CHAPTER 3 - Isolation & Cultivation of Microorganisms
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
______________ - a culture which contains a single species of organisms; a population of cells arising from a _________ cell
pure culture (axenic culture), single
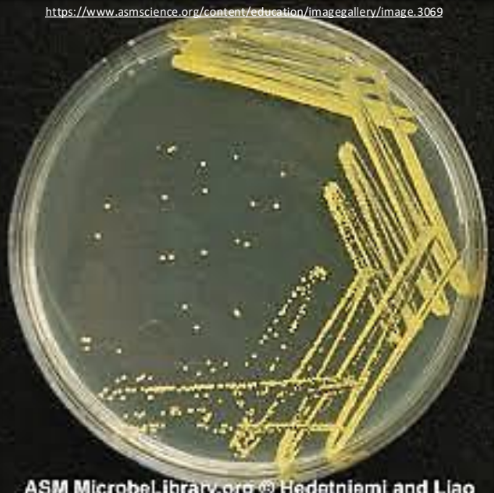
________________ - increasing the population of microorganisms by providing their nutritional and physical requirements
cultivation
___________ - extracellular substances which provide the cell with materials for building protoplasm and for energy generation
nutrients
__________________ - any nutrient material for growth and cultivation of microorganisms in the laboratory
culture medium
uses of culture medium
for growth and maintenance of microbial cultures
to favor the production of particular compounds
to study microbial action on some constituents of the medium
types of culture media, according to physical state:
liquid (broth)
semi-solid
solid
what is the solidifying agent used in a culture media?
agar/gelatin
types of culture media, according to physical state:
____________ - no solidifying agent
____________ - 0.1 - 0.5% solidifying agent
_____________ - 1.5 - 2.0% solidifying agent
liquid (broth), semi-solid, solid
liquid and solid types of culture media
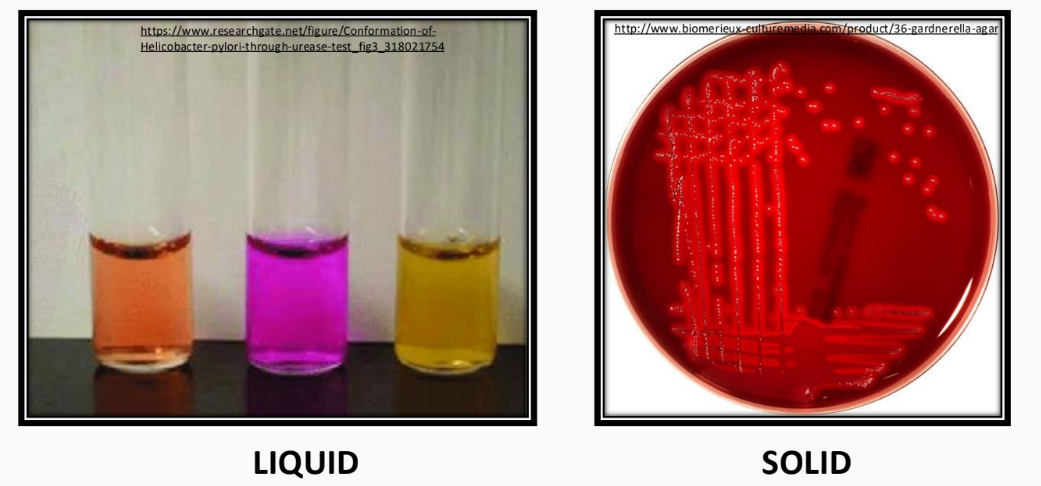

if you want to see motility of a microorganism, what type of culture media should u use?
semi-solid
types of culture media according to chemical composition:
synthetic
complex
a type of culture media in which all components are chemically defined.
