hematology exam 1 (all units combined)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is hematopoiesis?
The production, development, differentiation, and maturation of all blood cells
What is hematology?
The study of blood
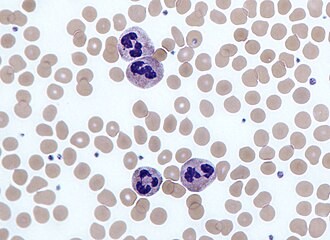
What WBC is this?
Neutrophil, help fight infection then are later destroyed. They start in the peripheral blood then are released into bone marrow. 10-15 micrometers
What WBC is this?
Eosinophil, regulator of inflammation and ability to kill parasites, 12-17 micrometers, starts in peripheral blood then released into bone marrow and lives in the tissues for a short time, increased eosinophils could mean, drug reaction, skin disorders, parasitic infestations, ect.
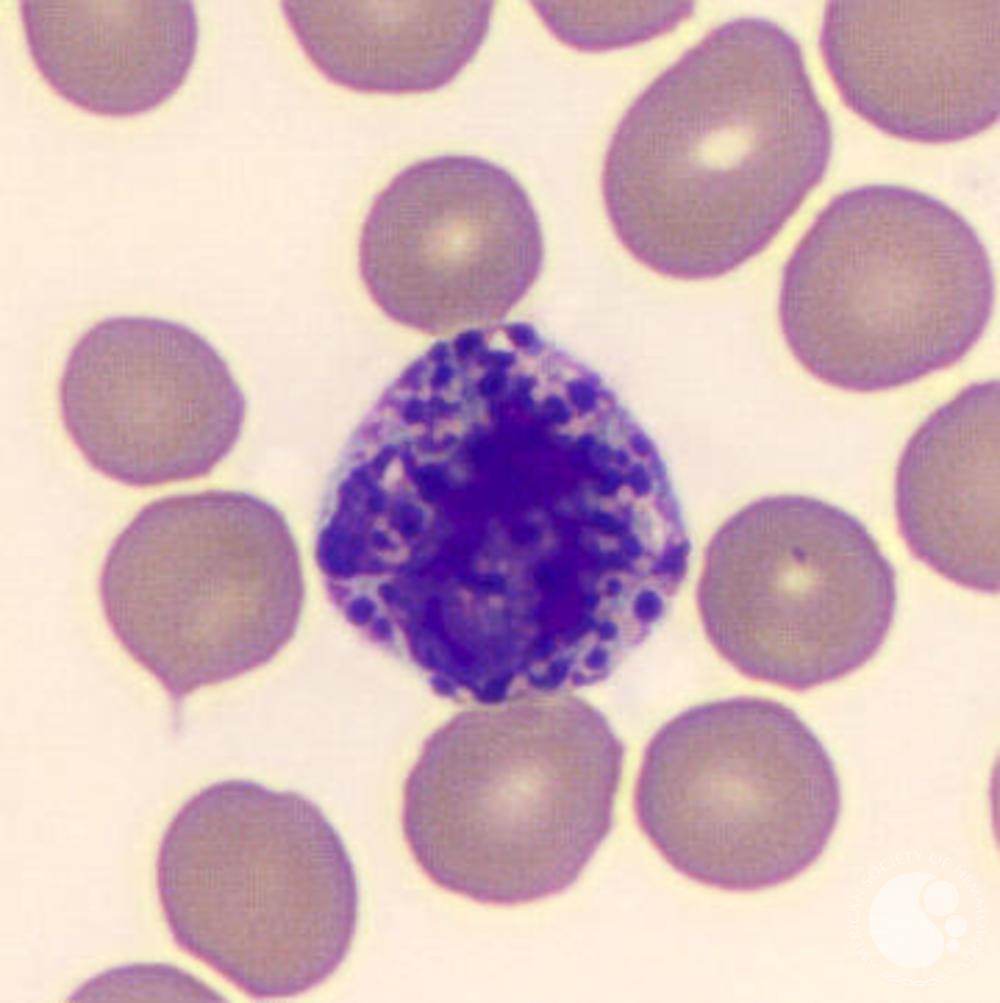
What WBC is this?
Basophil, 10-15 micrometers like neutrophils but occupies a larger portion of the cell, can be a dark purple or blue and contains granules
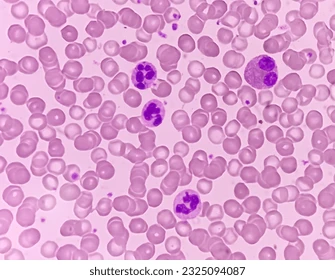
What WBC is this?
Monocyte, has azure dust, can help fight infection and initiate adaptive immunity, pastel purple look, 13-25 micrometers
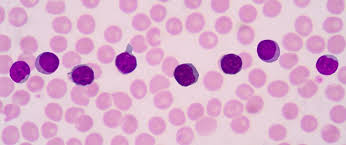
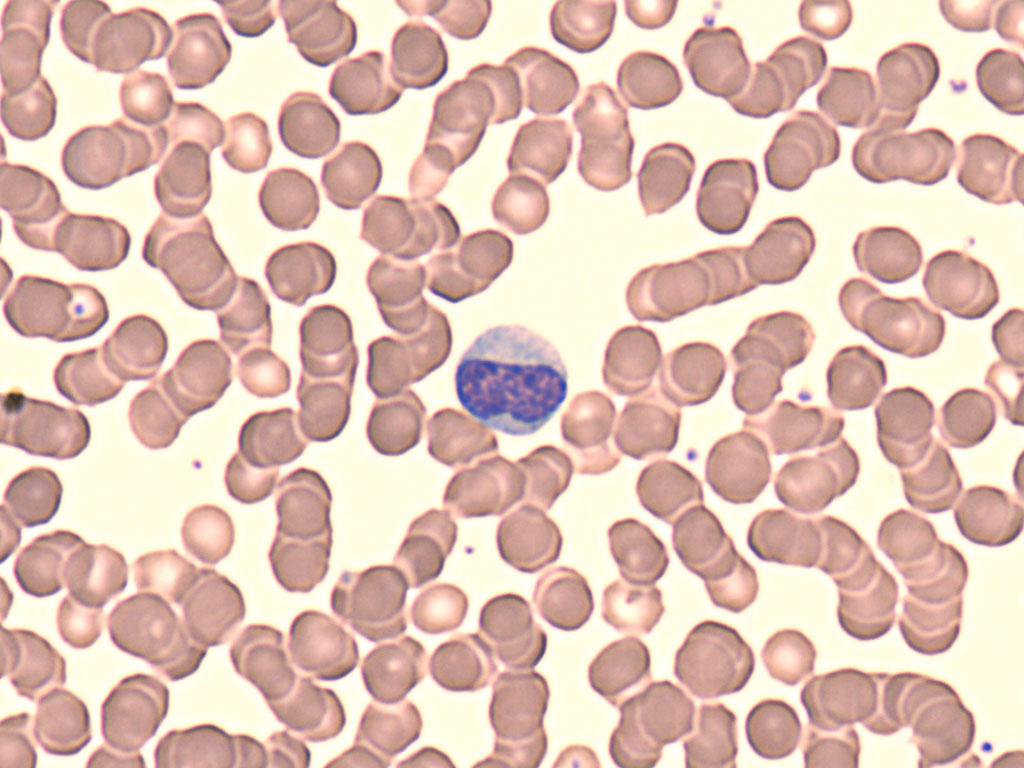
What WBC is this?
