8. Cell: The Unit of Life
1/272
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pretty much every line from NCERT. Suitable for those studying for IAT and probably also NEET. Question mode: Flashcards only. Answer mode: Answer with Definition. Good luck!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
273 Terms
Why is cell the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms?
Unicellular organisms are capable of
independent existence
performing the essential functions of life
Anything less than a complete structure of a cell does not ensure independent living.
Who saw and described the first live cell?
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek
Who discovered a cell nucleus?
Robert Brown
Who discovered that plants are made of various different kinds of cells?
Matthias Schleiden
Who discovered that animal cells have a plasma membrane but no cell wall while plant cells have a cell wall?
Theodore Schwann
What was Schwann’s hypothesis?
Schwann proposed the hypothesis that the bodies of animals and plants are composed of cells and products of cells.
Who first explained that cells divided and new cells are formed from
pre-existing cells?
Rudolf Virchow
What is meant by: Omnis cellula-e cellula
new cells are formed from pre-existing cells
What are the two postulates of today’s cell theory?
all living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells.
all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Why was Schleidan’s and Schwann’s theory incomplete?
Because they couldn’t explain where cells that made up animals and plants arose from.
Cells that have membrane bound nuclei are called ________.
Cells that have membrane bound nuclei are called eukaryotic.
Cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus are called ________.
Cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus are called prokaryotic.
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, a semi-fluid matrix called ________ occupies the volume of the cell.
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, a semi-fluid matrix called cytoplasm occupies the volume of the cell.
The ________ is the main arena of cellular activities in both the plant and animal cells.
The cytoplasm is the main arena of cellular activities in both the plant and animal cells.
Besides the nucleus, the eukaryotic cells have other membrane bound distinct structures called _________.
Besides the nucleus, the eukaryotic cells have other membrane bound distinct structures called organelles.
____________ cells do not have membrane-bound organelles.
(prokaryotic / eukaryotic)
prokaryotic
Ribosomes are only found in eukaryotic cells. True or False?
False.
Ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in all cells – both eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic.
Animal cells contain another non-membrane bound organelle called __________ which helps in cell division.
Animal cells contain another non-membrane bound organelle called centrosome which helps in cell division.
________ cells contain another non-membrane bound organelle called centrosome which helps in cell division.
(animal / plant)
animal