synthetic
a type of culture media in which no all components are chemically defined
complex
examples of complex culture media (according to chemical composition)
potato infusion (plant origin)
beef extract (animal origin)
yeast extract (microbial origin)

Types of culture media according to principal function, purpose or application
General purpose
Differential
Selective
Enrichment
Assay
a type of culture media that can support most or all types of species; with the use of Nutrient Agar (NA) and Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA)
General Purpose

a type of culture media that is used for enumeration of molds
Potato Dextrose Agar
a type of culture media that distinguishes one type of bacteria from another; with the use of special reagents like __________
Differential, pH indicators/dyes
An example of a pH indicator/dye
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMBA)
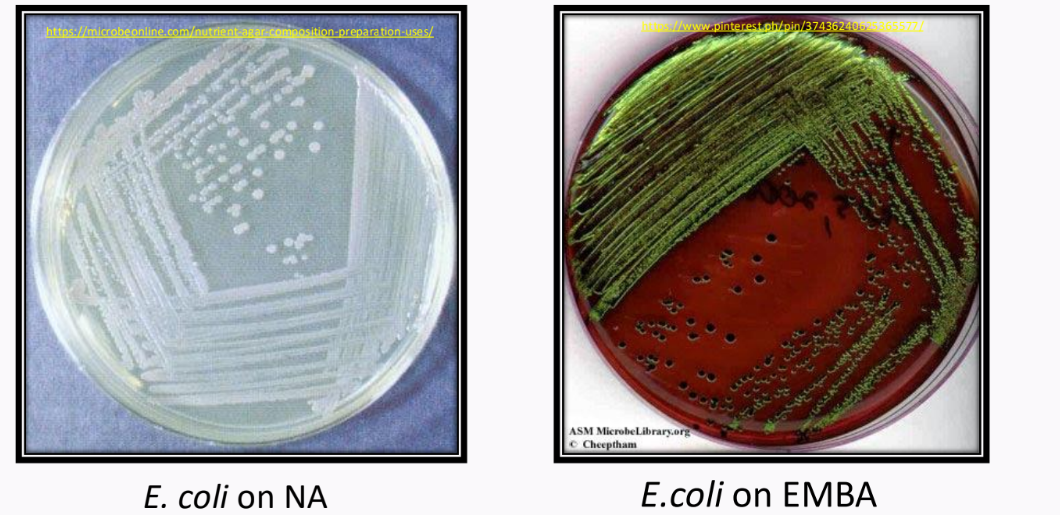
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMBA)
on NA = normal