Lymphocyte, round, arises for progenitor cells and liver then later comes to the bone marrow, 6-15 micrometers
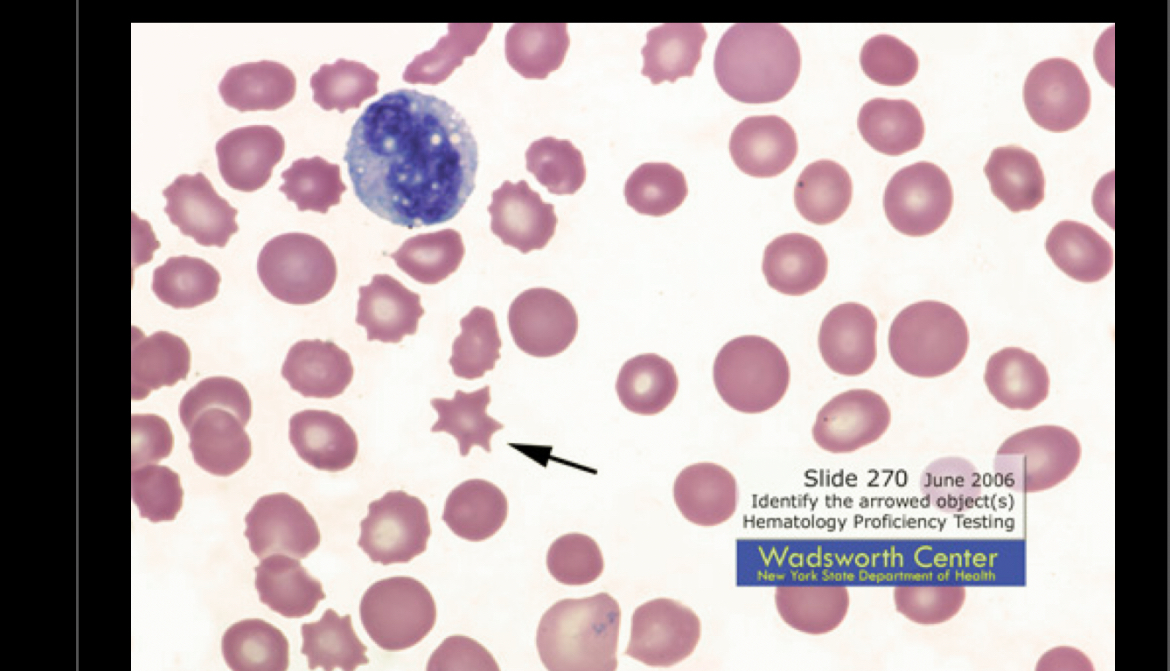
What RBC is this?
Acanthocytes, can have around 3-9 spikes, excess cholesterol, decreased lecithin, can be seen in liver disease, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, McLeod syndrome, lecithin cholesterol
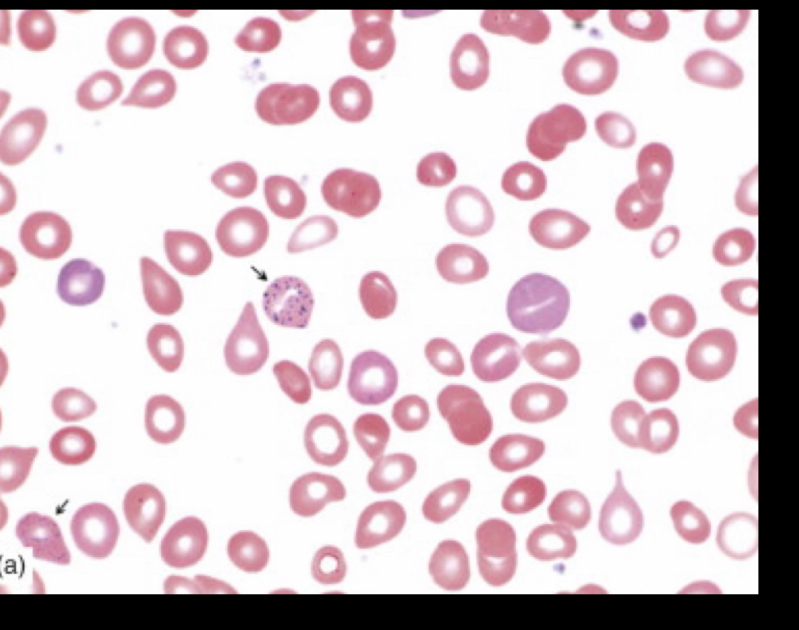
What RBC is this?
Basophilic stippling, a result of RNA and mitochondrial remnants, has a bunch of granule dots.