What is present in animal cells that helps in cell division that isn’t present in plant cells?
centrosome
What is the typical size of a prokaryotic cell?
1-10 μm
What is the typical size of a eukaryotic cell?
10-100 μm
What is the typical size of a mycoplasma?
0.1-0.3 μm
What is the typical size of a bacterium?
1-5 μm
What is the typical size of an RBC?
7 μm
What is the typical size of viruses?
0.02-0.2 μm
What is the full form of PPLO?
Pleuro Pneumonia Like Organisms
Do prokaryotic cells multiple more slowly or more quickly than eukaryotic cells?
more quickly
Which type of prokaryotic cell does not have a cell wall?
mycoplasma
How is genetic material present in prokaryotic cells?
The genetic material is basically naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane.
What is the main genetic material inside a prokaryotic cell called?
nucleoid / genophore
In addition to the genomic DNA (the single chromosome/circular DNA), many bacteria have ___________________________________________________.
In addition to the genomic DNA (the single chromosome/circular DNA), many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA (plasmids).
What do plasmids do in bacteria?
The plasmid DNA confers certain unique phenotypic characters to such bacteria.
The plasmid DNA confers certain unique phenotypic characters to such bacteria. What is an example of one such character?
One such character is resistance to antibiotics.
What do prokaryotic cells have that eukaryotic cells do not have?
Prokaryotes have something unique in the form of inclusions. A specialised differentiated form of cell membrane called mesosome is the characteristic of prokaryotes. They are essentially infoldings of cell membrane.
