Sikhism (Updated)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
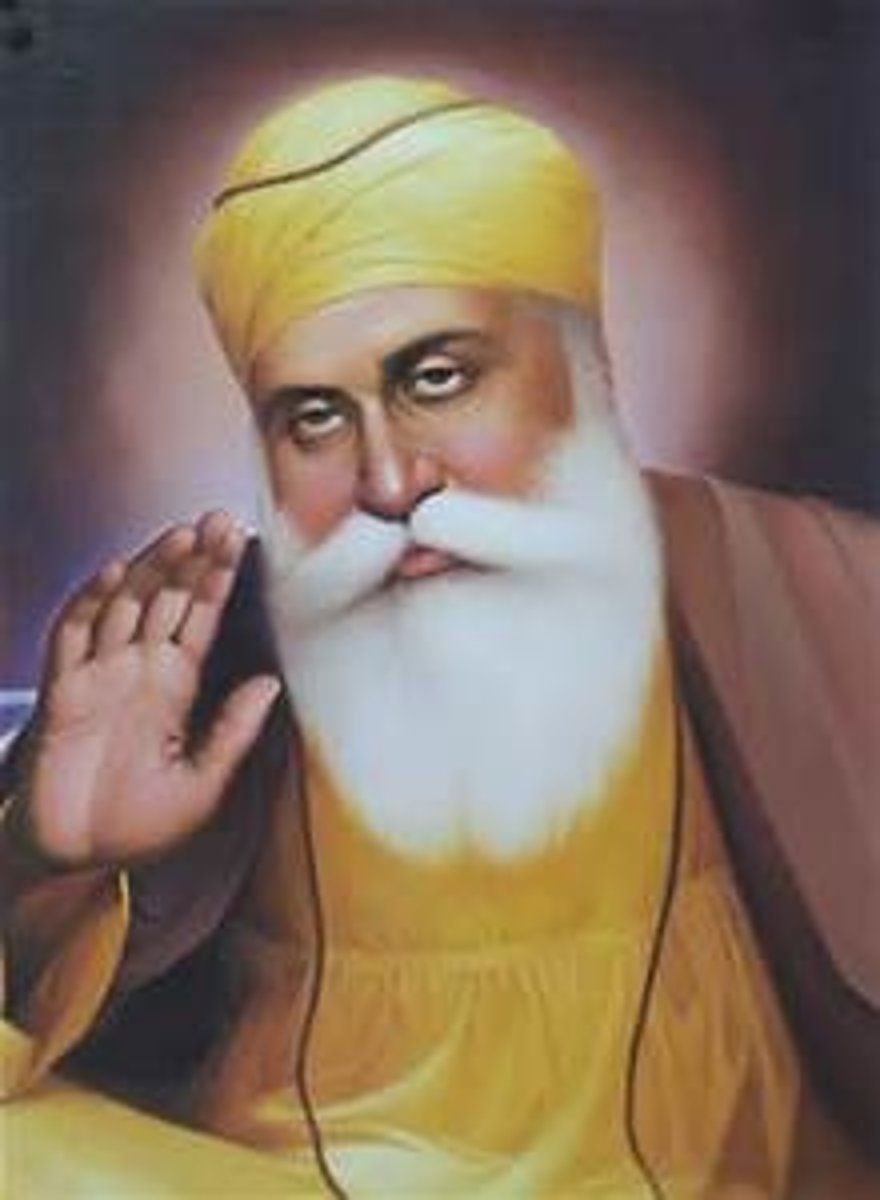
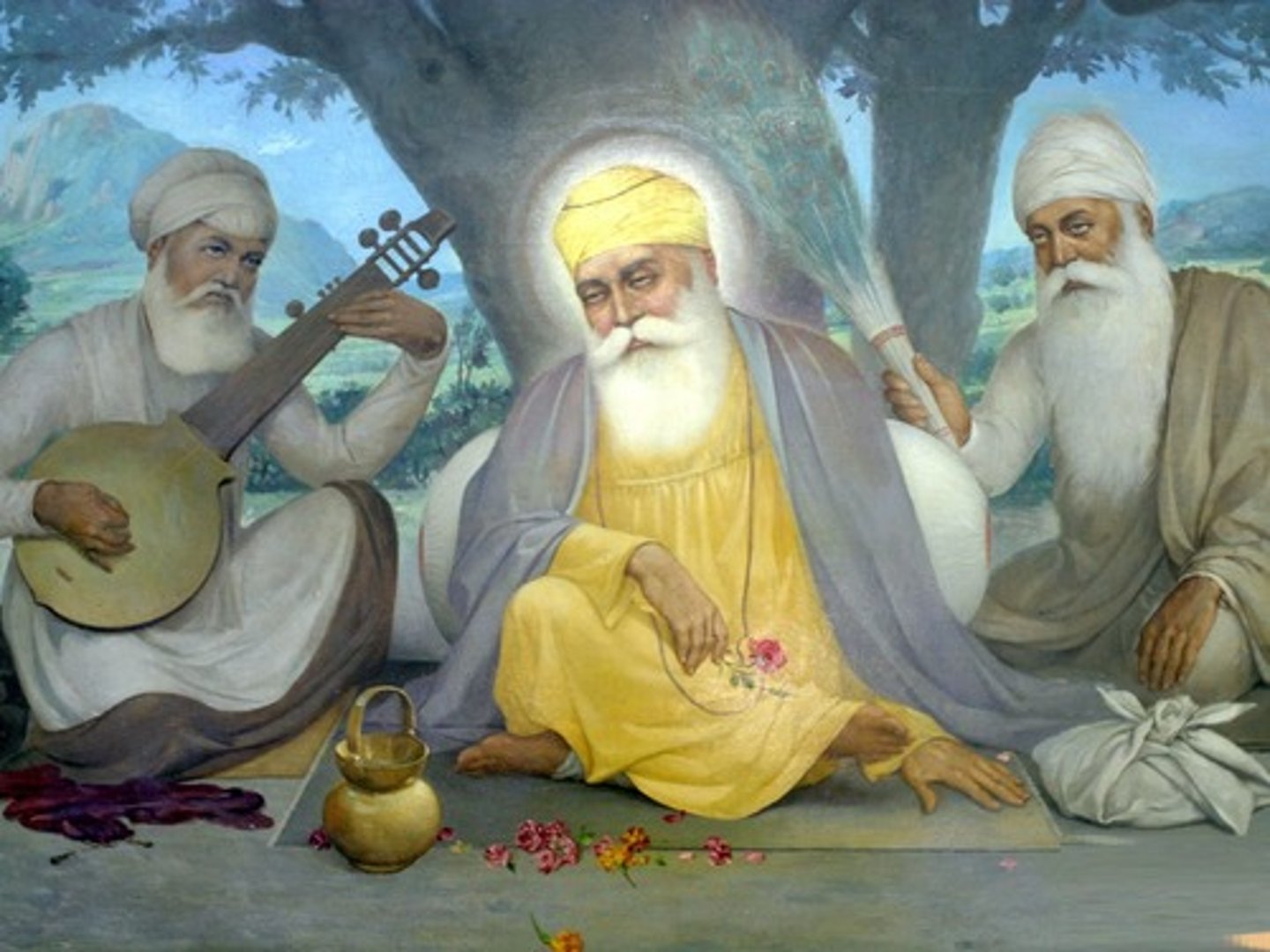
Who is Guru Nanak?
This is the first of the ten living Sikh Gurus and founder of Sikhism. He was born in the Punjab province of what is now Pakistan in 1469 and died in 1539. At the age of 30 he had a transcendent religious experience.

What is Ik Onkar?
These are the first words of the Mool Mantar, which mean "There is one God" or "There is one reality."

What is the Mool Mantar?
These are the opening words of the Guru Granth Sahib. Eleanor Nesbitt translates them as "There is one god, named truth, the creator, without fear, without hate, timeless in form, beyond birth, self-existent, (known by) the grace of the Guru."

What are the Three Pillars of Sikhism?
These are the foundational beliefs of Sikhism: naam japna, kirat karni, and vand chakna.

What is naam japna?
This is the continual external meditation on God's name.
What is kirat karni?
This is the emphasis on earning an honest living.
What is vand chakna?
This is the practice of sharing one's wealth and resources with the community.
What is naam simran?
This is the inner meditation on God's name and essence.

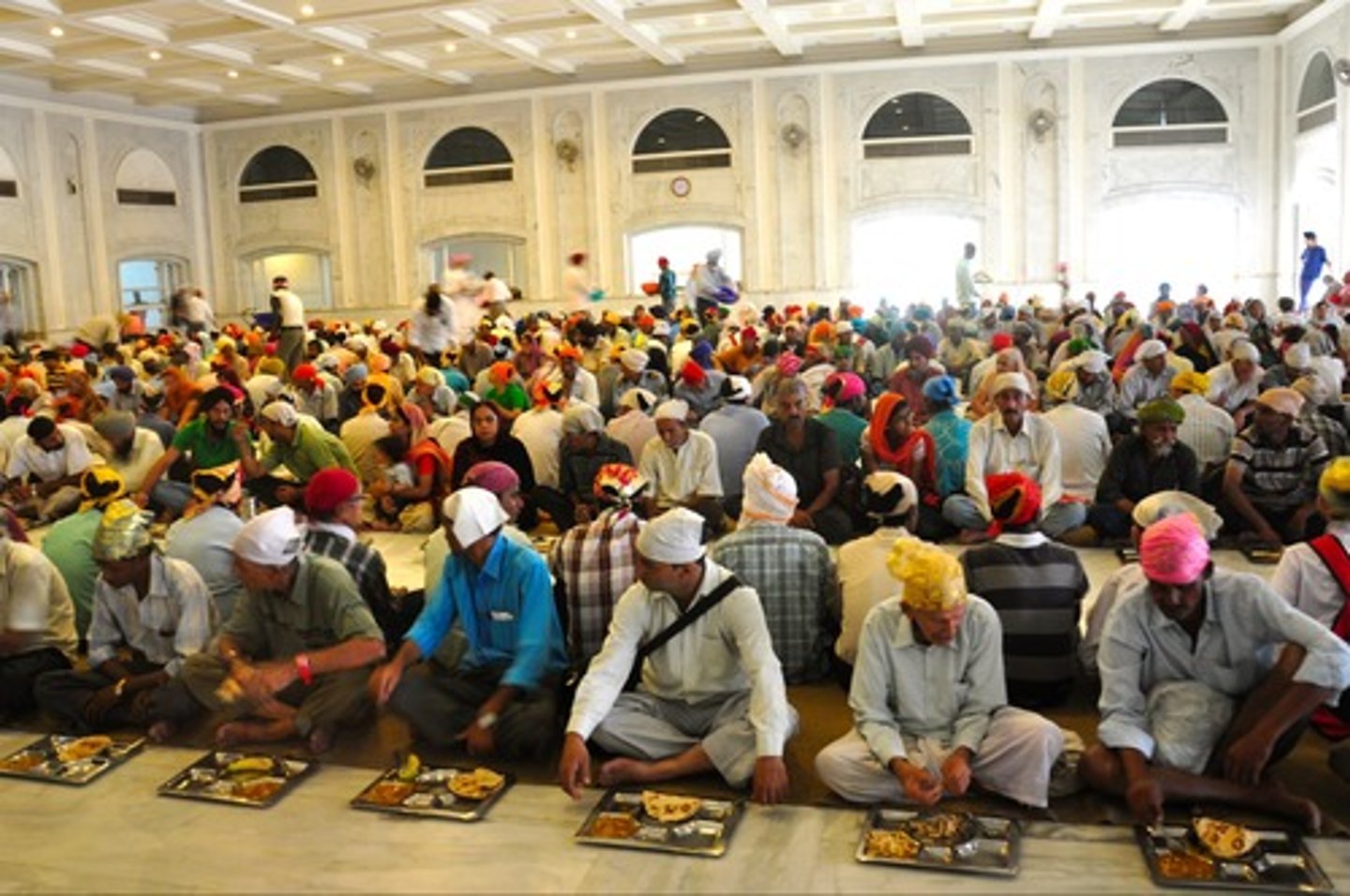
What is a langar?
This is a communal meal shared across all boundaries (racial, ethnic, linguistic, religious, gender, etc.) at a gurdwara.

