Intro to Cell Biology
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Two cell types
\-prokaryotes
\-eukaryotes
\-eukaryotes
2
New cards
prokaryotes
\-bacteria and archaea
\-lack a nucleus and internal membranes
\-relatively simple
\-no organelles
\-lack a nucleus and internal membranes
\-relatively simple
\-no organelles
3
New cards
eukaryotes
\-multicellular animals, plants and fungi, and unicellular protists
\-have a nucleus and extensive internal membrane system
\-have a nucleus and extensive internal membrane system
4
New cards
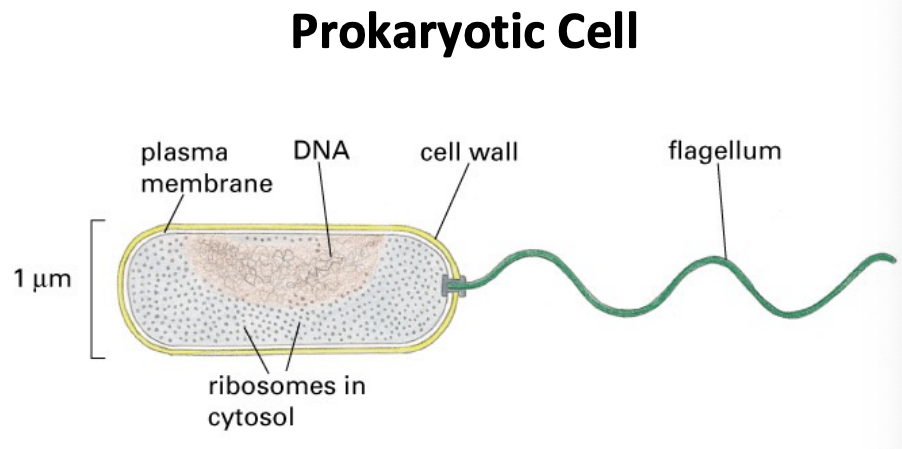
Basic structure of prokaryotic cell
\-plasma membrane
\-DNA
\-cytoplasm
\-nucleoid
\-ribosomes
\-flagellum
\-extracellular matrix
\-cell wall
\-some have lipopolysaccharide
\-DNA
\-cytoplasm
\-nucleoid
\-ribosomes
\-flagellum
\-extracellular matrix
\-cell wall
\-some have lipopolysaccharide
5
New cards
DNA
\-contains genes that encode proteins
\-transcribed into RNA and translated into proteins by ribosomes
\-transcribed into RNA and translated into proteins by ribosomes
6
New cards
Ribosomes
\-synthesizes proteins from RNA
7
New cards
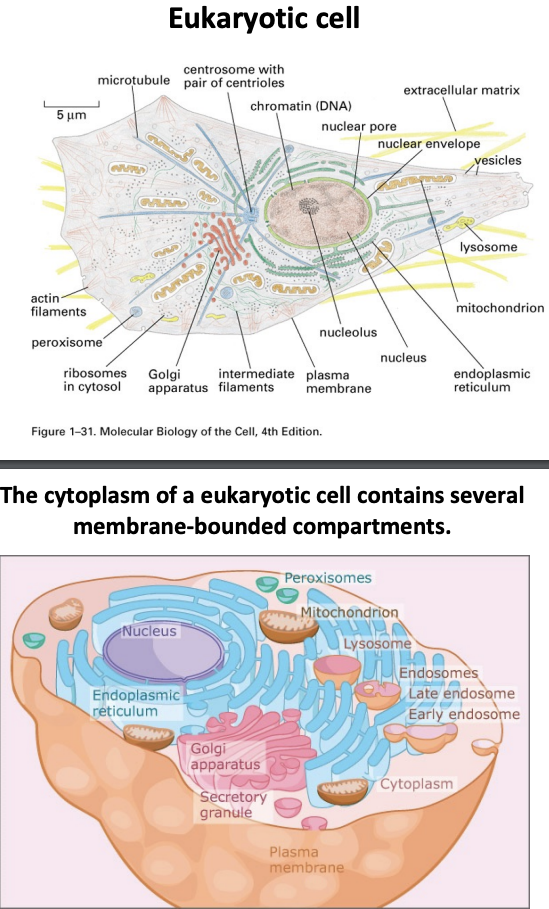
basic structure of eukaryotic cell
\-plasma membrane
\-internal membranes and organelles (spherical vesicles, sheets and tubules perform special functions)
\-cytoskeleton
\-nucleus
\-mitochondria
\-extracellular matrix
\-has internal membrane bound organelles
\-internal membranes and organelles (spherical vesicles, sheets and tubules perform special functions)
\-cytoskeleton
\-nucleus
\-mitochondria
\-extracellular matrix
\-has internal membrane bound organelles
8
New cards
plasma membrane
\-lipid bilayer
\-boundary of cell that allows it to create an internal environment different from the external environment
\-special systems exist to transport both small and large molecules across this barrier
\-boundary of cell that allows it to create an internal environment different from the external environment
\-special systems exist to transport both small and large molecules across this barrier
9
New cards
cytoplasm
\-the soluble internal content of the cell
\-the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell contains several membrane bounded compartments
\-the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell contains several membrane bounded compartments
10
New cards
nucleoid
\-in prokaryotic cells
\-area in which circular DNA is concentrated
\-area in which circular DNA is concentrated
11
New cards
flagellum
\-outside prokaryotic cells
\-a unique proton driven structure
\-a threadlike structure that helps them to swim
\-a unique proton driven structure
\-a threadlike structure that helps them to swim
12
New cards
extracellular matrix
\-material made by cells and deposited outside the plasma membrane
\-helps cells attach to, and communicate with, nearby cells, and plays an important role in cell growth, cell movement, and other cell functions.
\-involved in repairing damaged tissue.
\-includes cell wall and sometimes lipopolysaccharide capsule
\-helps cells attach to, and communicate with, nearby cells, and plays an important role in cell growth, cell movement, and other cell functions.
