ACT
1/52
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Punctuation, Commas
Extra information
Dash or comma on either side
Usage and Mechanics
Avoiding Redundancy
Restating already shared information
Transitions: Same Direction v.s. Contrast
Transitions steps
Are the transitions needed
If so, form a bridge, determining whether in the same or a different direction
Usage and Mechanics
Moving, deleteing, or adding
Portion should be related to all parts of what comes before and after it
Usage and Mechanics
Main Goal
If it is the main goal, all paragraphs should give details on it.
Negative number to odd power
keep negative
Negative number to even power
becomes positive
Logarithms Solving: Rewriting Logarithms
Logx#=n
Ex: logx36=2
x^n=#
x²=36
Graphing points on a line
A,B,D,C
If B is between A and C
D is between B and C
CD<BC because CD is within BC
Log base is never
never negative
Order of operations
PEJMDAS, left to right
Coefficient
Number next to the variable
Constants
Real numbers
Algebra Fundamentals:Key Definitions
Greater Common Factor GCF
Largest Number that Goes into Both
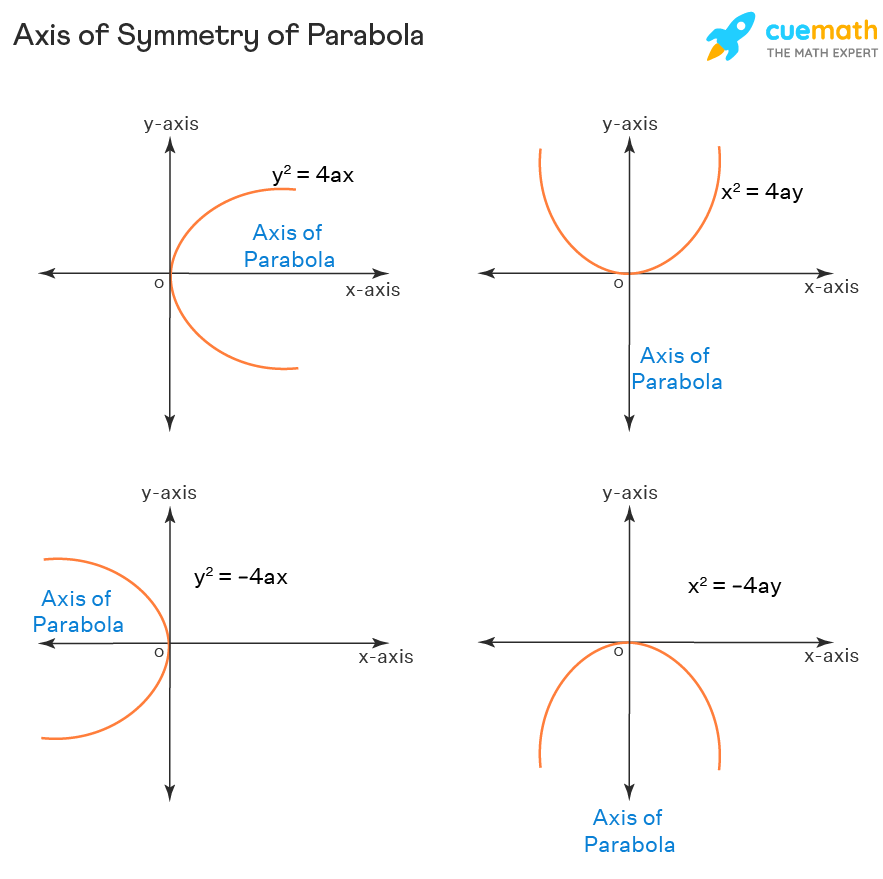
Main Graphs and Transformations:
Porabola Vertical Axis of Symmetry
Vertical
Triangles: Pythagorean Theorem
a²+b²=c²
leg²+leg²=hypotenuse²
Geometry Fundamentals: Angles and Coordinate Plane
Slope
(Δy)/(Δx)=
(rise)/(run)=
(amount up or down)/(amount left or right)
Up and right: positive +
Down and left: negative -
Altitude of triangle
Vertical distance between vertex and base
(y-coords of vertex)- (y-coords of base)
Probability:Basic Probability
Probability of n
P(n)
x!
