Principles of Chemistry Exam Style Qs
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Describe how magnesium atoms and chlorine atoms form magnesium ions and chloride ions. (3)
m1: magnesium transfers electrons to chlorine m2: magnesium loses two electrons m3: chlorine gains an electron
Describe the structure and bonding in indium (3)
a strong electrostatic force of attraction between m1: positive ions m2: and a sea of delocalised electrons m3: in a lattice
A major use of magnesium oxide is as a refractory material, which is a material that can withstand very high temperatures.
Explain, in terms of its structure and bonding, why magnesium oxide has a very high melting point. (4)
m1: consists of positively and negatively charged ions m2: strong electrostatic force of attraction m3: many ions in a giant lattice m4: requires a lot of energy to separate the ions
Explain why sodium bromide has a higher melting point than hydrogen bromide (3)
m1: sodium bromide is joined by ionic bonding m2: hydrogen bromide has intermolecular forces of attraction m3: ionic bonding stronger than intermolecular forces of attraction
The electronic configurations of atoms of sodium and chlorine are
Na 2.8.1
Cl 2.8.7
Describe the changes in the electronic configurations of sodium and chlorine when these atoms form sodium chloride. (3)
m1: sodium loses electron m2: chlorine gains an electron m3: Na becomes 2.8 and Cl becomes 2.8.8
state what is meant by the term isotopes (2)
m1: atoms of the same element m2: with different masses
A catalyst increases the rate of decomposition of the hydrogen peroxide.
Describe a method you could use to show that the manganese(IV) oxide is acting as a catalyst in this reaction. (4)
m1: perform reaction with and without catalyst m2: control concentration or volume of hydrogen peroxide m3: measure time to fill gas jar with oxygen m4: oxygen produced more quickly
Explain why diamond has a very high melting point (4)
M1 – giant covalent M2 – strong (covalent) bonds M3 – lot of (thermal/heat) energy required M4 – to break bonds
Hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in water to form solution A. Hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in methylbenzene to form solution B. A teacher adds a piece of magnesium ribbon to each solution.
Explain why she observes effervescence with solution A but not with solution B. (3)
m1: effervescence due to hydrogen m2: solution A is acidic as it contains HCl m3: solution B is not acidic
Describe how you could obtain a pure, dry sample of the insoluble solid from the final reaction mixture. (3)
m1: filter off the precipitate m2: wash with pure water m3: dry in a warm oven
A student uses the precipitation method to prepare lead(II) bromide.
The equation for the reaction she uses is
Pb(NO3 )2 (aq) + 2NaBr(aq) → PbBr2 (s) + 2NaNO3 (aq)
Describe how she could use solutions of lead(II) nitrate and sodium bromide to obtain a pure, dry sample of lead(II) bromide. (5)
m1: mix the two solutions m2: together m3: stir m4: filter m5: wash with water m6: dry in heat
The student wants to obtain a pure, dry sample of hydrated zinc nitrate crystals from the dilute solution.
One method is to leave the solution so that all the water evaporates.
Describe another method, involving crystallisation, that the student could use. (4)
m1: heat/boil to partially evaporate the water m2: leave to crystallise m3: filter to remove excess liquid m4: dry in oven
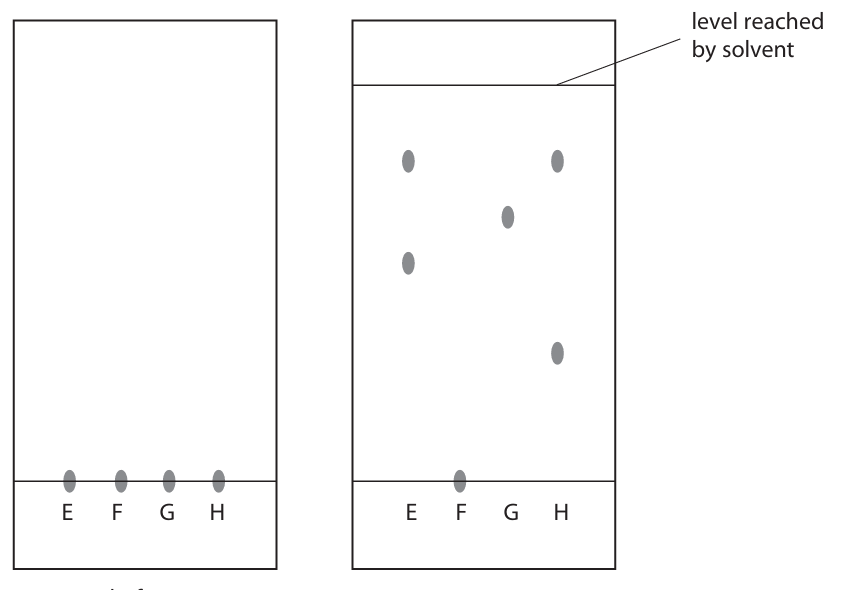
Describe how the student should complete the experiment after placing the four spots on the paper. (4)
m1: place in beaker m2: solvent below baseline m3: leave until solvent rises m4: leave until dyes dry
Describe the structure and bonding in indium → Group 3. (3)
m1: positive ions m2: delocalised electrons m3: lattice
Explain why sodium bromide has a higher melting point than hydrogen bromide. (3)
m1: sodium bromide ionic bonding m2: hydrogen bromide has intermolecular forces of attraction m3: ionic bonding stronger
Describe, in terms of electrons, how an atom of calcium reacts with two chlorine atoms to form calcium chloride. You may use a diagram in your answer (3)
m1: loss and gain of electron
m2: for direction of transfer
m3: for number of electrons transferred
Explain why potassium sulfide has a high melting point. (3)
m1: strong m2: electrostatic forces of attraction m3: large amount of energy required to overcome these forces
Explain why magnesium chloride has a high melting point. (3)
m1: attraction between ions is strong m2: lots of ions in structure m3: therefore a lot of thermal energy is required to overcome this attraction and break down the lattice