What is the Adi Granth?
This sacred scripture was the precursor to the Guru Granth Sahib, which was compiled by Guru Arjan in 1604 in the Gurmukhi script, primarily in Punjabi.

What are the Five Ks?
These were established by Guru Gobind Singh in 1699 in order to unify and distinguish the members of the Khalsa. They include the following: (1) kesh (uncut hair); (2) kangha (comb); (3) kirpan (sword); (4) kachera (cotton shorts); and (5) kara (steel or iron bangle).

What is the Guru Granth Sahib?
This is the sacred scripture of Sikhism written down by the Gurus in the Gurmukhi script, primarily in Punjabi. Guru Gobind Singh finalized the scripture and declared it to be the eleventh, final, and eternal Guru in 1708 as he neared his death.

What is Baisakhi?
This is the Sikh harvest festival that also marks the day in which Guru Gobind Singh formed the Khalsa in 1699. It is celebrated on April 13th/14th.
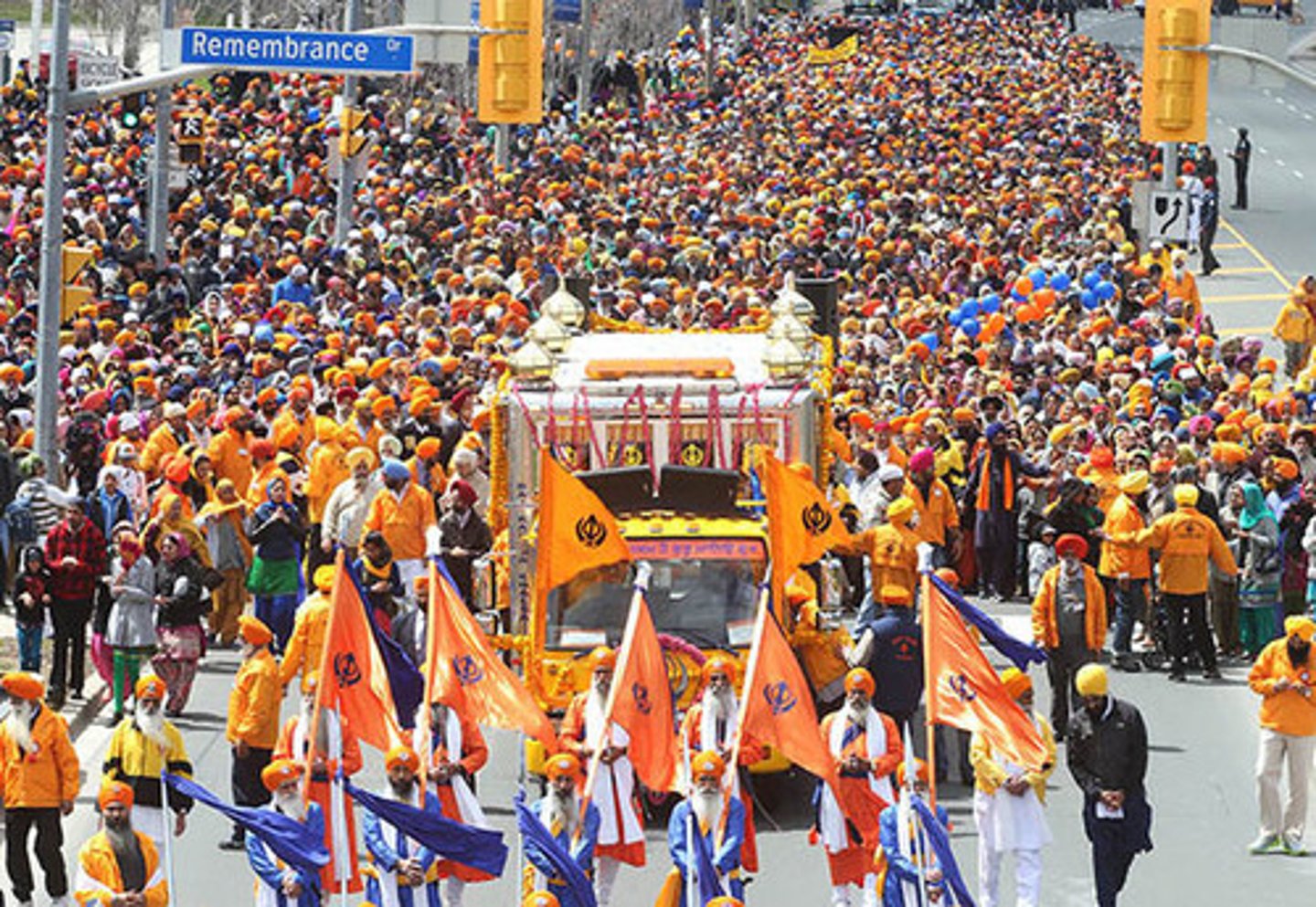

What is the Khalsa?
This was created in 1699 by Guru Gobind Singh to signify that a Sikh was prepared to fully dedicate himself or herself to the Sikh way of life outlined by the ten living Gurus and the Guru Granth Sahib.
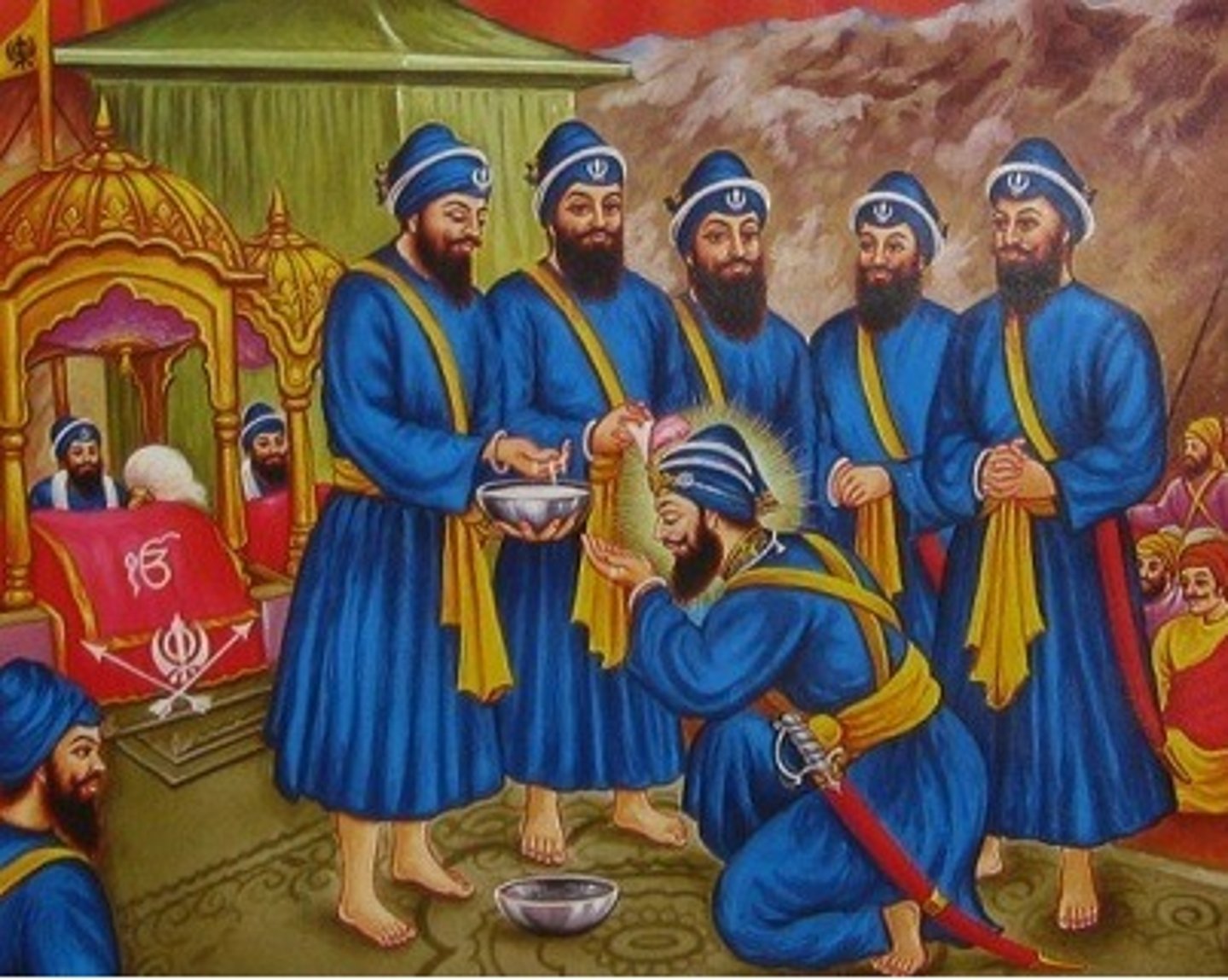

Who are the Panj Pyare?
Known as the Beloved Five, these were the first five Sikhs to be initiated as members of the Khalsa in 1699.

