OT423: MIDTERM
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Basic Awareness of self, The nature of effective helping, Communication, Communicating with Cultural Sensitivity ,Communicating with Persons Who Have Disabilities , IDENTIFYING AND RESOLVING MORAL DILEMMAS,
Last updated 4:51 PM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
1
New cards
Therapeutic communication
Speaks, Listening, develops trust ,Having a level of self-awareness helps you have quality therapeutic communication
2
New cards
effective helping
the systematic application of mental health counselling and other professional skills into every day interactions by health care providers to help individuals who seek mental health care
3
New cards
Humanistic Communication
that places the patient in a position of informed, equal and inevitably responsible for any positive outcomes in the helping process.
“intervention“
“intervention“
4
New cards
Hemiparesis
Is weakness or the inability to move on one side of the body, making it hard to perform everyday activities like eating or dressing.
5
New cards
what factors impact behavior?
* Needs
* Values
* Cognition
* Emotions:
* Values
* Cognition
* Emotions:
6
New cards
Which one of these is appropriate in a therapeutic relationship?
* **Sympathy: you feel similar things**
* Pity :(with a negative connotation)
* Pity :(with a negative connotation)
7
New cards
INTERPERSONAL INTERACTION PROCESS- **EMPATHY**
1\. self-Transposal
2\. crossing over – find ourselves in the same frame of reference/ their lived world
3\. A momentary merging of another person in a unique moment of shared meaning.
2\. crossing over – find ourselves in the same frame of reference/ their lived world
3\. A momentary merging of another person in a unique moment of shared meaning.
8
New cards
Self-transposal
cognitive thinking of myself in the position of the other. Trying to imagine what it must be like for the patient.
\*\* This is not empathy.
sets the stage for empathy to occur.
\*appropriate. cog thinking of putting yourself
\*\* This is not empathy.
sets the stage for empathy to occur.
\*appropriate. cog thinking of putting yourself
9
New cards
Level 5: Cliché’ Conversation. No genuine human sharing takes place.
“ its cold outside” elevator chat
10
New cards
Level 4 – Reporting facts-almost nothing personal revealed.
Little pieces of factual information
11
New cards
Level 3- Personal ideas and judgments- information is shared in response to the patient's conversation.
1. Starting to get to know your client
2. Ask about family members
12
New cards
Level 2- Feelings and Emotions- True friendship and caring require rapport is established.
1. Can be friends with a pt.
2. Rarity
13
New cards
Level 1 – Peak communication- openness, honesty, respect, and love are required.
\
1. Intimate relationship
2. Never be at the level
3. Not appropriate
1. Intimate relationship
2. Never be at the level
3. Not appropriate
14
New cards
Communication
the purpose of giving and receiving information by means of gestures, words and tone of voice…”. The context must also be considered!
15
New cards
Communication component/ skills
* Verbal expression
* Listening
* Written
* Non verbal expression
* Listening
* Written
* Non verbal expression
16
New cards
active listening
* ==**Restatement**==- repeating the words of the speaker as you have heard them.
* ==**Reflection**==- verbalizing both the content and implied feelings of the sender. The purpose is to express in words the feelings
* ==**Clarification**-== summarizing or simplifying the sender’s thoughts and feelings and resolving confused verbalizations into clear, concise statements.
* ==**Reflection**==- verbalizing both the content and implied feelings of the sender. The purpose is to express in words the feelings
* ==**Clarification**-== summarizing or simplifying the sender’s thoughts and feelings and resolving confused verbalizations into clear, concise statements.
17
New cards
“I” messages, **Congruence:**
Indicates that the words and the music match. Congruence is present when
*what I say matches what I do and what I feel.*
* Ownership of your own actions and feelings
* Avoid preconceived notions
*what I say matches what I do and what I feel.*
* Ownership of your own actions and feelings
* Avoid preconceived notions
18
New cards
Table 6.1:BELIEFS OF EFFECTIVE HELPERS
1\. Subject/ discipline
1\. Subject/ discipline
Effective helpers are committed to discovering the personal meaning of knowledge and converting it to belief.
