Dysphagia
Sensation of food getting stuck,
Choking, coughing,
Pocketing food in cheeks,
Delayed or exaggerated swallowing
what does nausea stimulate
Stimulates vomiting center in brain stem,
what is nausea usually accompanied by
anorexia, watery salivation, pallor,
sweating, and tachycardia.
what is vomiting
Involuntary or voluntary forceful ejection of chyme from the stomach up through the esophagus and out of the mouth
what is the medical word for vomiting
emesis
what does yellow/green colored vomit mean
bile in vomit
gi obstruction
What is hematemesis and what does it indicate?
blood in vomit - looks like coffee grounds
upper GI bleed is often indicated
Deep Brown colored emesis
indicate content from the lower intestine.
Undigested food emesis
Caused by conditions that impair gastric emptying.
Antiemetics
Medications used to prevent or treat nausea and vomiting.
what is an example of a Serotonin Antagonist
Ondansetron (Zofran)
when should we not use ondansetron
pregnancy and long QT syndrome
what are side effects of ondansetron
headache
diarrhea
dizziness
cardiac arrythmias
what is an example of a Dopamine antagonist
promethazine, prochlorperazine.
when should we not use promethazine/ prochlorperazine.
- in children and elderly
- if clients are taking other respiratory depression medications
what are side effects of promethazine/ prochlorperazine.
restlessness
anxiety
face spasms
drowsiness
hypotension
sedation
anticholinergic
respiratory depression
what is an example of a Anticholinergics
Scopolamine - helps with salavation