What is Punjab?
This is a state in northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is the birthplace of Guru Nanak and Sikhism. The majority of the world's Sikhs (30 million) live here.
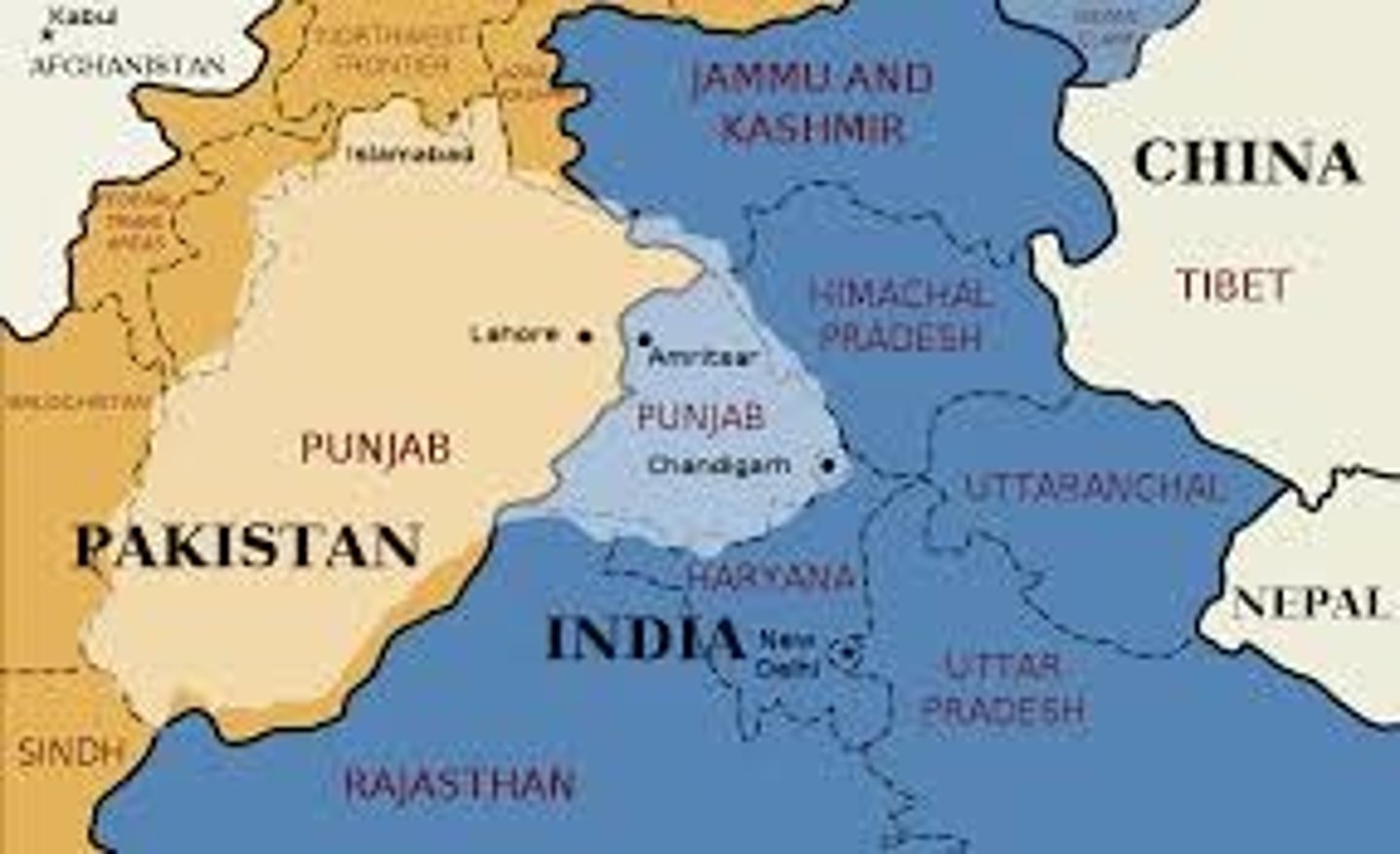
What is an ethnoreligion?
This is a religious community that is closely associated with a particular ethnic group, language, and geographic location. Although Sikhism is intimately connected to the Punjab, Punjabi language, and Punjabis, nevertheless, Sikhism is open to all people.

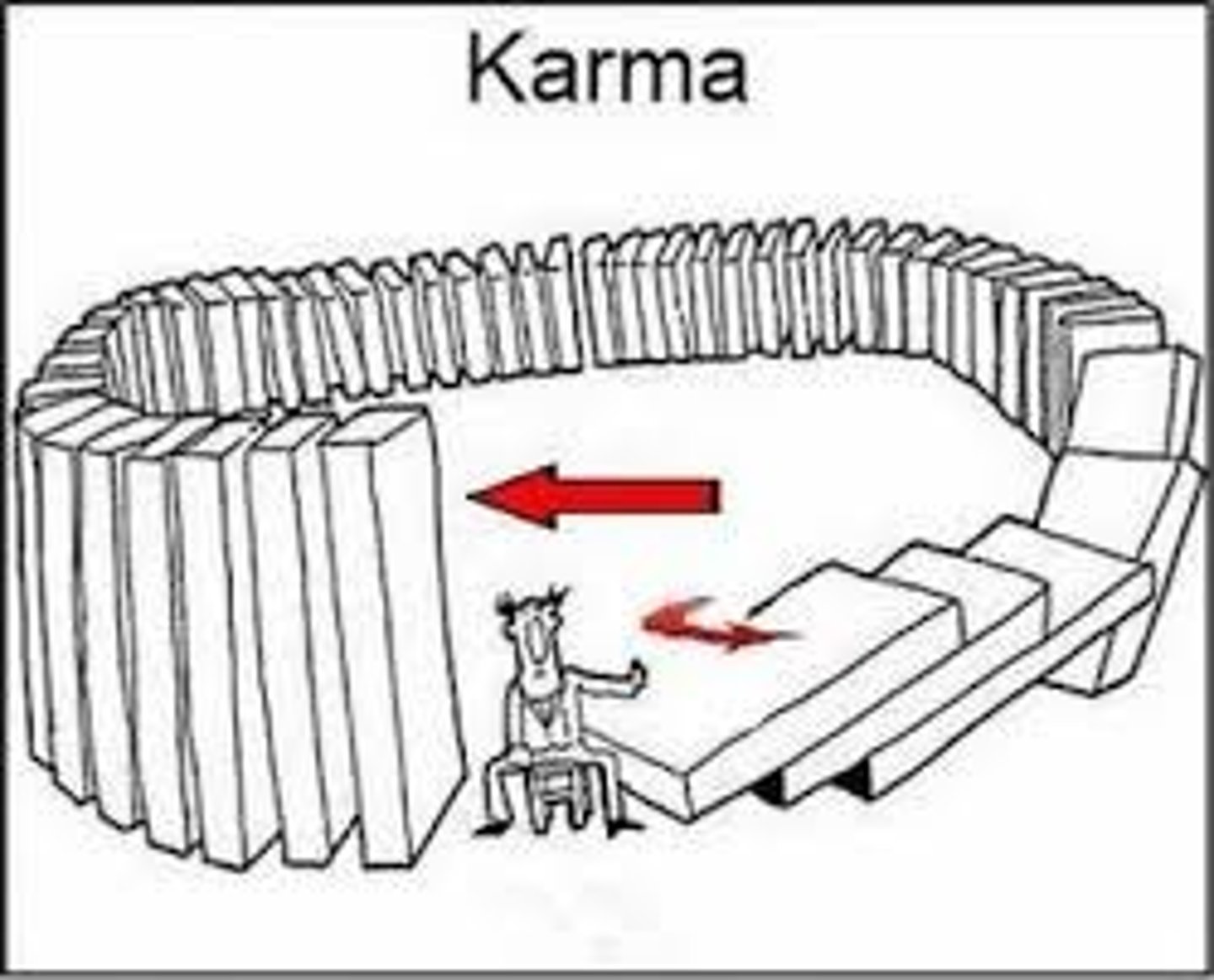
What is karma?
This is the belief that one's actions in life, whether good or bad, will affect your place in a future life.
What is dharma?
Unlike Hinduism's caste-based understanding of this, Sikhism preaches a universal, shared moral duty for all of humanity.

What is samsara?
This is the nearly endless cycle of life, death, and rebirth in Sikhism.