\-involved in repairing damaged tissue.
\-includes cell wall and sometimes lipopolysaccharide capsule
13
New cards
cytoskeleton
\-network of filaments inside cells
\-provides structural and organizational framework of cells
\-provides oriented railroad tracks for transporting vesicles, etc
\-provides structural and organizational framework of cells
\-provides oriented railroad tracks for transporting vesicles, etc
14
New cards
nucleus
\-DNA organized here so it can be used and replicated (transcription, splicing, mRNP assembly)
15
New cards
mitochondria
\-energy supply
\-makes ATP from sugars, fatty acids, amino acids
\-signaling center in some cells - damage induced death (apoptosis)
\-makes ATP from sugars, fatty acids, amino acids
\-signaling center in some cells - damage induced death (apoptosis)
16
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum
proteins are synthesized here with the help of ribosomes
17
New cards
golgi apparatus
\-processing of proteins occurs here
18
New cards
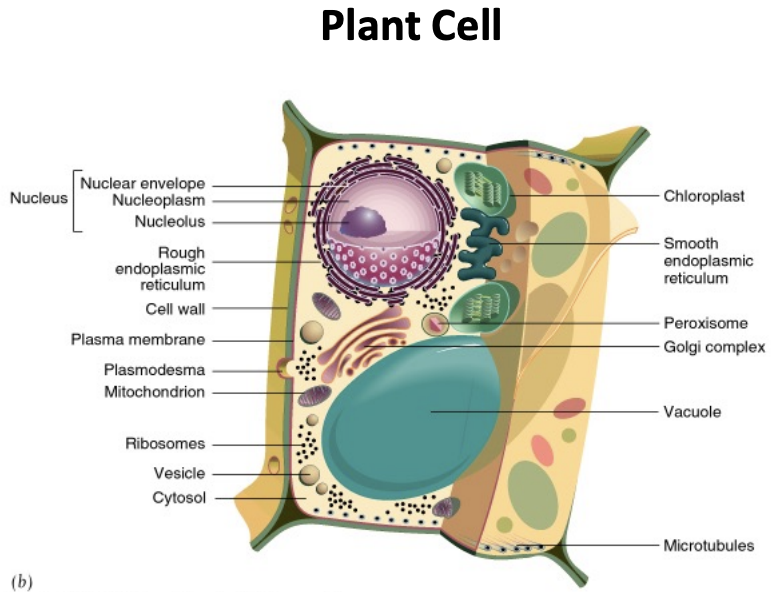
plants and algae
\-eukaryotic cells with something extra
\-in addition to components of eukaryotic cells, they have chloroplasts and cell walls
\-in addition to components of eukaryotic cells, they have chloroplasts and cell walls
19
New cards
chloroplasts
\-make ATP from sunlight
\-photosynthesis
\-photosynthesis
20
New cards
cell walls
\-rigid cellulose walls (extracellular matrix)
\-define shape of cells and tissues
\-for protection and strength (counter osmotic turgor pressure)
\-prevents movement
\-define shape of cells and tissues
\-for protection and strength (counter osmotic turgor pressure)
\-prevents movement
21
New cards
Original Cell Theory
\-robert hook studying plants
\-cells are not formed randomly
\-cells are not formed randomly
22
New cards
modern cell theory
1. All living things are made of one or more cells
2. The cell is structural and functional unit of all living things
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division
4. Cells contains heredity information which is passed from cell to cell division
5. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition
6. All energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) of life occurs within cells
23
New cards
basic shared properties of cells include
\-being composed of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
\-having a high degree of complexity
\-encoding information in genes
\-being delineated from the rest of the world by a membrane
\-being able to reproduce themselves
\-being able to acquire and utilize energy
\-being able to carry out mechanical activities
\-being able to respond to stimuli
\-being capable of self regulation
\-being capable of evolving
\-Note: not all cells have all these at all points in their life (cells lose ability to reproduce, lose nuclei and organelles)
\-having a high degree of complexity
\-encoding information in genes
\-being delineated from the rest of the world by a membrane
\-being able to reproduce themselves
\-being able to acquire and utilize energy
\-being able to carry out mechanical activities
\-being able to respond to stimuli
\-being capable of self regulation
\-being capable of evolving
\-Note: not all cells have all these at all points in their life (cells lose ability to reproduce, lose nuclei and organelles)
24
New cards
what organizes cells and determines their properties?
