kin 100 - muscles of the abdominal walls
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is the anterolateral abdominal wall made up of?
external oblique
internal oblique
transverse abdominals
rectus abdominus
what is the fiber direction of external obliques?
anteroinferior (hands in pockets)
what does the inferior edge of the aponeurosis of the external oblique create?
the inguinal ligament
what are the inguinal ligament’s attachmetn styles?
anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle
internal oblique fiber direct
anterosuperior
transverse abdominal fiber pattern
horizontal fiber pattern
the 3 anterolateral muscles of the abdominal walls in order of superficial to deep
external obliques
internal obliques
transverse abdominals
what happens when 3 of the anterolateral abdominal wall muscles meet?
so the aponeuroses all meet in the midline of the trunk and form the linea alba
what are the actions of the 3 layers of muscles of the anterolateral border?
compression and support of the abdominal viscera (soft internal organs inside the abdominal cavity)
flexion of the trunk
rotation of the trunk
what is rectus abdominus? what does it run vertically between?
its the abs
its bilateral
it runs vertically between the ribs and the pubic symphysis
what is the purpose of linea alba
its a white line that seperates hte left and right rectus abdominus muscles
what are tendinous intersecitons?
they are litearlly intersections between cunks of the rectus abdoninus, making the 6-8 pack we see.
they seperate the rectus abdominus into 6-8 chunks
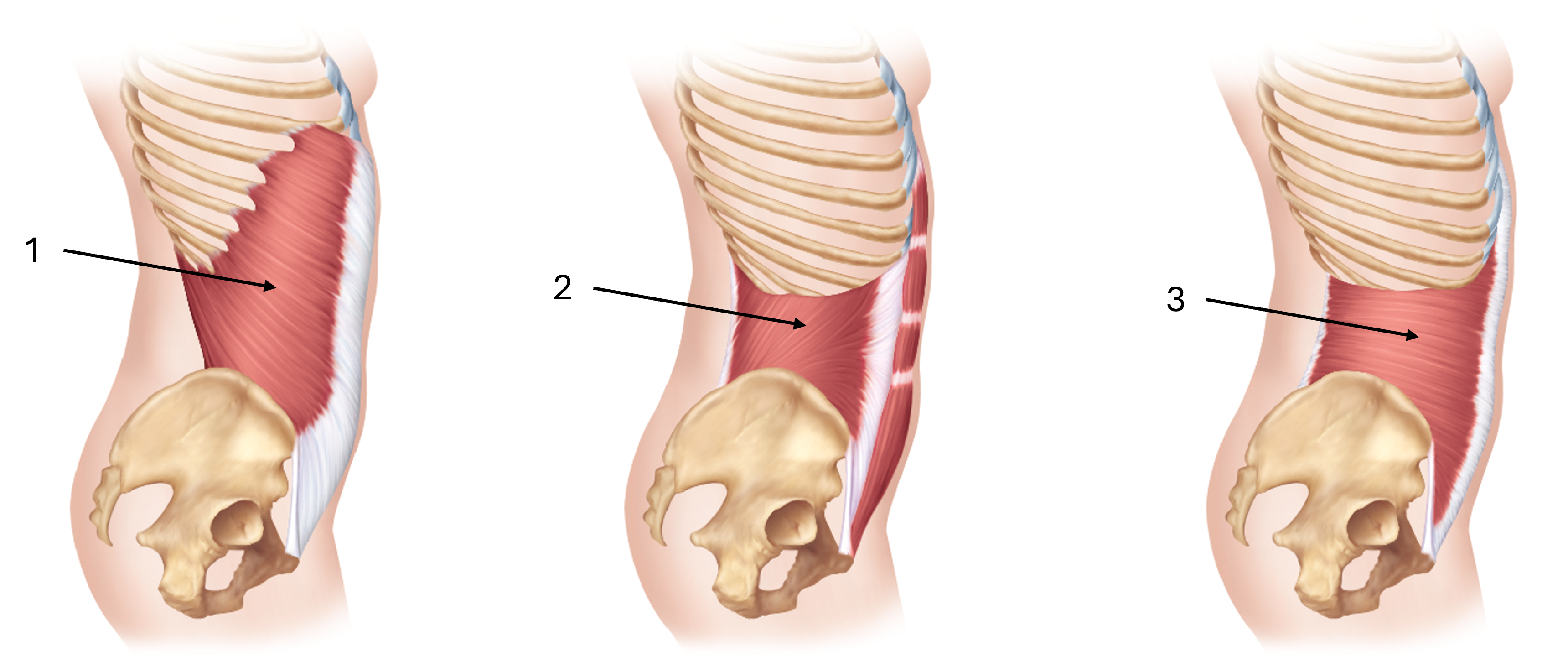
label this diagram of the obliques
external oblique (anteroinferior fiber direction)
internal oblique (anterosuperior fiber direction)
transverse abdominal (horizontal fiber direction)
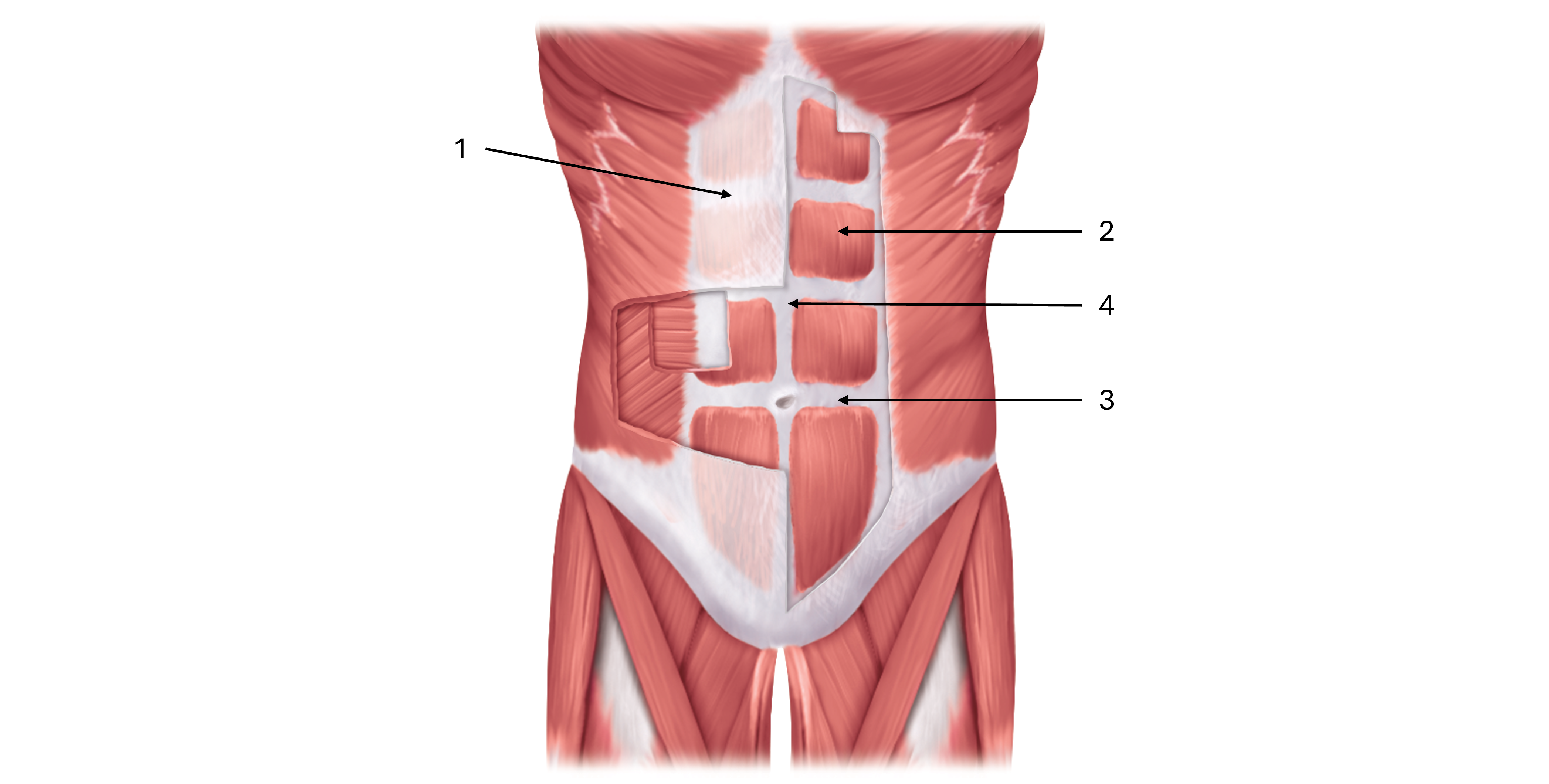
label this diagram of the rectus abdominus
rectus sheath
rectus abdominus
tendinous intersection
linea alba
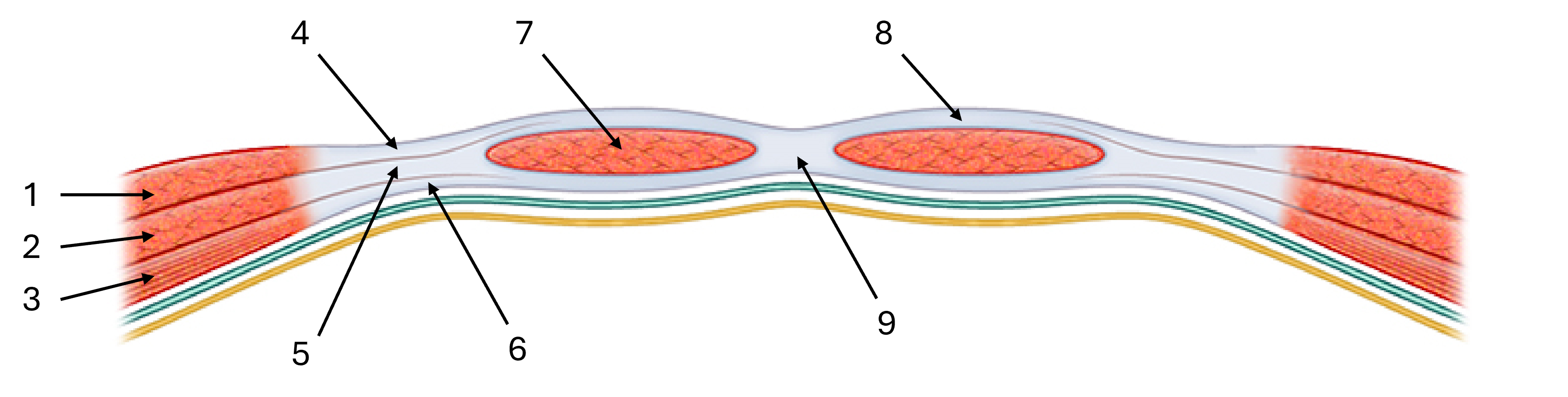
label this diagram of the rectus sheath
external oblique
internal oblique
transverse abdominal
aponeurosis of external oblique
aponeurosis of internal oblique
aponeurosis of transverse abdominal
rectus abdominus
linea alba
rectus sheath
what is the rectus sheath?
when the aponeuroses of the external obliques + aponeuroses of internal oblique basicaly just combine, and create this sheath that covers the front of the rectus abdominus muscles
what are the 3 openings of the diaphragm?
caval opening
esophageal hiatus
aortic hiatus
what structure comes out of the caval opening? and at what vertebrae?
the inferior vena cava at level of T8
what structure comes out of the esophageal hiatus and at what vertebrae?
esophagus, at T10
what structures comes out of the aortic hiatus and at what vertebrae?
aorta, T12
where does the diaphragm attach?
the periphery of the margins of the thoracic cage and superior lumbar vertebrae
what does the heart sit on?
sits on the central tendon of hte diaphragm!!!
what is the diaphragm described as?
a domed muscle that seperates the thoax from the abdomen
label this diagram of the diaphragmatic openings
caval opening
inferior vena cava
T8
esophageal hiatus
esophagus
T10
aortic hiatus
aorta
T12
mnemonics for diaphragmatic openings
I ate 10 eggs at noon (I, 8, 10, E, A, 12)
they open, and then they go on hiatus
what are the 5 ligaments of the diaphgram? what view can you see them from?
1: midline median arcuate ligament
2: bilateral medial arcuate ligaments
2: bilateral lateral arcuate ligaments
what structure does the midline median arcuate ligament arch over? what structure does it form?
it arches over the aorta! specifically the abdominal aorta
forms the aortic hiatus
what does the bilateral medial arcuate ligament arch over?
the psaos major muscles!!
what do the bilateral lateral arcuate ligaments arch over?