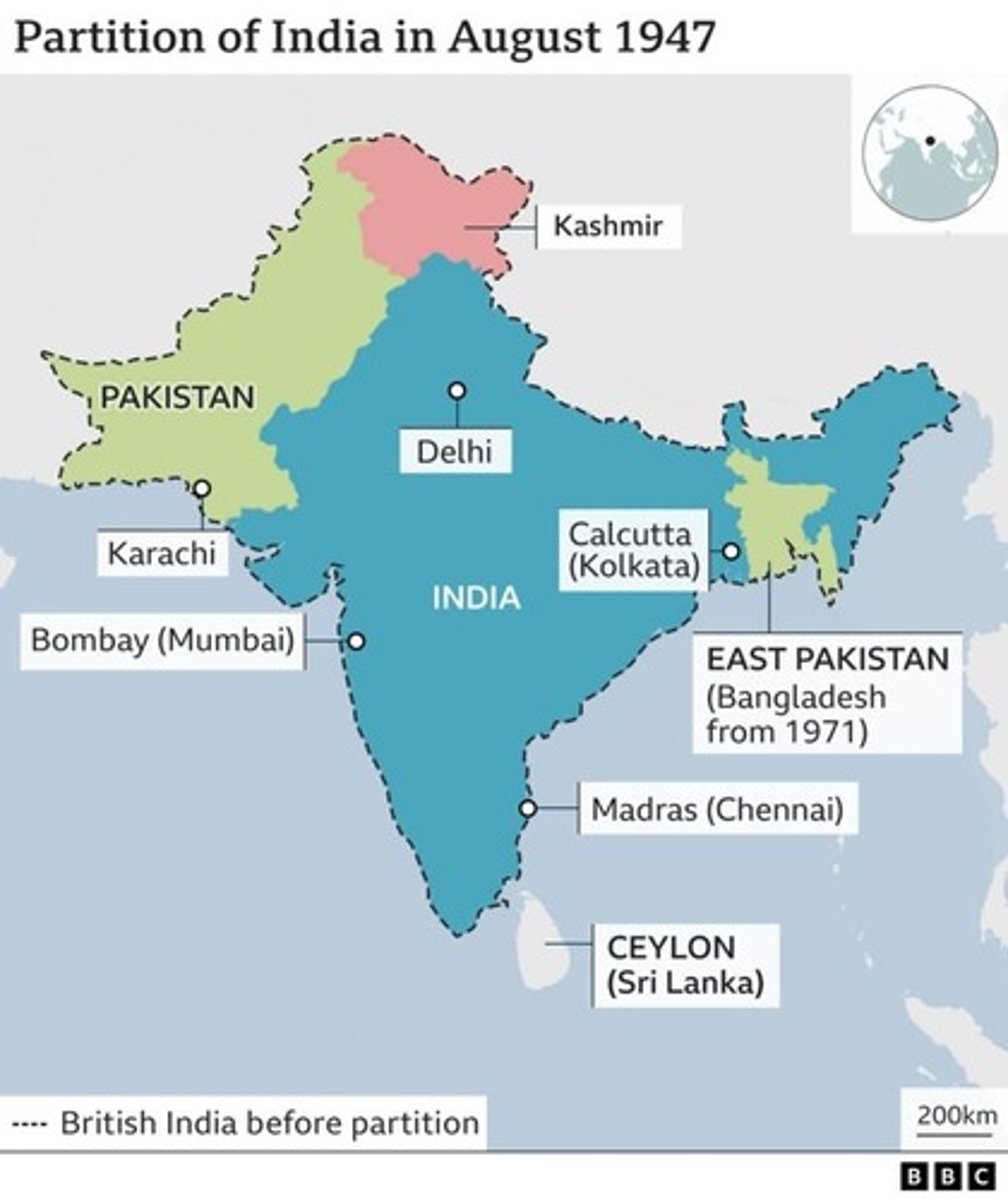
What is the partition of India and Pakistan?
On account of this, the state of Punjab, was split between the new nations of "Muslim" Pakistan and "Hindu" India.
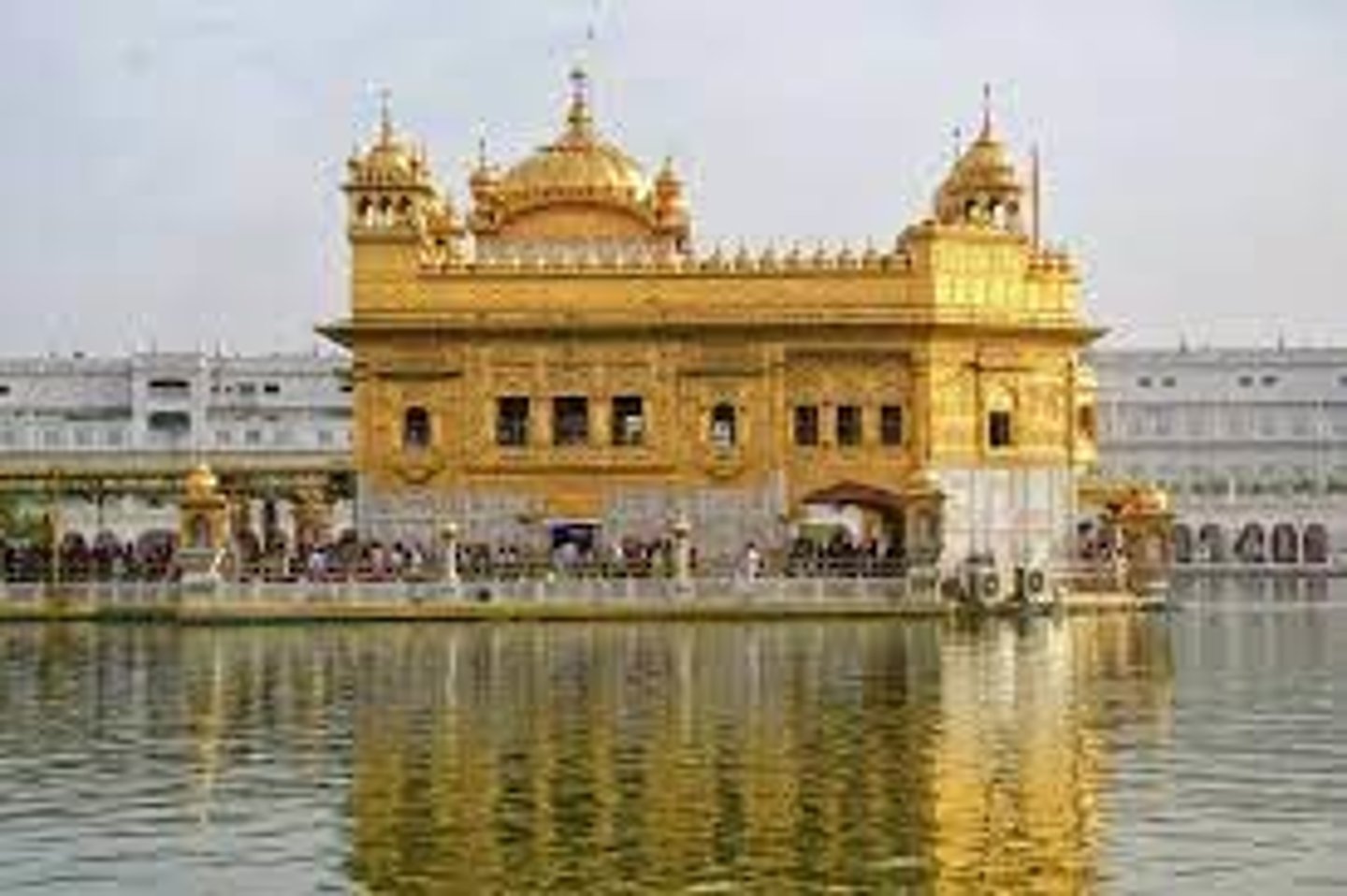
What is the Golden Temple?
Known as the Harmandir Sahib or House of God, this is holiest gurdwara in Sikhism. It is located in Amritsar, India and was consecrated in 1604 by Guru Arjan.

What is guru?
This is Sanskrit for teacher.

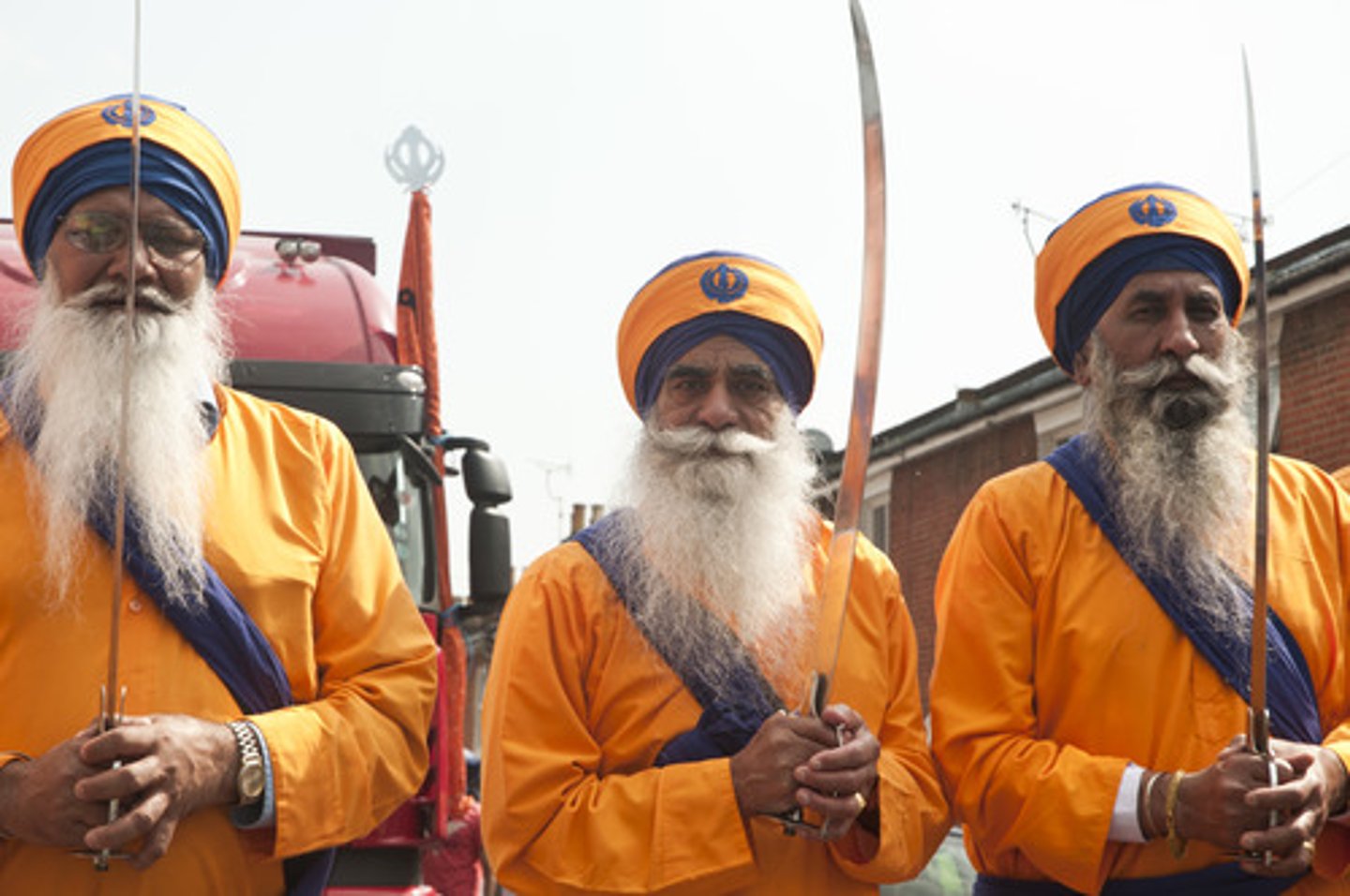
What is Sikh?
This is Punjabi for student.

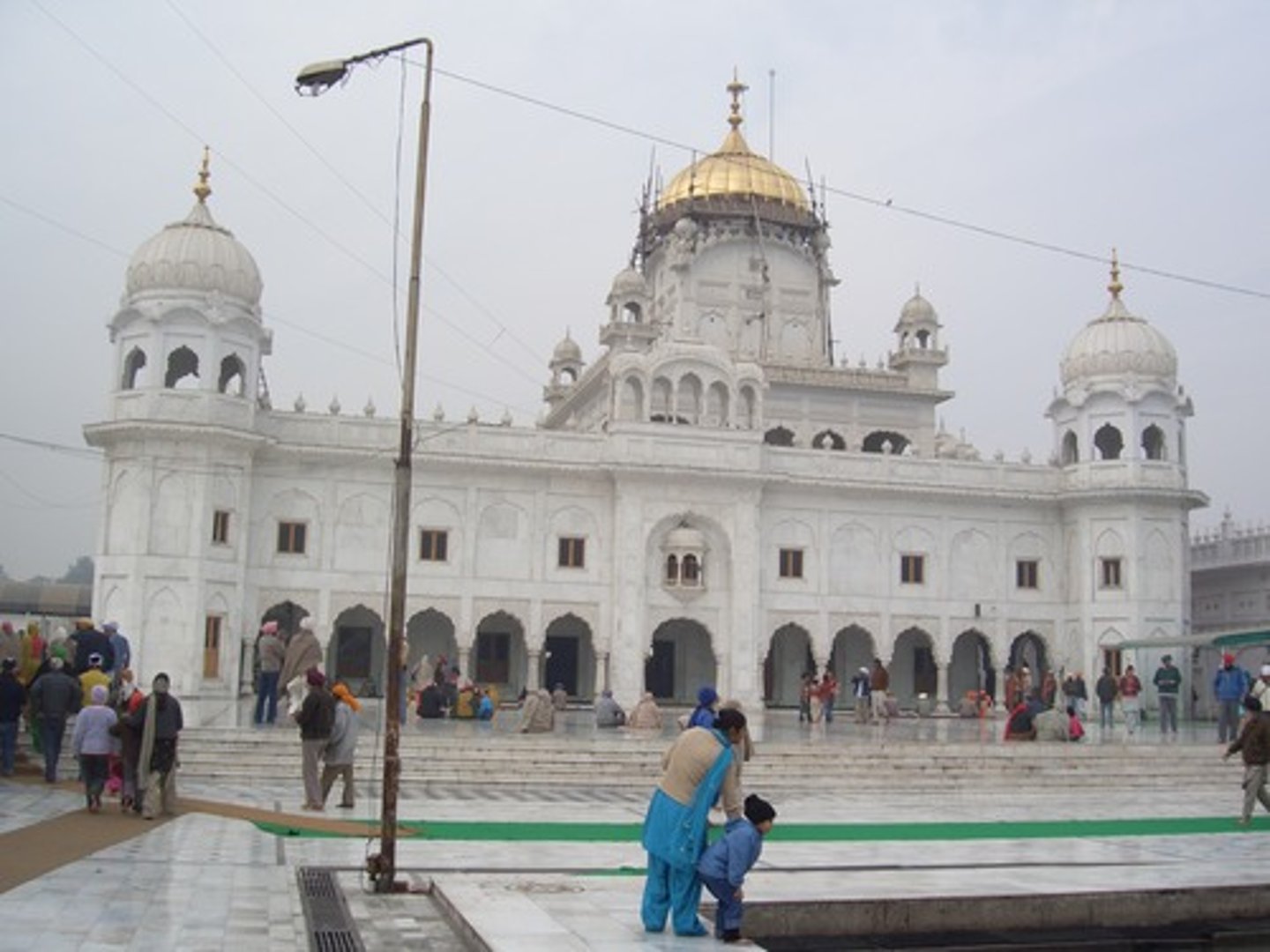
What is a gurdwara?
This is a Sikh place of worship.