Was to know information
Was to know information
19
New cards
Table 6.1:BELIEFS OF EFFECTIVE HELPERS
2\. Helpers FOR
2\. Helpers FOR
frame of reference that emphasizes facts, things, organization, money, etc
Internal: feelings, values belief
External: money, organizational goals.
Internal: feelings, values belief
External: money, organizational goals.
20
New cards
Table 6.1:BELIEFS OF EFFECTIVE HELPERS
3\. Beliefs about people
3\. Beliefs about people
* A source of satisfaction in professional work rather than a source of suspicion and frustration
* Your goal is really to facilitate
* Your goal is really to facilitate
21
New cards
Table 6.1:BELIEFS OF EFFECTIVE HELPERS
4\. Helper’s self-concept
4\. Helper’s self-concept
* Therapeutic presence for the other is made possible by a strong sense of self, personal fulfillment, and of personal adequacy.
* Personal boundaries and fulfillment
* Personal boundaries and fulfillment
22
New cards
Table 6.1:BELIEFS OF EFFECTIVE HELPERS
5\. Helper’s purpose
5\. Helper’s purpose
* They see themselves as altruistic, oriented toward assisting people rather than simply responding to selfish needs.
* The big picture
* Altruism: selfless code of principles
* The big picture
* Altruism: selfless code of principles
23
New cards
Table 6.1:BELIEFS OF EFFECTIVE HELPERS
6\. Beliefs about appropriate methods and approaches
6\. Beliefs about appropriate methods and approaches
* Effective helpers are more oriented toward people than toward rules and regulations or things.
* Ppl oriented, client-centered
* facilitate someone through their own choice and be masters of their own environment
* Ppl oriented, client-centered
* facilitate someone through their own choice and be masters of their own environment
24
New cards
Culture
Is the social behaviors and norms found in human societies.
25
New cards
Culture shock
* As the stress experienced when individuals can not meet their everyday needs as they would in their own culture
* what you learn in your own culture does not work in a new culture
* what you learn in your own culture does not work in a new culture
26
New cards
**WHY ARE POPULATION SHIFTS SO IMPORTANT TO HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS?**
Its important to know race and age bc it gives us insight what population we will be working with .
27
New cards
IDEIA – individuals with disabilities education improvement act
An example of the federal government safeguarding the rights for the provision of **culturally competent** care for all children with disabilities.
28
New cards
**Culturally Competent**
* Cultural competence = cultural sensitivity= intercultural communication
* a set of congruent behaviors, attitudes, and policies that come together in a system, agency, or among professionals to work in cross-cultural situations.
* TALK TO YOUR PTS
* research
* continuing learning
* need to be sensitive to a client’s beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors regarding their illness, injury, or disability.
* a set of congruent behaviors, attitudes, and policies that come together in a system, agency, or among professionals to work in cross-cultural situations.
* TALK TO YOUR PTS
* research
* continuing learning
* need to be sensitive to a client’s beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors regarding their illness, injury, or disability.
29
New cards
Belief
What people think is true
30
New cards
Behaviors
What people do.
31
New cards
Attitudes
How people feel about something
32
New cards
Explanatory Model (Kleinman)
* Etiology, the onset of symptoms, pathophysiology, course of sickness, and treatment for the particular problem being addressed.
* On the cultural level, there may be differences between the explanatory model of the family and the explanatory model of the healthcare professional
* enhance our PPI(patient practitioner interactions)
* On the cultural level, there may be differences between the explanatory model of the family and the explanatory model of the healthcare professional
* enhance our PPI(patient practitioner interactions)
33
New cards
PPI
Patient Practitioner Interactions
34
New cards
Three questions a healthcare professional should ask when working with clients to avoid potential biases?
1\. How is this client like all human beings?
2\. How is this client like some human beings?
3\. How is this client like no other human being?
2\. How is this client like some human beings?
3\. How is this client like no other human being?