\-genes
25
New cards
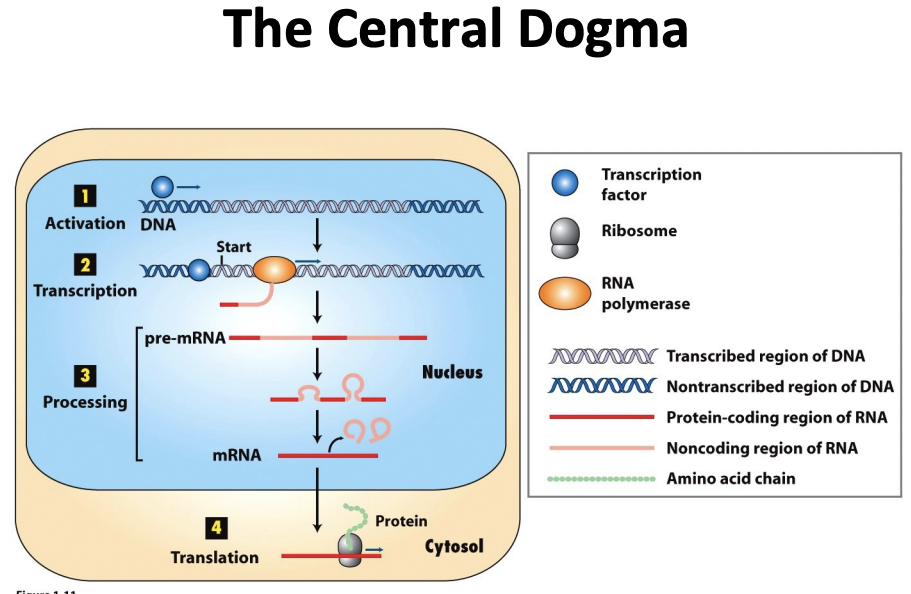
the central dogma
\-a phrase that refers to our current understanding of how info is encoded in our cells in the form of genes in our DNA
\-these genes are expressed producing proteins that do useful work
\-genes organize the cell
\-these genes are expressed producing proteins that do useful work
\-genes organize the cell
26
New cards
gene expression
\-(grey) gene in the DNA that will encode a protein
\-(blue circle) transcription factor which are proteins that interact with DNA and help activate the expression of a gene, bring in rna polymerase to the region so that the DNA can be transcribed into mRNA
\
\-preRNA goes through splicing to get rid of introns and left with mRNA
\-mRNA is exported from the nucleus and encounters ribosomes that translate mRNA into a protein (make peptide bonds between amino acids)
\-(blue circle) transcription factor which are proteins that interact with DNA and help activate the expression of a gene, bring in rna polymerase to the region so that the DNA can be transcribed into mRNA
\
\-preRNA goes through splicing to get rid of introns and left with mRNA
\-mRNA is exported from the nucleus and encounters ribosomes that translate mRNA into a protein (make peptide bonds between amino acids)
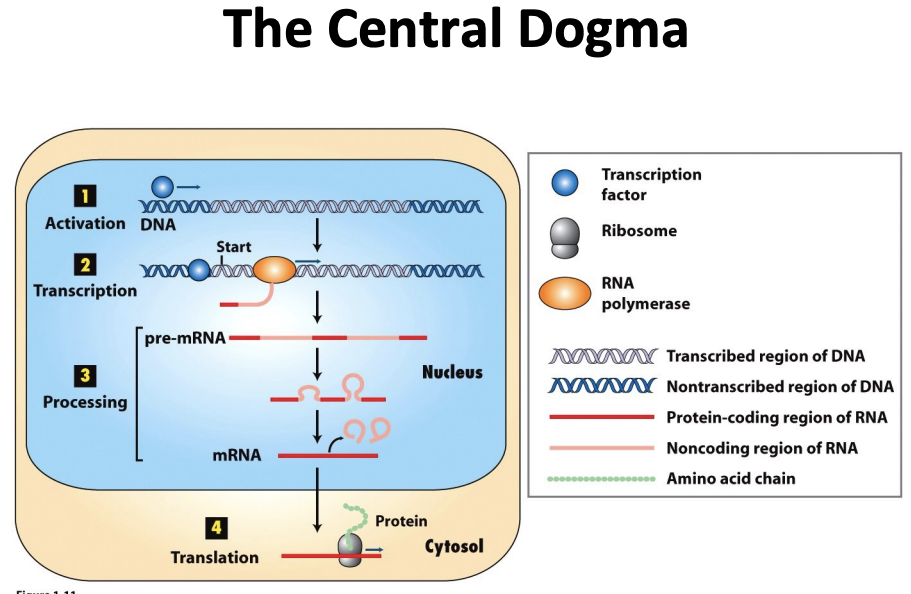
27
New cards
genetic information flow
\-DNA codes for mRNA, mRNA codes for protein sequence
\
\-DNA is transcribed to mRNA in the nucleus, mRNA leaves nucleus and is translated into protein by ribosomes, tRNA, amino acids
\
\-DNA also codes for small RNA species that don’t encode proteins, but regulate the stability of mRNAs (i.e. microRNA; miRNA ).
\
\-In general (but not always!) one gene codes for one protein.
\--Genes can be alternatively spliced, proteins can be cleaved into multiple active species
\
\-Proteins fold into specific shapes to make:
\--Enzymes, which carry out chemical reactions
\-–Structural proteins, which provide organization
\-–Regulatory molecules, which provide information (switches)
\
\-Proteins are the workhorses of cells; they directly do many things cells do and catalyze the production of non-protein constituents of cells.
\
\-Changes in DNA sequence (mutations) produce heritable changes in protein structure, function and expression. This is the basis for evolution
\
\-DNA is transcribed to mRNA in the nucleus, mRNA leaves nucleus and is translated into protein by ribosomes, tRNA, amino acids
\
\-DNA also codes for small RNA species that don’t encode proteins, but regulate the stability of mRNAs (i.e. microRNA; miRNA ).
\
\-In general (but not always!) one gene codes for one protein.
\--Genes can be alternatively spliced, proteins can be cleaved into multiple active species
\
\-Proteins fold into specific shapes to make:
\--Enzymes, which carry out chemical reactions
\-–Structural proteins, which provide organization
\-–Regulatory molecules, which provide information (switches)
\
\-Proteins are the workhorses of cells; they directly do many things cells do and catalyze the production of non-protein constituents of cells.