What is a mesosome?
Special membranous structure, which is formed by the extensions of plasma membrane into the cell.
The cell envelope of bacteria consists of a tightly bound three layered structure. What are the names of the layers?
Glycocalyx (outermost layer)
Cell Wall (middle layer)
Plasma Membrane (innermost layer)
Bacteria can be classified into two groups on the basis of the differences in the cell envelopes and the manner in which they respond to the staining procedure developed by Gram.
What are the two groups?
Gram-positive bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria
What are Gram-positive bacteria?
Bacteria that respond positively to the staining procedure developed by Gram.
i.e., bacteria that retain staining after being washed
What are Gram-negative bacteria?
Bacteria that respond negatively to the staining procedure developed by Gram.
i.e., bacteria that do not retain staining after being washed
What is a slime layer?
A glycocalyx when it is a loose sheath
What is a capsule?
A glycocalyx when it is thick and tough
Glycocalyx differs in composition and thickness among different bacteria. It could be a loose sheath called the ___________ in some, while in others it may be thick and tough, called the _______.
Glycocalyx differs in composition and thickness among different bacteria. It could be a loose sheath called the slime layer in some, while in others it may be thick and tough, called the capsule.
What is the function of cell wall in bacteria? (2 points)
The cell wall:
determines the shape of the cell
provides a strong structural support to prevent the bacterium from bursting or collapsing.
A special membranous structure is the mesosome which is formed by the extensions of plasma membrane into the cell. These extensions are in the form of ________, ________ and ________.
A special membranous structure is the mesosome which is formed by the extensions of plasma membrane into the cell. These extensions are in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
A special membranous structure is the mesosome which is formed by the extensions of plasma membrane into the cell. These extensions are in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
What functions do they help in? 6 things
cell wall formation
DNA replication
distribution to daughter cells
respiration
secretion processes
increasing the surface area of plasma membrane and enzymatic content
In some prokaryotes like cyanobacteria, there are other membranous extensions into the cytoplasm called ___________ which contain pigments.
In some prokaryotes like cyanobacteria, there are other membranous extensions into the cytoplasm called chromatophores which contain pigments.
What are chromatophores?
Extensions of plasma membrane into the cytoplasm in some prokaryotes, which contain pigments
Bacterial cells may be motile or non-motile. If motile, they have _________________________________________________.
Bacterial cells may be motile or non-motile. If motile, they have thin filamentous extensions from their cell wall called flagella.
