Subjective Exam
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Subjective Examination
Patient Profile
Symptoms
mechanism of onset
type/description/location
behavior (SINS)
Origin of Symptoms
other musculoskeletal/neuromuscular origins
non-musculoskeletal origins
review of systems with special screenings and questions
Patient Reported Outcome Measures
Risk Factors
Adhesive Capsulitis: ages 40-65 years, female>male, diabetes, thyroid disease
Shoulder Fracture: older, female adults
Acromioclavicular Sprain/Strain: ages <40 years, male 5x more likely than females
Labral Tear: 30-50 years
DeQuervain’s Synovitis: Female > male; individuals why text frequently
Lateral Epicondylitis: ages 40-50 years; tennis players; RUE hand dominance
Wrist Fracture: risk increases with age
Patient Profile Cont.
Occupation and Recreation
uterus/repetitive - overhead
acute trauma - arm outstretched, fall
Social/Home Situation
are basic needs being met?
support system
Hand Dominance
Patient Goals and Expectations
Symptoms: Mechanisms of Onset
New occurrence vs previous episodes
Gradual - chronic overuse
Sudden - acute trauma (FOOSH)
Acute exacerbation of overuse
Pattern of flares and remissions (rheumatoid arthritis-progression overtime
Symptoms Type/Description
clicking, popping, clunking
heaviness, weakness, dead-arm
locking
apprehension
painful arc
parastesias
numbness
Symptoms: Location
specific and localized - pointing with one finger
generalized area involving the shoulder region
investigate if symptoms include areas above and or below the joint of interest
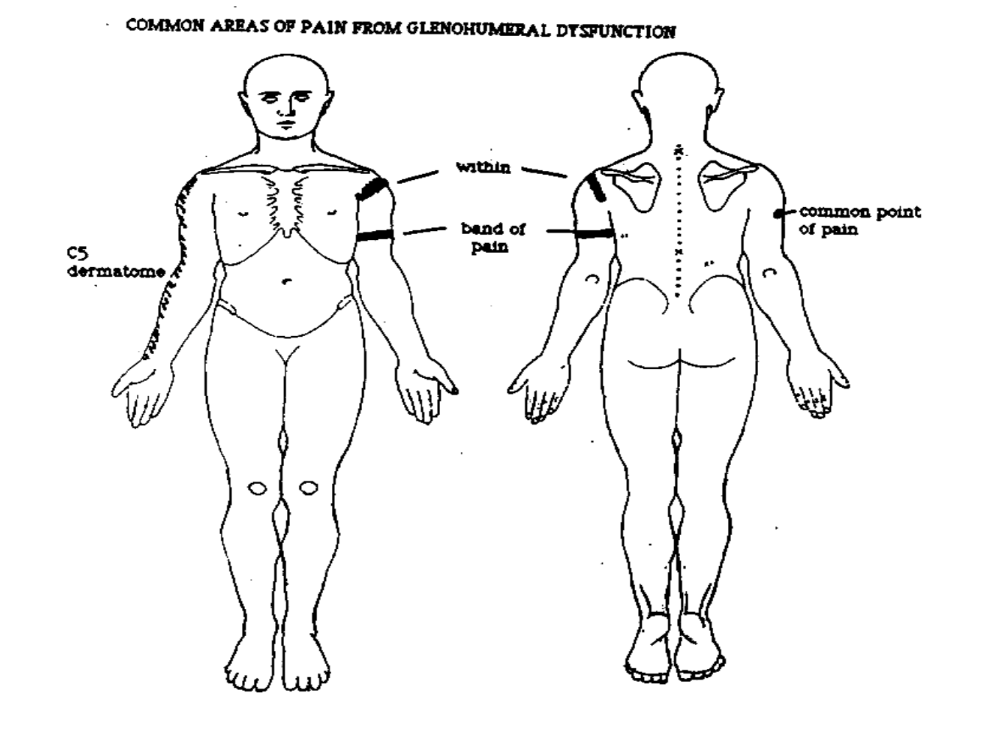
Common Areas of G-H Joint Pain Referral
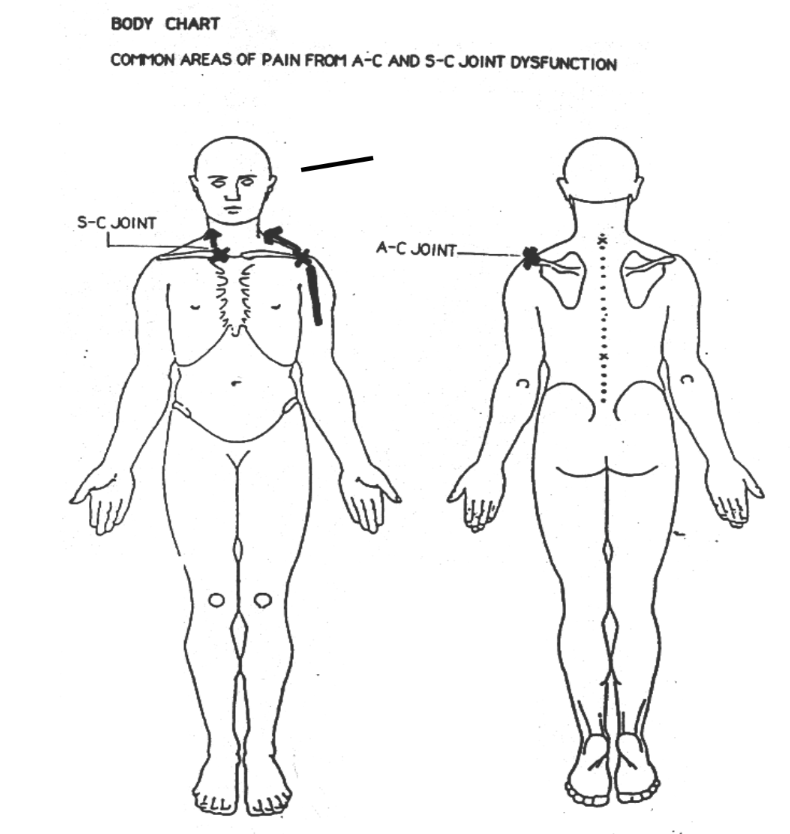
Common Areas of A-C & S-C Joint Pain Referral
Behavior of Symptom: Aggravating
reach up, across, behind
carrying
lifting
throwing
sleeping - on shoulder, back
cervical spine movement
Behavior of Symptoms: Easing
rest
movement
support
position
pillow
sling
medications, heat/cold modalities
Behavior of Symptoms: 24 Hours
awakened from sleep
inability to lie on affected side
ability to fall back to sleep
sleeping position
rising
AM/PM
Framework to Determine the appropriate rigor/intensity of examination
SINS
S: Severity
I: Irritability
N: Nature
S: Stage
SINS - Severity
S: Severity - seriousness of the problem
intensity level (pain scale: 0/10, 1-3/10 min, 4-6/10 mod, 7-10/10 (max)
constant or intermittent
type of symptoms
limitations of activities
complexity of presentation
patients may present with a range of severity
SINS - Irritability
I: Irritability: degree of tissue response/action
type of aggravation
amount of aggravation - time to provoke an increase in symptoms from the lowest baseline
the level to which symptoms increase; at least ask for type and amount of activity that provokes the highest level