\
\-Changes in DNA sequence (mutations) produce heritable changes in protein structure, function and expression. This is the basis for evolution
28
New cards
genomes, genes, and proteins
\-we now know the complete sequence of the genomes of many organisms
\-we can “read” the gene sequences to predict the potential complement fo proteins (proteome) of many organisms
\-prokaryote needs 1000-4000 different proteins to make a cell
\-eukaryote needs 30000 to make a complex cell
\-we can “read” the gene sequences to predict the potential complement fo proteins (proteome) of many organisms
\-prokaryote needs 1000-4000 different proteins to make a cell
\-eukaryote needs 30000 to make a complex cell
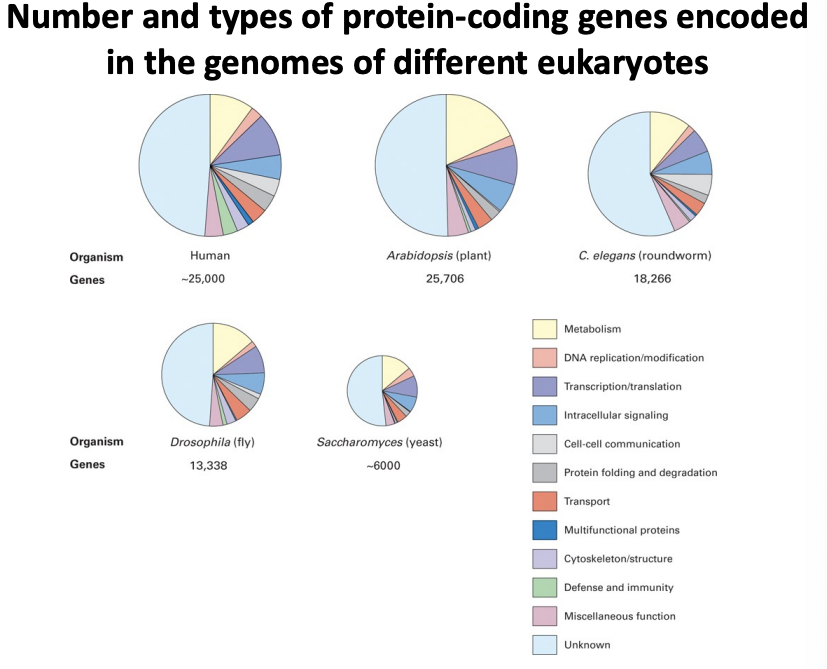
29
New cards
not all of the information in a cell is encoded directly in DNA in a form we can read
\-While knowing the gene sequences of an organism can tell us exactly which proteins its cells are capable of producing, it can’t directly tell us how a cell works or what it will do.
\
\-Remember that while all the cells of an individual organism contain identical copies of its DNA sequence, a cell does not express all of its genes all of the time.
\
\-In any given cell, some genes are “turned on”, some are “turned off”. Some are expressed at high levels, some low. This is known as differential gene expression. Transcription factors are the proteins that bind DNA and can activate or repress the transcription of genes.
\
\-Depending on which genes are being transcribed (the transcriptome\*) and translated, a cell will express a particular suite of proteins that helps define the potential of that cell.
\
\-One of the central goals of cell biology is to understand how the interactions of different combinations of proteins and other cellular components are dynamically coordinated to give rise to the amazing diversity of cell types and behaviors.
\
\-\*Our increasing ability to sequence the mRNAs of individual cells (“RNAseq”), even almost every cell of an embryo, at different time points, is getting us much closer to uncovering the true differential gene expression state of cells and organisms.
\
\-Remember that while all the cells of an individual organism contain identical copies of its DNA sequence, a cell does not express all of its genes all of the time.
\
\-In any given cell, some genes are “turned on”, some are “turned off”. Some are expressed at high levels, some low. This is known as differential gene expression. Transcription factors are the proteins that bind DNA and can activate or repress the transcription of genes.
\
\-Depending on which genes are being transcribed (the transcriptome\*) and translated, a cell will express a particular suite of proteins that helps define the potential of that cell.
\
\-One of the central goals of cell biology is to understand how the interactions of different combinations of proteins and other cellular components are dynamically coordinated to give rise to the amazing diversity of cell types and behaviors.
\
\-\*Our increasing ability to sequence the mRNAs of individual cells (“RNAseq”), even almost every cell of an embryo, at different time points, is getting us much closer to uncovering the true differential gene expression state of cells and organisms.
30
New cards
what gives rise to the diversity of cell types and behaviors we see if all the cells of an organism contain identical copies of its DNA sequence?
differential gene expression
31
New cards
differential gene expression (transcription factors)
\-transcription factors are proteins that interact with specific DNA regulatory sequences associated with genes (promoter and enhancer elements) to modulate transcription by RNA polymerases
\
\-different cell types are using different transcription factors
\
\-different transcription factors will only activate certain genes
\
\-ex: as muscle cells develop, they have transcription factors myody that can bind to the regulatory sequences of genes that encode proteins that are responsible for muscle function.
\
\-different cell types are using different transcription factors
\
\-different transcription factors will only activate certain genes
\
\-ex: as muscle cells develop, they have transcription factors myody that can bind to the regulatory sequences of genes that encode proteins that are responsible for muscle function.