Bacterial flagellum is composed of three parts. What are they?
Filament
Basal body
Hook
What is the longest portion of a flagellum called?
the filament
Besides flagella, there are two surface structures in bacteria, however they do not play a role in motility. What are the structures?
pili
fimbriae
What are pili?
The pili are elongated tubular structures made of a special protein. They are surface structures on bacteria and stuff that do not play a role in motility
What are fimbriae?
The fimbriae are small bristle like fibres sprouting out of the cell.
What is the function of fimbriae?
In some bacteria, they are known to help attach the bacteria to rocks in streams and also to the host tissues.
What is the function of pili?
They can join two bacteria together so that their cytoplasm is exchangable.
What is the typical size of ribosomes?
about 15 nm by 20 nm
What are the subunits of ribosomes in prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cell organelles?
30S and 50S
Are prokaryotic ribosomes 70S or 80S?
70S
In prokaryotic cells, several ribosomes may attach to a single mRNA and form a chain called ____________ or _________.
In prokaryotic cells, several ribosomes may attach to a single mRNA and form a chain called polyribosomes or polysome.
What is a polysome / polyribosome?
In prokaryotic cells, several ribosomes may attach to a single mRNA and form a chain called polyribosomes or polysome.
What is the function of ribosomes that are part of a polysome?
The ribosomes of a polysome translate the mRNA into proteins.
What are inclusion bodies in prokaryotic cells?