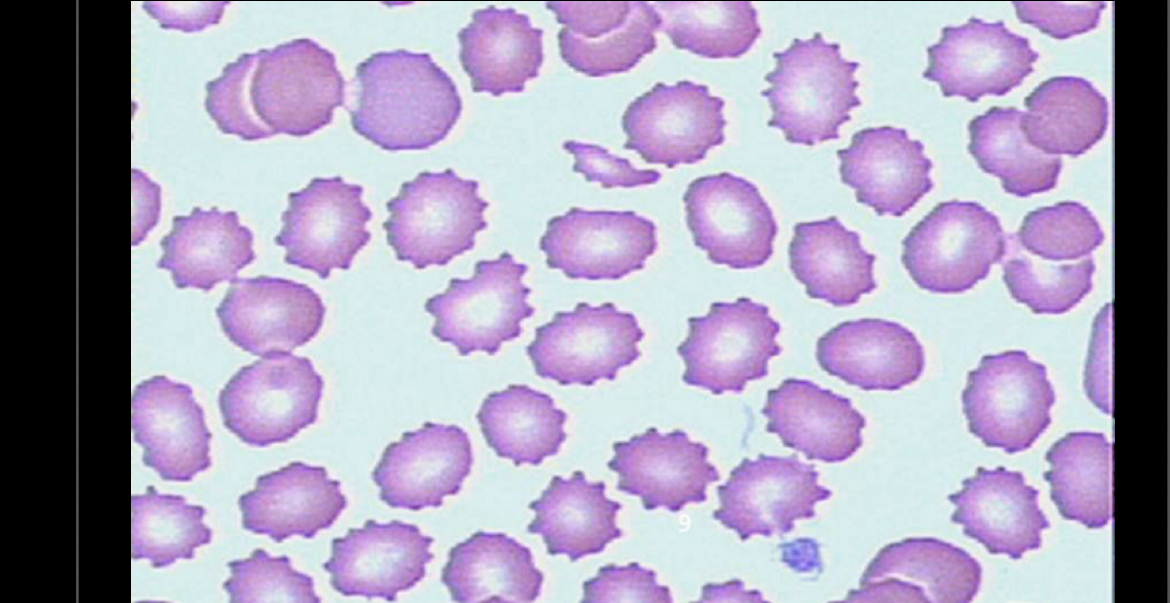
What RBC is this?
Burr cell (echinacyte), spike look, can be seen with peptic ulcers, burns, renal insufficiency, ect…
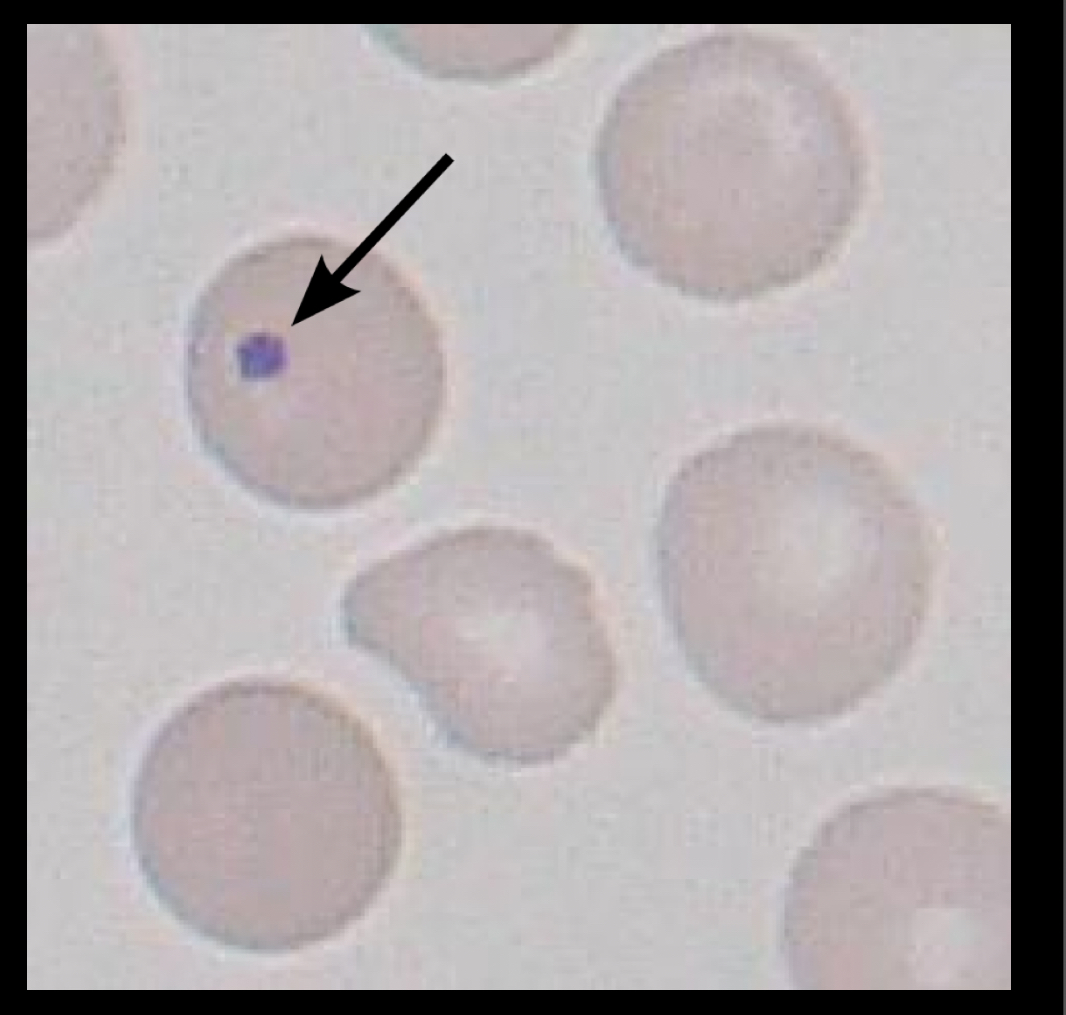
What RBC is this?
Howell-jolly body, remnants of DNA, located in the cytoplasm, spleen normally removes inclusions from cyptoplasm but when spleen can’t keep up bone marrow comes, happens with anemia and postsplenectomy.