35
New cards
which one of the following is the best way to use an “I“ statement?
\
* “You don't tell me you're running late.”
* “You were talking to that client for half an hour.”
* “I felt lonely when you did not come home to have dinner with me all week.”
* “You don't tell me you're running late.”
* “You were talking to that client for half an hour.”
* “I felt lonely when you did not come home to have dinner with me all week.”
36
New cards
Collectivistic
* “We“ identity
* high levels of communication
* Group goals
* Surrounding circumstances
* Verbal communication
* strong emphasis on relationships
ex: A fam that takes care of one another
Asia, Africa, Central and South America and Pacific Island Societies
* high levels of communication
* Group goals
* Surrounding circumstances
* Verbal communication
* strong emphasis on relationships
ex: A fam that takes care of one another
Asia, Africa, Central and South America and Pacific Island Societies
37
New cards
High Context Cultures
Collectivistic
38
New cards
Low Context Cultures
Individualism
39
New cards
Individualism
* “I” identity
* individual goals
* management of time
* privacy
* task oriented
ex: CEO of a company
* individual goals
* management of time
* privacy
* task oriented
ex: CEO of a company
40
New cards
The Concept of Face
Maintaining a claimed sense of self-dignity or regulating a claimed sense of self-humility in interaction.
41
New cards
Monochromatic time
Low Context Cultures
set schedule from 9-12 lunch 1-5 dinner
set schedule from 9-12 lunch 1-5 dinner
42
New cards
Polychromic time
high context cultures
Based on human interaction
Based on human interaction
43
New cards
Personal space is perceived as private
Low Context Cultures
44
New cards
Individuals space is frequently shared with subordinates and centralized or shared in an information network.
High Context Cultures
45
New cards
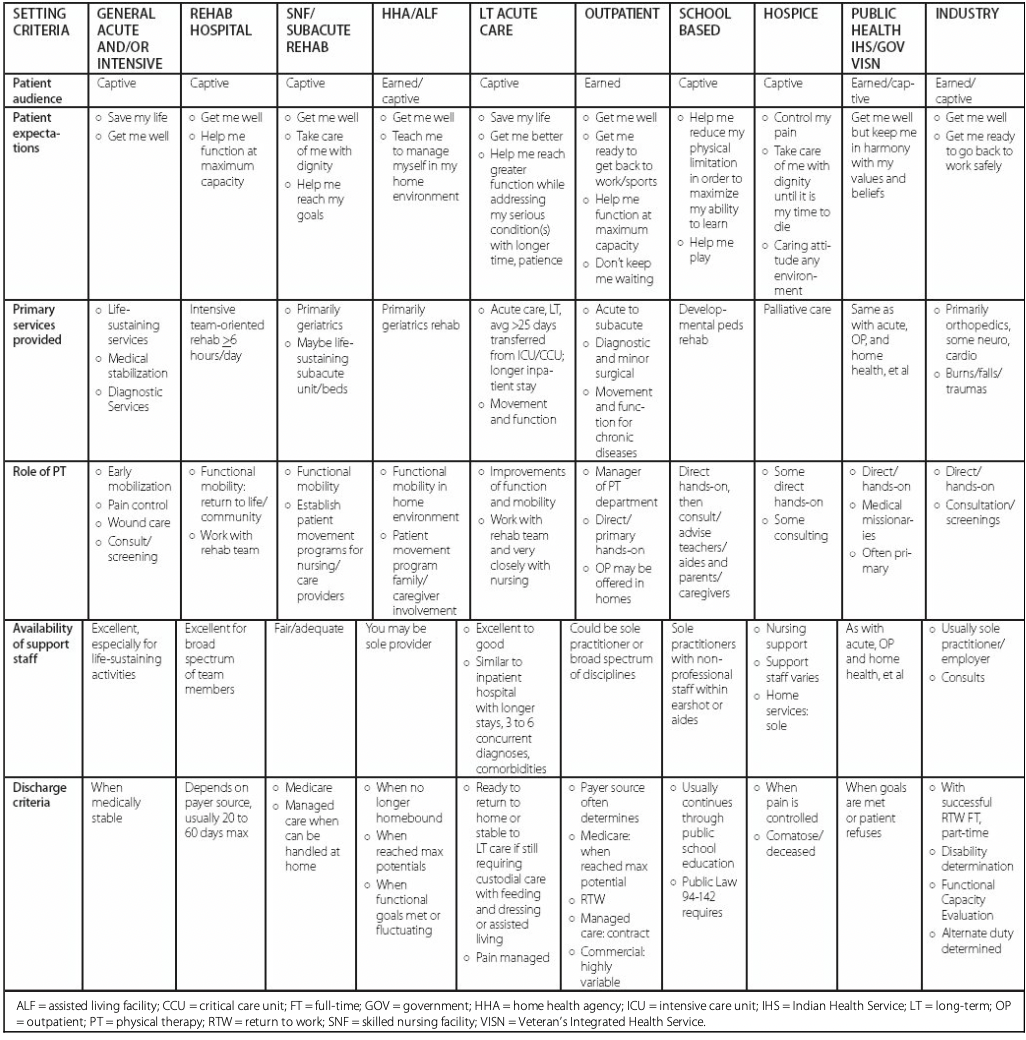
OVERVIEW COMPARISON OF TREATMENT SETTINGS
* General Acute and Or Intensive- save my life
* Rehab Hospital – help me achieve max function
* SNF/Sub acute rehab
* HHA/Assisted Living Facility-
* Acute Care
* School-based-
* Hospice – control my pain
* Outpatient- don’t keep me waiting
* Public Health-
* Industry – get me ready to go back to work
* Rehab Hospital – help me achieve max function
* SNF/Sub acute rehab
* HHA/Assisted Living Facility-
* Acute Care
* School-based-
* Hospice – control my pain
* Outpatient- don’t keep me waiting
* Public Health-
* Industry – get me ready to go back to work
46
New cards