the quadratus lumborum muscles
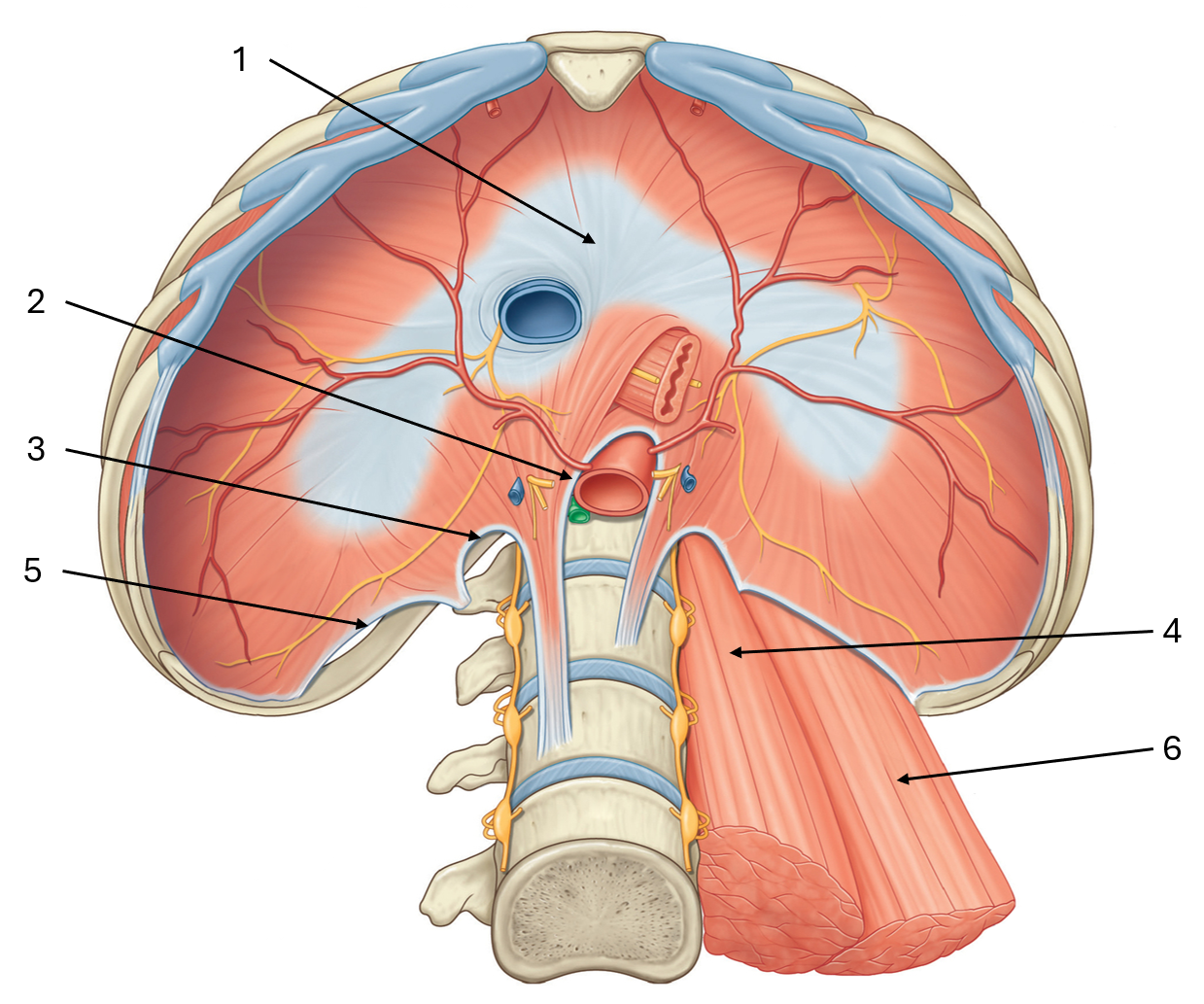
label this diagram of the inferior view of the diaphgram
central tendon
median arcuate ligament
medial arcuate ligament
psoas major
lateral arcuate ligament
quadratus lumborum
what is the posterior abdominal wall made up of?
psoas major
iliacus
quadratus lumborum
psoas major (attachments, actions)
prox: lateral aspect of lumbar vertebrae/transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
distal: lesser trochanter of femur
actions:
thigh flexion
trunk flexion (bilateral contraction)
trunk lateral flexion (unilateral contraction)
whats something interesting about psoas minor?
its present in some individuals only
vestigial muscle?
iliacus (prox, distal, actions)
prox: iliac fossa
distal: lesser trochanter of femur
action: thigh flexion (doesn’t touch vertebrae so it doesnt do anything with the trunk)
what muscle does psaos major unite with? whats it called?