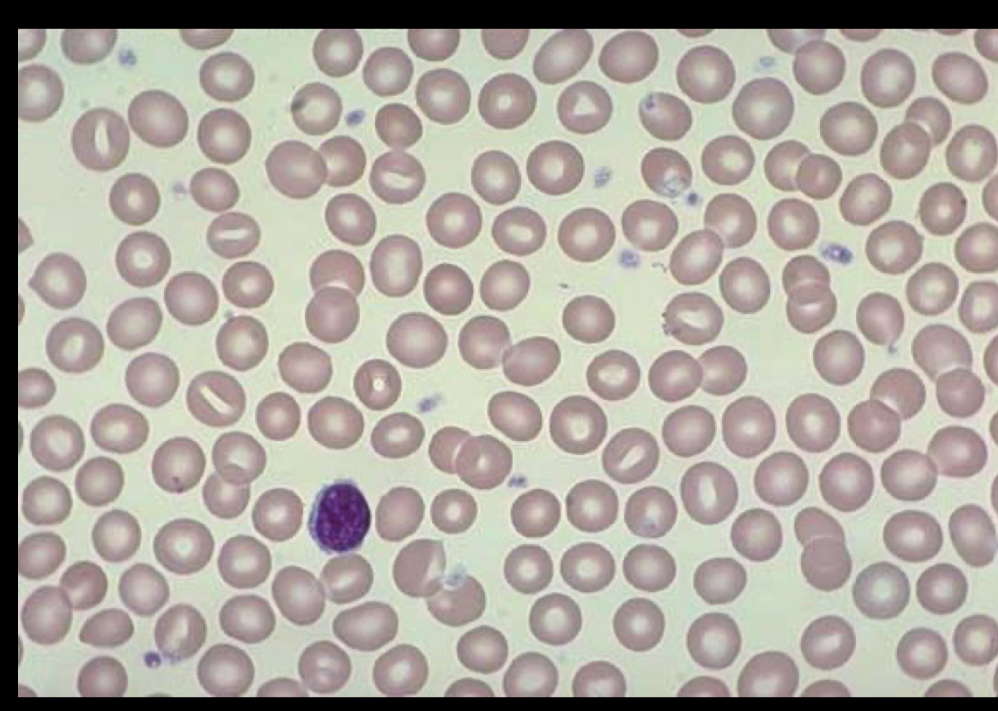
what RBC is this?
Normocytes, just normal sized RBC, normally nothing abnormal
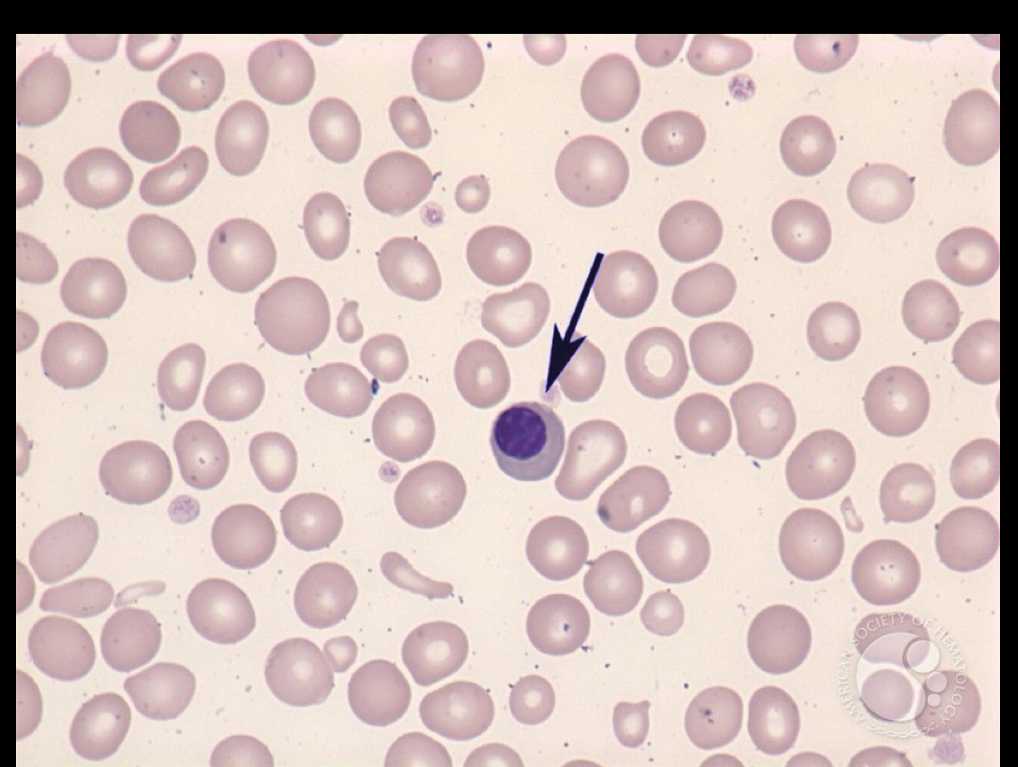
What RBC is this?
nRBC
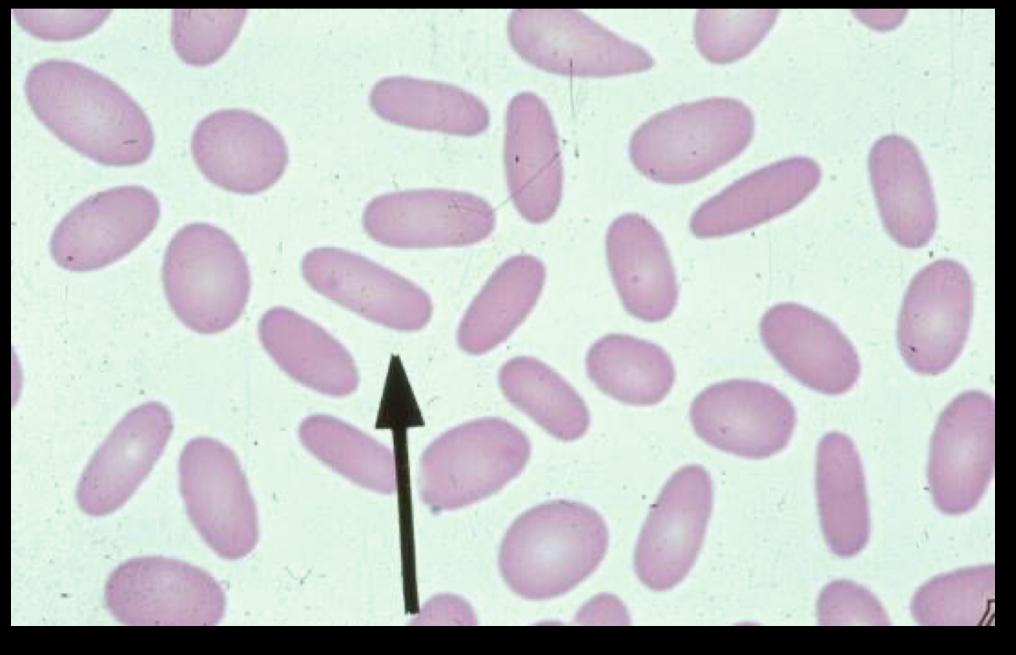
What RBC is this?
Ovalocytes, normally seen with anemia, oval shaped
Describe leukopoiesis and the primary purpose of WBC’s
Leukopoiesis is the process of WBC production and WBC’s fight infection, disease, and foreign substances.