Implicit Meanings in Culture
high context communication the vast majority of the information is already understood,
ex: The supervisor coming to see the facility, everyone knows the deal and behaviors might change.
ex: the concept of awkward silence
ex: The supervisor coming to see the facility, everyone knows the deal and behaviors might change.
ex: the concept of awkward silence
47
New cards
Nonverbal communication
These include gestures, positioning of the body, and tenseness of the facial expressions.
48
New cards
Personalismo
Getting to know the healthcare professional as a person and helps establishing rapport
49
New cards
Somatization
Reporting physical symptoms when a person is experiencing psychological distress. Bc in some cultures where complaints of anxiety, worries, and depression are perceived as signs of weakness.
50
New cards
Six Universal Aspects of Healthcare In All Cultures
1. Healthcare specialist @@applies a name to a problem@@
2. The qualities of a healthcare professional are important. @@The professional must be perceived as caring, competent, approachable,@@ and concerned with identifying and finding solutions to the problem
3. The healthcare @@professional must establish credibility@@ through the use of symbols and trappings of status that are familiar to the culture.
4. The practitioner places @@the client’s problems in a familiar framework.@@ \*\*(this implies recognition of the client’s explanatory model by the practitioner).
5. The healthcare @@practitioner applies a set of techniques@@ meant to bring relief.
6. Interactions between the client and @@practitioner occur at a special time and place.@@
51
New cards
**Language assistance services**
* The patients preferred language in writing and verbally offer language assistance services at no cost to each patient consumer with limited English proficiency.
* Research demonstrated using professional interpreter services significantly increases satisfaction with patient-provider communication.
* Research demonstrated using professional interpreter services significantly increases satisfaction with patient-provider communication.
52
New cards
Spirituality as Culture and Health Care
* Spirituality is a basic human experience.
* Connection with other people and environment
* Literature suggests that spirituality/ religion are linked with health outcomes
\
* Connection with other people and environment
* Literature suggests that spirituality/ religion are linked with health outcomes
\
53
New cards
What causes a disability?