Who is Waheguru?
This is the name of God in Sikhism.

What is nirguna?
This is the ineffable, transcendent nature of God.

What is sarguna?
This is the immanent, manifest nature of God.
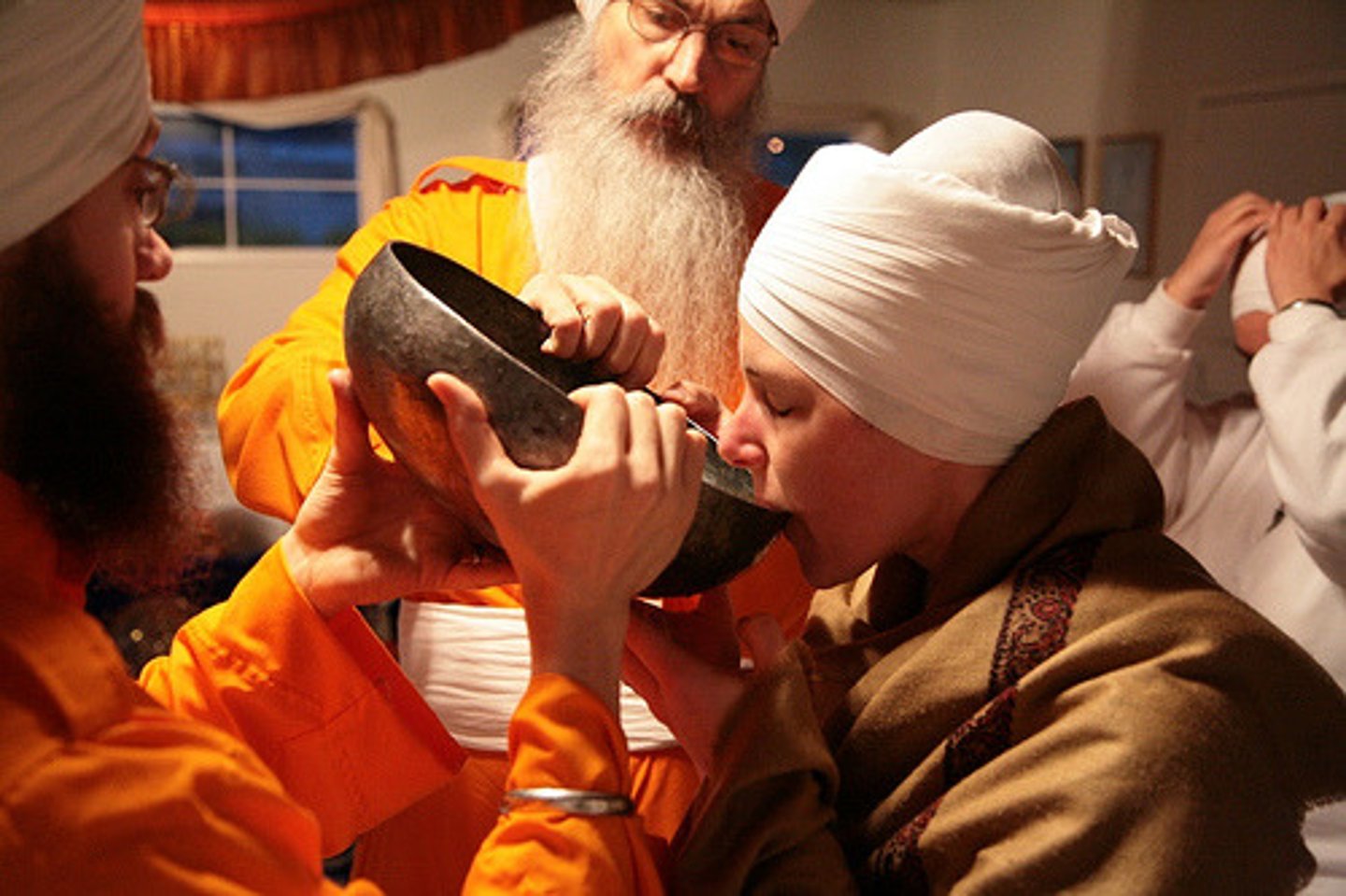
What is amrit?
This is the sugar water that is prayed over and stirred during initiation into the Khalsa. It is considered a type of baptismal water.

What is katha?
This is an exposition, analysis, and discussion of a passage from the Guru Granth Sahib. It is somewhat equivalent to a Christian sermon.

What is singh?
Literally meaning lion, this is the name given to every baptized male.

What is kaur?
Literally meaning princess, this is the name given to every baptized female.

Who are the Sikh Gurus?
(1) Guru Nanak (1469-1539)
(2) Guru Angad (1504-1552)
(3) Guru Amar Das (1479-1574)
(4) Guru Ram Das (1534-1581)
(5) Guru Arjan (1563-1606) (executed)
(6) Guru Hargobind (1595-1644)
(7) Guru Har Rai (1630-1661)
(8) Guru Har Krishan (1656-1664)
(9) Guru Tegh Bahadur (1621-1675) (executed)
(10) Guru Gobind Singh (1666-1708)
(11) Guru Granth Sahib
Apart from the Guru Granth Sahib, all of the Gurus came from a Hindu background.
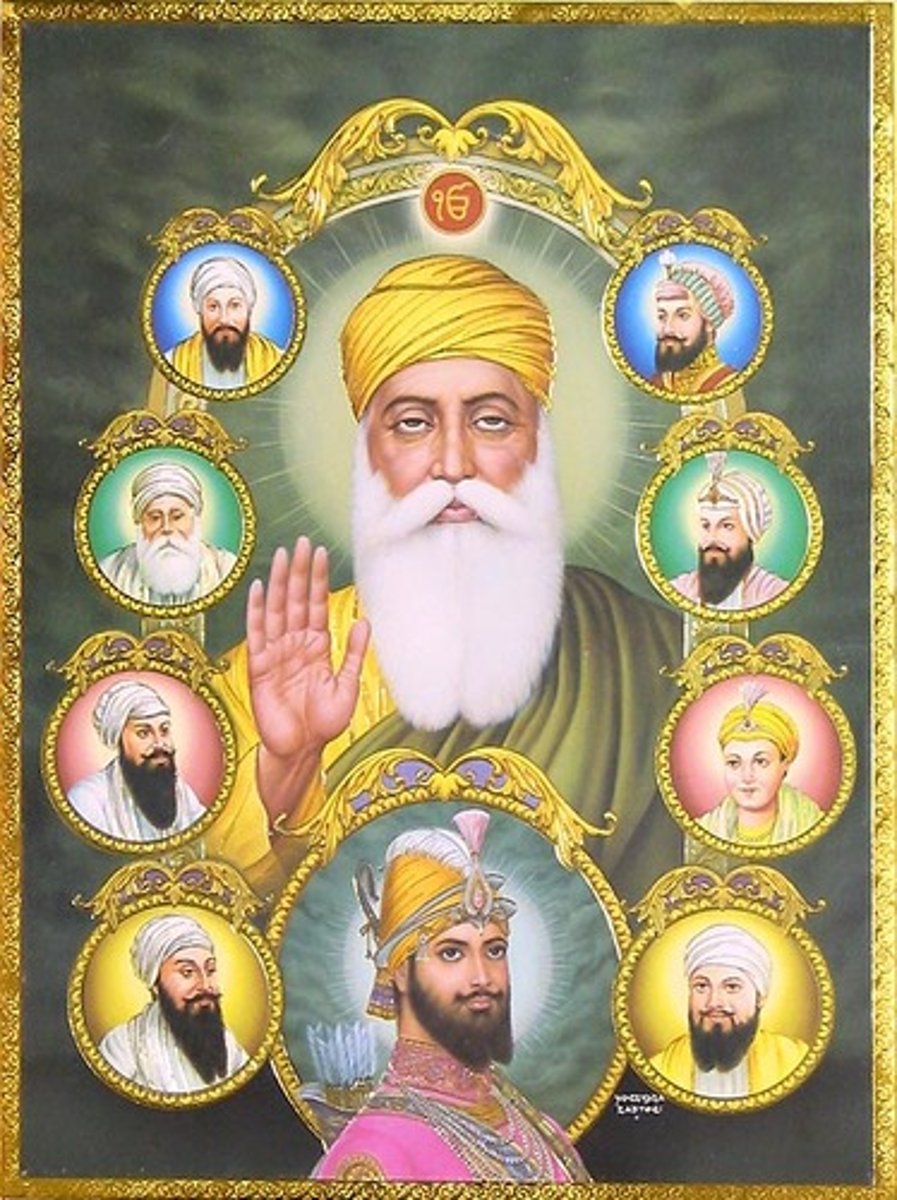

What are Janamsakhis?
Literally meaning birth stories, these are the hagiographical accounts of the life and death of Guru Nanak.

What is the Kali Yuga?
In many of the Indian religious traditions, including Sikhism, this is the final age of degeneration and narcissism.