List the maturation sequence of the granulocytic series.
Myeloblast, promyelocyte, myelocyte, metamyelocyte, band, segmented neutrophil (least mature-mature)
Name four morphologic features that are helpful in differentiating the cells of the granulocytic series.
Size, staining colors, N:C ratio, shape
Define the major CD markers for each individual leukocyte.
T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes, monocytes, NK, neutrophils
Define the function of the myeloid stem cell relative to the lymphoid stem cell.
Helps innate immune cells, helps rapid immune responses and carries oxygen.
Characterize the difference between absolute and relative values.
Absolute value is the number of cells present in the blood stream while, relative value is the percentage of a cell.
Describe the lymphatic system and its relationship to lymphocyte production
Filters blood or fluid, balances antibody generation, lymphopoiesis. The lymphatic system has a clear fluid that bathes tissues also hops with circulation.
Describe the role of T cells, B cells, and NK cells
T cells identify and destroy infected cells and tumors, B cells secrete antibodies and help activate T cells, NK cells helps resist or kill bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Describe the significance of the field of hematology in relation to sickness and health.
Our WBC are what try to prevent sickness and keep us healthy but sometimes it can’t and we get sick, hematology can see RBC disorders, cancer, and hereditary diseases and can also give possible treatment, they can also see low vitamins, cholesterol, ect…
List the basic parts of a compound microscope.
Eye piece/ ocular, objectives (magnification), iris diaphragm (increases and decreases light), stages, adjustment knobs
Discuss the function and magnification of each of the microscope objectives.
10x = low power, 40x = high dry, 100x = oil immersion
Identify appropriate corrective actions when encountering routine problems with the operation of a microscope.
Use correct side of slide, open both diagrams for more light, wipe off 40x lens with lint free paper, clean eye piece with lens cleaner to remove dust, remove dust from light source.
Describe standard precautions as related to biological hazards.
Treat all specimens as potential source of infection, PPE, hand washing.
Describe safe work practices for PPE and disposal of biologic hazards.
Gloves, gowns, lab coats, safety glasses/glass shields, use puncture resistant containers for sharps, no food, drink, paper, notebooks, no dangly jewelry, close towed shoes, short nails, facial hair trimmed, long hair pulled back.
Describe the components of quality assurance in the hematology lab.
Ensures lab testing reliability. Could be errors in labeling, data entry, testing time. Make sure we are proficient with testing performance and standardized competency testing.
Define penalties and post analytic variables, delta checks, accuracy precision, reproductive ability in reference intervals.
Pre analytic affect the sample before and post analytic occur after testing. Delta checks are historical checks of the lab, results can help identify pre analytical errors.
Define the components of hematopoietic with respect to production, development, maturation, and differentiation of blood cells.
Helps production of new cells and maturation, involves spleen, bone marrow, liver. Starts in the yolk sac and ends in the bone marrow.
Describe organs used for hematopoietic throughout fetal and adult life.
Starts in the yolk sac at 2 weeks then moves to the spleen and liver, thymus lymph nodes then to the bone marrow 7 months after birth, adult life is in the bone marrow and partially the liver and spleen.
Describe the four functions of the spleen.
Filter blood, store blood, produce white blood cells, recycle iron.
Differentiate between intramedullary and extra medullary hematopoiesis.
Intramedullary is normal process of blood cell formation in the bone marrow while extra medullary happens outside of the bone marrow.
Define the morphologic classification of anemias.
Microcytics, normocytic, macrocytic
List and define the components of the complete blood count.
White blood count, red blood count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, MCV, MCH, MCHC, platelet count, RDW.
Describe clinical conditions that cause valid shifts in mean corpuscular volume.
Cold ablutions, transfusion therapy, reticulocytes.
Recognize normal and critical values in automated CBC
Normal values are
WBC: 4.8-10.8 × 10^9/L
RBC: males 4.7-6.1 × 10^12 /L, females 4.2-5.4 × 10^12/L
Hgb: males 14-18 g/dL, females 12-16 g\dL
Hct: males 42-52%, females 37-47%
MCV: 80-100 fL
MCH: 27-31pg
MCHC: 32-36%
RDW: 11.5-14.5%
Platelet count: 150-450 × 10^9/L
Describe the bone marrow response to effective erythropoiesis.
Helps release new reticulocytes and RBC’s, restores homeostasis.
Define importance of correlation checks in CBC
Part of quality assurance, rule of three.
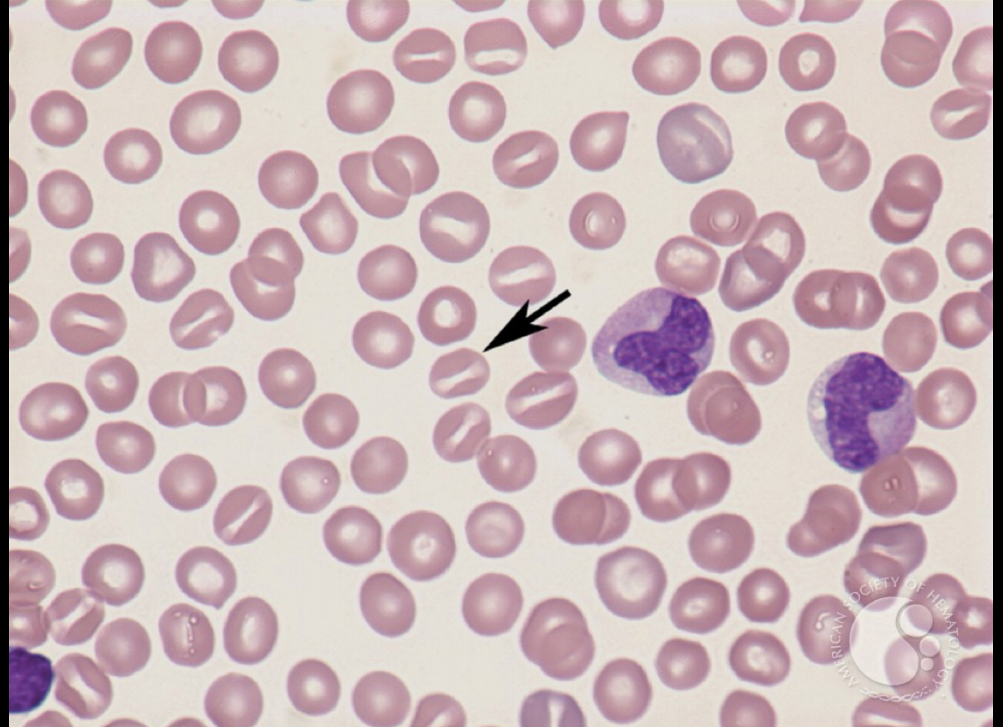
What RBC is this?