* Learning disability
* Amputation
* Schizophrenia
* Paralysis
* Pain
* Bipolar
* Amputation
* Schizophrenia
* Paralysis
* Pain
* Bipolar
54
New cards
The Power of Words
* We need to remember real people have these disorders.
* Language is a powerful symbol. It demonstrates our understanding of concepts
* Language influences beliefs, attitudes, expectations, and the course of events.
* Language is a powerful symbol. It demonstrates our understanding of concepts
* Language influences beliefs, attitudes, expectations, and the course of events.
55
New cards
Results of Labeling
* a negative stigma
* dehumanization
* disempower
* physical barriers
* dehumanization
* disempower
* physical barriers
56
New cards
Active Vs. Passive tense
•“being confined to a wheelchair
•Using a wheelchair
•Using a wheelchair
57
New cards
Being Vs. Having
•Being a quadriplegic
•Person who has quadriplegia
•Person who has quadriplegia
58
New cards
**Disability**
A condition of the person.
59
New cards
**Handicapped**
Used to describe the accrued result of multiple barriers (emotional physical social environments) imposed by society which prevents an individual in assuming a desired role in society.
60
New cards
ICF
Framework that incorporates health conditions and their effects as well as environmental factors.
61
New cards
Aging with A Disability
•Life expectancy of persons with a disability have increased.
•Age related changes combined with the factors of a disability can lead to long term disabilities
•Asking clients questions about their daily routines habits and patterns can aid in identifying a secondary condition before it becomes a serious threat.
•^^How are you sleeping?^^
^^•Any pain?^^
^^•Feeling tired?^^
•Age related changes combined with the factors of a disability can lead to long term disabilities
•Asking clients questions about their daily routines habits and patterns can aid in identifying a secondary condition before it becomes a serious threat.
•^^How are you sleeping?^^
^^•Any pain?^^
^^•Feeling tired?^^
62
New cards
Secondary Conditions
Persons with disability are more likely to report additional conditions.
ex:
•Chronic Pain
•Muscles spasms
•Depression
•Anxiety
•Isolation
ex:
•Chronic Pain
•Muscles spasms
•Depression
•Anxiety
•Isolation
63
New cards
**Healthy People 2030**
•**Vision**
A society in which all people can achieve their full potential for health and well-being across the lifespan.
•**Mission**
To promote, strengthen, and evaluate the nation’s efforts to improve the health and well-being of all people.
•**Foundational Principles**
The following foundational principles guide decisions about Healthy People 2030:
A society in which all people can achieve their full potential for health and well-being across the lifespan.
•**Mission**
To promote, strengthen, and evaluate the nation’s efforts to improve the health and well-being of all people.
•**Foundational Principles**
The following foundational principles guide decisions about Healthy People 2030:
64
New cards
OT Implications
•Raise awareness
•Recognize perceptions and biases
•You are obligated to recognize the abilities of all people.
•Be aware of the influence of your language and general presence
•Recognize perceptions and biases
•You are obligated to recognize the abilities of all people.
•Be aware of the influence of your language and general presence
65
New cards
Ethics
study of moral behavior
66
New cards
Moral Decisions
right Vs. Wrong
67
New cards
Descriptive Statistics \n
morals of a group or culture
68
New cards
Normative Ethics
Establishing a moral system
69
New cards
ETHICAL DECISION-MAKING IN THE 21ST CENTURY
* Changing health care/human service environments require efficiency, competence, attention to functional outcomes
* Services are commonly provided in fast paced environments – attn. to bottom line
* Need for competence performing multiple tasks and solving multiple problems quickly
* Departments are often small - limited peer interaction/ supervision
* Services are commonly provided in fast paced environments – attn. to bottom line
* Need for competence performing multiple tasks and solving multiple problems quickly
* Departments are often small - limited peer interaction/ supervision
70
New cards
Ethical issues
Situations which one believes to have moral challenges
71
New cards
Ethical analysis
helps identify issues and conflicts between values (often reflect personal, institutional; professional values)
* ex: Code of Ethics, Contracts, policies, etc.