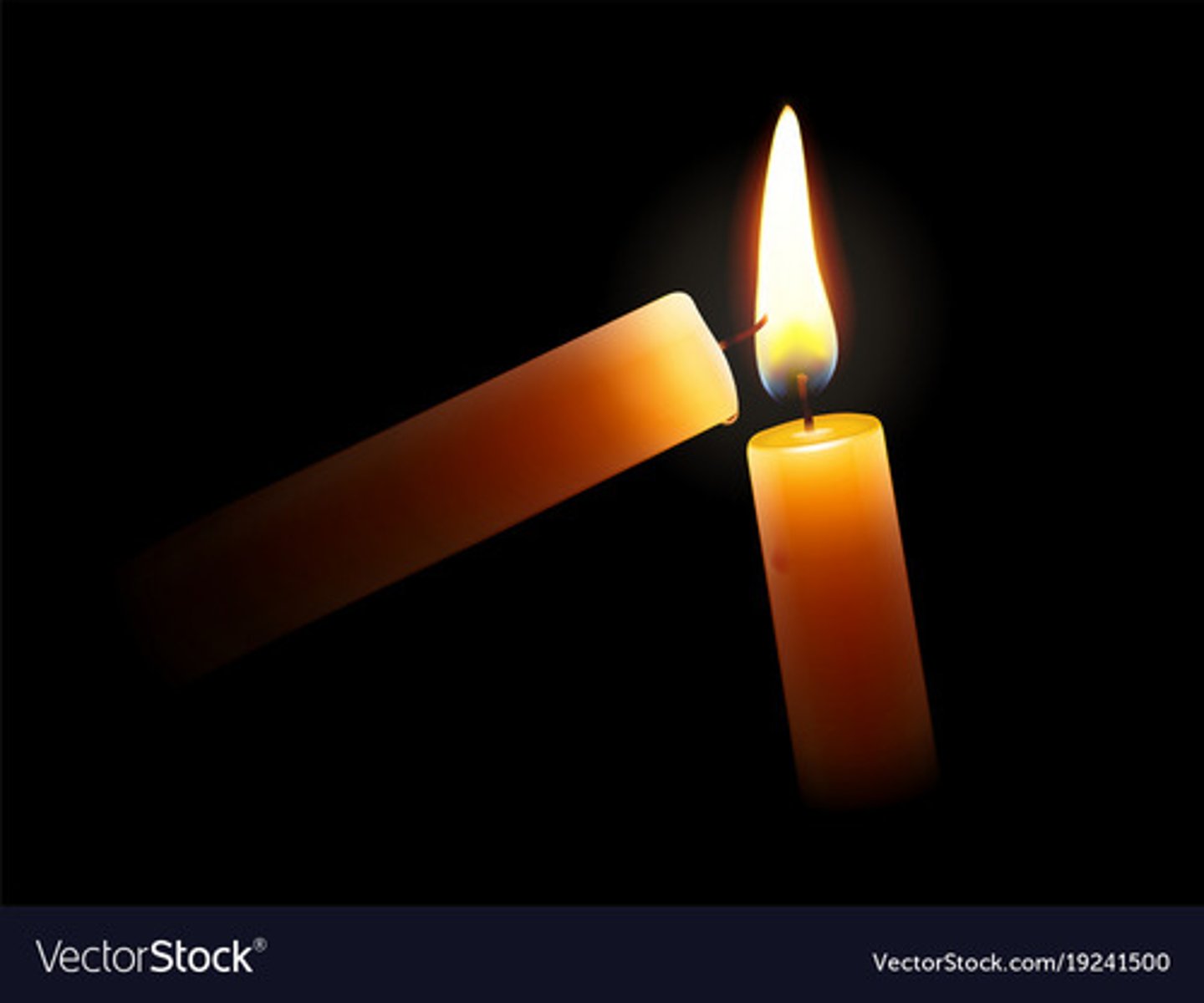
What is the lighting of a candle?
Sikhs liken the passing of knowledge and life from one Guru to the next to this.

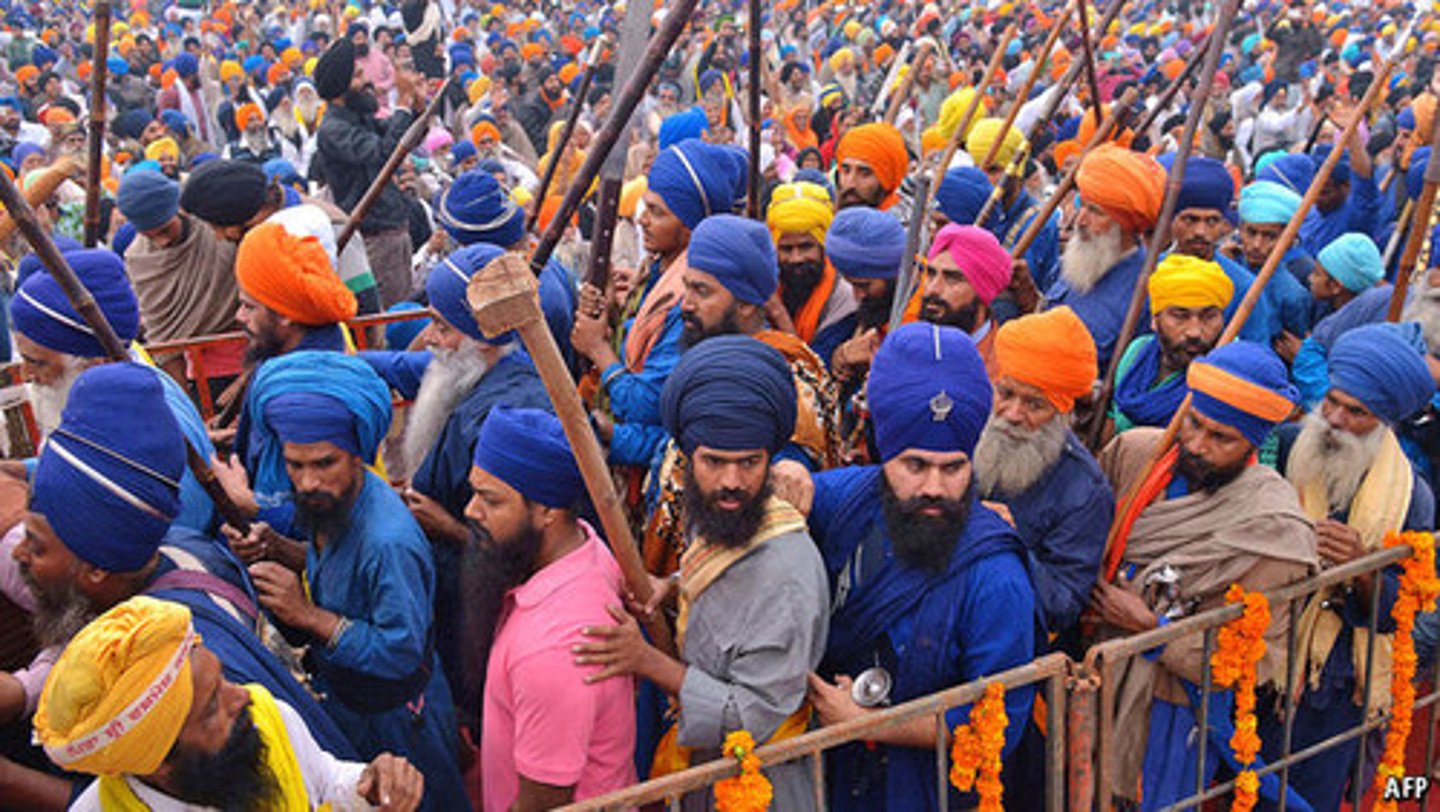
What is the panth?
Literally meaning path in Sanskrit, this is another term for the worldwide Sikh community.

What is mukti?
This enlightenment or spiritual liberation results in the escape from samsara. This is referred to as moksha by Hindus and nirvana by Buddhists.

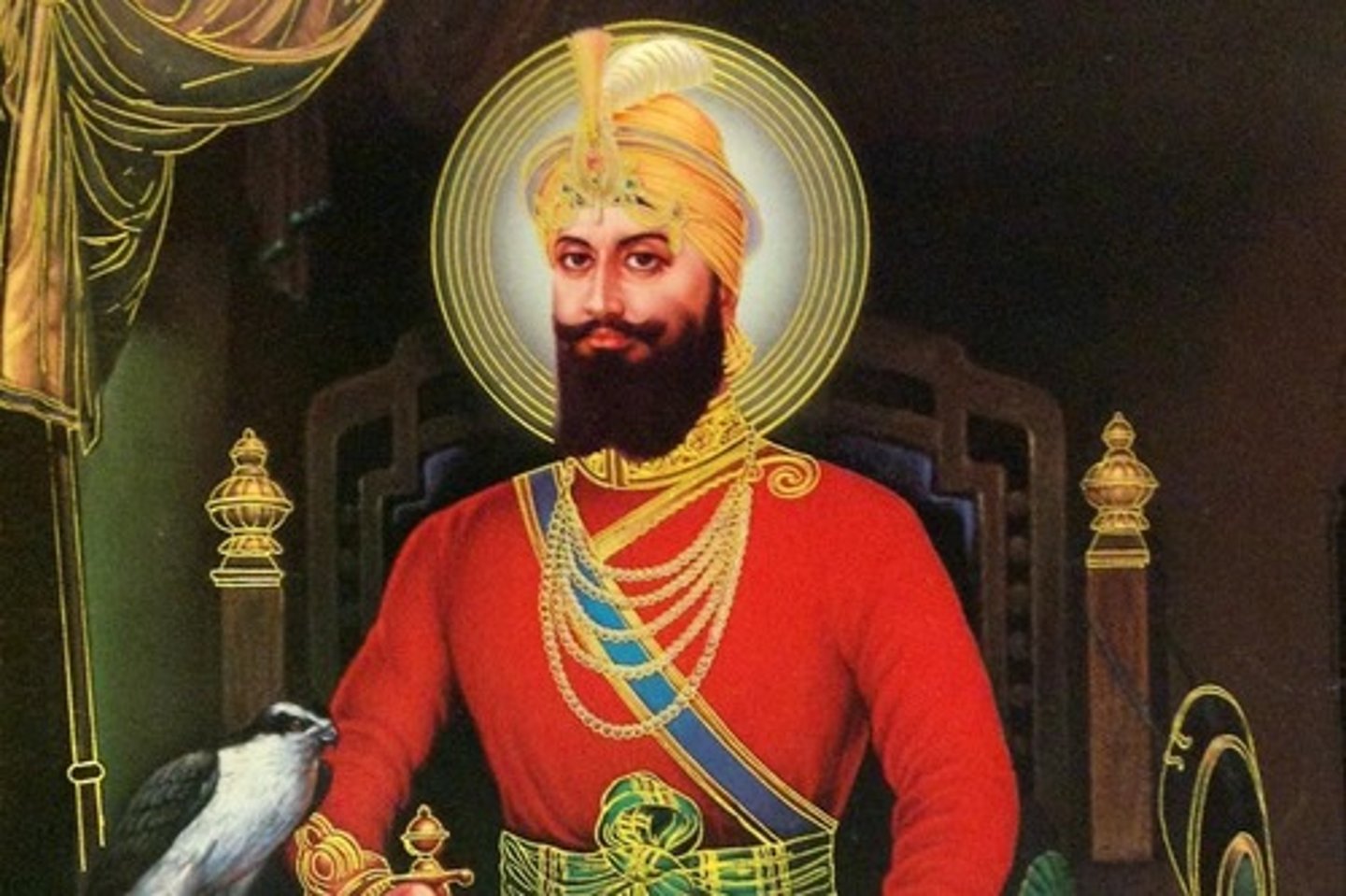
Who is Guru Gobind Singh?
This was the tenth and final human Guru who instituted the khalsa, finalized the Guru Granth Sahib, and declared it the final, living Guru. He died in 1708.