Stomatocytes, can appear with arrogated areas, seen with elevated sodium intake, poor made slide, hereditary, alcoholic conditions.
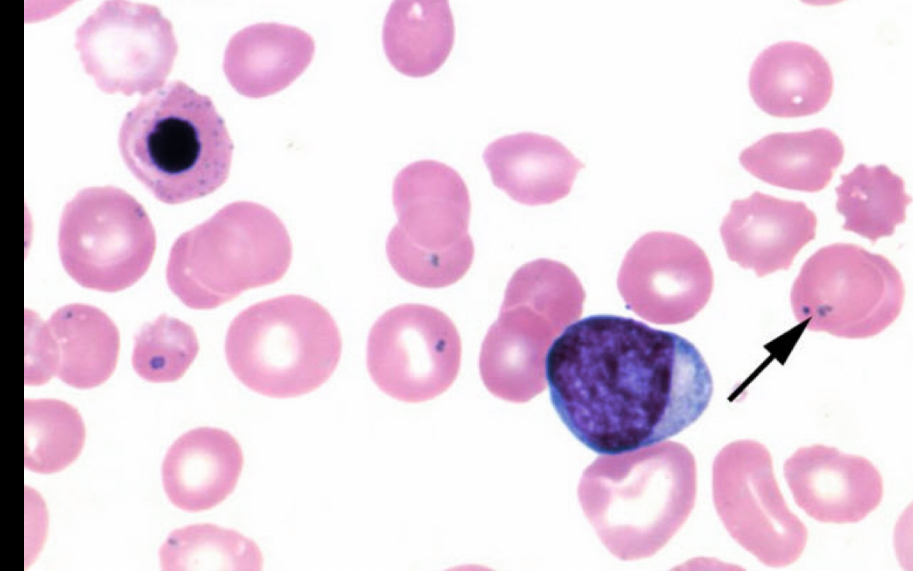
What RBC is this?
pappenheimer body, small dots are close together and normally close to edge, dots contain iron, can be seen with asplenia, sideroblastic anemia, megaoblastic anemia, other anemias.
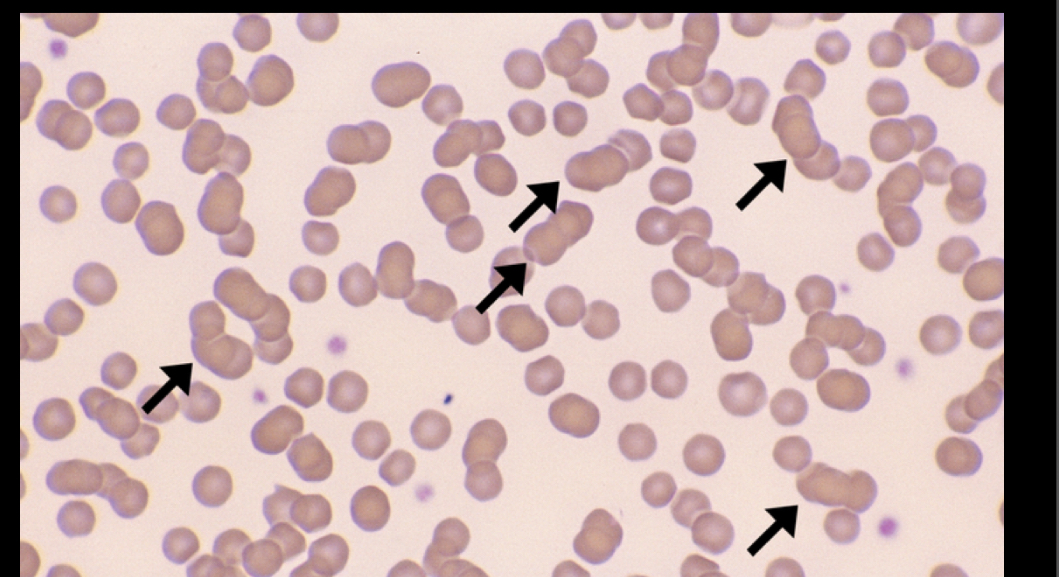
What RBC is this?
Rouleaux, looks like stacked coins, can indicate increased protein levels in the kidneys, can be found with inflammation and acute infections, multiple myeloma, cancer of plasma cells, diabetes, pregnancy, tissue disease, liver disease.
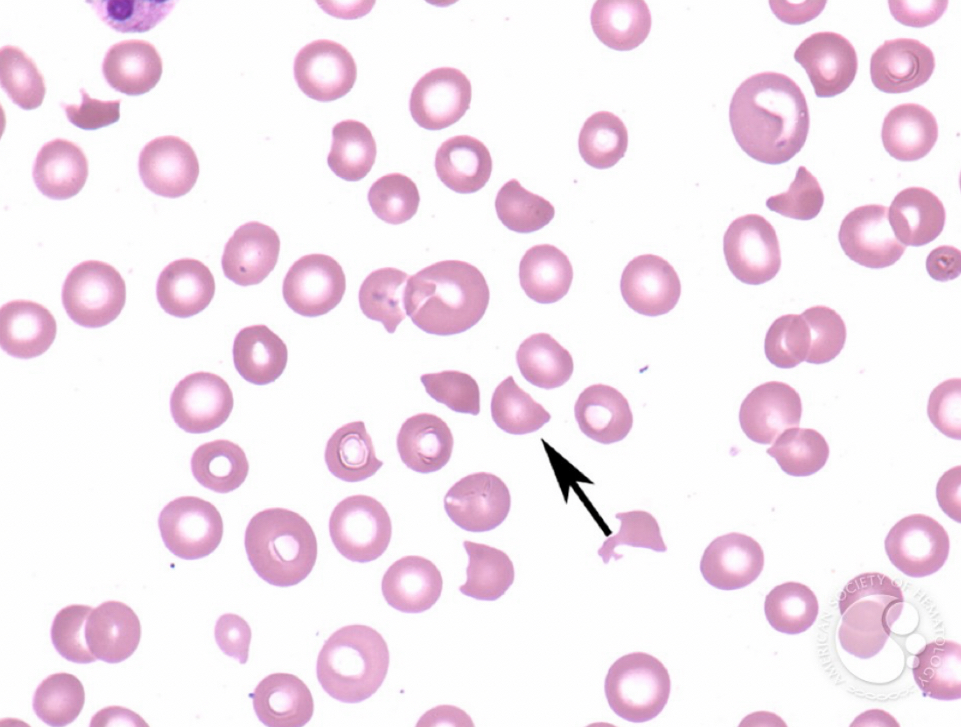
What RBC is this?