psoas major unites with iliacus, makes iliopsoas
whats tenderloin in humans?
psoas major
quadratus lumborum (prox, distal, actions)
prox: 12th rib and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
distal: iliac crest
actions:
trunk extension (bilateral contraction)
trunk lateral flexion (unilateral contraction)
3 terminal branches of the lumbar plexus that we’ll be studying?
femoral nerve
obturator nerve
lumbosacral trunk
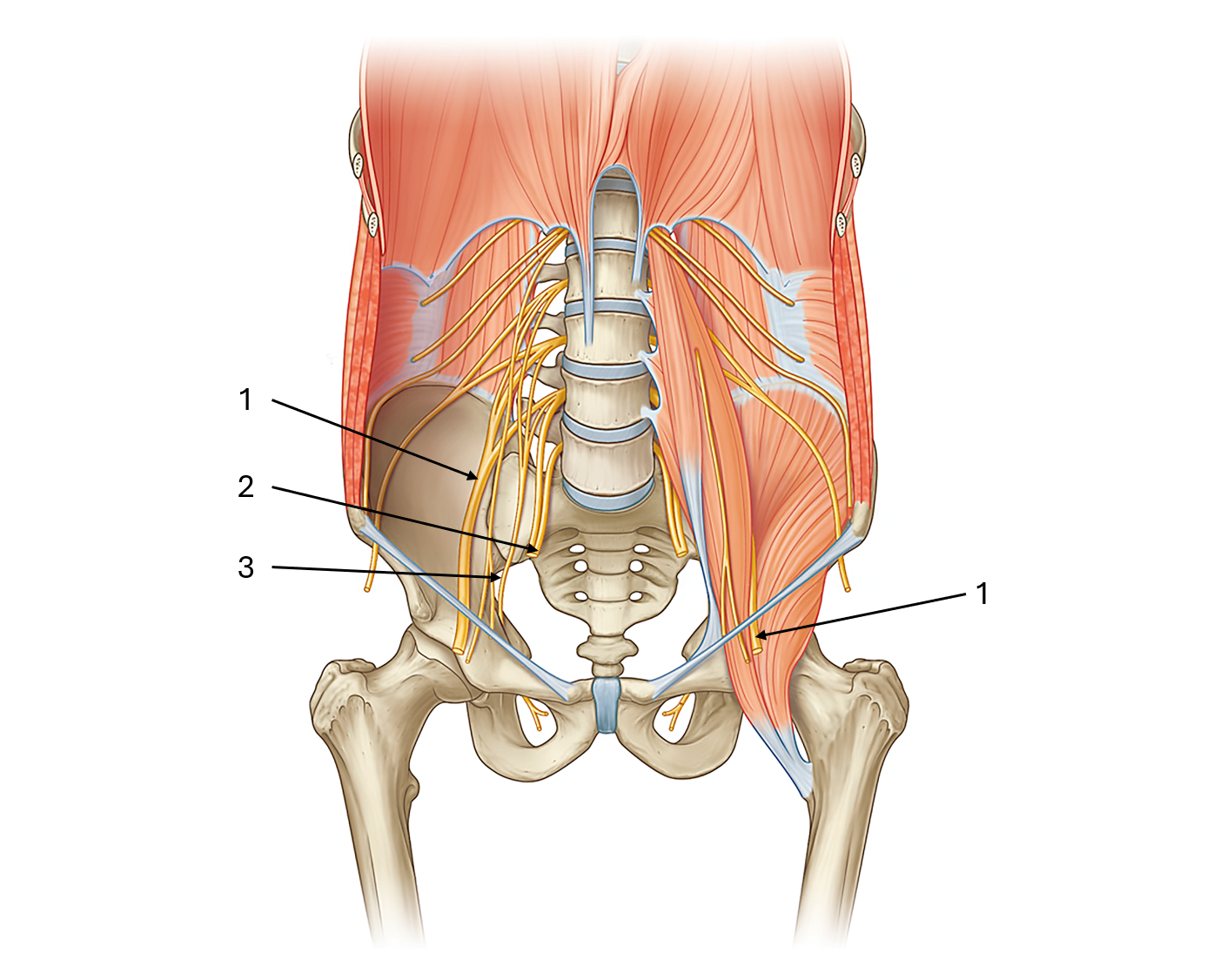
label this diagram of the lumbar plexus
femoral nerve
lumbosacral trunk
obturator nerve