* ex: Code of Ethics, Contracts, policies, etc.
72
New cards
Value based care
Pt. has to actually make progress → Outcomes
(replacing RUGs)
(replacing RUGs)
73
New cards
How can staff skills impact decision making?
* Here is my practice act(therefore I cannot do this)
* Give me continuing education credits to do this with further pts.
* Give me continuing education credits to do this with further pts.
74
New cards
**Ethical problems**
1. Ethical temptations
2. Ethical Distress
1. Ethical temptations
2. Ethical Distress
1. know what to do but you may stand to benefit and don’t want to do the right thing.
2. know what you have to do but may be constrained
75
New cards
Ethical Dilemmas
Deal with which is better or worse
76
New cards
4 behaviors that are progressively developmental required for mature moral/ ethical decision making
1. Moral sensitivity – know how you impact others
2. Moral judgment – what is right or wrong
3. Moral motivation – prioritizing moral vs. Personal values
4. Moral Character – implementation skills
77
New cards
ethical situation
situation that requires an ethical compass but not to a high degree
78
New cards
What PRESSURES TO COMMIT UNETHICAL BEHAVIORS
* Value- based care
* Healthcare reform
* Patient demands
* Payer demands
* Financial burdens
* Heavy work load
* Staff skills
* Lack of resources
* Healthcare reform
* Patient demands
* Payer demands
* Financial burdens
* Heavy work load
* Staff skills
* Lack of resources
79
New cards
NOK
Next of Kin
80
New cards
DME
Durable medical equipment
81
New cards
How to access an ethical dilemma ?
1. ETHICAL COMPONENT
2. CODE OF ETHICS
3. TRY TO FIGURE OUT WHAT WILL GIVE YOU THE MOST ETHICAL OUTCOME
82
New cards
**Compassion fatigue (CF)**
has been defined as the lessening of one’s ability to empathize due to exposure to trauma and suffering.
83
New cards
Compassion fatigue : SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
* short
* procedural
* count your time
* not the best listener
* don’t see the bigger pic
* resp filled with emotion
* procedural
* count your time
* not the best listener
* don’t see the bigger pic
* resp filled with emotion
84
New cards
positive stress
can result from having many opportunities
ex: too many job offers
ex: too many job offers
85
New cards
negative stress
an result from an inability to solve a problem
86
New cards
Stress developmental model
Life situation → Perception → Emotion → Physiological Response → Disease
87
New cards
Perception
Can dictate your world concept , world view
88
New cards
Burnout
Is a state of emotional and physical exhaustion that results from intense and long standing professional stress
89
New cards
Burnout signs and symptoms:
* You may start with enthusiasm and optimism and then realize the demands of your job exceed your expectations.
* Detachment
* Drawing sharp boundaries between work and home
* Withdrawal
* Less creative treatment sessions
* By the book responses
* Less time spent with patients/ people
* Engaging in compulsive behaviors
* Applying for other jobs
* Headaches
* Stomach aches
* Detachment
* Drawing sharp boundaries between work and home
* Withdrawal
* Less creative treatment sessions
* By the book responses
* Less time spent with patients/ people
* Engaging in compulsive behaviors
* Applying for other jobs
* Headaches
* Stomach aches
90
New cards
Causes of Burnout
* Workload
* Understaffed
* Overload of same type of conditions
* Unable to be creative due to lack of time
* Role Ambiguity
* Unclear job description
* Unclear job expectations
* Role Conflict
* Large team with minimal communication
* physicians may make choices about care without the input from other health care professionals
* The professionals self esteem
* Inability to set clear boundaries with patients or staff
* New grads tend to set unrealistic optimistic goals for patients and then fail to meet them
* Understaffed
* Overload of same type of conditions
* Unable to be creative due to lack of time
* Role Ambiguity
* Unclear job description
* Unclear job expectations
* Role Conflict
* Large team with minimal communication
* physicians may make choices about care without the input from other health care professionals
* The professionals self esteem
* Inability to set clear boundaries with patients or staff
* New grads tend to set unrealistic optimistic goals for patients and then fail to meet them
91
New cards
Burnout Intervention
* Stay present/ stay in the now
* Having a realistic perspective
* Ask clarifying questions
* Lowering staff to patient ratios
* Doing less stressful tasks (reading journal articles, planning patient research, student education) allows one to limit intense interactions.