Schistocytes, look like a bite is taken out, can be seen with anemia, disseminated intrascular coagulation, kidney failure, low vitamin b12, low iron.
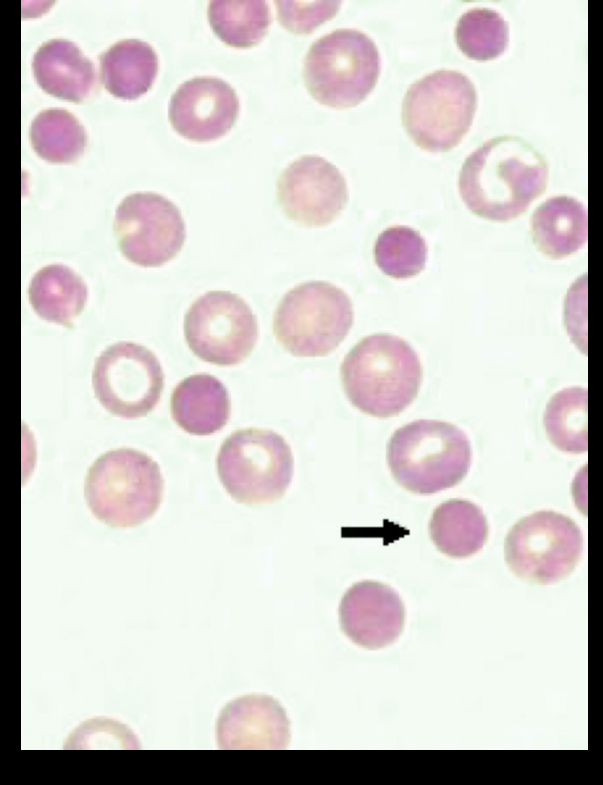
What RBC is this?
Spherocytes, circle solid shape, can be seen with heredity anemia, have shorter life spans in the blood stream.
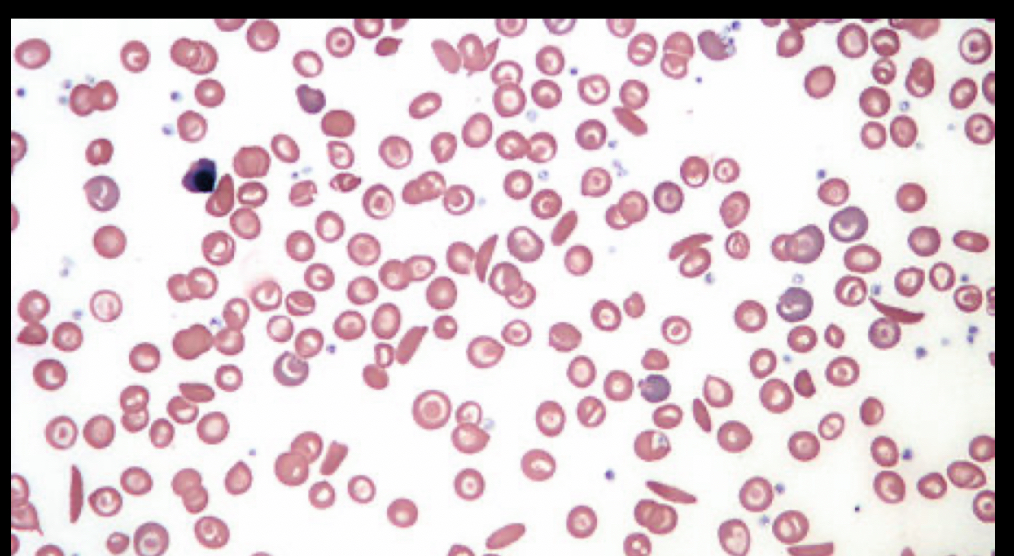
What RBC is this?
Sickle cell, crescent shaped, reduced life spans, caused by sickle hemoglobin, aren’t stretchy like normal cells so when trying to get though kidney and spleen they get smashed and damaged, reversible sickle cell can be back to normal with oxygen but irreversible cannot.
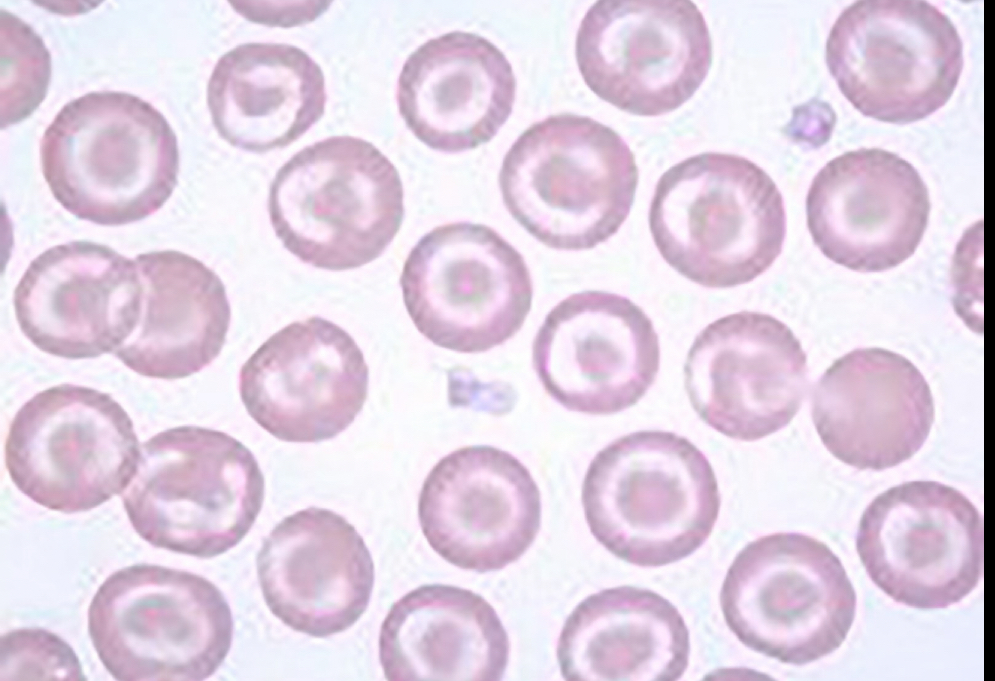
What RBC is this?
