Chapter 8- BOOK- Development of B and T lymphocytes
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Central/primary lymphoid tissues
Bone marrow for B cells and thymus for T cells
Secondary lymphoid tissues/peripheral
lymph nodes, spleen, mucosal tissue
Positive selection
Cells with R that bind weakly to self antigens survive
Negative selection
lymphocytes which bind strongly to self reactive receptors must be eliminated to prevent autoimmune diseases→ self tolerant
Development of B lymphocytes: stromal cells
a network of specialized nonlymphoid connective tissue which produce signals for develpment
Have adhesive contact with lymphocytes + provide cytokines and chemokines that contribute to differentiation + proliferation
First step of development of B cell
Hematopoeitic stem cells differentiate into lymphoid myeloid primer multipotent progenitors (LMPPs)
LMPPS
produce 3 major subsets of progenitors:
EILP→ produces ILCs
CLP→ mostly B cells (pro-B cells)
ETP→ T cell progenitors
Interleukin-7 (IL-7)
Cytokine secreted by bone marrow stromal cells
ESSENTIAL for growth and survival of innate lymphoid cells
Composed of 2 polypeptides
B cell development
CLP → pro B cell→ receive proliferation ans survival signals from IL-7→ immature B cell→ Mature B cell
Pro B cell
Rearrangement is initiated→ induced expression of RAG1 and RAG2
Early: Joining of D and J segment
Late: Joining of V to DJ segment
Has: IL-7 R, Kit (CD117)
Successful rearrangement→ production of 2 u heavy chains→ if not → elimination (NON productive)
Pre B cell
Pre B receptor is formed
Heavy chain is formed + surrogate light chains
Progression to light chain rearrangement
Large→ proliferates→ small→ cease expression of the surrogate light chains
Express u heavy chain alone
Immature B cell
Express Ig M at cell surface
Stop light chain gene rearranement
Mature B cells
Produce delta heavy chain + u heavy chain
Ig M + Ig D
TdT
Expressed in pro B cell during heavy chain rearrangement
Adds non template nucleotides (N-nucleotides) between gene segments
Helps with the diversity of the BCR
Found mostly in heavy chains
Pre B cell R rests production of heavy chain
Is the heavy chain produced functioning?
How? Incorporate a functional heavy chain into a receptor that can signal its successful production.
Absence of light chains-loci not rearranged→use 2 surrogate light chains
Surrogate light chains
Pro cells make 2 surrogate proteins that can form a similar surrogate light chain and can pair with u chain to form pre B cell R
The assembly of pre BCR signals to B cell → productive rearrangement→ The cell is a PRE B cell now
Ig Beta and Ig alfa chains
Pro and pre B cells
They are signaling components of the BCR complex on mature B cells→ they transduce signals by interaction with tyrosine kinase through cytoplasmic tails
Crossliniking
Pre B cell receptor and signaling
Checkpoint between pro and pre B cell
Allelic exclusion
To prevent the formation of 2 successful receptors of different antigen specificity
Signaling by the pre B cell receptor→ allelic exclusion
Only one of the 2 allels is expressed in a diploid cell
Occur in both heavy and light chain loci
Signaling from pre B cell R (allelic exclusion)
3 ways to promote heavy chain allelic exclusion:
Reduces the V(D)J recombinase activity by reducing RAG1, RAG2
Reduces RAG-2 by indirectly causing the protein to be targeted for degradation
Reduces access of heavy chain locus recombinase machinery
→ pre B cell receptor signaling→ profund reduction in numbers of pre B cells and mature B cells that develop
Pre- B cells function
Large pre B cells become small
RAG are produced again in small
Rearrangement of light chain occur
Rearrangement only one allele at a time
If VJ rearrangement fails from one allele→ use the other allele→ can happen multiple times
Isotypic exclusion
Light chain only express one type of chain kappa or lambda
Kappa rearranges first→ most common
When is Ig M expressed?