when should we not use Scopolamine
in patients with urinary retention/obstruction
asthma
narrow angle glaucoma
what is an example of a Antihistamine
dimenhydrinate (dramamine) - helps with motion sickness
what is an example of a Benzodiazepines
lorazepam
when should we not use lorazepam
clients with CNS depression
angle-closure glaucoma
severe hypotension
severe pain
pregnancy/ breastfeeding
what medication helps suppress chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting (CINV)
Lorazepam suppresses this condition.
Extrapyramidal Symptoms
Side effects associated with certain antiemetics.
what are two congenital defects
cleft lip and esophageal atresia
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus.
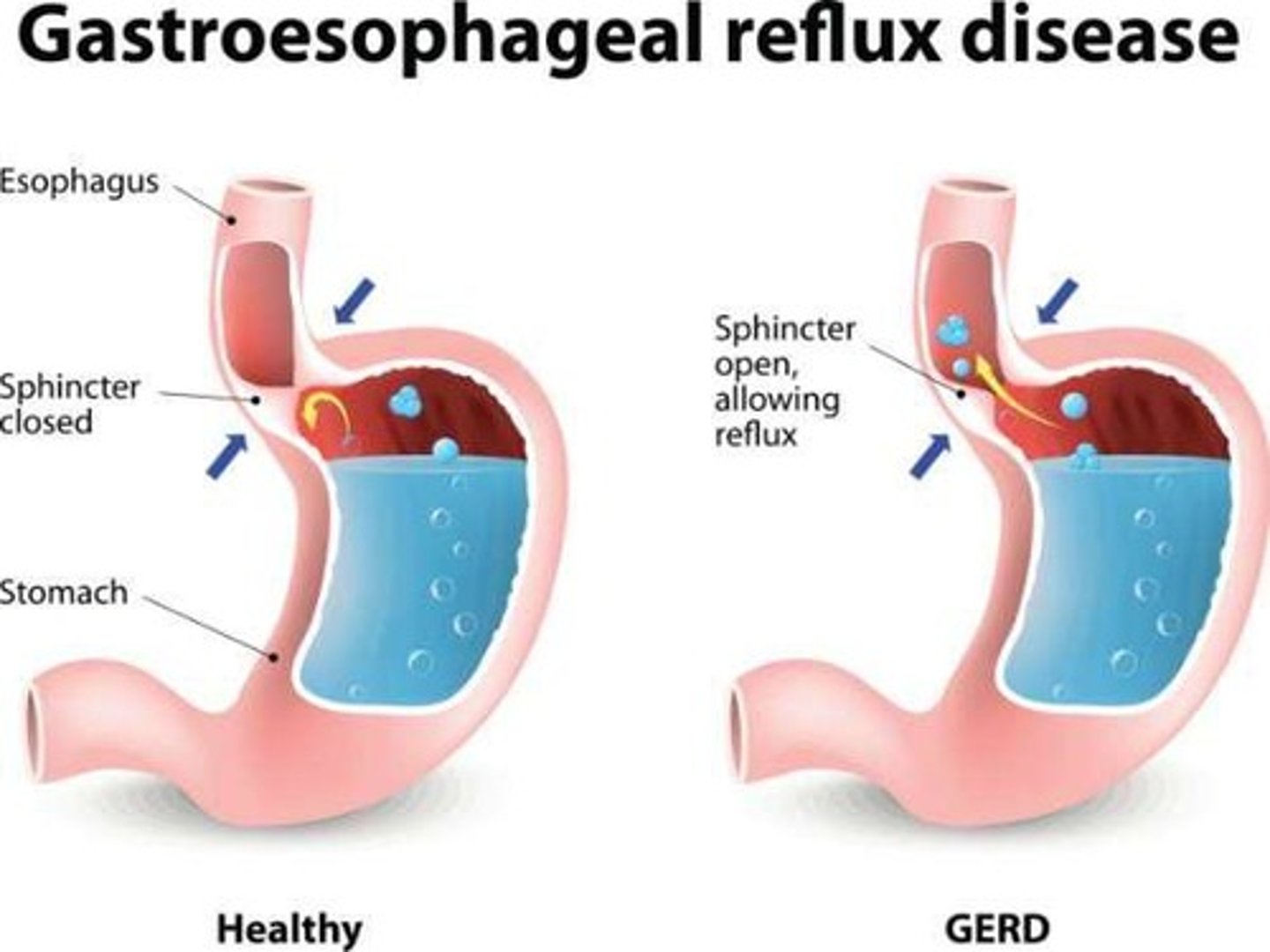
Pathophysiology of GERD
Increased abdominal pressure, weak lower esophageal sphincter, delayed gastric emptying.
Complications of GERD
Barrett's esophagus and esophageal strictures (narrowing caused by scar tissue).
Causes of GERD
Foods (acidic food, carbonated beverages, chocolate, mints), smoking, hiatal hernia, obesity, pregnancy, certain medications, lying down immediately after eating.
Clinical Manifestations of GERD in adults
Indigestion (aka heartburn), epigastric pain, dysphagia, regurgitation of food.
Clinical Manifestations of GERD in kids
Dysphagia, anorexia, irritability, sudden or inconsolable crying, feeding problems.
Hiatal Hernia
Portion of the stomach protrudes through an opening in the diaphragm.
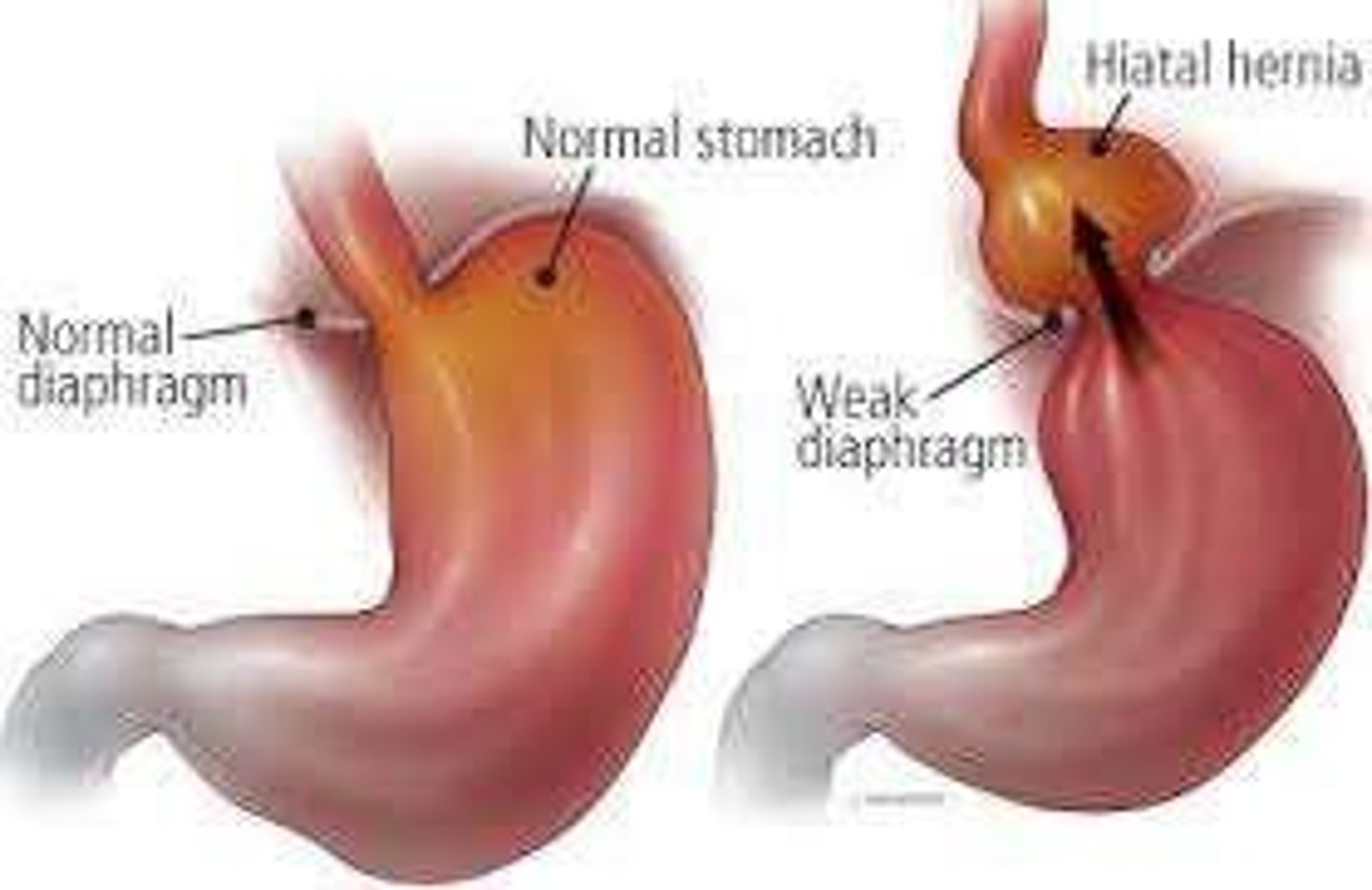
Causes of Hiatal Hernia