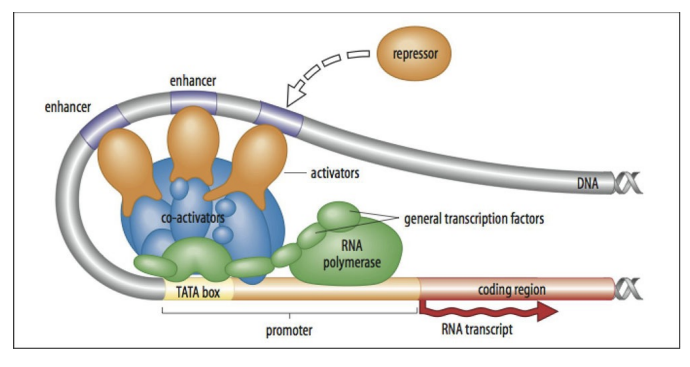
32
New cards
differential gene expression (epigenetic modifications)
\-DNA is wrapped around histone to give it a higher order structure (make a chromatin)
\-there are enzymes that can add chemical groups to histones or DNA to alter the structure of the chromatin
\-Chromatin modifications can affect how well transcription factors can access DNA to turn genes off/on, therefore affecting gene expression
\-Chromatin modifications represent epigenetic changes that regulate the access to regulatory sequences and thus regulate transcription
\-These changes can be passed on to daughter cells and can thus be heritable. Heritable changes in the gene expression of a cell without changes to the underlying DNA sequence is the classical definition of epigenetics
\-there are enzymes that can add chemical groups to histones or DNA to alter the structure of the chromatin
\-Chromatin modifications can affect how well transcription factors can access DNA to turn genes off/on, therefore affecting gene expression
\-Chromatin modifications represent epigenetic changes that regulate the access to regulatory sequences and thus regulate transcription
\-These changes can be passed on to daughter cells and can thus be heritable. Heritable changes in the gene expression of a cell without changes to the underlying DNA sequence is the classical definition of epigenetics
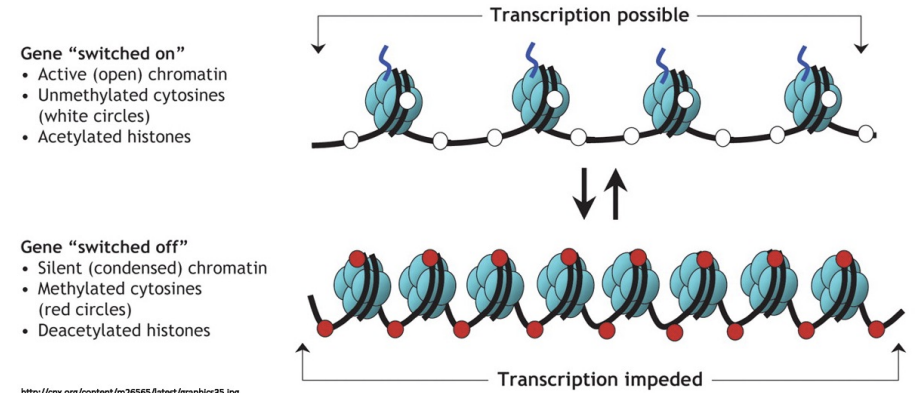
33
New cards
epigenetic changes
\-independent of the genes
\-changes in the genetic output that is not occurring from changes of the DNA sequences, instead from chemical modifications on the histones
\-changes in the genetic output that is not occurring from changes of the DNA sequences, instead from chemical modifications on the histones
34
New cards
differential gene expression (miRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, siRNAs and RNAi)
\-code for RNA that won’t turn into mRNA but have their own functions like regulating other genes
\
\-genes are already expressing mRNAs, but these noncoding RNA are interfering with mRNAs so that they don’t get turned into proteins
\
\-We now know that cells also express non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting sequence-related mRNAs.
\
\-Endogenously-expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs, as well as foreign double-stranded RNA (viral, experimental), are processed into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).
\
\-siRNA production leads to the destruction or inhibition of complementary mRNAs, by a process called RNA interference (RNAi) because they are similar
\
\-Dicer is the protein that cuts the double-stranded RNA, which is then assembled into an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that inhibits or destroys the targeted RNA.
\
\-we can study functions of genes in cells using this by creating RNA that can go into siRNA to block native RNA
\
\-genes are already expressing mRNAs, but these noncoding RNA are interfering with mRNAs so that they don’t get turned into proteins
\
\-We now know that cells also express non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting sequence-related mRNAs.
\
\-Endogenously-expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs, as well as foreign double-stranded RNA (viral, experimental), are processed into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).
\
\-siRNA production leads to the destruction or inhibition of complementary mRNAs, by a process called RNA interference (RNAi) because they are similar
\
\-Dicer is the protein that cuts the double-stranded RNA, which is then assembled into an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that inhibits or destroys the targeted RNA.
\
\-we can study functions of genes in cells using this by creating RNA that can go into siRNA to block native RNA
35
New cards
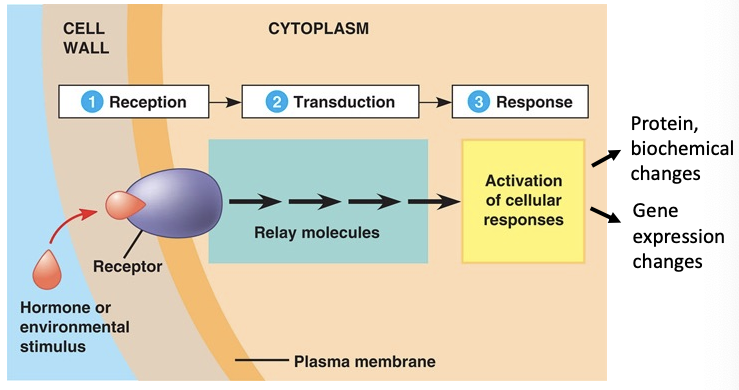
signal transduction pathways
\-information is passed between and within cells through this
\-cells develop complex, dynamic signaling pathways and gene regulatory networks
\
\-receptor protein binds to hormone and changes its shape so it can stick to other proteins that are influenced and info is relayed and ultimately causes a cellular response (protein or biochemical changes, gene expression changes)
\
\-outside signals can change gene expression (not always)
\-cells develop complex, dynamic signaling pathways and gene regulatory networks
\
\-receptor protein binds to hormone and changes its shape so it can stick to other proteins that are influenced and info is relayed and ultimately causes a cellular response (protein or biochemical changes, gene expression changes)
\
\-outside signals can change gene expression (not always)
36
New cards
Not all of the information in a cell is encoded directly in DNA in a form we can read
Ultimately, the state of a cell depends on a dynamic interplay between its genes and environment. The study of cell biology seeks to identify and understand the pathways and mechanisms that mediate this process in a variety of contexts.