What is the Dasam Granth?
These are the collected writings of the tenth Guru, Guru Gobind Singh. This is the second holiest text in Sikhism.

What are the five realms?
Guru Nanak outlined these:
(1) Dharam Khand: the realm of righteous action
(2) Gian Khand: the realm of knowledge
(3) Saram Khand: the realm of spiritual effort
(4) Karam Khand: the realm of grace
(5) Sach Khand: the realm of truth, which includes complete enlightenment and unification with Waheguru.

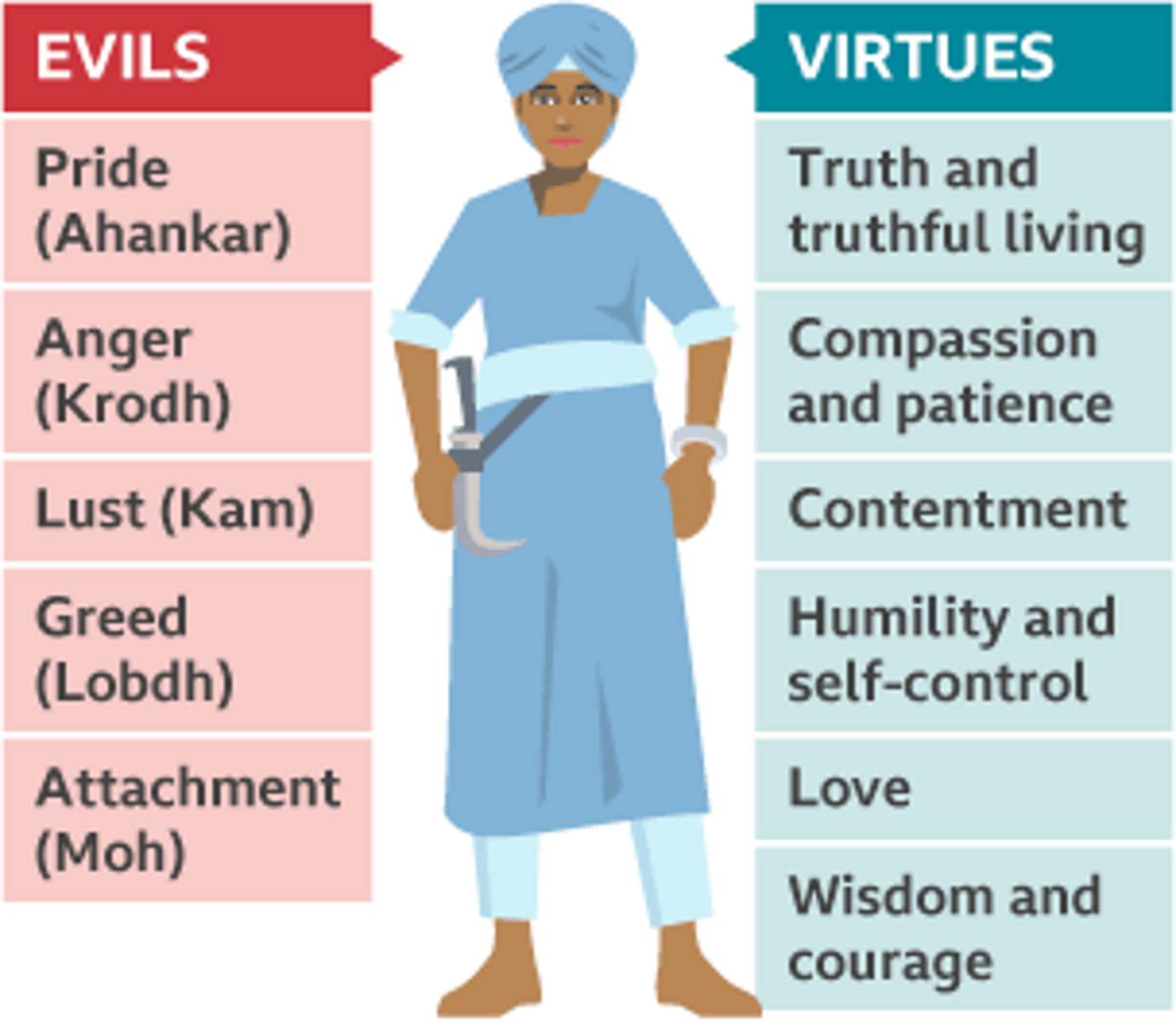
What are the five Sikh vices?
Kam, krodha, lobh, moh and ahankar: Lust, anger, greed, attachment, and pride.
What is haumai?
This is the inclination toward being egocentric rather than God-centric.

What is maya?
This is the illusory nature of the observable world.

What is manmukh?
Literally turned toward the self, i.e., living selfishly.

What is gurmukh?
Literally turned toward the Guru, i.e., living a Guru-centered life.

What is path?
This is the recitation of the Guru Granth Sahib.
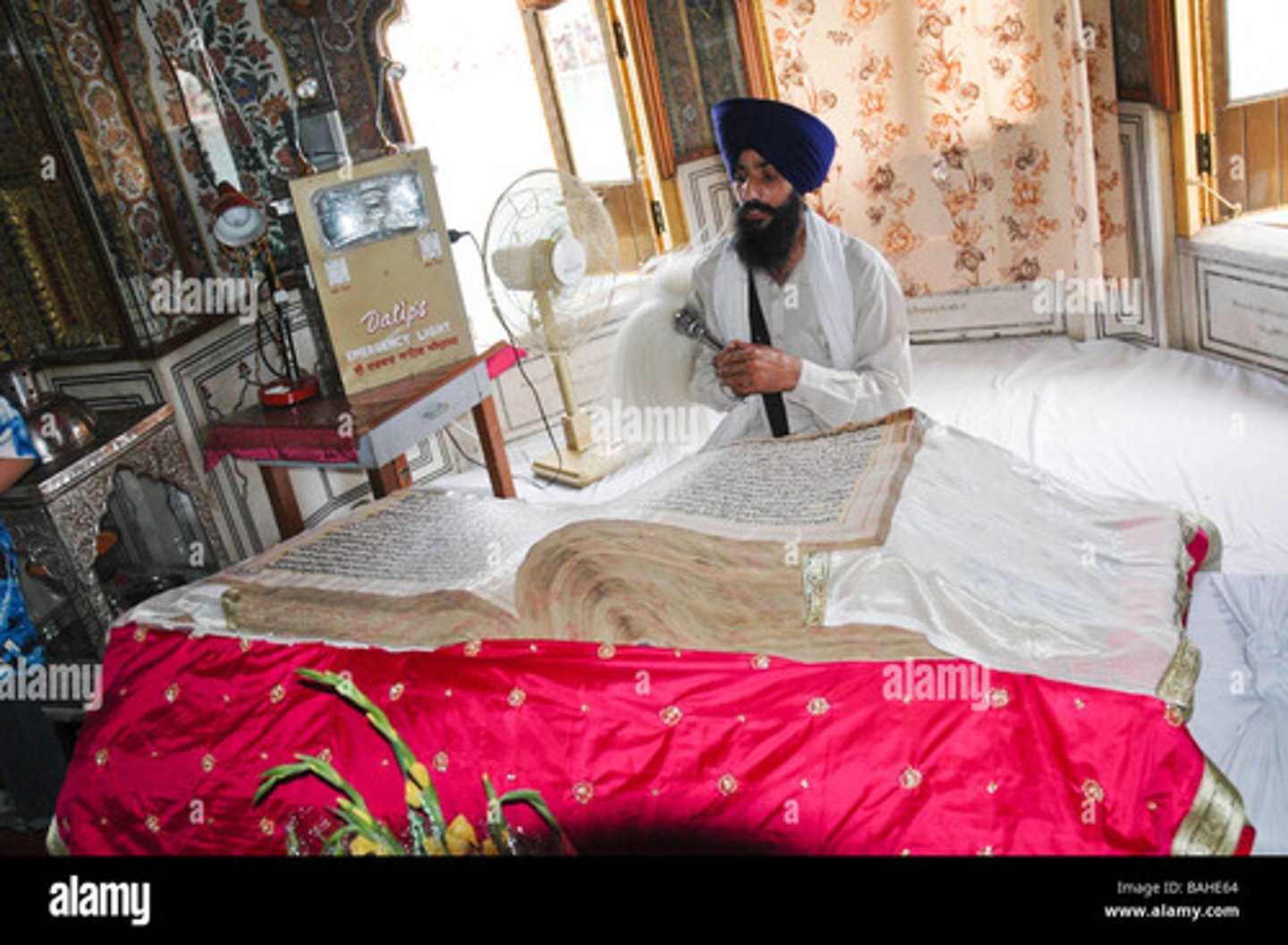

What is kirtan?
This is the devotional or meditative singing of the Guru Granth Sahib.
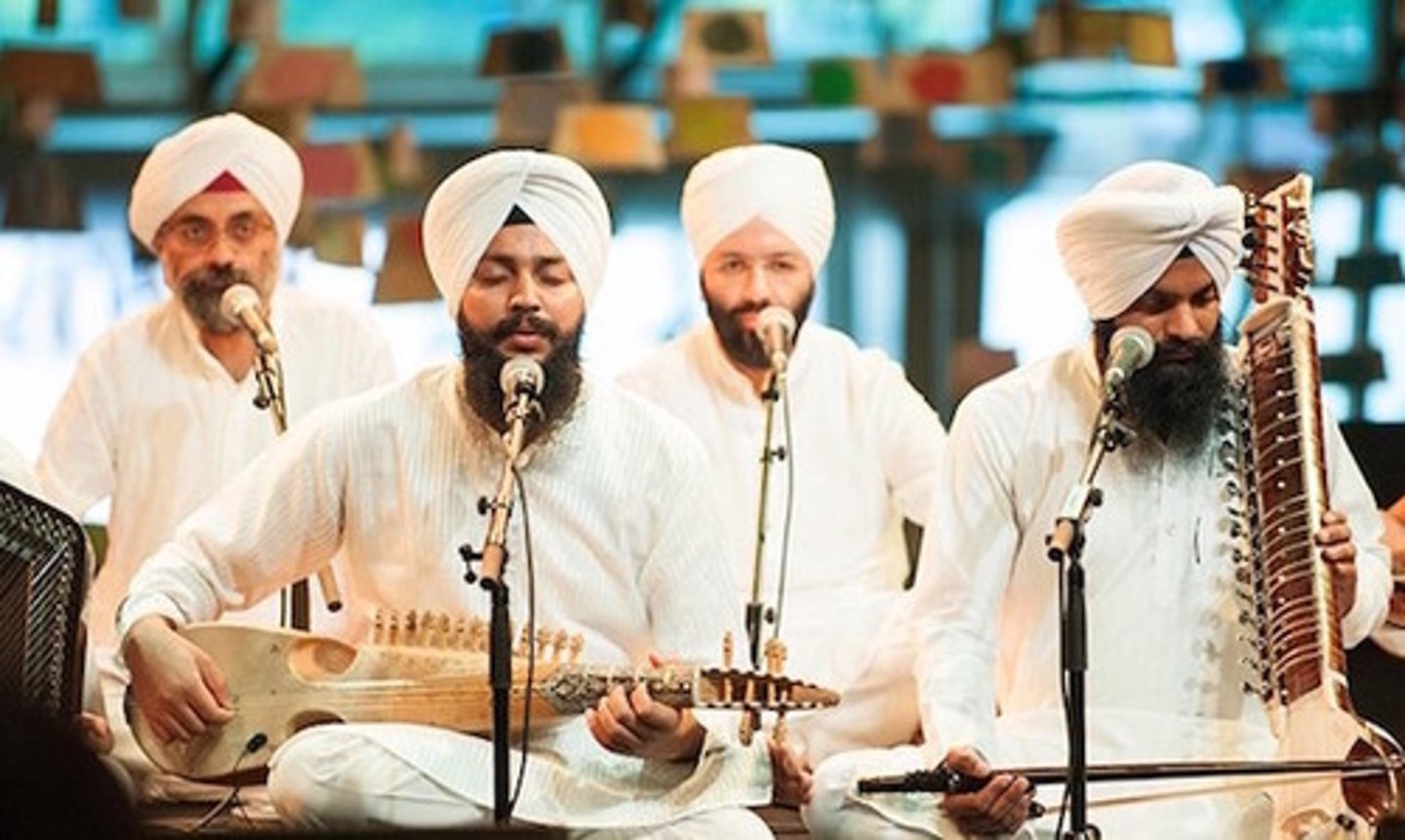