Once a rearranged light chain has paired with a u chain it can be expressed on the cell surface
The pre B cell becomes an immature B cell
Immature B cell
Antigen R is if first tested for self antigens or autoreactivity
Autoreactivity cells are eliminated or replace receptor by receptor editing
Enter the spleen
Central tolerance
Arises in a central lymphoid organ- bone marrow
Elimination of autoreactive B cells
Transitional B cells
B cells emerge from bone marrow into the periphery , not fully matured
Final maturation occur in periphery
Express mostly Ig M but little Ig D
(the opposite expression in a mature B cell)
Follicular dendritic cells
FDCs
Non hematopoetic cells in B cell follicles, captures antigens for recognition by B cell antigen receptors
Follicles
Part of the lymph node where transitional B cells enter
Provides signals for B cell survival
Complete their maturation here
Transitional stages for transitional B cells
Called T1 and T2
Then enter B cell pool
Defined by the abscence or presence of CD21
Follicular B cells
Reside in spleen and other peripheral organs
Marginal zone B cells
Minor population of B cells in spleen
Tyrosine kinase Syk
Involved in signaling from B cell receptor
Without SYK→ fail to develop mature B cells
Survival or mature B cells
B1 B cells
Subset of B cells involved in the innate defense
Source of natural antibodies→ consistently produced antibodies secreted prior infection
Recognize polysaccharides
DONT need T cells → produce IgM within 48 hours (no T present)
Development of T cells
Mature in thymus
Thymic stroma → T cell precursors embedded in a network of epithelia→ unique environment for development
Progenitor T cell
Cells entering thymus lack cell surface molecules
Their receptor gene is not rearranged
Early thymic progenitors ETPs
In thymus, receive signal from thymic epithelial cells transduced through a receptor called Notch to switch on specific genes
Notch signaling
Required through the T cell development
Increase the expression of 2 transcription factors
Essential for commitment to T cell lineage
Also induces expression of IL-7 alfa chain important cytokine-
Double negative thymocytes/ double positive
Absence of both CD4 and CD8 or presence of both
Regulation of T cell rearrangement
Cells that fail the rearrangement of the Beta chain locus → death
Successful rearrangement→ express beta chain protein→ next stage is called DN4 stage→ proliferation→ loss off CD25 expression
Pre T cell receptor
Th expressed Beta chains pair with a surrogate pre-Tcell receptor alfa chain called pTalfa→ assembly of pre TCR (analogous to the pre-beta R)
Expressed with CD3→ provide signaling components of receptor
Double positive thymocytes
Alfa chain locus rearranges
Alfabeta TCR is produced
One of the 2 receptor molecules (CD4/CD8) is down regulated → single positive thymocytes
Thymus structure
2 main regions:
Peripheral cortex and the central medulla
T cell development occur in cortex
Only mature single positive thymocytes are present in the medulla
Development of T cell
Progenitors entering to the outer cortex→ here double negative thymocytes proliferates
Positive selection- MHC molecules+epithelial cells +receptors
Developing T cells migrate from cortex to medulla
Negative selection in medulla→ dendritic cells express co-stimulatory molecules
delta-gamma TCR
Found primarly in epithelial and mucosal sites
Lack expression of CD4 and CD8
Mostly component of the innate
Can differentiate into dentritic epidermal T cells DETCs
Successful synthesis of rearranged Beta chain (alfa/beta T cells)
Allows the production of a pre -T cell receptor that triggers cell proliferation and blocks further Beta chain gene rearrangement
T cell receptor alfa chain gene
Comparable to kappa and lambda in Ig→ they dont have any D gene segments and are rearranged after their partner receptor chain has been expressed
Can produce two types of alfa chains→ expression of the TCR is not sufficient to shut of rearrangement of gene
Big difference between T cell and B cell devlopment
Multiple alfa chain are produced and rearranged and tested with the same beta chain
Not occur in B cells
Positive and negative selection of T cells
Positive selection=the rescue of a double positive cell from programmed cell death and their maturation into single positive cells
Negative selection= if maturing thymocyte has strong reactivity to a self antigen found in the medulla→ cells with weaker levels of self reactivity→ differentiate
Peptide:self MHC complexes
Only thymocytes whose receptors interact with self peptide:MHC complexes can survive and mature into naive CD4 or CD8 cells
Positive selection functions
Coordinates the expression of CD4 or CD8 with the specificity of the TCR
CD4 cells have R recognizing peptides bound to MHC class2→ become cytokine secreting helper T cells
CD8 cells recognize MHC 1→ become cytotoxic T cells
Positive selection determines the phenotype
Co receptors in positive selection
MoreBind to MHC: CD4 and CD8
Recruit- Lck= tyrosine kinase→ initiates signaling
The signal is only initiated with cells that have TCR bound to MHC→ survival
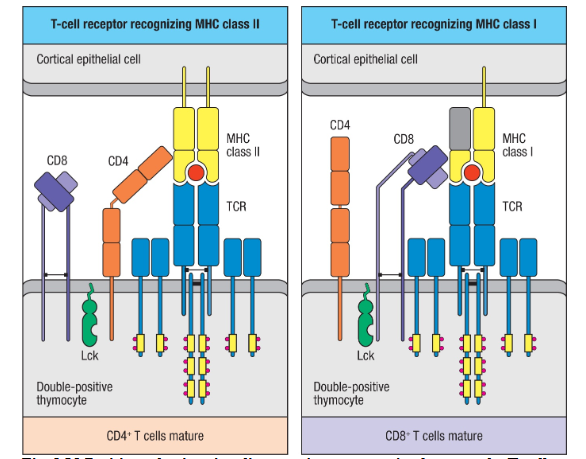
Stromal cells in positive selction
Important! Close contact with double positive cells
Display the MHC molecules to the T developing cell
Negative selection function
T cell reacting strongly to self antigens are deleted
More receptor specificity must be positively selected tha nehatively selected→ otherwise no T cells produced
AIRE
Autoimmune regulator
Gene controlling the expression of tissue specific proteins in thymic medulla→ lengthens transcripts that would otherwise be terminated
Fasciliatetes negative selection by proimoting expression of tissue specific antigens in epithelial cells
Affinity hypothesis
The choice between pos and neg selection is thought to depend on the strength of the self peptide:MHC binding by the TCR
Low affinity→ positive selection
High affinity→ apoptosis
T reg cell subset
A population of CD4+ T cells that function to maintain self tolerance
TCR have moderate high affinity for self peptides
Invariant NKT cells (iNKT cells)
Express a receptor called NK1.1 receptor
Part of the early response in immune defense
Recognize CD1 molecule rather thanMHC molecules
Thymic emigration
After 1-2 weeks of maturation in thymic medulla→enter blood stream
Emigration requires recognition of the lipid molecule S1P by the G protein coupled receptor S1PR1→ expressed by thymocytes during final maturation
Why does not a mature naive lymphocyte + self antigen lead to cell death? But with a pathogen?
Infection→ inflammation
Induces expression of co-stimulatory molecules on the antigen-presenting dendritic cells→ cytokines promote activation of lymphocytes