the type of easing factor and how long it takes to decrease the symptoms to the lowest//baseline level
latency of aggravation of symptoms; symptoms that come on or increase well after cessation of the provoking/aggravating factor, which might make the actual aggravating factor more difficult to determine
Types of Irritability
Max Irritability: takes a relatively short time to aggravate and longer to ease
Mod-max: characteristics from both mod and max presentations
Mod irritability: it takes approximately the same time to aggravate and ease
Min-mod: characteristics from other mod and max presentations
Min irritability: it takes a relatively long time to aggravate and shorter to ease
SINS - Nature
Nature: Type of problem
non-musculoskeletal - requires referral to other health care professional
neuromusculoskeletal or musculoskeletal - requires further investigation by the pt and potentially outside referral
mechanical - symptoms related to or reproducible by movement or posture
contractile vs non contractile - tissue involvement
chemical - signs of inflammatory process; underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
SINS - Stage
S: Stage: current status of the problem based on time since onset on current presentation
progression/stability of sx (getting better, getting worse, or staying the same)
described as either acute, subacute, chronic based on tissue healing properties
one may identify a problem as chronic with exacerbation if they have had the problem previously
persistant acute: acute presentation despite a longer time since onset that would be termed or associated with a chronic problem; sx never decreased from being more highly irritable
Origin of Symptoms
patient center approach
symptoms originating from other musculoskeletal/neuromuscular origins
symptoms originating from non-musculoskeletal origins
Potential musculoskeletal/neuromuscular origins of symptom referral to the shoulder region
cervical spine joints
cervical spine nerves
referral from nervous tissue (spinal nerve roots C4, C5)
Nervous Tissue
Any neurological tissue including the brain, spinal cord > peripheral nerves
Motor Impairment
Muscular weakness
Sensory Impairment
Change in sensation
increased, decreased, loss, numbness, tingling
Injury to Nerve
Can result in motor and/or sensory impairment
Proximal to Peripheral Brachial Plexus
Spinal cord → cervical nerve root → ventral ramus → BP roots → BP trunks → BP divisions → BP Cords → Peripheral Nerves
Peripheral Nerve Injury - Posterior Interosseous Syndrome
Originates from the deep branch of the radial nerve
the deep branch of the radial nerve originates from the posterior cord (C5-C8 and T1) of the brachial plexus
results in motor impairment only: weakness to the supinator, wrist and finger extensors