What are ardas?
This is the liturgical prayer recited by a representative (granthi) of the Sikh congregation. It is recited at the conclusion of ceremonies with everybody standing up. It includes praising the Gurus, Sikh devotion and heroism, and Waheguru.

What is a granthi?
This is a ceremonial reader of the Guru Granth Sahib and caretaker of a gurdwara.

What is sewa?
This is altruistic service or selfless action that is used as a means to build moral character.

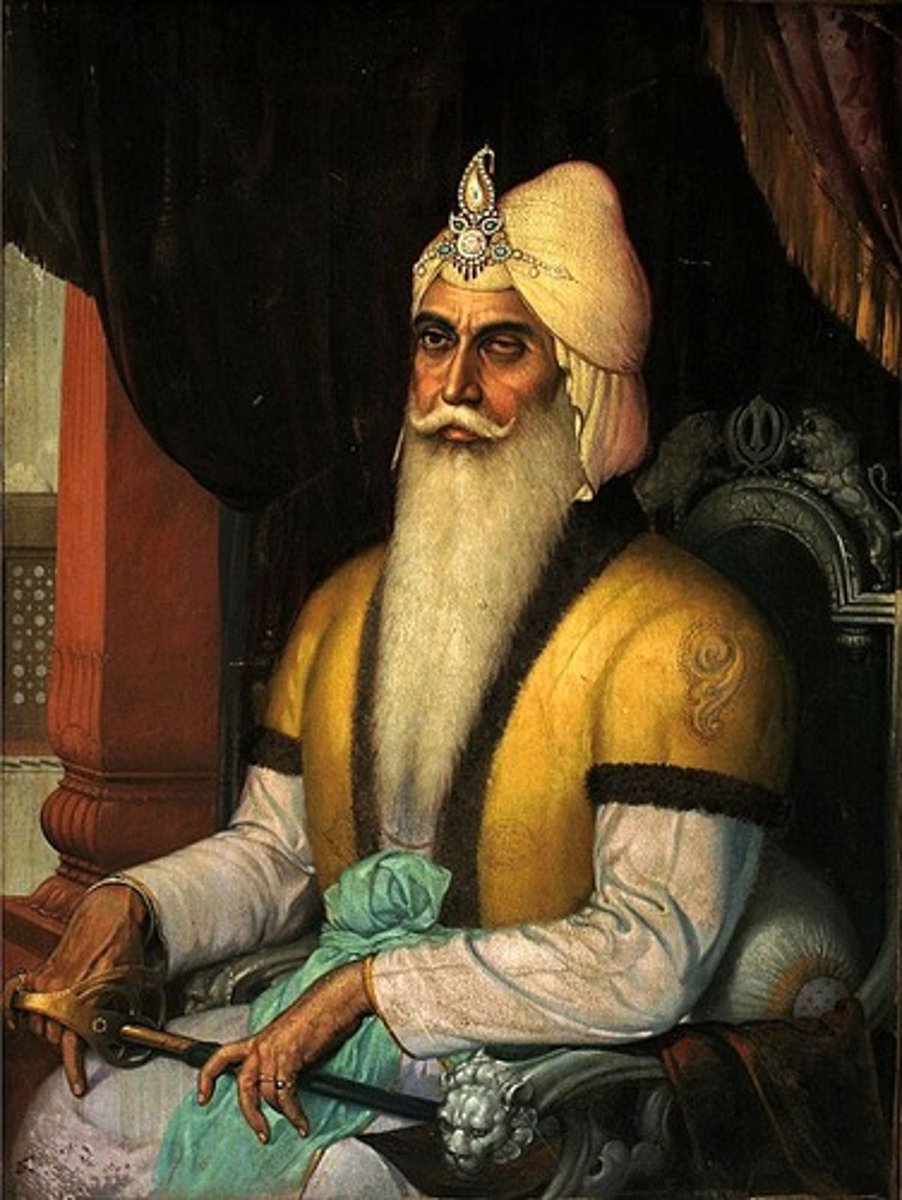
Who is Ranjit Singh (1780-1839 CE)?
He was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire in India.

What is prakash?
This is the ceremonial opening of the Guru Granth Sahib each morning.

What is sukhasan?
This is the ceremonial closing of the Guru Granth Sahib each night.

What are the four main Sikh rites?
Naming of children, marriage, amrit initiation (khalsa), and death.

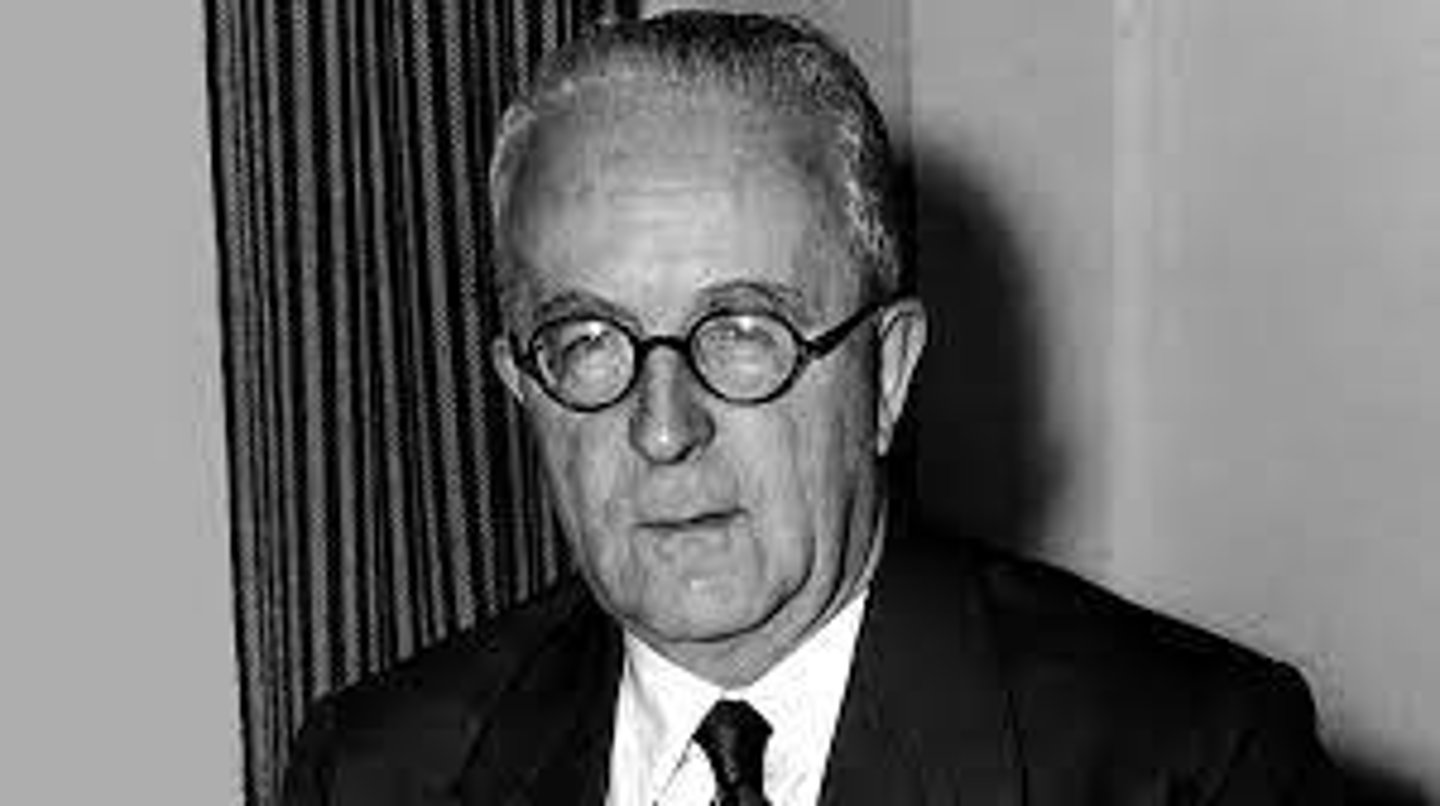
Who is Cyril Radcliffe (1899-1977 CE)?
This is the British lawyer who was appointed the task of dividing India and Pakistan in 1947.

What is the Koh-i-Noor?
This is one of the largest diamonds in the world. It is now part of the British Crown Jewels; however, it is believed to have been a prized Sikh possession.

Who is Dalip Singh (1838-1893 CE)?
He was the youngest son and the last Maharaja of the Sikhs. He was raised in Britain, converted to Christianity, and reverted back to Sikhism later in life.

What is the Rahit Maryada?
This is the Sikh code of conduct that was codified in the 1950s.

What are the nitnem banis?
These are the five required daily prayers for Sikhs. They include three morning prayers, an evening prayer, and a bedtime prayer.

Who are the Mughals?
This group established a Muslim empire that existed from 1526 to 1857 and controlled most of India. The relationship between Sikhs and these Muslim rulers was quite tumultuous.
What is a sangat?
This is any Sikh congregation at a local gurdwara.

What is miri piri?
This is the doctrine established by Guru Hargobind that the Sikh Gurus possess both temporal (miri) and spiritual (piri) authority.

What is a martyr?
This person is killed because of their religious beliefs. In Sikhism, this includes Guru Arjan and Guru Tegh Bahadur, who were both executed by the Mughals.

What is jot?
This is the divine light of God that is found inside all of us.

What is nadar?
This is God's boundless grace that is granted as a result of an individual's actions.

What is gurprasad?
This is God's boundless grace that is granted through the Gurus.

What is bani/shabad?
These two words are often used interchangeably to refer to the divine word of God as found in the sacred scriptures of the Sikhs.