37
New cards
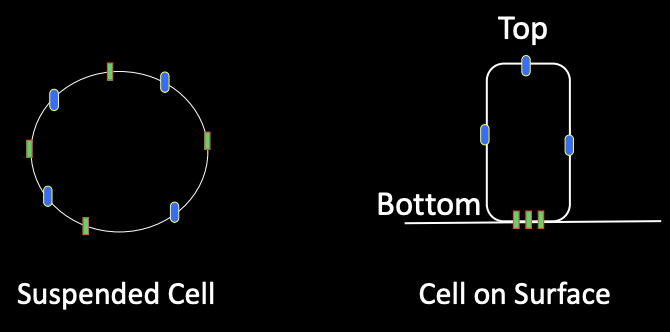
cellular organization in suspension and adhesion
\-A simple example of how cells with the same genes can display different behaviors depending on their environment
\-signal changes protein that changed shape
\-Signal transduction, new interactions of existing proteins, perhaps changes in gene expression and use of the new proteins
\-signal changes protein that changed shape
\-Signal transduction, new interactions of existing proteins, perhaps changes in gene expression and use of the new proteins
38
New cards
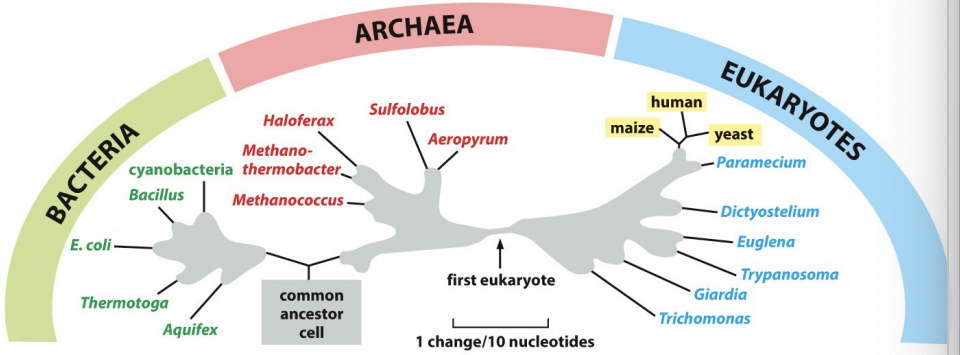
common ancestry
\-Best evidence suggests a common ancestry for all organisms on earth
\
\-The fact that the fundamentals of life processes (DNA, RNA, protein as well as certain metabolic pathways) are similar in all cells argues that there was a “common ancestor cell.” If there were other cells, their progeny did not survive to present. DNA sequence comparisons give the best resolution for evolutionary relationships.
\
\-organisms that have most similar DNA sequences are highly related bc have not accumulated a lot of mutations
\
\-The fact that the fundamentals of life processes (DNA, RNA, protein as well as certain metabolic pathways) are similar in all cells argues that there was a “common ancestor cell.” If there were other cells, their progeny did not survive to present. DNA sequence comparisons give the best resolution for evolutionary relationships.
\
\-organisms that have most similar DNA sequences are highly related bc have not accumulated a lot of mutations
39
New cards
how did the first cell arise? (current best guess)
– There was a soup of organic molecules that was created abiotically (by non-living processes).
\
– Polynucleotides (of RNA?) formed RNA is genetic material that has both catalytic and information encoding capability
\
– Lipid bilayers formed boundaries, encapsulating contents
\
– This probably occurred \~0.5-1 billion years after the formation of the earth (3.5 billion years ago)
\
– DNA eventually evolved as a storage medium for information, proteins took over catalytic roles, and RNA continues to serve as the intermediary.
\
– Polynucleotides (of RNA?) formed RNA is genetic material that has both catalytic and information encoding capability
\
– Lipid bilayers formed boundaries, encapsulating contents
\
– This probably occurred \~0.5-1 billion years after the formation of the earth (3.5 billion years ago)
\
– DNA eventually evolved as a storage medium for information, proteins took over catalytic roles, and RNA continues to serve as the intermediary.
40
New cards
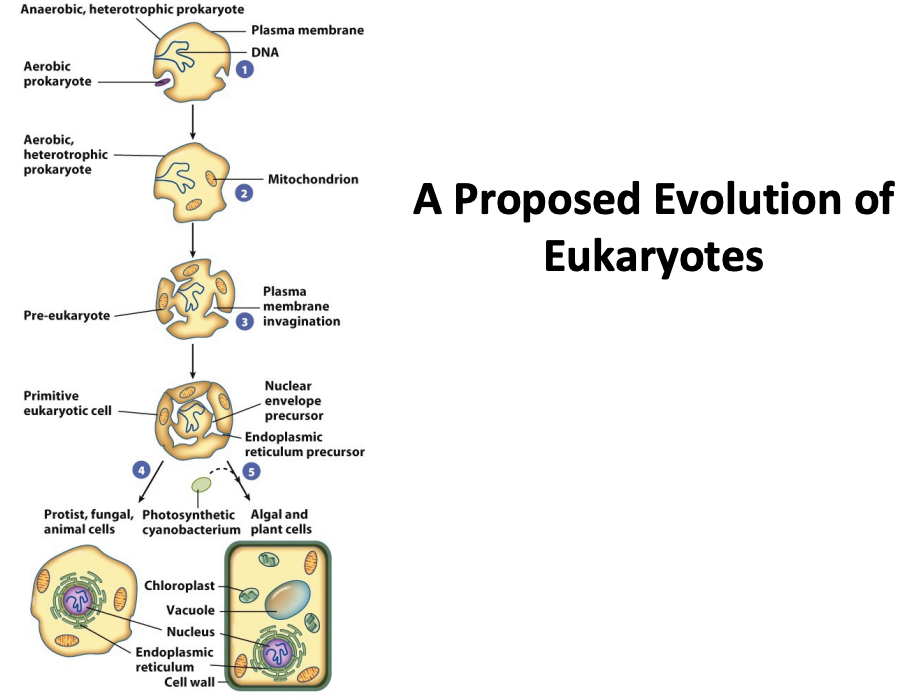
presumed evolution of cells
Prokaryotes
– Evolved first
– Simpler cells, but simpler does not mean inferior: They grow in a vast number of environments (including extremes that we could not survive). There’re a lot more of them than there are of us!
\
Eukaryotes
– Evolved from prokaryotes, perhaps via processes involving internalization and symbiosis\*. Today, mitochondria and chloroplasts can’t live outside cell.
– More complex cells need more genes, so the nucleus may have evolved to keep track of the increasingly large genome, or as a splicing compartment.
– Evolved first
– Simpler cells, but simpler does not mean inferior: They grow in a vast number of environments (including extremes that we could not survive). There’re a lot more of them than there are of us!