multiply all numbers from 0 to x
Product of all positive integers less than or equal to x
2!= 2×1= 2
Graphing sine and cosine; Graphing cosine
Amplitude
how high up and low down below and above the midline
coefficient in front of a trig function
Ex: ½cos (3x+pi)
½=amplitude
x*-x
-x²
Rare and Random: Matrices
row*column
r*c
Ex: [2×2]
2 rows, 2 columns
Rare and Random: Matrices
Multiplying Matrices
Must have same inner numbers, or undefined
Ex: [2×3][3×2] can multiply, while [2×3][4×3] undefined
Main graphs and transformations
General form of porabola
y=x²
Linear Systems Word Problems
How to cancel base of power
log on both sides
10(2x-1/x)=1
(2x-1)/x=log10 1
Probability: Advanced Probability
(want)/(total possible)
Distance and Average Speed: Average Speed
distance/time
Distance and Average Speed
1 Rev
Circumference
Circumference
πd
Solving Radicals and Exponents: Simplifying Radicals
Simplify x^√
x^1/n
Ex: √3=3^1/2
Solving Radicals and Exponents: Simplifying Radicals
Exponents Equal
Exponents equal when bases the same
Ex: 3²=3^x
x=2
Solving Radicals and Exponents: Simplifying Radicals
Solve Equation with Radicals
Want both sides to have the same base
Mean, Median, and Mode
Arithmetic Sequence
± the same # between each terms
Ex: .75, 1.75, 2.75, 3.75, 4.75, 5.75, 6.75
Mean, Median, and Mode
Mean the same as Median
An arithmetic sequence, add app up and divide, get the middle term
Ex: .75, 1.75, 2.75, 3.75, 4.75, 5.75, 6.75
Circles: arc length
θ/360
arc length/circumference
arc length/πd
Law of Sines: Area of a SAS Triangle
½(ab)(sin c°)
Probability: Advanced Probability
Expected Value of x given different values of x
Multiply all (x values) by the (probability of x values)
Add all of them together
Natural Science (Dual)/Social Science (Single) Specific Information
Don’t try to remember, find where it is introduced and read carefully
Science ACT tips
Don’t read for the data representation (graph) sections
Always Refer back fro debating scientists sections and experiments
Watch for trick questions where all agree on IF, but not HOW
Check units
Read the questions carefully and check for trick answers
Focus on the study with the most detail that rather than just saying the “repeated the steps of X study“
Experiments: Identifying Mathematical Relationships and Trends
Balanced Chemical Equations
The ratios of coefficients of chemicals in a chemical equation must remain balanced
Ex:
(Ni^2+)+(2Oh^-)+(H2O)=Ni(OH2)H20»»
(3Ni²+)+(6OH^-)+(3H2O)=3Ni(OH2)H2O
Experiments: Understand Experimental Design
Control
One where the independent variable is kept constant for comparison
Experiments: Find details from figure, table or diagram
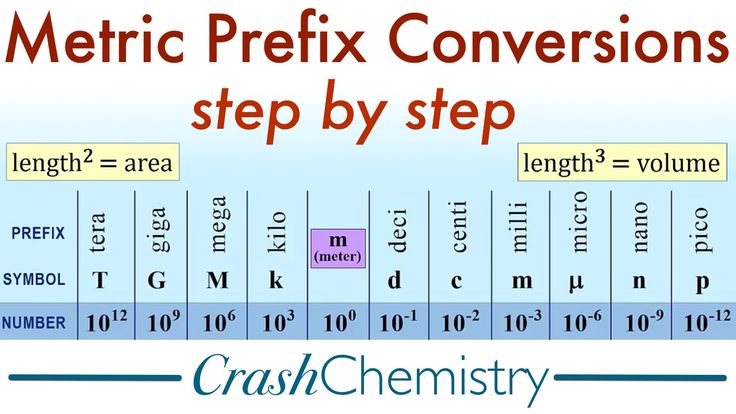
Metric unit conversions
Experiments: Understand basic Scientific Content
Equation for Photosynthesis
Plants take in water, light, and carbon dioxide, then produce glucose (sugars) in their leaves for energy, and oxygen which humans breathe:
Carbon dioxide+water+light→glucose+oxygen
Experiments: Understand Scientific Design
Minimum and Maximum
Least and greatest amount
Experiments: Understand Scientific Design
y=0
Completely straight line, doesn’t go up or down
Experiments: Understand Scientific Design
Absolute value/Magnitude
Getting further away from 0
Experiments: Understand Scientific Design
Like and Opposite charges
Like charges repel
Opposite charges atrtact
How to evaluate for f(x) for c
Rewrite the equation
Plug in c for every x in the equation
How to solve for composite functions
Take f(x) and plug it into g(x) function etc.
Combining Units When Adding and Subtracting
Goal is to get the x on one side and numbers on the other
Need to be very careful that operations are performed on both sides
Make sure to remember rules about solving absolute value, simplifying exponents, combining fractions, and distributing negative signs
Multiplying & Dividing in Algebraic Equations
Goal is to get x on one side and numbers on the other
Be careful to perform operations on both sides
Linear Equations for Word Problems
Read the problem carefully to define the variables of interest (for which you are solving)
Create the linear equations based on the information in the problem
Use substitution or elimination to solve for one of the variables
Solve for the other variable based on your answer in 3.