Weakening of diaphragm muscles, increased abdominal pressure, trauma, congenital defects.
Clinical Manifestations of Hiatal Hernia
Indigestion (heartburn), frequent belching, epigastric and/or chest pain, dysphagia.
Worsening Factors of Hiatal Hernia
Lying down, especially after eating; eating large meals; bending over; coughing.
what is a Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists
Block H2 receptors which suppress secretion of gastric acid.
what conditions do we use Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists
prevent/treat GI ulcers,GERD, heartburn
Side Effects of Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists
CNS effects (lethargy, hallucinations, confusion), constipation, N/V/D.
Examples of Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists
famotidine, cimetidine, ranitidine.
When Should We Not Use Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists?
Caution: Pregnancy, Elderly, COPD, KF.
Nursing Implications for Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists
Stop smoking; avoid smoking after last dose of day; don't take with antacid.
what is a Proton Pump Inhibitor
Blocks basal and stimulated acid production and reduces gastric acid secretion.
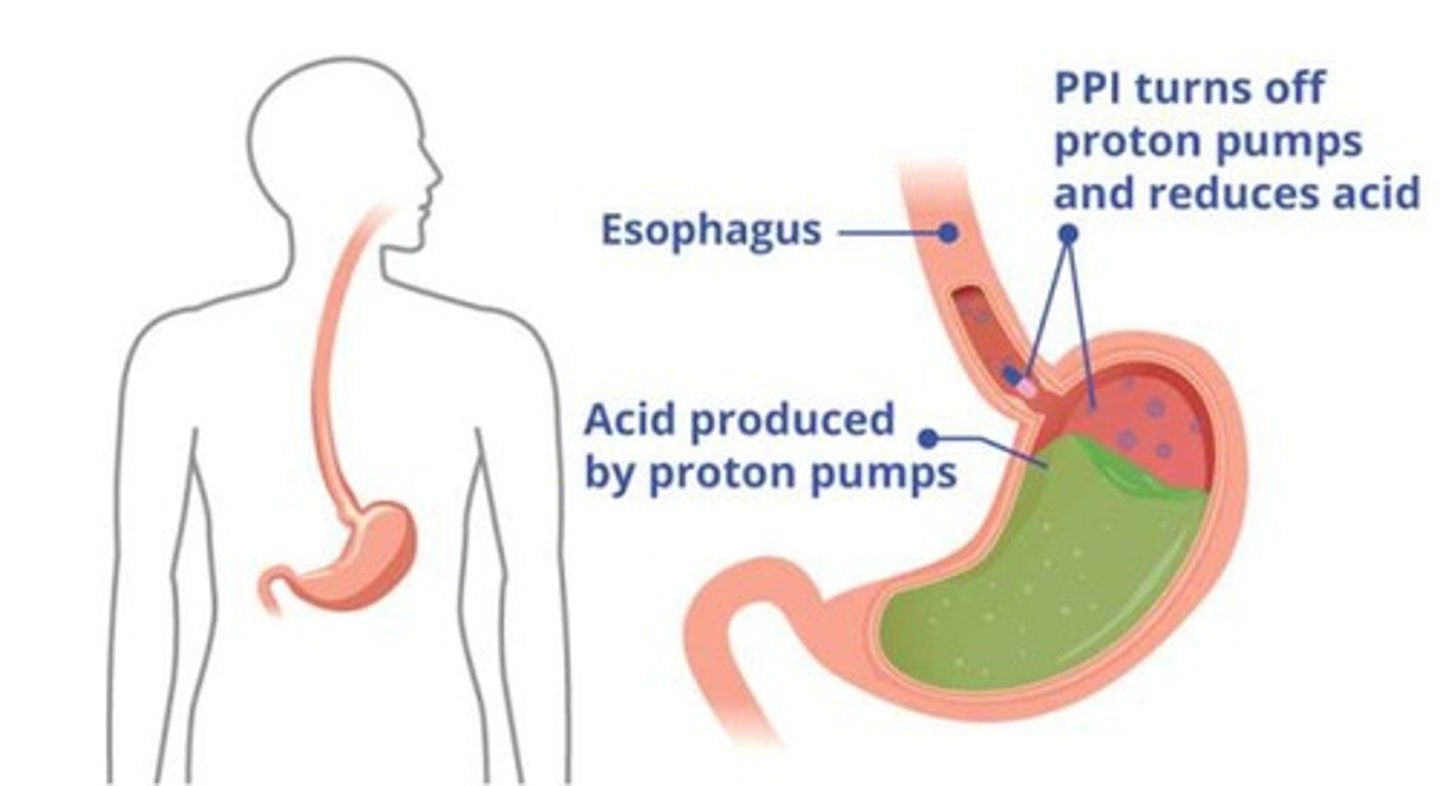
what is a proton pump inhibitor used for
to prevent/treat GI ulcers, GERD, and stress ulcers
Side Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors
Pneumonia,
osteoporosis and fractures, hypomagnesemia,
C. diff diarrhea.
Examples of Proton Pump Inhibitors
pantoprazole, omeprazole.
When Should We Not Use Proton Pump Inhibitors?