injury to the posterior cord of the brachial plexus results in sensory and motor impairments
sensory: regions of the upper extremity innervated by nerves from C5-C8 and T1
motor: muscles innervated by C5-C8 and T1
Cervical Spine Screen
AROM and AROM with overpressure

Cervical Spince Screen: Additional Tests/Measures
Additional Screening Measures
PROM cervical spine
myotomes (resisted isometrics)
dermatomes (sensory assessment)
upper limb neural tension tests
quadrant test
deep tendon reflexes
Referred Pain from Muscle Tissue
trigger points
hyperirritable regions/spots to palpation within skeletal muscle or fascia
palpable densities within muscle fiber
causes: prolonged immobilization, excessive use
Potential Origin of Symptom Referral to the Shoulder Region Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Symptoms follow a glove or stocking pattern
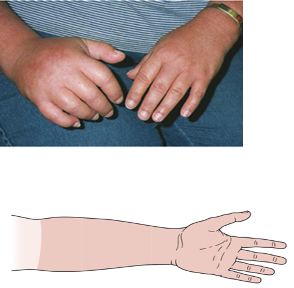
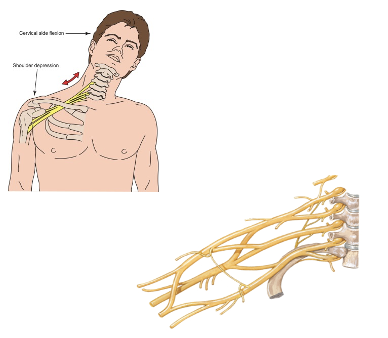
Potential Origin of Symptom Referral to the Shoulder Region
Symptoms follow innervation from the brachial plexus
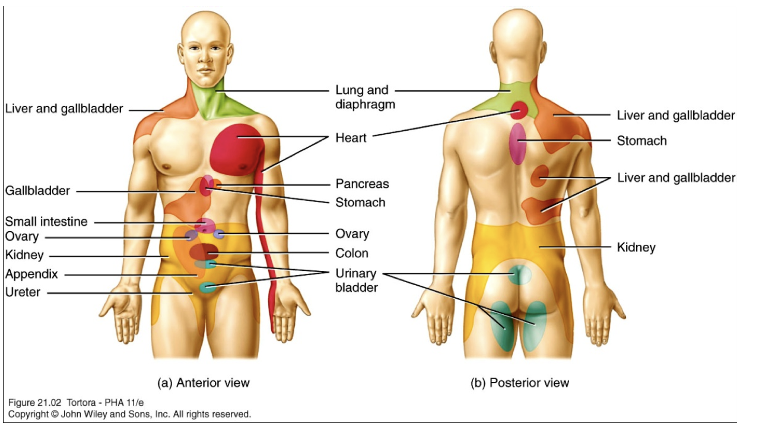
Non Musculoskeletal Origin of Symptom Referral to the Shoulder Region
Spleen Rupture Referred Pain
Pain in L shoulder
Gallbladder/Liver/Stomach Referred Pain
Pain in R shoulder and scapular region
Diaphragm Referred Pain
Pain front of either or both shoulders/upper trapezius region
Cardiac Referred Pain
Pain in L shoulder, scapula, axilla, scapular region (and/or arm, neck, jaw)
Pancost Tumor (Apical lobes of lung) Referred Pain
Pain in R or L shoulder, ulnar distribution UE
Pancreas Referred Pain
L shoulder and/or thoracic spine
Pancoast’s Tumor
Tumor located in apex of lungs
symptom presentation can mimic TOS
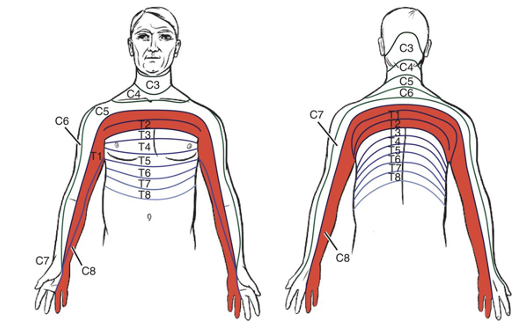
C8, T1, T2 dermatomes
lower trunks of brachial plexus
C8-T1 nerve roots
initially sharp posterior shoulder pain
pain in axilla and sub scapular regions
Psychogenic Pain
Beliefs, fears, emotions, assumptions
Special Screen Questions
General health, smoking, thyroid disease
change in appetite
weight loss or gain
bowel/bladder issues or changes
fever/chills
skin changes/hair loss/nail bed
other pain, stiffness, swelling, redness
fatigue
respiratory symptoms
numbness
gait disturbance
headaches/dizziness
coughing, sneezing
Diagnostic Tests
Imaging
x-ray
MRI
CT
Bone scan
blood draws
nerve conduction velocity tests
stimulation of a nerve to identify impairments in the speed of nerve conduction
electromyography tests
stimulation of a muscle to identify impairments of the ability of a nerve to stimulate muscle activity
Patient Reported Outcome Measures
SPADI (shoulder pain and disability index)
DASH (disability of the arm, shoulder, hand)
quick-DASH
Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index
Time Functional Arm and Shoulder Test (TFAST)
Shoulder Performance Activity Test (SPAT)