\
Eukaryotes
– Evolved from prokaryotes, perhaps via processes involving internalization and symbiosis\*. Today, mitochondria and chloroplasts can’t live outside cell.
– More complex cells need more genes, so the nucleus may have evolved to keep track of the increasingly large genome, or as a splicing compartment.
41
New cards
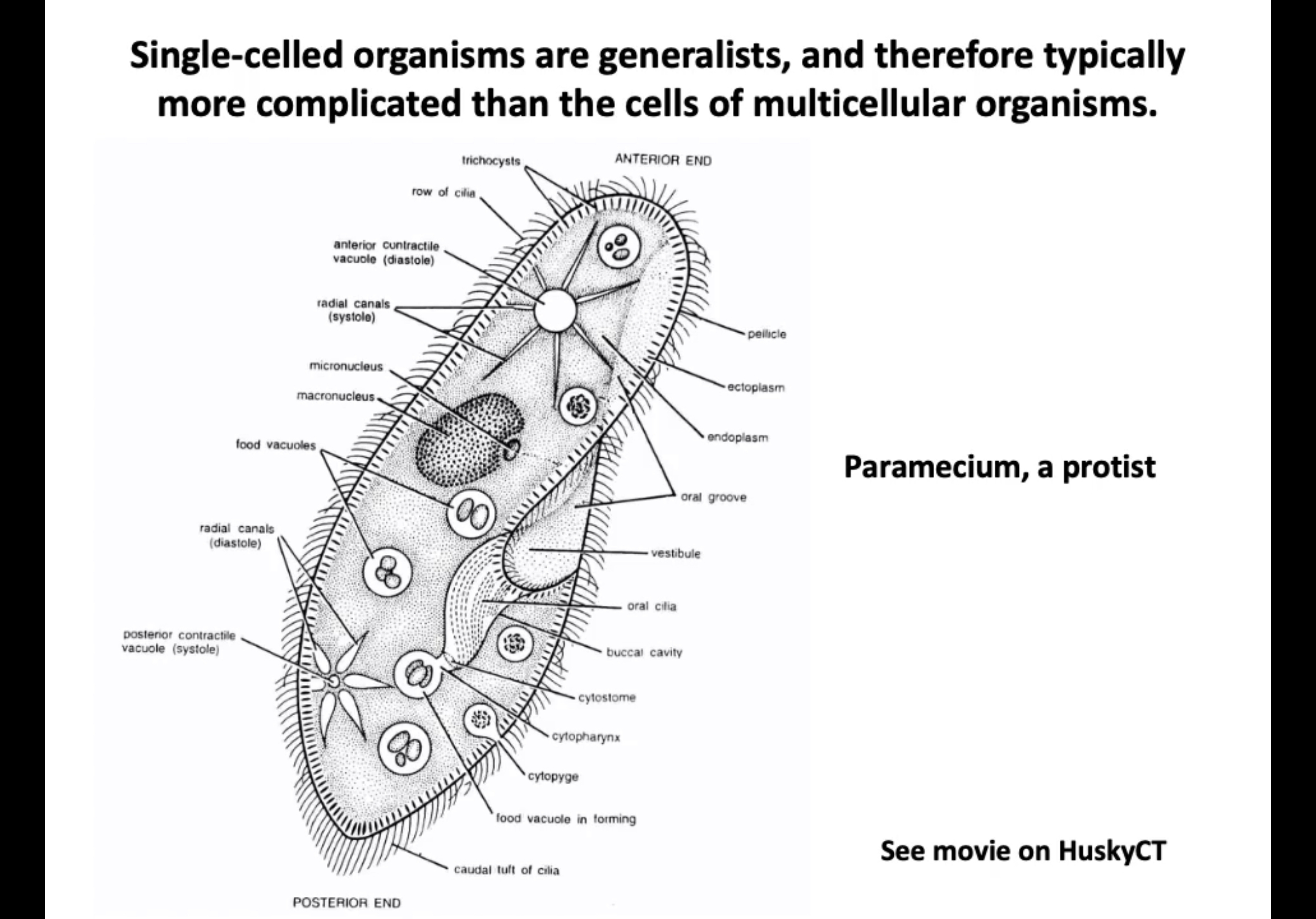
organismal complexity
\-Single eukaryotic cells can be very complex while specialized cell types allow higher order organismal complexity
\-Cells can take on an incredible variety of forms
\-Single-celled eukaryotic organisms (protists) are generalists. They can do it all. They are therefore typically more complicated than the cells of multicellular organisms.
\-Specialized cells of multi-cellular organisms may be more limited in what they can each do, but the whole is much greater than the sum of the parts.
\-Multicellular development allowed the evolution of larger and more complex organisms.
\
\-a protist
\-Cells can take on an incredible variety of forms
\-Single-celled eukaryotic organisms (protists) are generalists. They can do it all. They are therefore typically more complicated than the cells of multicellular organisms.
\-Specialized cells of multi-cellular organisms may be more limited in what they can each do, but the whole is much greater than the sum of the parts.
\-Multicellular development allowed the evolution of larger and more complex organisms.