* Required vacation time
* Reg staff rotations (gaining variety)
* Taking your lunch break away from patient care areas
* Having a realistic perspective
* Ask clarifying questions
* Lowering staff to patient ratios
* Doing less stressful tasks (reading journal articles, planning patient research, student education) allows one to limit intense interactions.
* Required vacation time
* Reg staff rotations (gaining variety)
* Taking your lunch break away from patient care areas
92
New cards
Teaching
the process of instructing by precept, example, or experience
\
\
93
New cards
Learning
* A process where there is change in a subjects behavior to a given situation brought about by his repeated experience in that situation.
* through change in a persons verbal and non verbal behavior.
* through change in a persons verbal and non verbal behavior.
94
New cards
1. The Principles of Learning(Culture)
1\. Learning is influenced by the individuals inherent capacities, current assets and limitations, age, sex, interest, past and present culture group membership.
ex:
* teaching a baby to brush their teeth vs for adults
* culture:
\
ex:
* teaching a baby to brush their teeth vs for adults
* culture:
\
95
New cards
2. The Principles of Learning(distractions)
2\. Attention and perception influence learning
* *Make the environment minimally distracting*
* *Learners perceptions can be based on their past experiences*
* *Why must you consider this principle when facilitating learning.*
* learning in a loud env vs. quiet
* *Make the environment minimally distracting*
* *Learners perceptions can be based on their past experiences*
* *Why must you consider this principle when facilitating learning.*
* learning in a loud env vs. quiet
96
New cards
3. The Principles of Learning(motivate)
3\. The learners motivation is important.
* *Motivation is an internal process.*
* *Motivation to achieve goals*
* *The teacher will attempt to determine the clients source of motivation*
* facillate motivation is essential to achieve goals
* *Motivation is an internal process.*
* *Motivation to achieve goals*
* *The teacher will attempt to determine the clients source of motivation*
* facillate motivation is essential to achieve goals
97
New cards
4. The Principles of Learning(CC)
4\. Learning goals set by the individual are more likely to be attained than goals set by someone else.
* *Client-centered*
* *client focused attention*
* *Active participation is the goal setting process*
* doing something you want vs. what someone else wants
* *Client-centered*
* *client focused attention*
* *Active participation is the goal setting process*
* doing something you want vs. what someone else wants
98
New cards
5. The Principles of Learning(why)
5\. Learning is enhanced when the individual understands what is to be learned and the reason for learning.
* *The therapist will describe what the client should learn and why they are being encouraged to learn this information.*
* *The therapist will describe what the client should learn and why they are being encouraged to learn this information.*
99
New cards
6. The Principles of Learning(DT)
6\. Learning is increased when it begins at the individual’s current level and proceeds at a rate that is comfortable for the individual.
* *Meet the client at their current level*
* *Evaluation will allow an OT to determine a client’s capabilities*
* **development theory** : working on current level of client
\
* *Meet the client at their current level*
* *Evaluation will allow an OT to determine a client’s capabilities*
* **development theory** : working on current level of client
\
100
New cards
7. The Principles of Learning(A/B)
7\. Active participation in the learning process facilitates learning
* Active participation includes
* **(A)** Learning through discovery
* *Learning about something that was previously unknown.*
* *Or they can lead to frustration, lack of learning*
* *If done right cant promote curiosity*
* (**B)** Learning through doing
* *Gaining skills through involvement*
* Active participation includes
* **(A)** Learning through discovery
* *Learning about something that was previously unknown.*
* *Or they can lead to frustration, lack of learning*
* *If done right cant promote curiosity*
* (**B)** Learning through doing
* *Gaining skills through involvement*