Lactation, pregnancy,
allergy, COPD/pneumonia prone.
Nursing Implications for Proton Pump Inhibitors
Do not crush, chew or break;
assess for GI bleeding.
what is a Mucosal Protectant do
Acidic environment of the stomach and duodenum changes this medication into a protective barrier over an ulcer preventing further injury.
what would we use mucosal protectant to treat/prevent
GI ulcers
Examples of Mucosal Protectant
sucralfate.
what is a side effect of a mucosal protect
constipation
When Should We Not Use Mucosal Protectant?
Allergy;
Caution: CKF, DM.
Nursing Implications for Mucosal Protectant
Avoid taking with phenytoin, digoxin, warfarin, and ciprofloxacin;
take 30 min before or after antacid.
what does an antacid do
Neutralizes or reduces acidity of gastric acid.

what are antacids used to treat/prevent
GI ulcers
GERD
Stress ulcers
Side Effects of Antacids
Constipation/Diarrhea,
fluid retention,
electrolyte imbalances,
metabolic alkalosis.
When Should We Not Use Antacids?
GI perforation or obstruction;
caution in abdominal pain.
Examples of Antacids
magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate
what does Prostaglandin E Analog do
decrease acid secretion,
increase the secretion of bicarbonate and protective mucus,
promote vasodilation to maintain submucosal blood flow.
Example of Prostaglandin E Analog
misoprostol.
When Should We Not Use Prostaglandin E Analog?
Pregnancy (Category X) and lactation.
Nursing Implications for Prostaglandin E Analog
Eat with meals and at bedtime;
avoid pregnancy;
give pregnancy test.