Target cells, look like bullseye, seen in peripheral blood and as an artifact slide, can be seen with iron deficiency, anemia, hemoglobin disease, liver disease, after splenectomy, cells form when hemoglobin is affected.
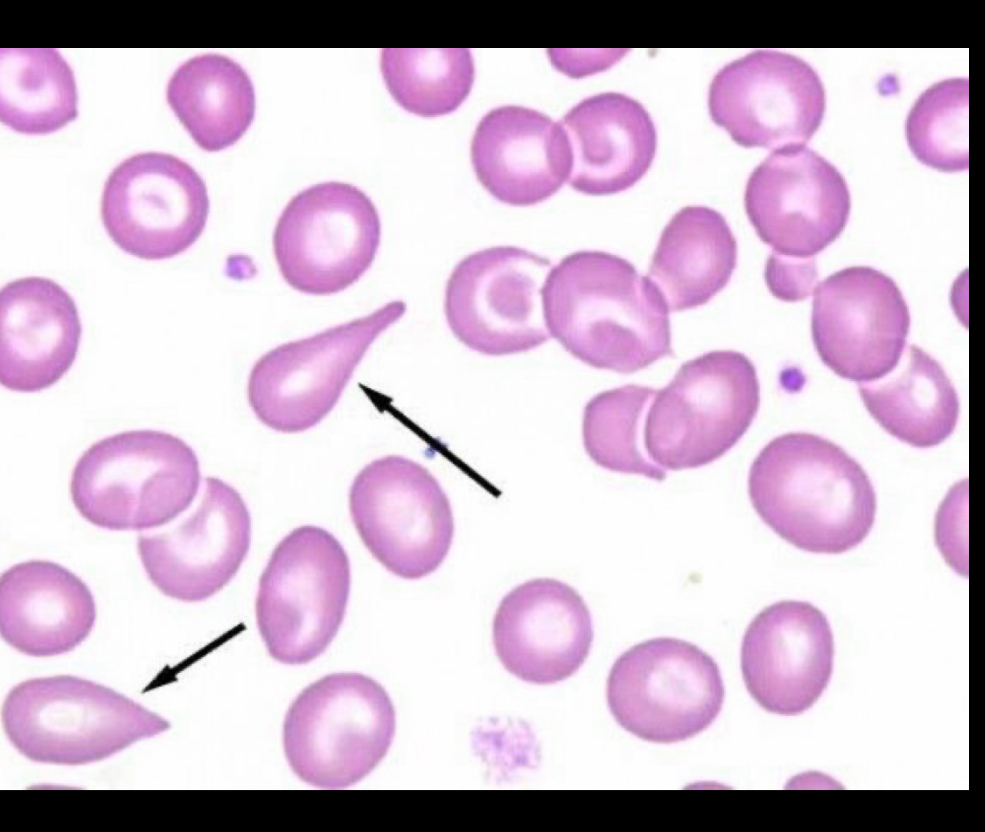
What RBC is this?
Tear drop cells, shaped like rain drop, seen in fibrosis, bone marrow disorders, splenic dysfunction, anemia
What is the normal mcg value and how do you calculate it?
Normal value is 80-100
Formula is MCV=(Hct/RBC) X 10
What is MCH normal value and how do you calculate it?
Normal value is 27-31pg
Formula is MCH= (Hgb/RBC)X 10
What is the normal MCHC value and how is it calculated?
32-36%
MCHC= (Hgb/Hct) X 100
What is the parameter formula for CBC?
Called RDW
(Standard deviation of red blood cell volume + mean MCV) X 100
Hemoglobin
The life giving substance of every RBC and the oxygen carrying component, takes 120 days.
Hemolysis
Death of cell through rupture of the cell membrane, occurs after the 120 days.
Outline erythropoietic production from origin to maturation with emphasis on stages of RBC development.
Starts in hemopoietic stem cell, common myeloid progenitor, MEP, then RBC development begins with pronormoblast, basophilic, polychromatophilic, ortho chromic, polychromatic, mature RBC.
Describe immature red blood cells with regard to nucleus: cyptoplasm ratio, cyptoplasm color, nuclear structure, and size.
cells are bigger and N:C ratio is larger, nuclear chromatin becomes more condense, colors get lighter. Pronormoblast (18-20 micrometers, 6:1 N:C), basophilic (16 micrometers, 6:1), polychromatophilic normoblast ( 13 micrometers, 4:1), orthochromic ( 8 micrometers, 1:1), polychromatic macrocyte ( 8 micrometers), mature (6-8 micrometers)
Clarify the role of erythropoietin in health and disease.
Helps stimulate the bone marrows then the marrow produces RBC which help carry oxygen through the body.
Differentiate between microcytic and macrocyte, and indicate the conditions in which size variations are seen.
Microcytic RBC are smaller and macrocyte are larger. Microcytic can be seen with anemia, thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, iron deficiency and overload. Macrocytes are seen with low B12, folic acid deficiency, liver disease, megaloblastic anemia.
Indicate the clinical conditions in which variations in hemoglobin content are seen.
Sickle cell, thalassemia, target cells
Describe the clinical conditions that show polychromatophilic cells
Anemia, pregnancy, iron deficiency,
Identify the pathophysiology and the clinical conditions that may lead to target cells, spherocytes, ovalocytes, elliptocytes, sickle cells, and fragmented cells.
Excess of membrane relative to cells cytoplasm can be caused by low hemoglobin to, liver disease, hemoglobin disorders, anemia
List the most common red blood cell inclusions and the disease states in which they are observed
Howell jolly bodies (splenectomy, anemia), pappenheimer body ( splenectomy, hemoglobinopathies, anemia), basophilic stippling ( lead intoxication, thalassemia), Heinz bodies ( unstable hemoglobin).
Describe the value of reticulocyte count relative to bone marrow function.
Most affective of assessing red blood cell generation, important indicator of bone marrow. Normal count: 0.5-2.0% adults, babies 2.0-6.0%.
Components of hemoglobin
Heme: 4 iron atoms 2+ surrounded by a ring, globin: 2 alpha and 2 beta chains made of amino acids.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins that help with inflammation in the body.
CD markers
Cell surface proteins that help identify cells.