Reserve material in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies (granules).
Gas vacuoles are found in which bacteria?
Gas vacuoles are found in blue green and purple and green photosynthetic bacteria.


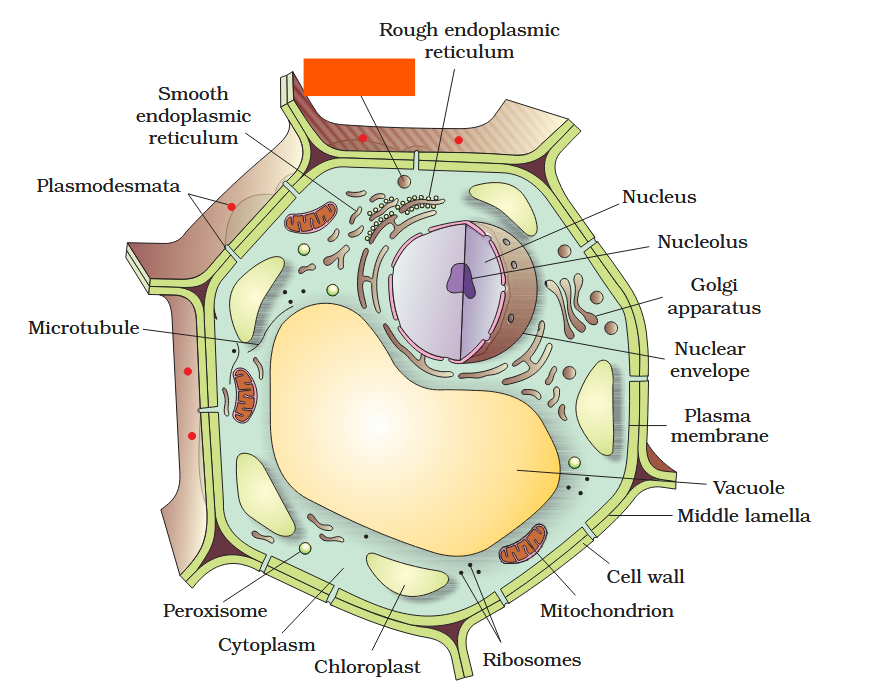
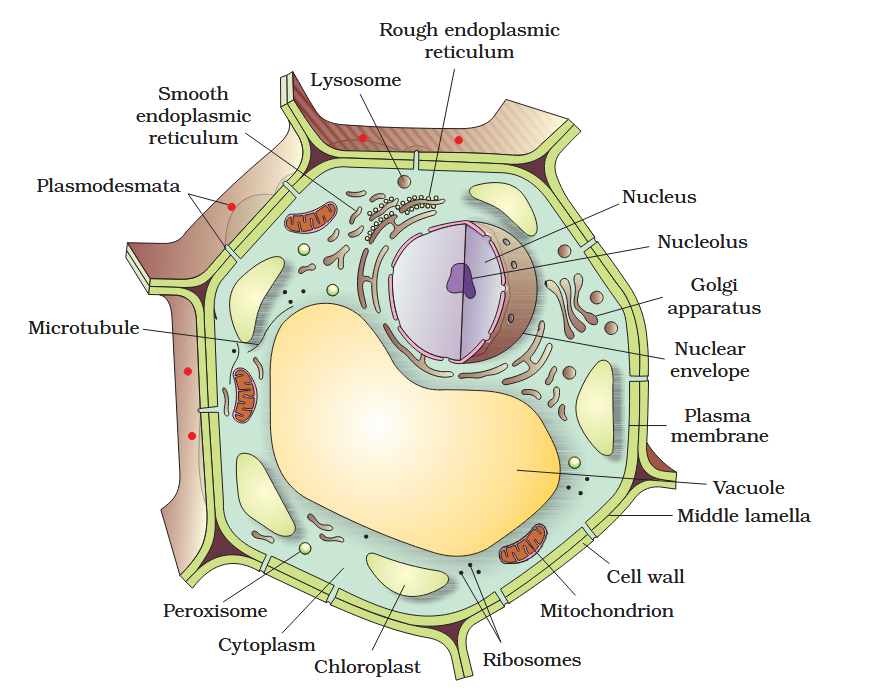
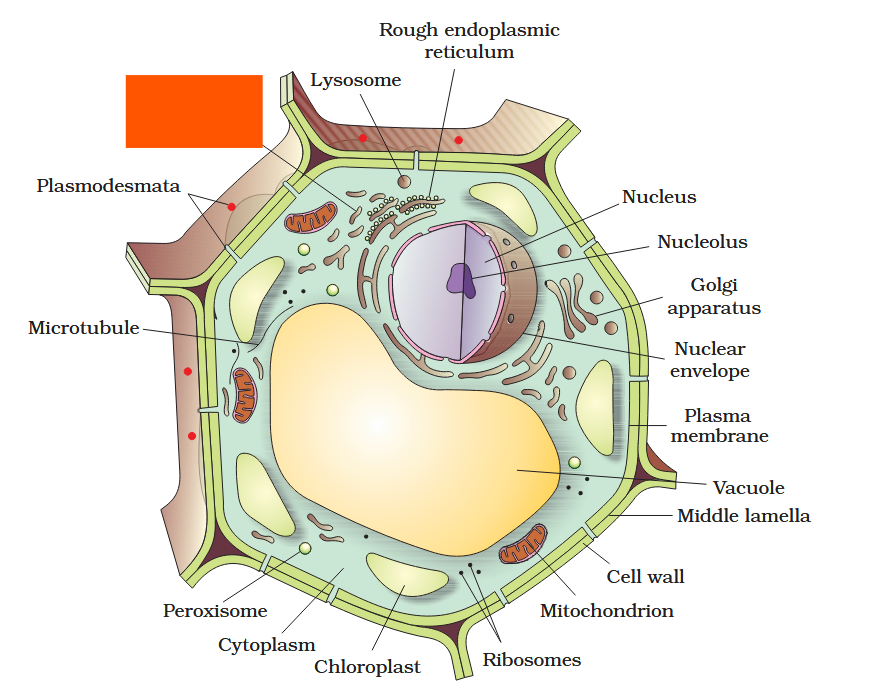

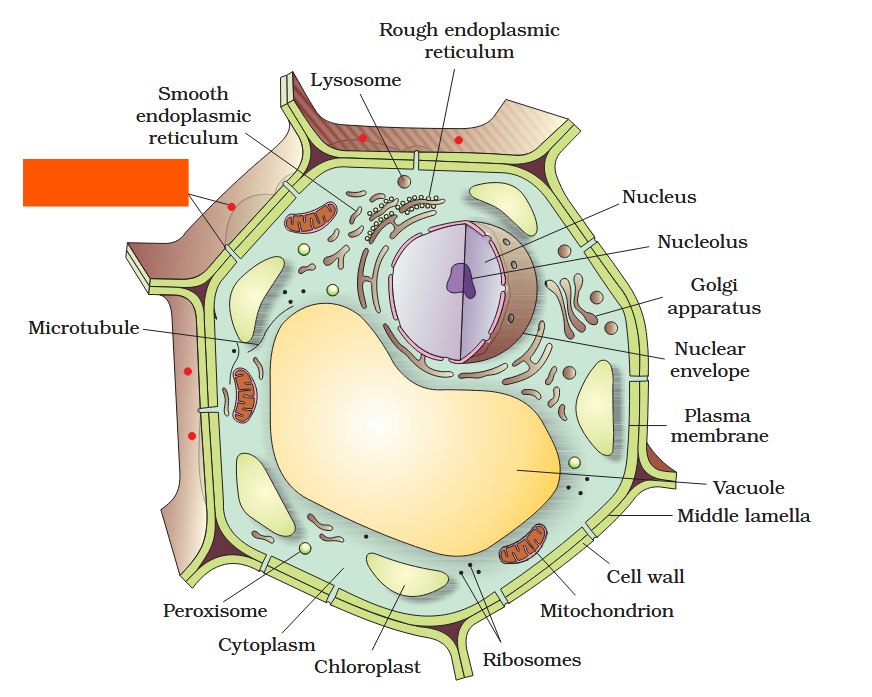

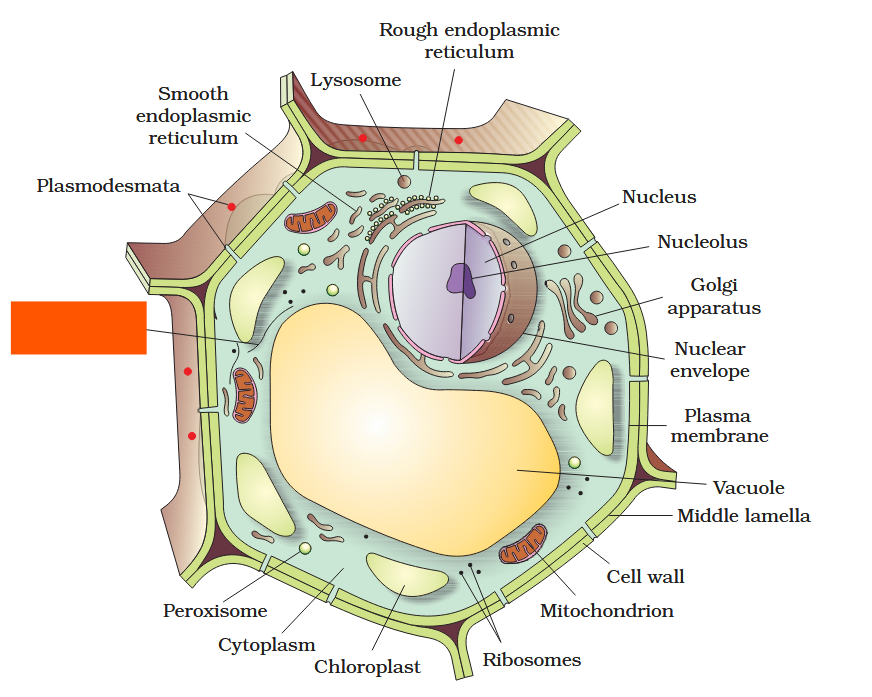
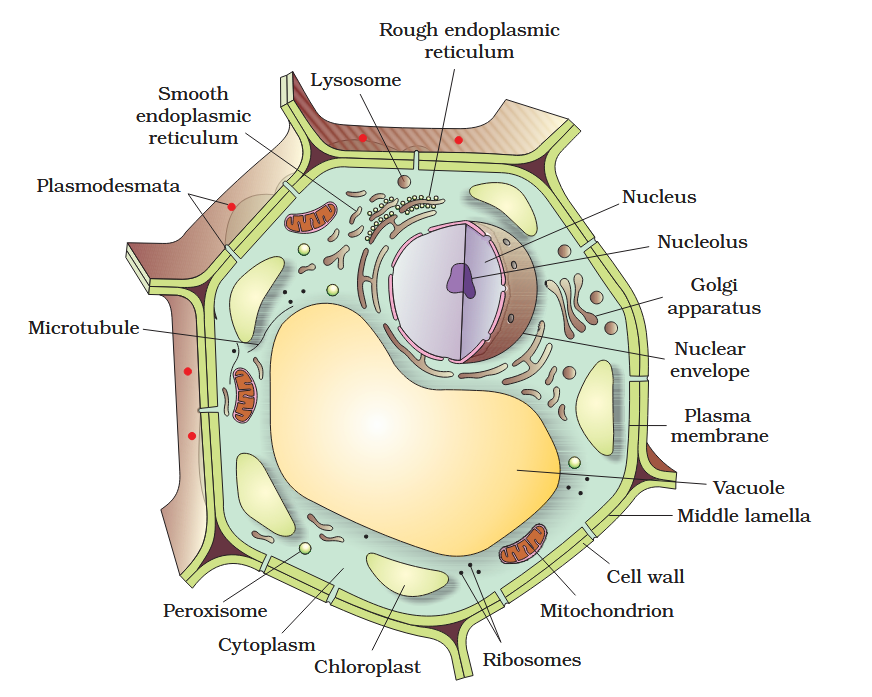
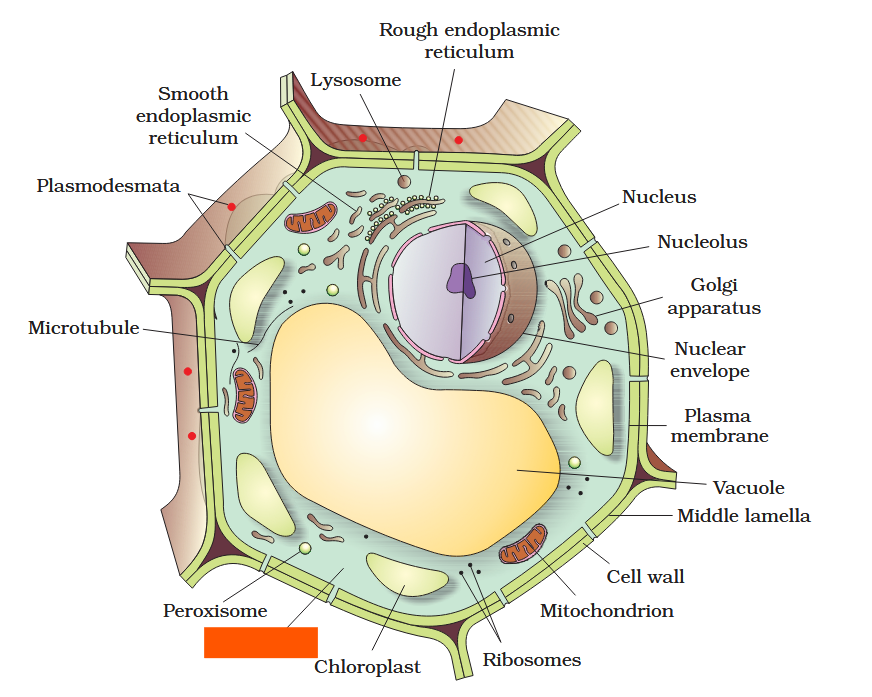
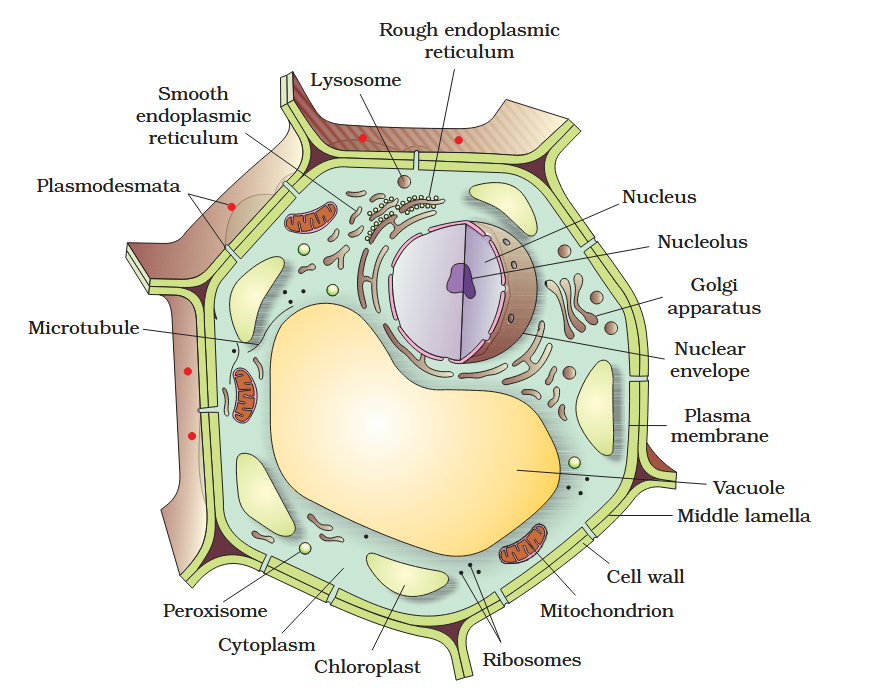
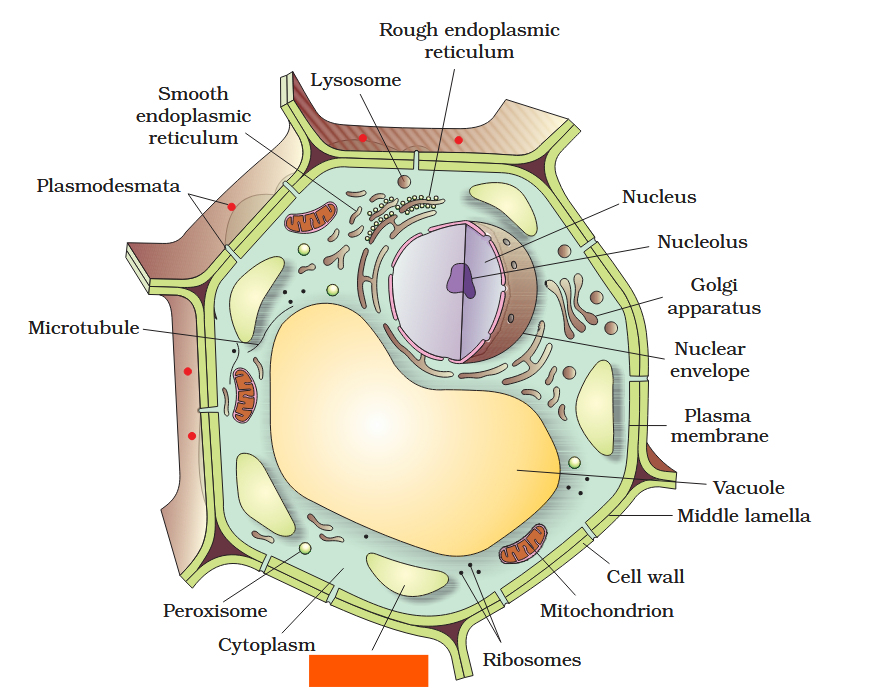
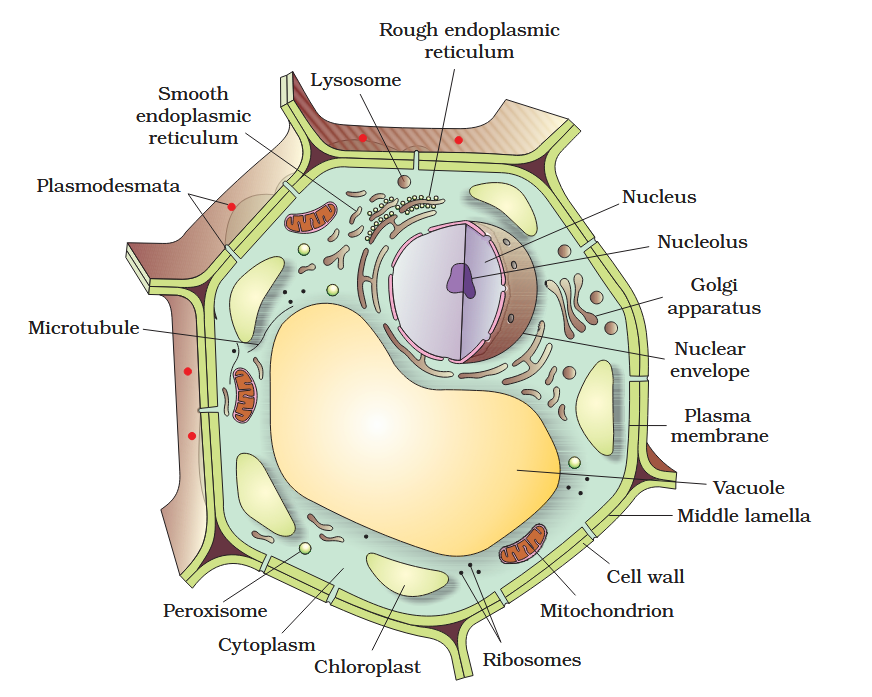
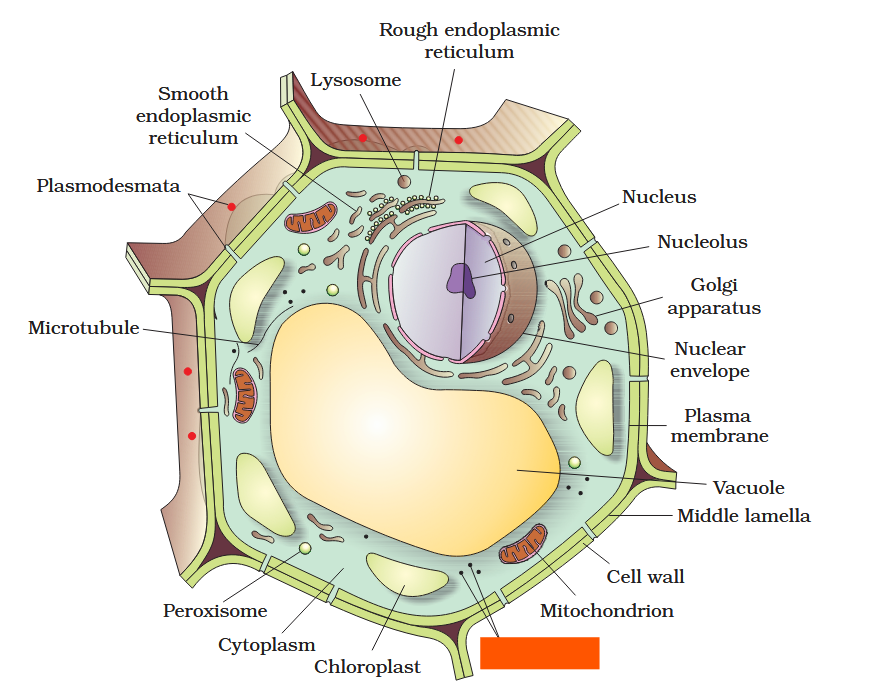
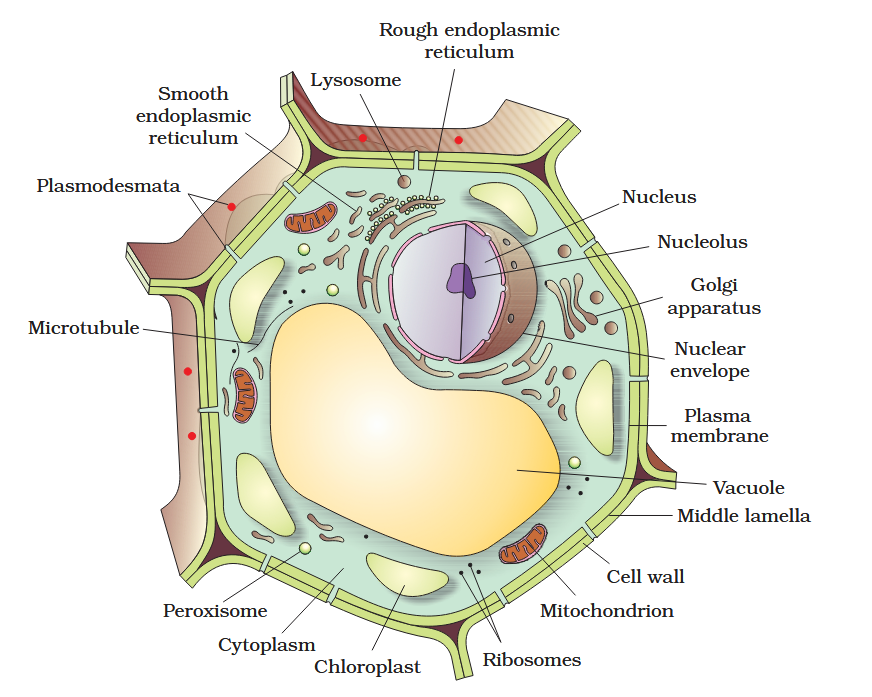
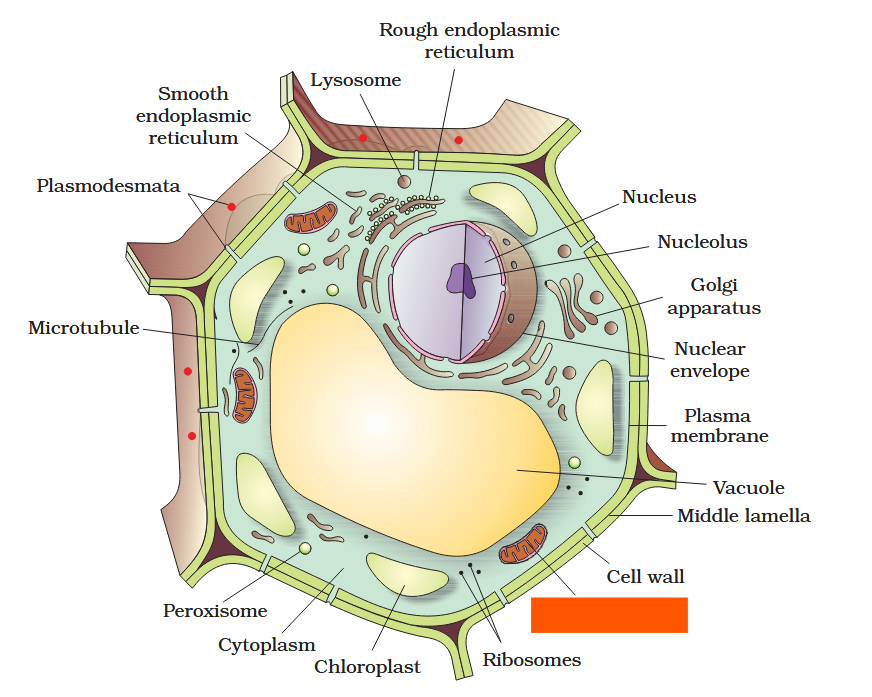
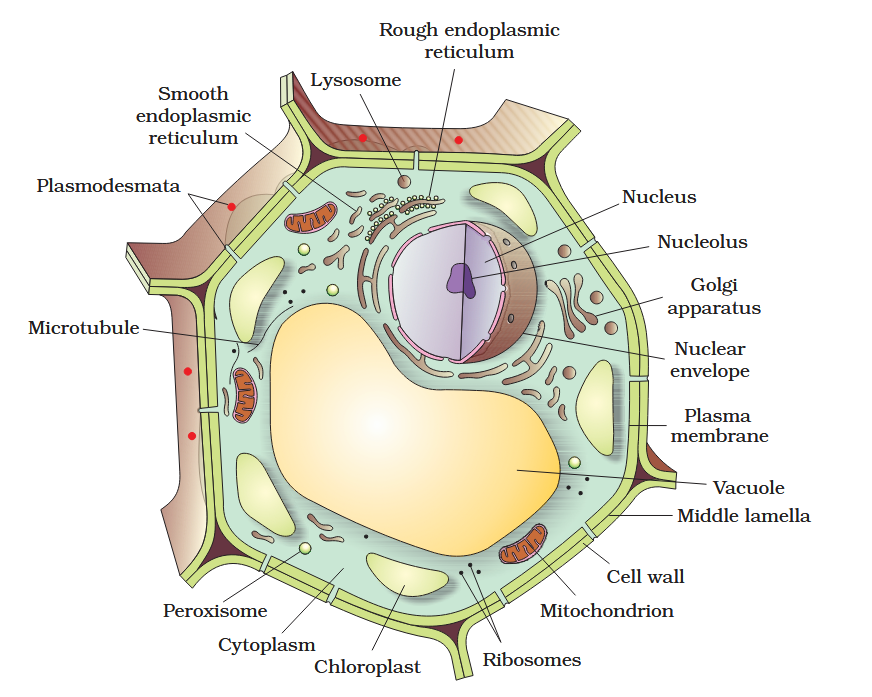

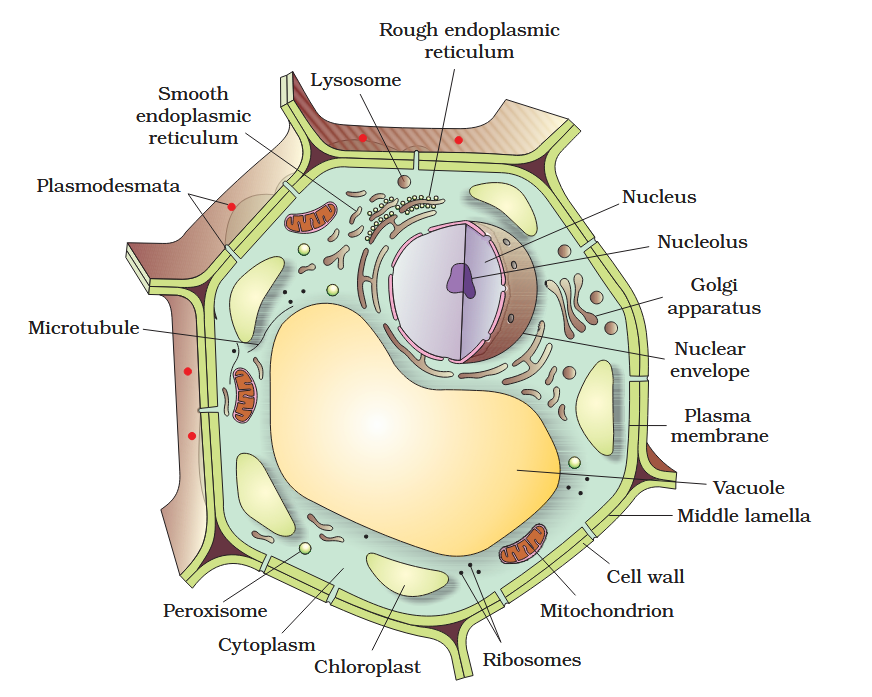

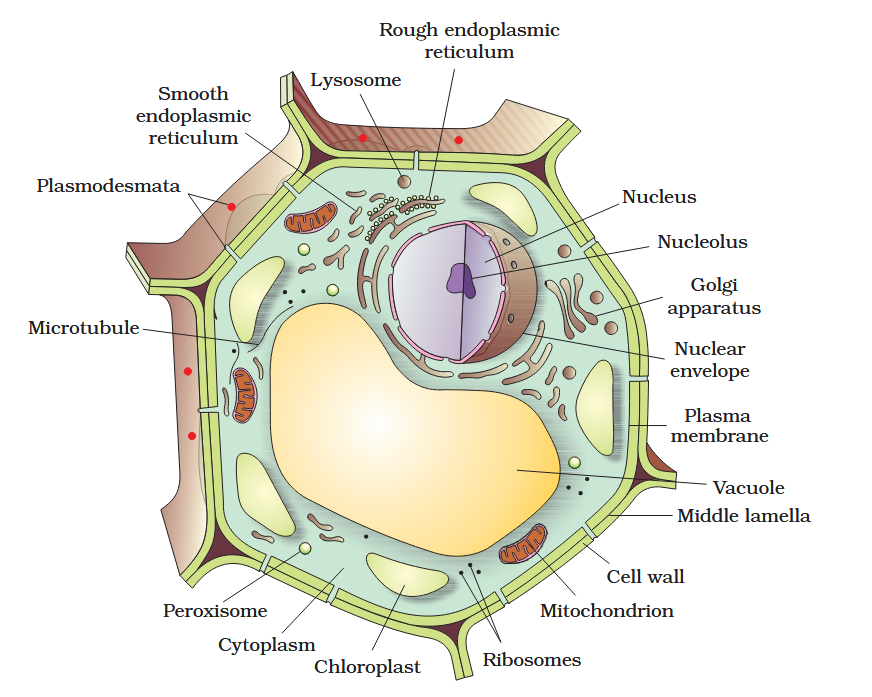
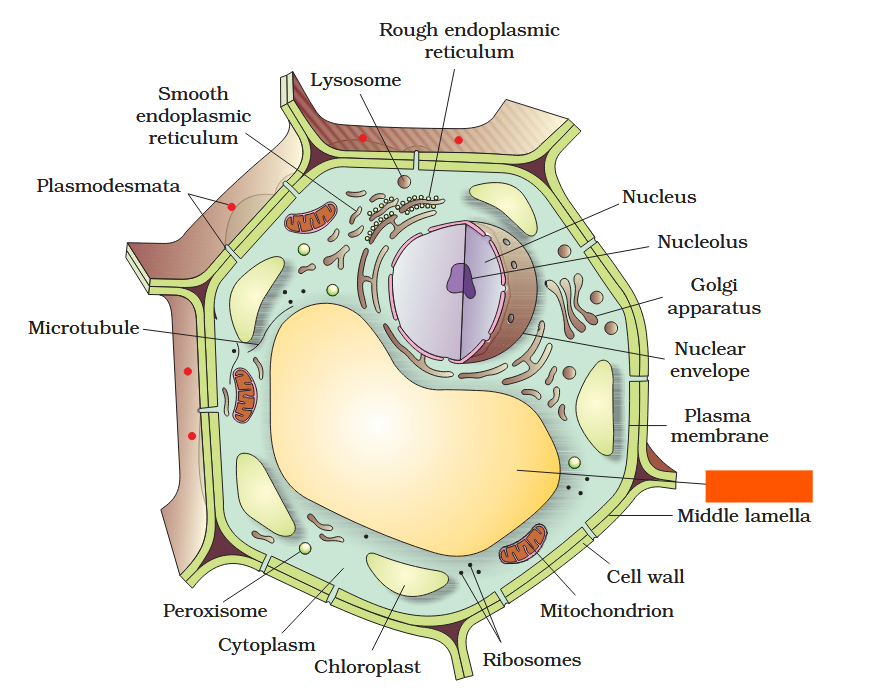
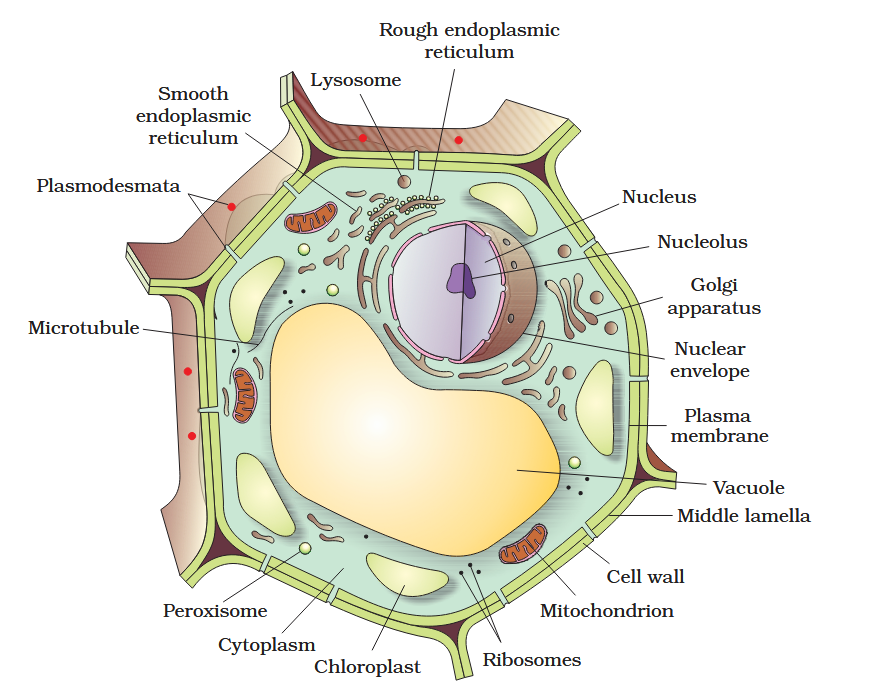
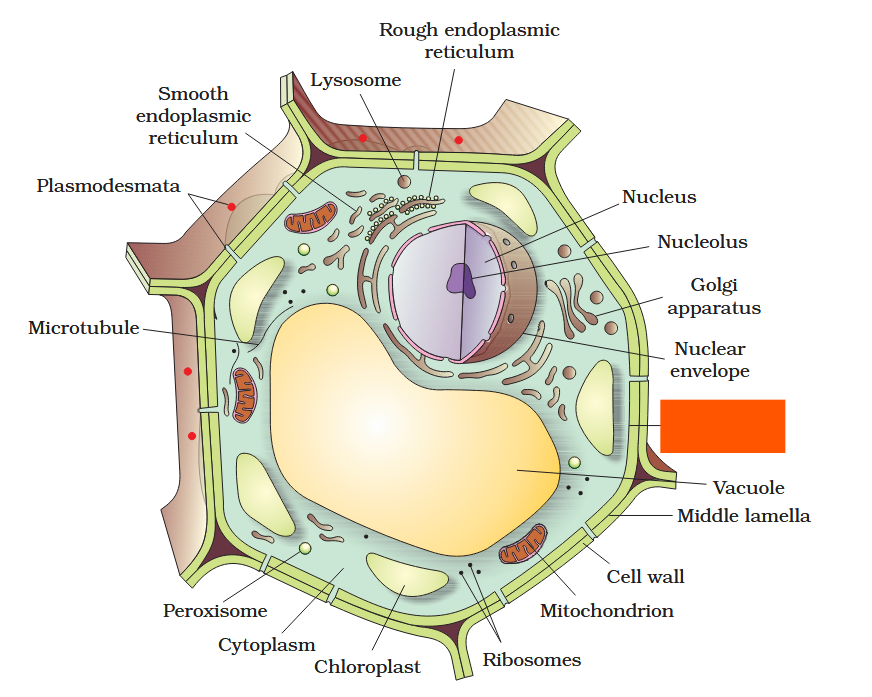

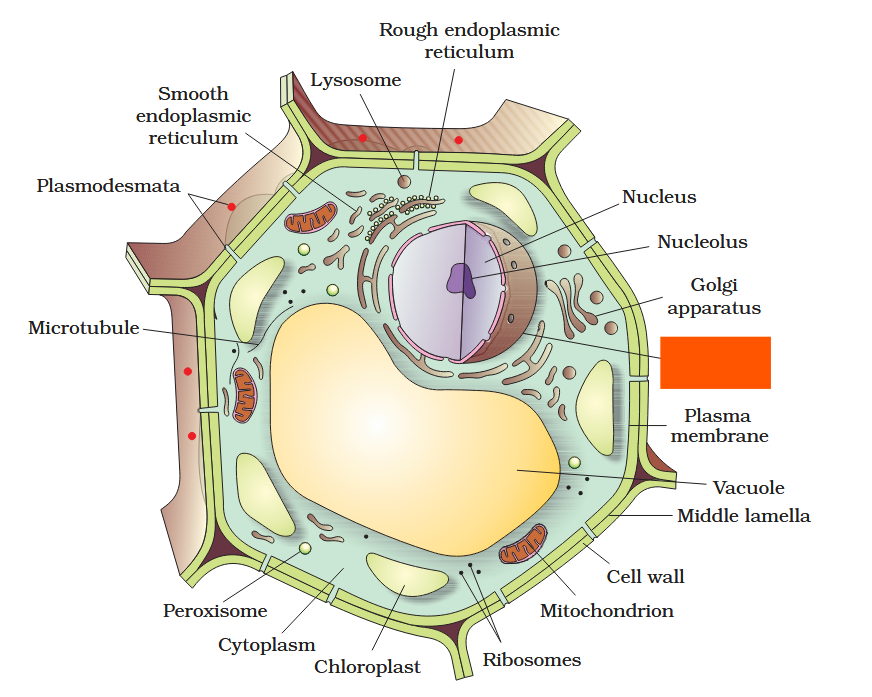
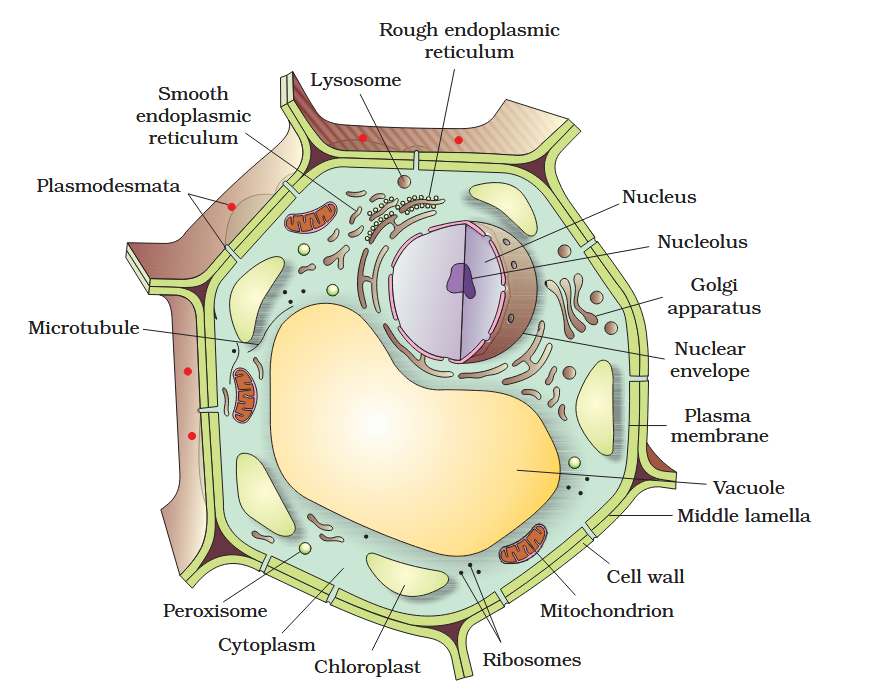

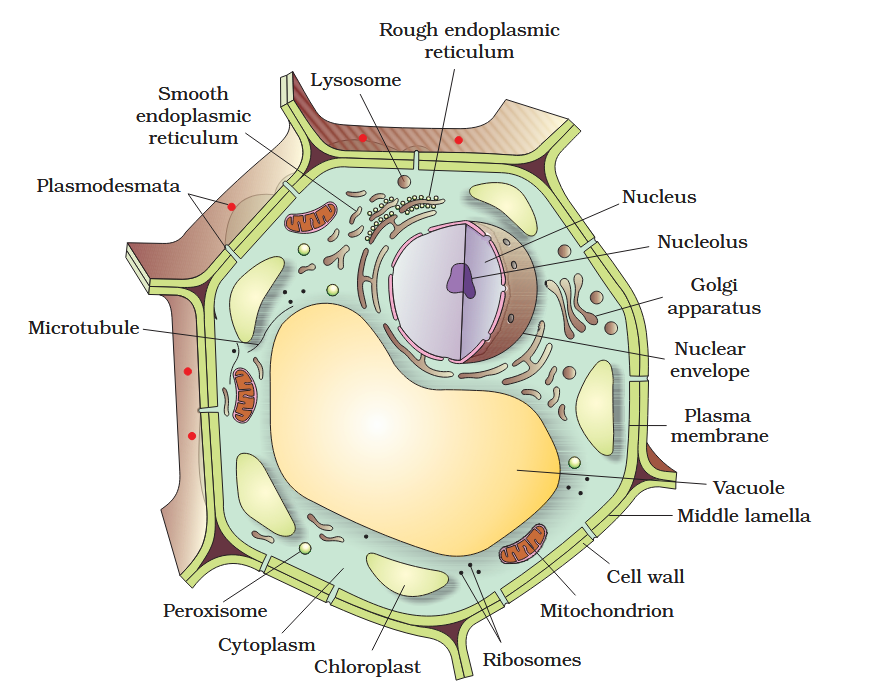
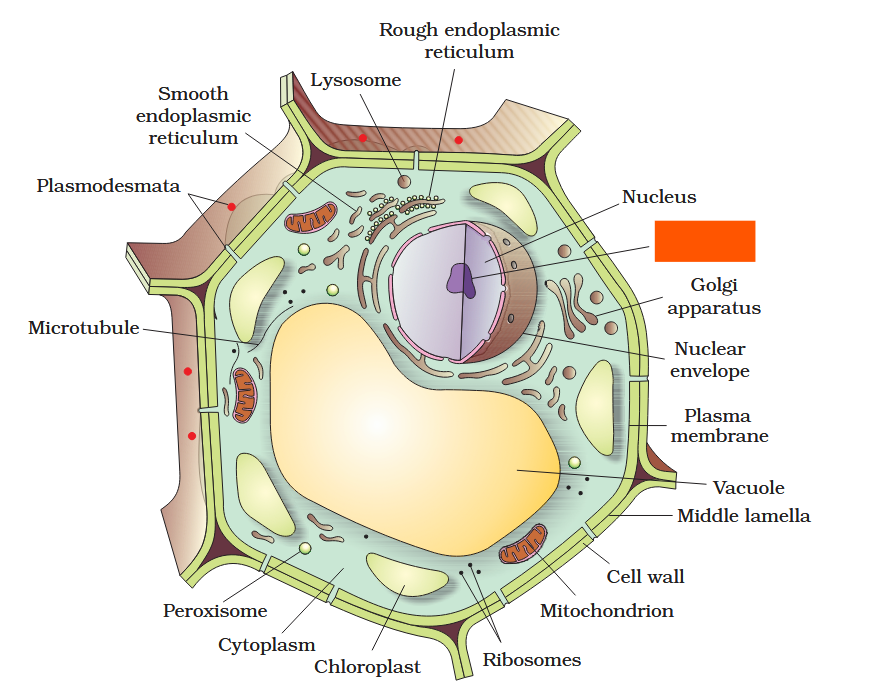
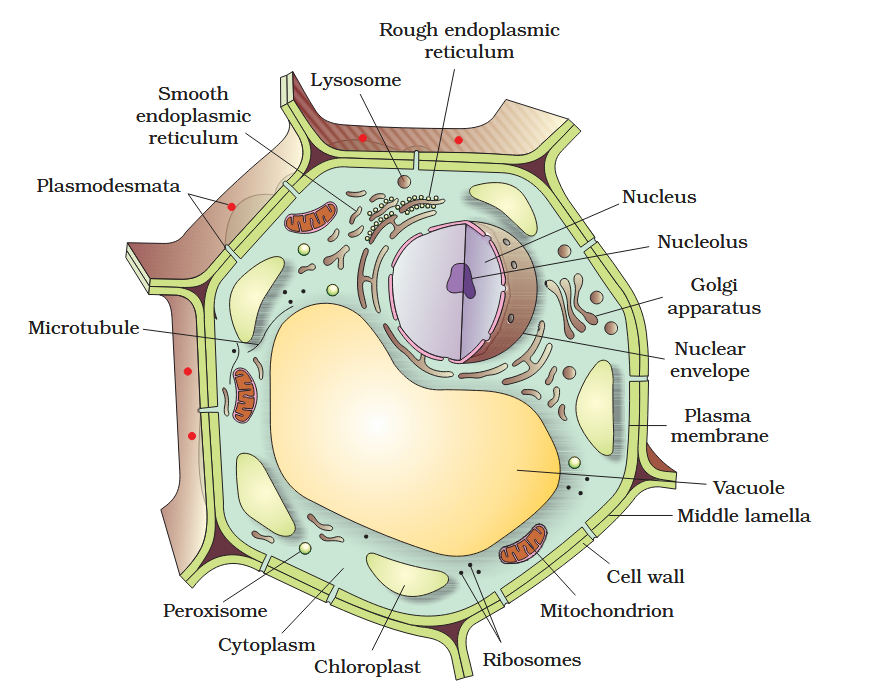


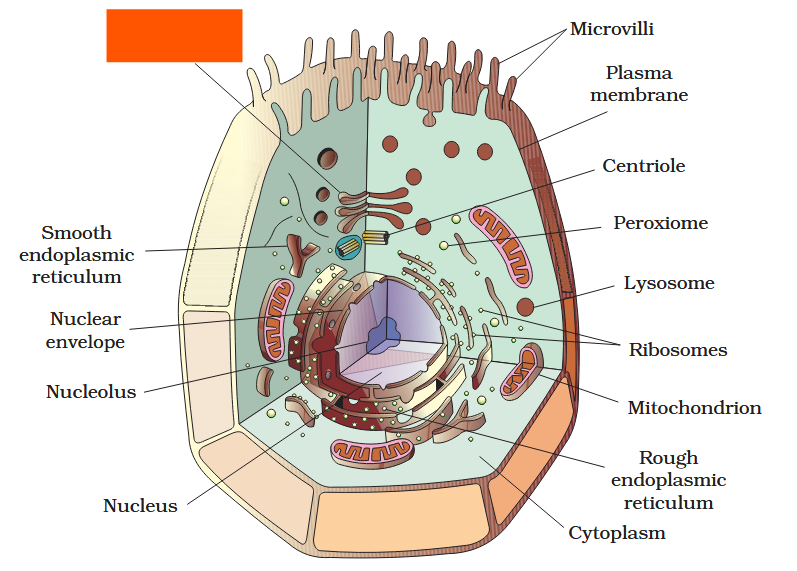

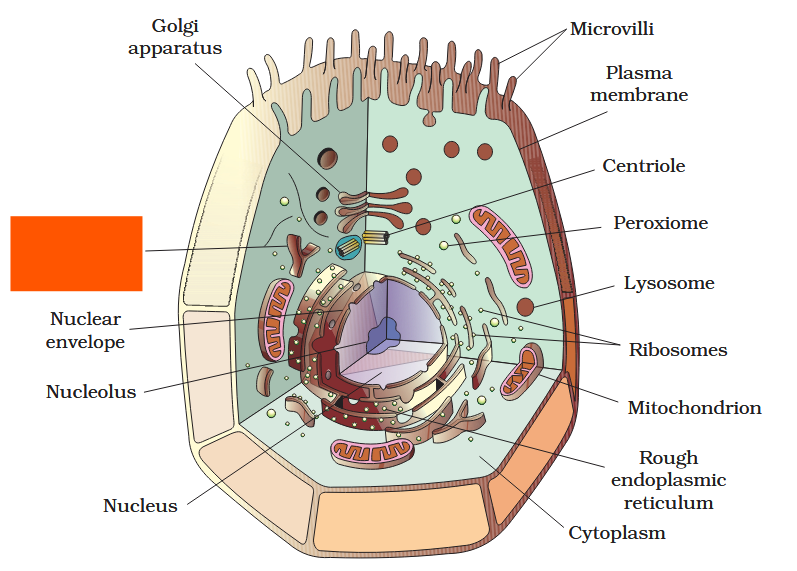
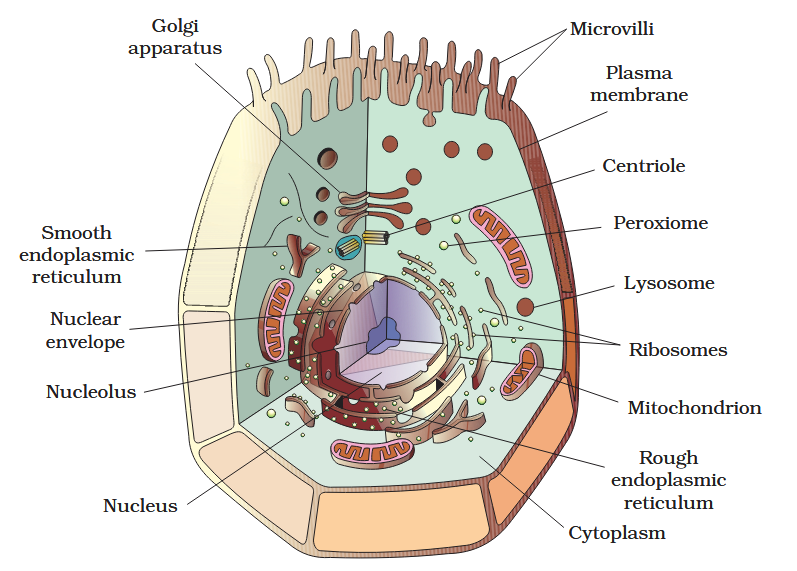
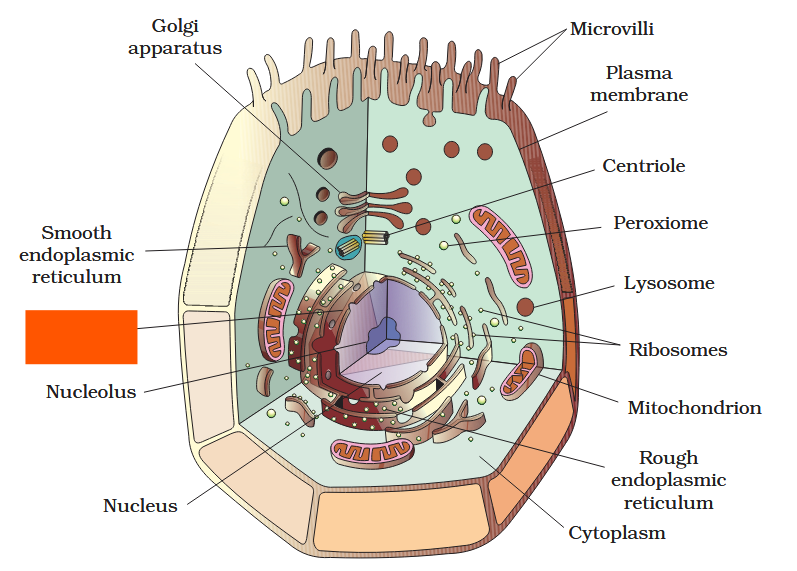
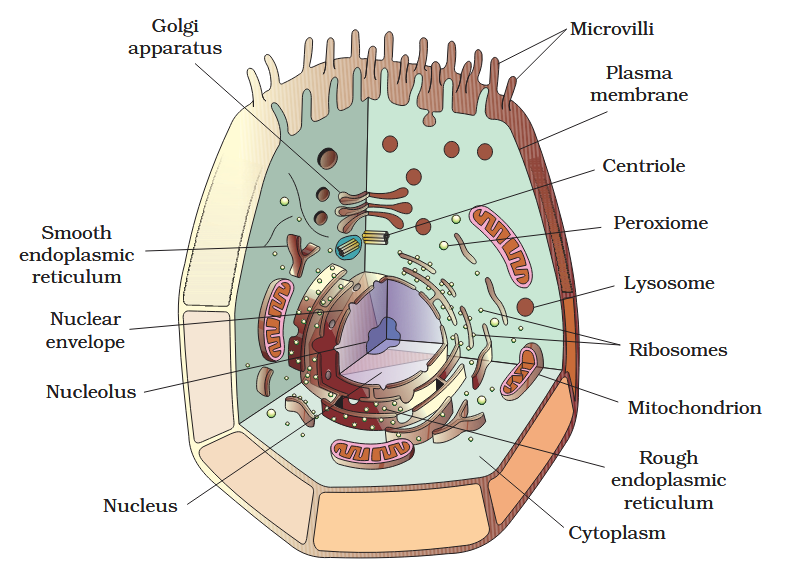
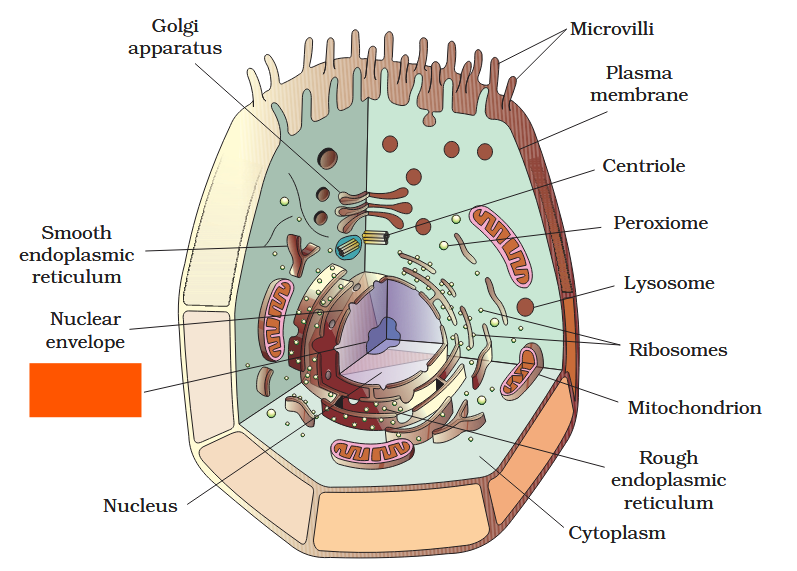
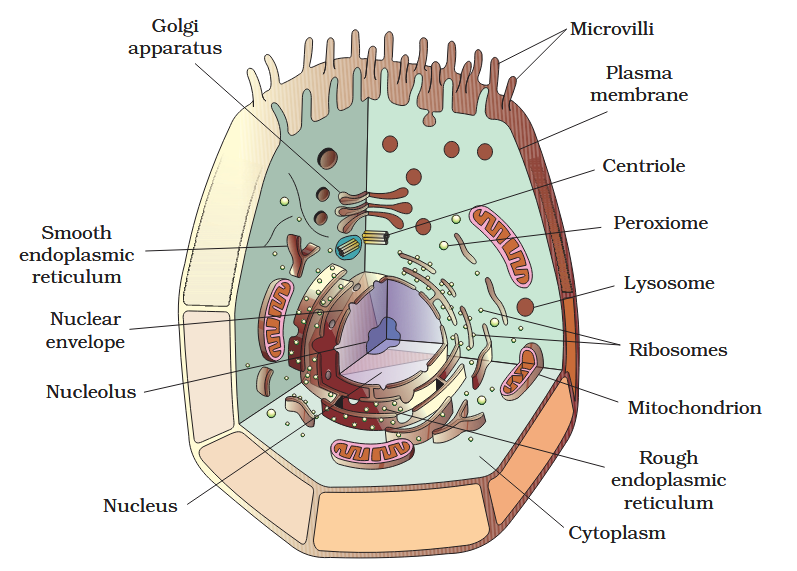
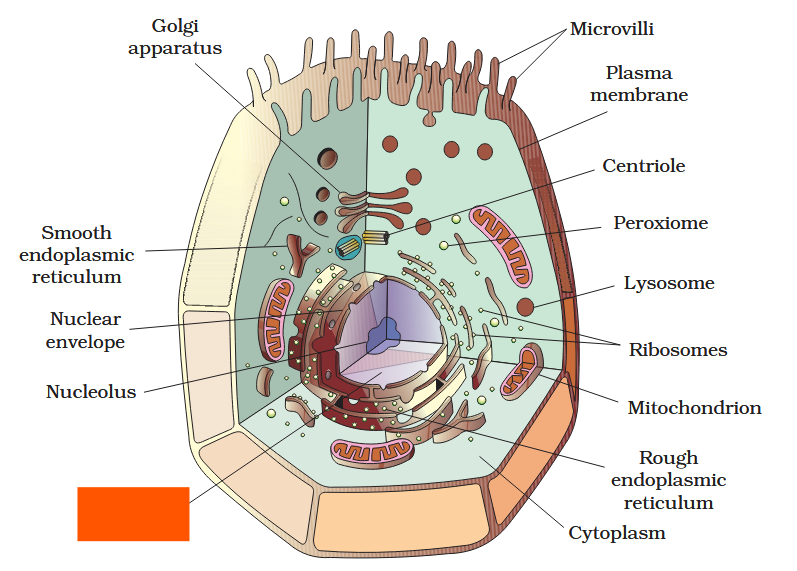

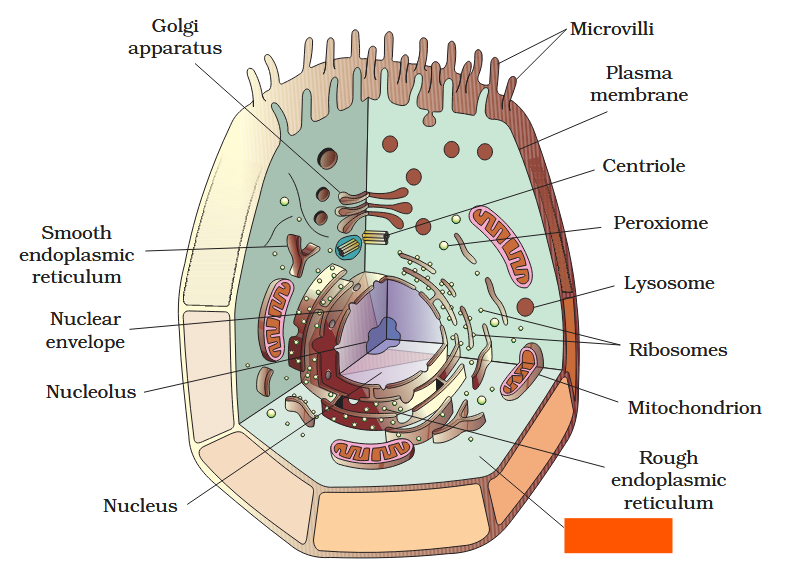