\
\-a protist
42
New cards
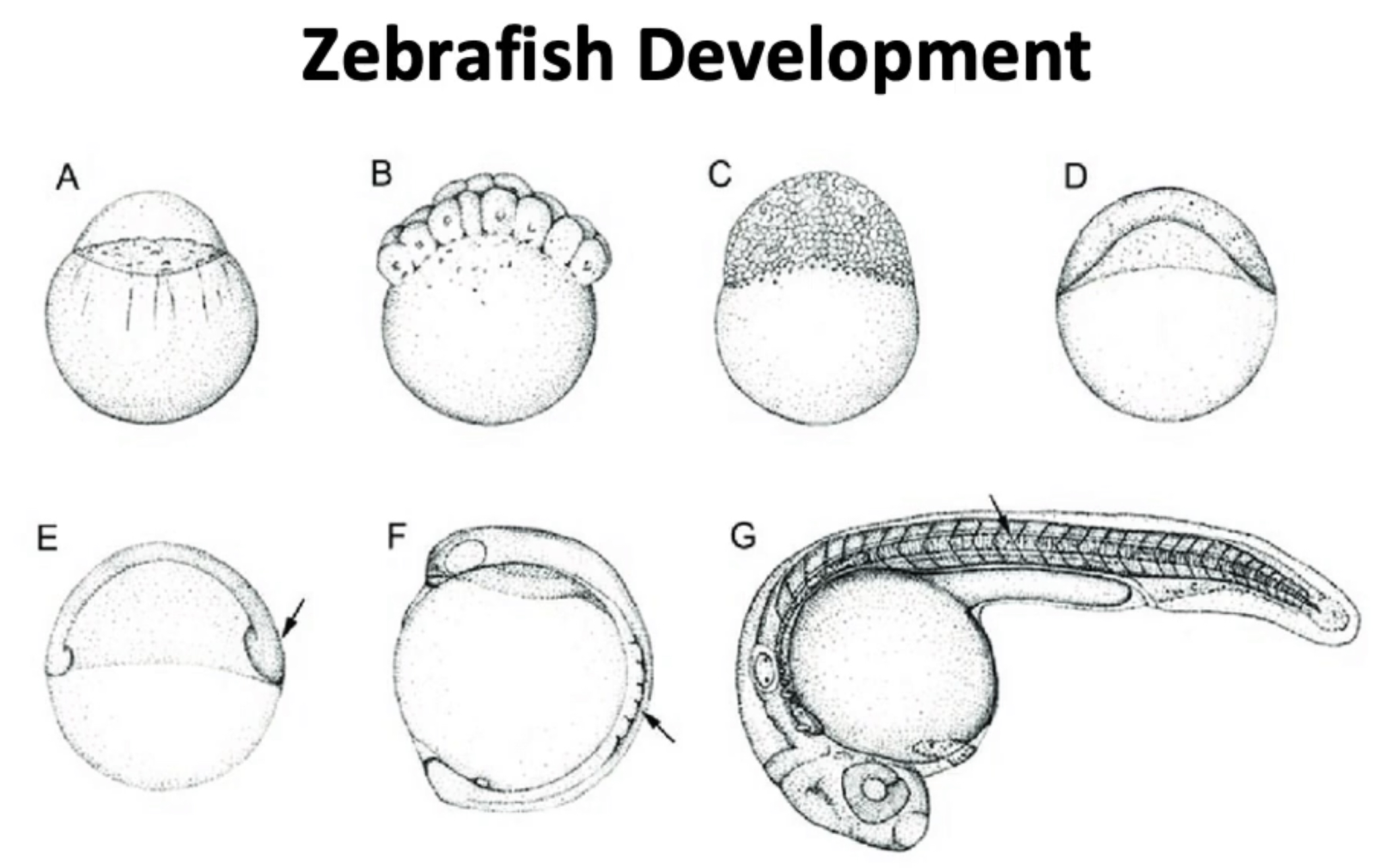
Developmental Biology
\-the study of how a multicellular organism forms from a single cell
\-Sperm fertilizes egg, creating a zygote
\-Zygote undergoes many cell divisions (proliferation)
\-Cell-cell signaling and differential gene expression leads to the generation of different cell types and behaviors (cell differentiation).
\-The coordinated proliferation, specification, and movement of cells generates the form of the embryo and adult (morphogenesis)
\
\-think of zebrafish development
\-Sperm fertilizes egg, creating a zygote
\-Zygote undergoes many cell divisions (proliferation)
\-Cell-cell signaling and differential gene expression leads to the generation of different cell types and behaviors (cell differentiation).
\-The coordinated proliferation, specification, and movement of cells generates the form of the embryo and adult (morphogenesis)
\
\-think of zebrafish development
43
New cards
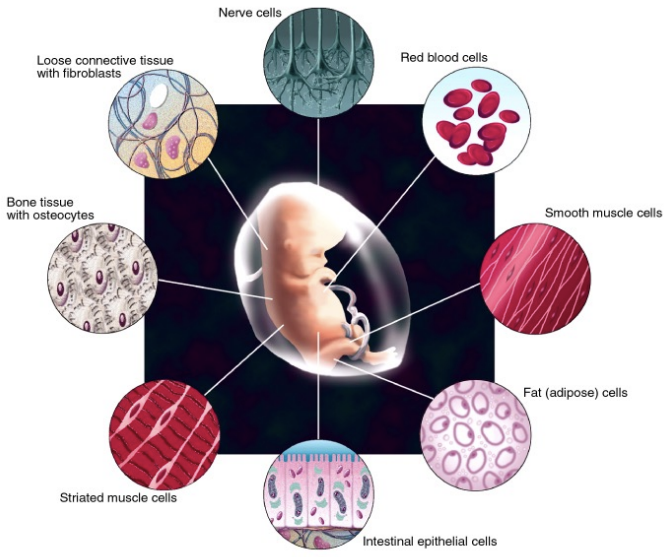
Cells in multicellular organisms
\-form tissues and organs
\-There are \~50 trillion cells of 200-250 broadly defined different types in a human adult.
\
\-allows specialization of cell types
\-There are \~50 trillion cells of 200-250 broadly defined different types in a human adult.
\
\-allows specialization of cell types
44
New cards
prokaryote forming a multicellular organism
Dictyostelium: a single-cell amoeboid protist that can transform into a multicellular organism by active intercellular signaling. Forms migrating “slugs” and fruiting bodies.
\
Myxobacteria, a prokaryote that can form a multicellular organism • Atypically large genome for prokaryote • Can aggregate to form swarms and fruiting bodies via cell-cell signals
\
Myxobacteria, a prokaryote that can form a multicellular organism • Atypically large genome for prokaryote • Can aggregate to form swarms and fruiting bodies via cell-cell signals