Particles
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Particle Zoo
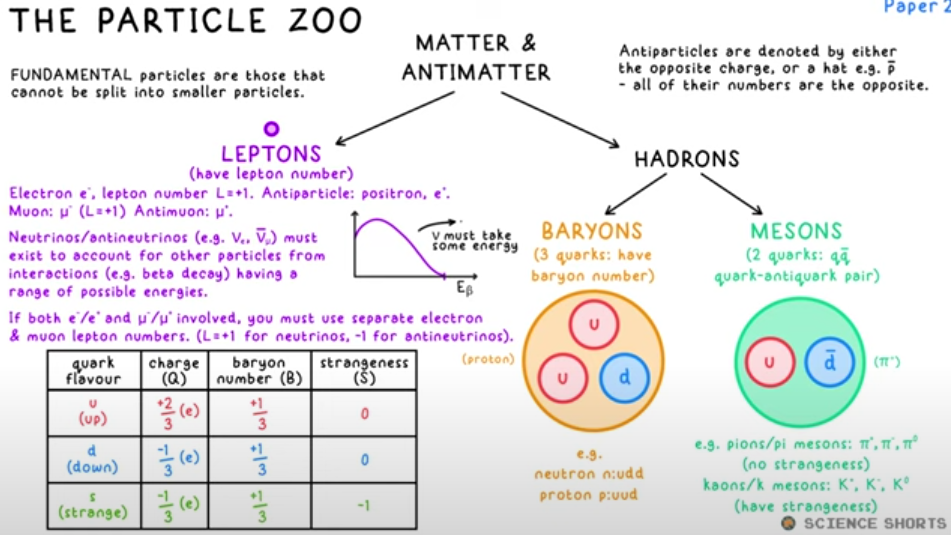
Leptons
Fundamental particles
E.g: Electron, muon, neutrino
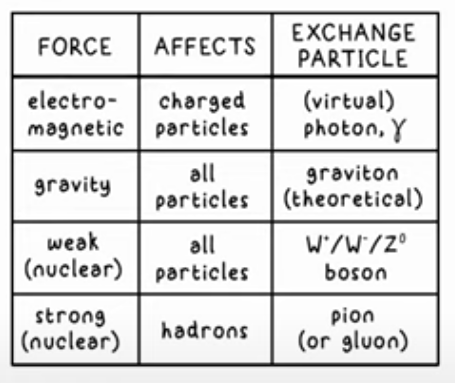
Particle Forces
There are 4 fundamental forces in the universe, each mediated by an exchange particle, whose role it is to carry the force between the particles
Neutrino and Antineutrino
These leptons must exist to account for other particles from interactions having a range of possible energies-
Strong Nuclear Force
Responsible or keeping nucleons together in a nucleus
When this strong force is in balance with the repulsive EM force between protons, the nucleus is stable
Conservation Rules
Charge Q, Baryon number B and Lepton number L must all be conserved in any interaction
Alpha Decay
Occurs in larger nuclei
Nucleus ejects Helium nucleus (2 protons + 2 neutrons)
Larger nuclei → Helium Nucleus + Smaller Nuclei
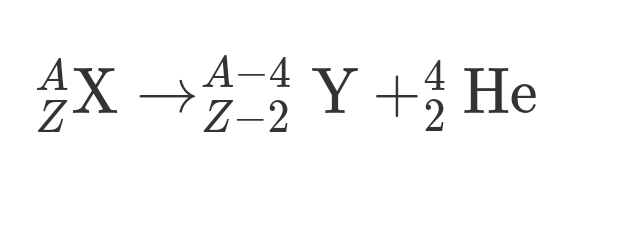
Beta Decay
Occurs in smaller nuclei
A neutron decays into a proton + electron
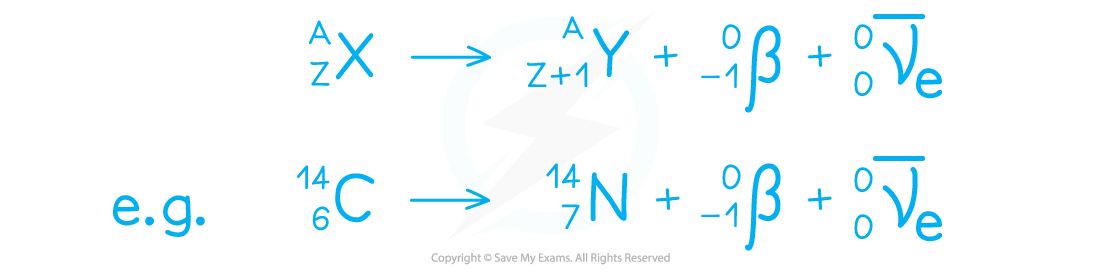
Gains proton, but mass is unchanged
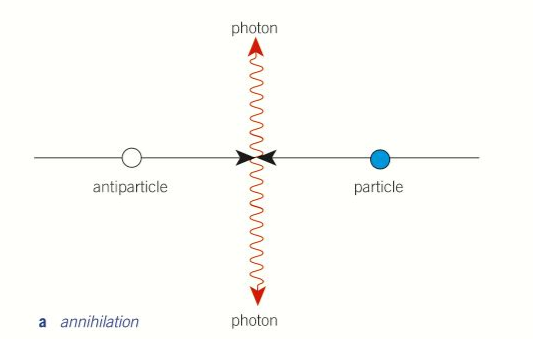
Annihalation
The result of a particle and its respective antiparticle meeting. All mass is converted to energy in the form of two photons
Einstein’s Theory of relativity
E = mc2
E = rest energy (J)
m = mass (kg)
c = speed of light (3.0 × 108 ms-1)
Minimum Energy of photons
2mc2 = 2hf
Pair Production
When a photon of sufficient energy is converted to its particle and antiparticle
Minimum frequency of photon required or pair production
hf = 2mc2
Energy levels
Specific, discrete levels of energy that electrons can take
Electrons can be excited to higher energy levels by
Colliding with a free electron
Absorbing a photon of energy equal to the difference in energy (all others will pass through)
De-excitation
When an electron drops in energy level back to the ground state, emitting photons.
Since E = hf = hc/λ, the bigger the drop in energy, the higher the frequency and the shorter the wavelength
If the incoming photon or free electron has enough energy, the electron can reach the ionisation level, causing it to leave the atom, leaving behind a positive ion
Electronvolt
1 eV = 1.6×10-19J