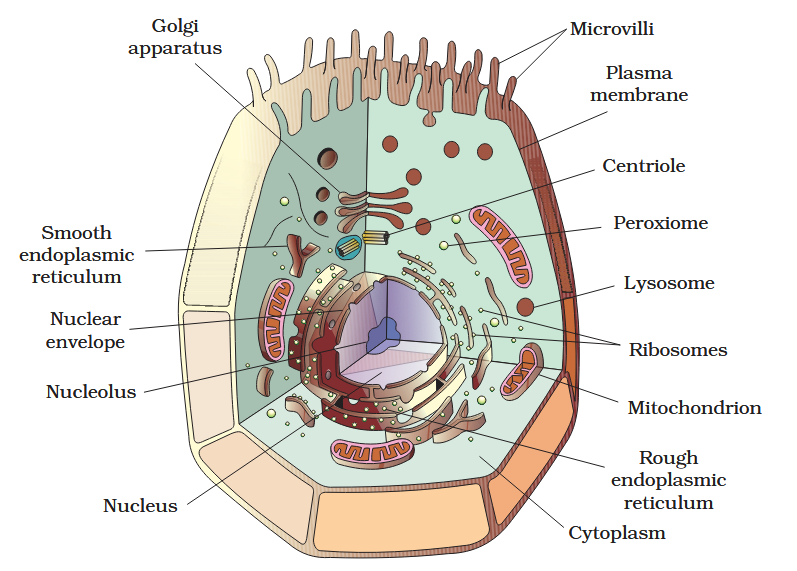
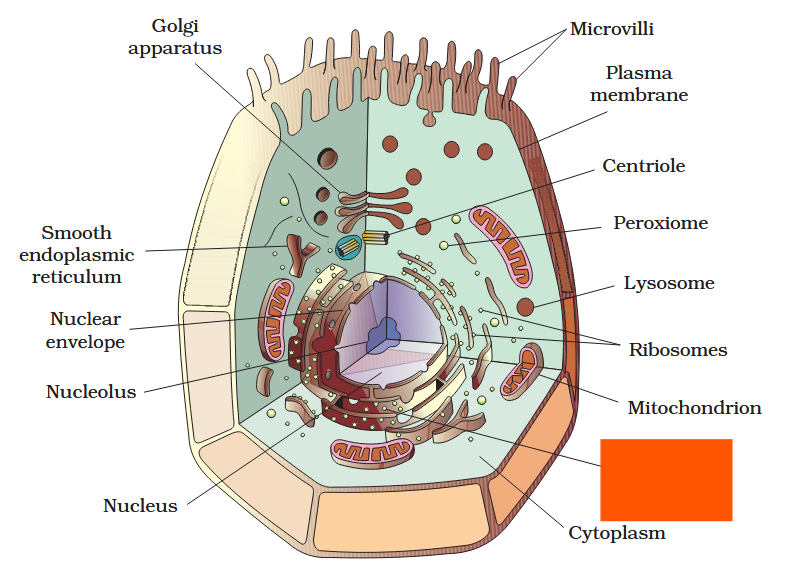
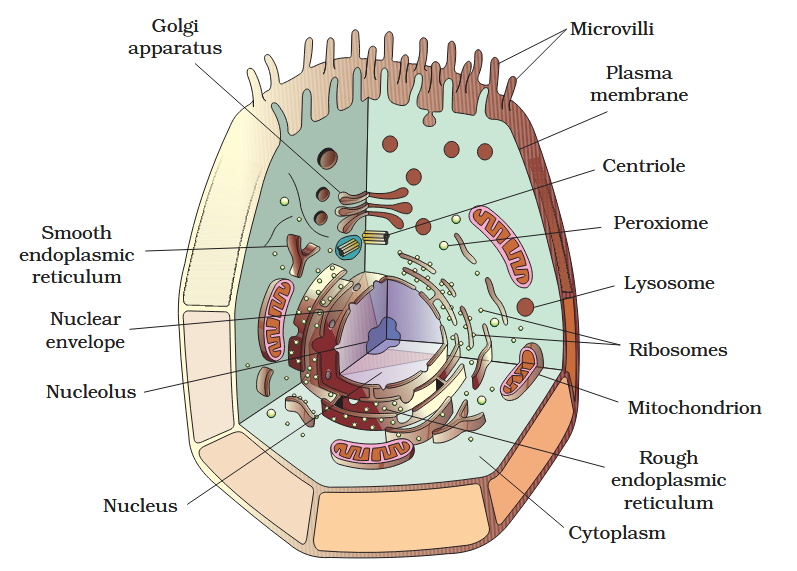
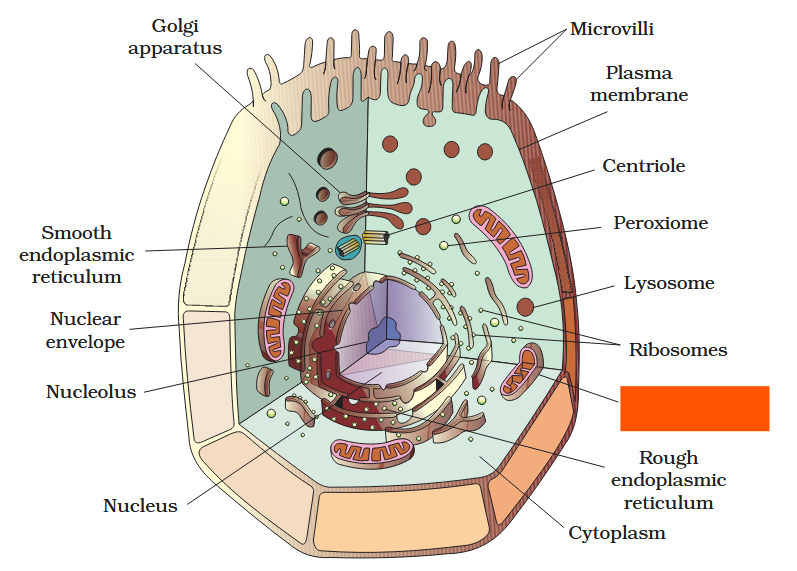
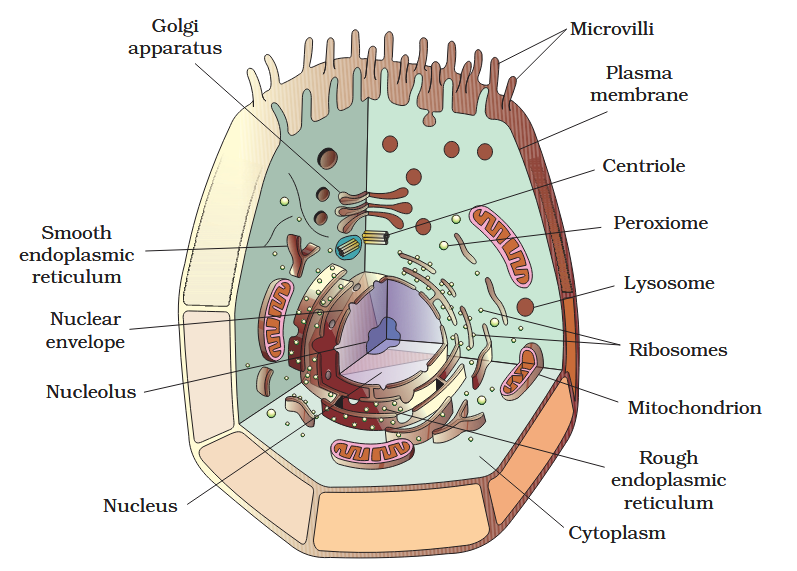

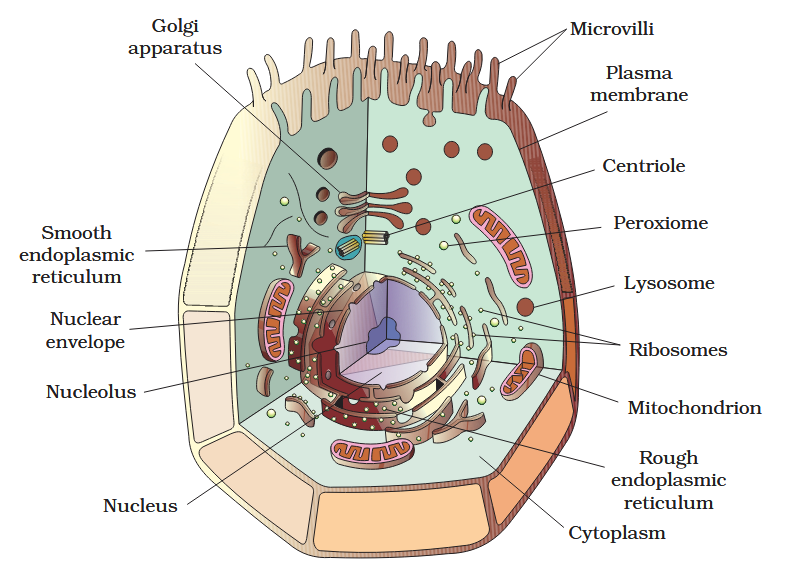
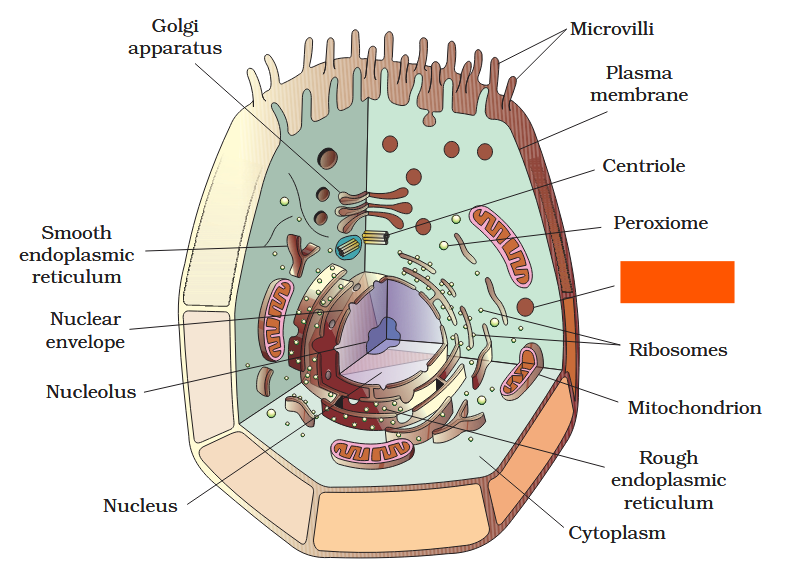
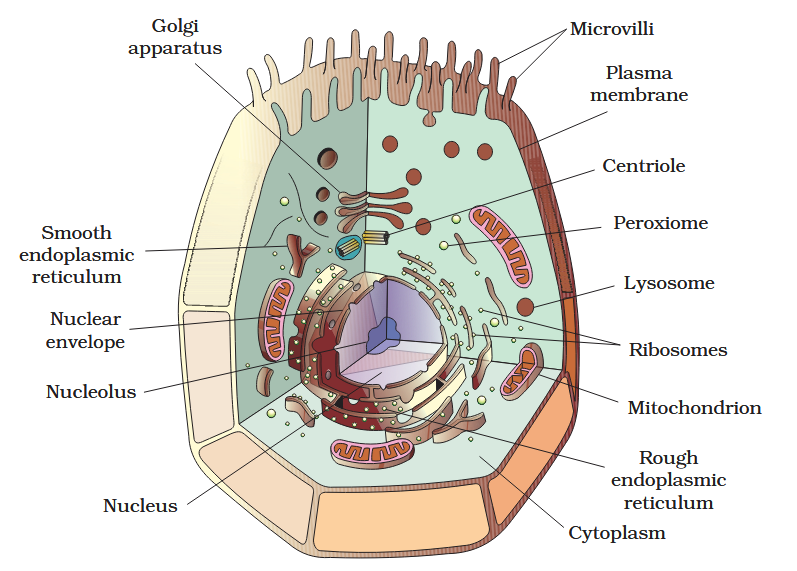
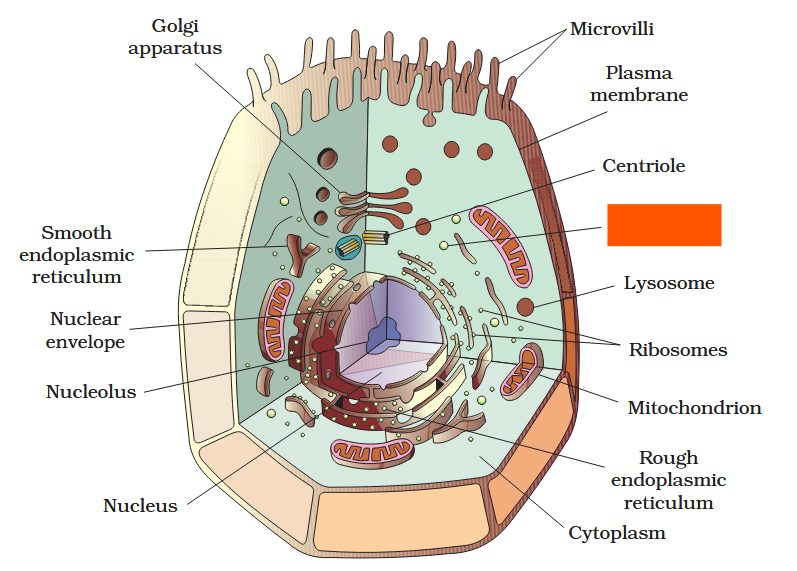
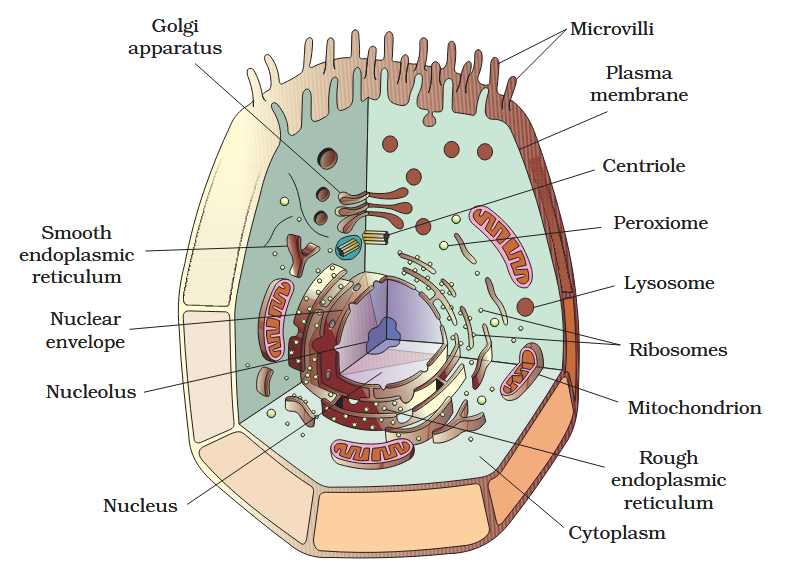
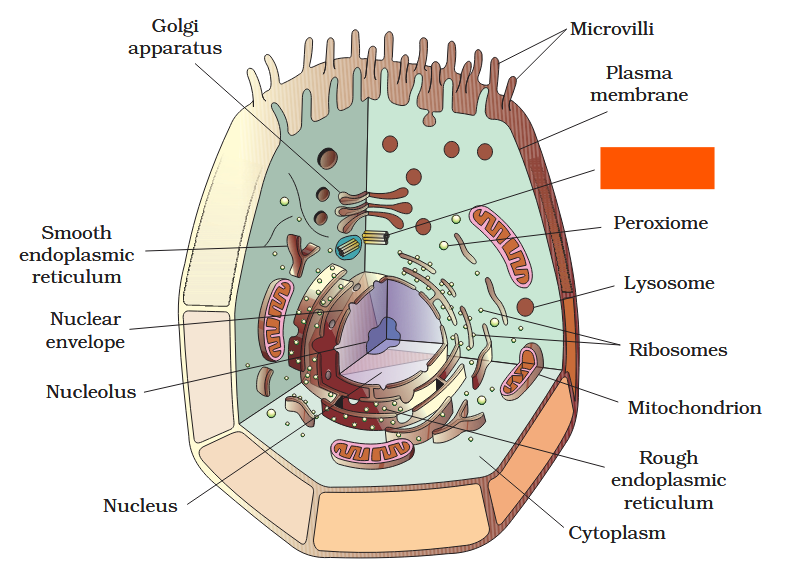

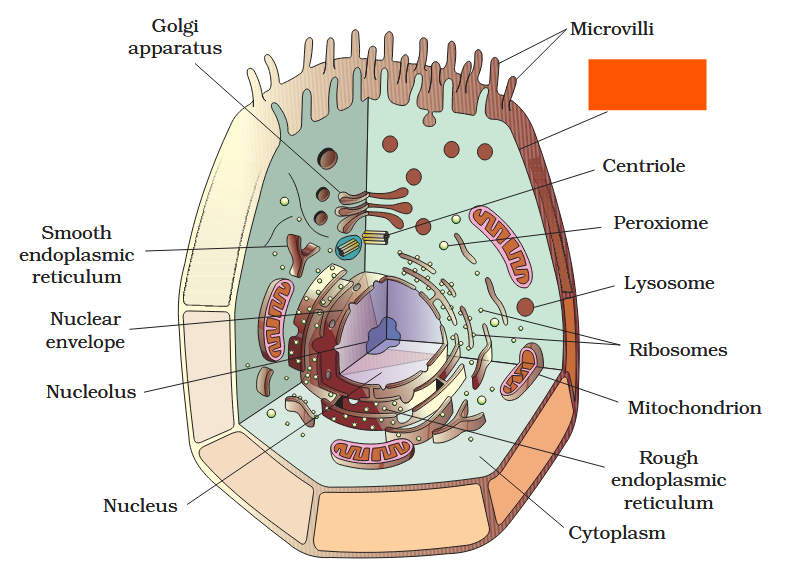
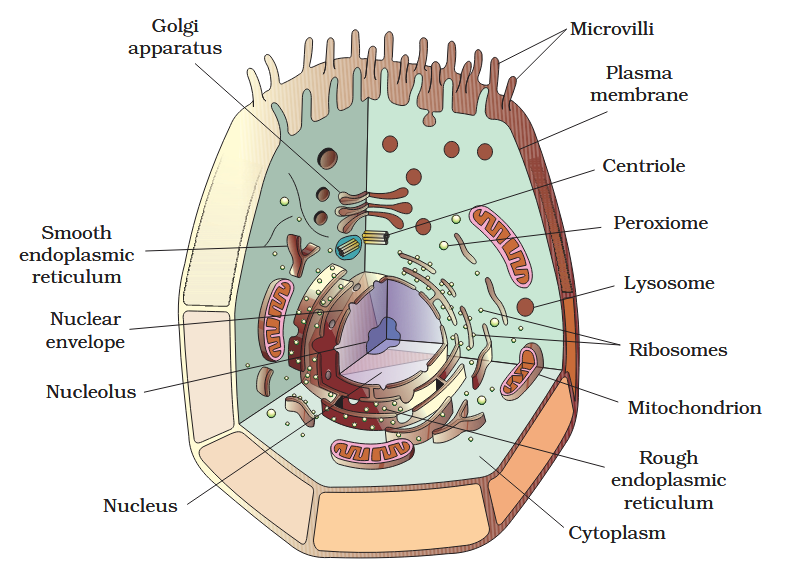
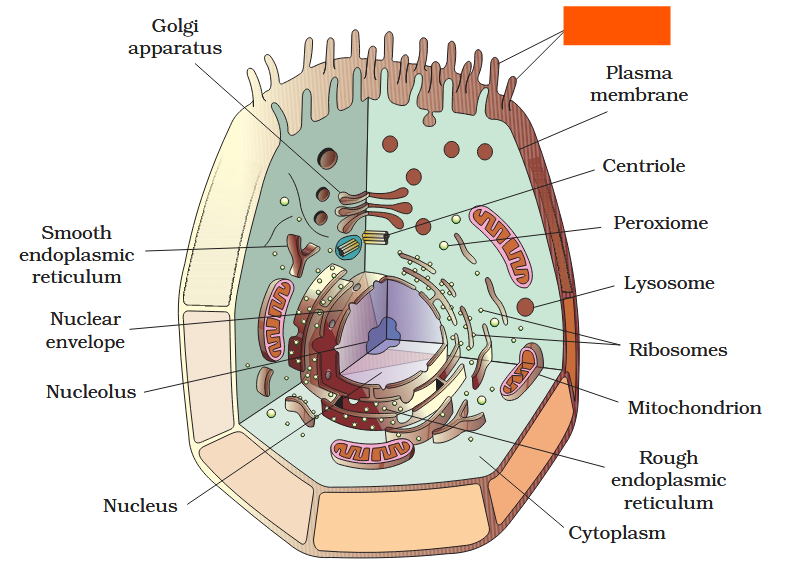
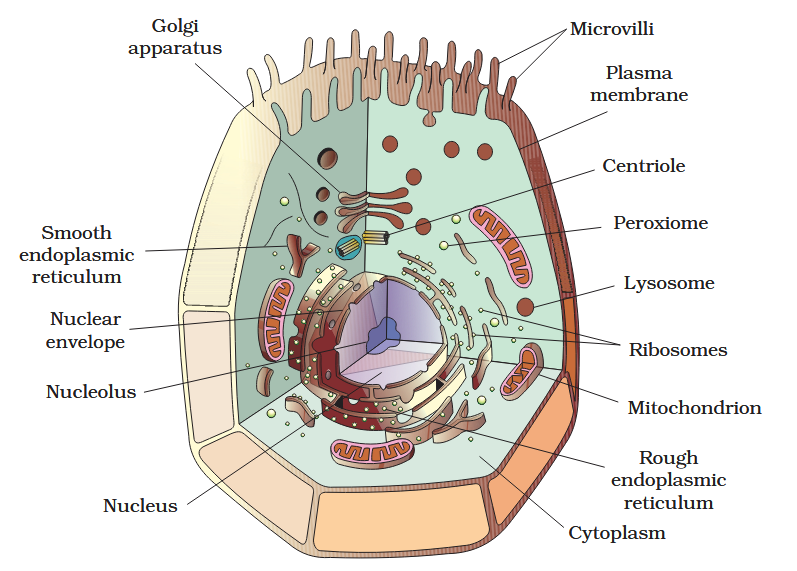
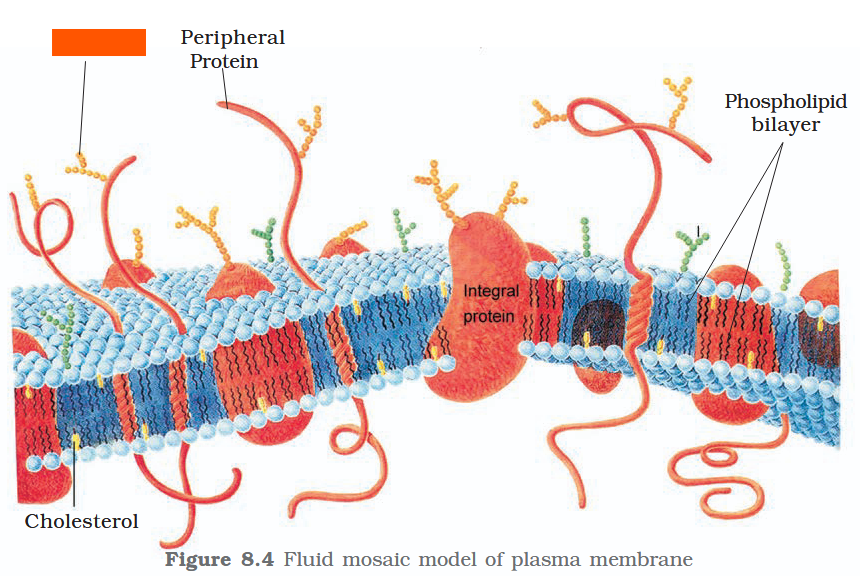
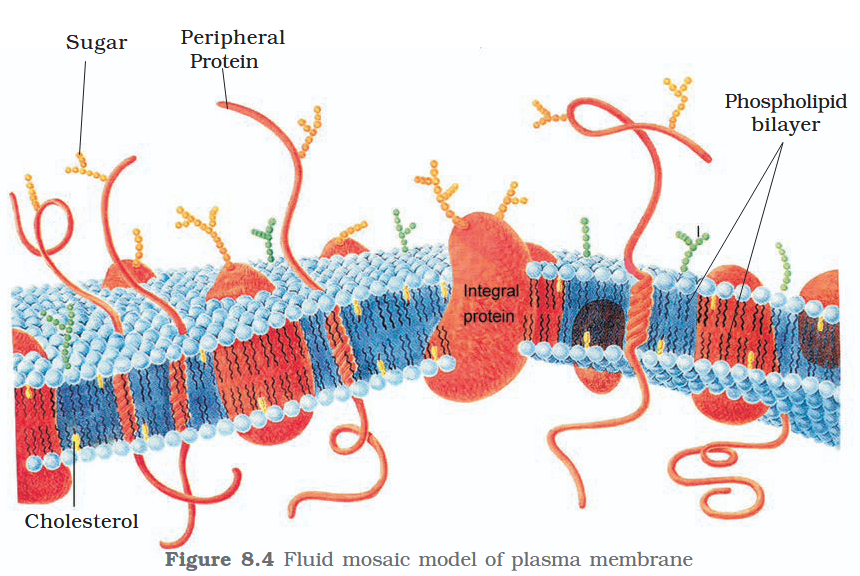

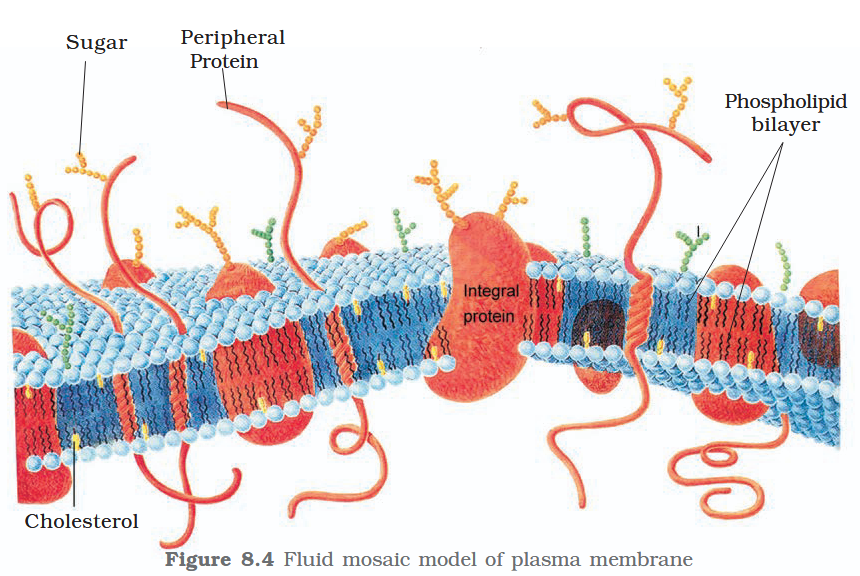
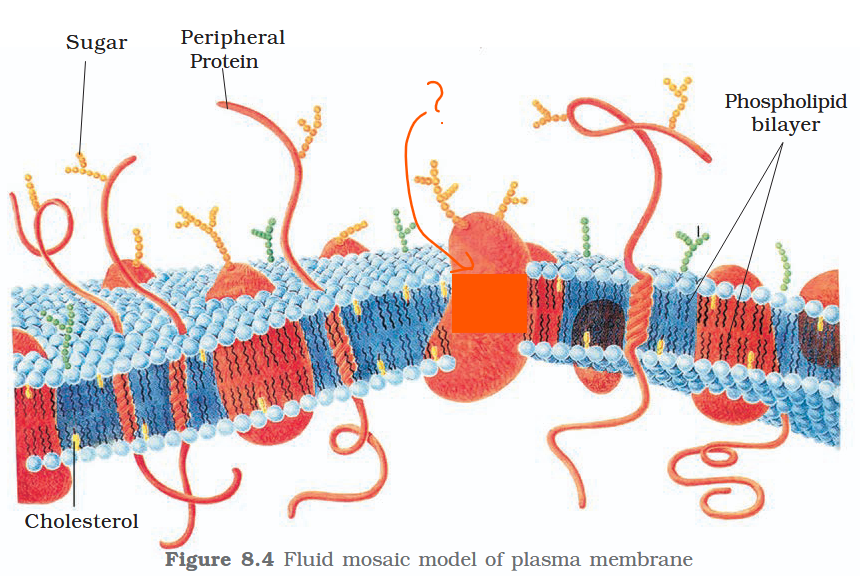
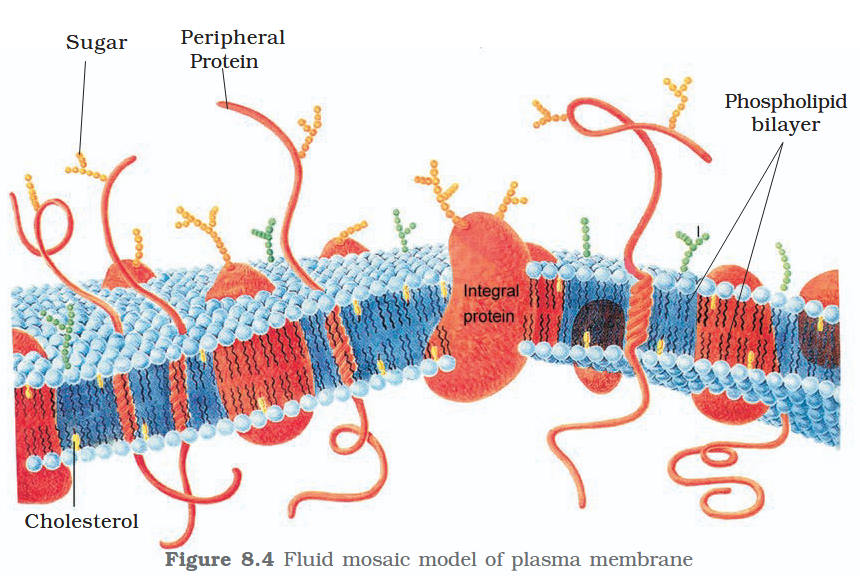
The detailed structure of the membrane was studied only after the advent of the electron microscope in the 1950s. Until then, how did scientists study cell membranes?
Chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in human red blood cells (RBCs), enabled the scientists to deduce the possible structure of plasma membrane.
The detailed structure of the membrane was studied only after the advent of the electron microscope in the 1950s. Meanwhile, chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in human red blood cells (RBCs), enabled the scientists to deduce the possible structure of plasma membrane.
What made RBCs a good candidate for these chemical studies?
They lack cell organelles so the only membrane that would yield results would be a cell membrane