on EMBA = with dyes that can inhibit gram-positiv
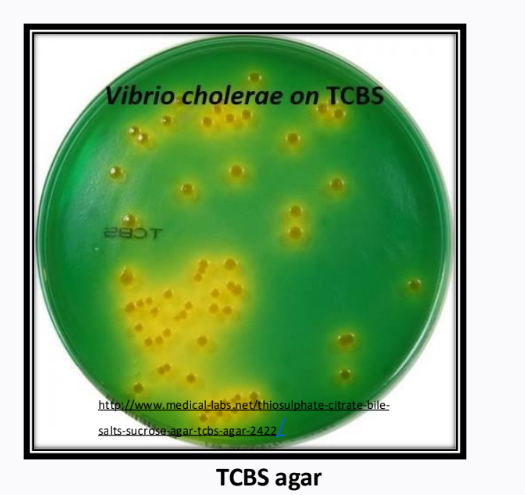
_____________ - a selective medium to separate vibrio species; very alkaline; yellow color means _________
Thiosulphate-citrate bile salt
CHROMagar Candida medium - different shades of blue/green color
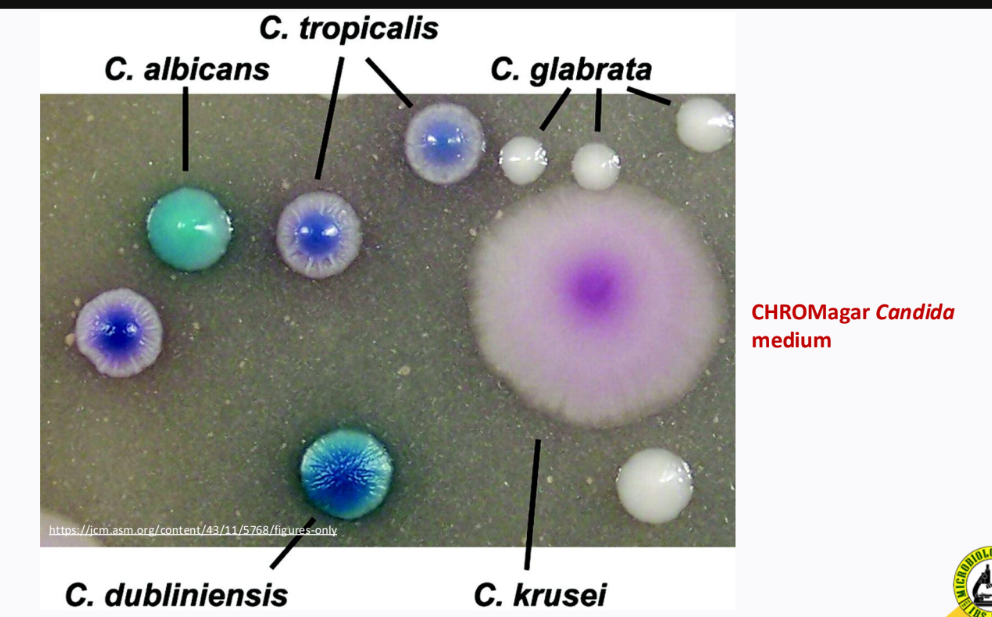
a type of culture media that allows the growth of a specific type of microorganism only; with ______________ agents (ex. salts, dyes, antibiotics)
Selective, selective
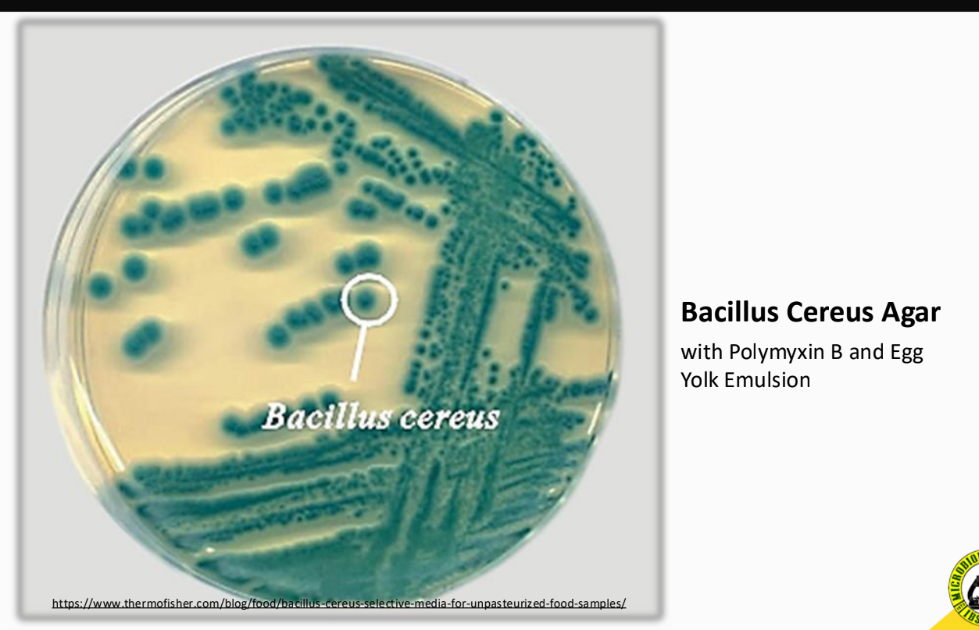
It is an example of selective culture media - _______________
Bacillus Cereus Agar; blue-green in color with white precipitates
a type of culture media that is used to increase the number of microorganisms with unusual physiological characteristics; with special nutrients (_______). Give an example of medium used
enrichment, Blood Agar
_____________ - useful in classifying streptococcal species; a substance that causes hemolysis is a ____________
Blood agar, hemolysin
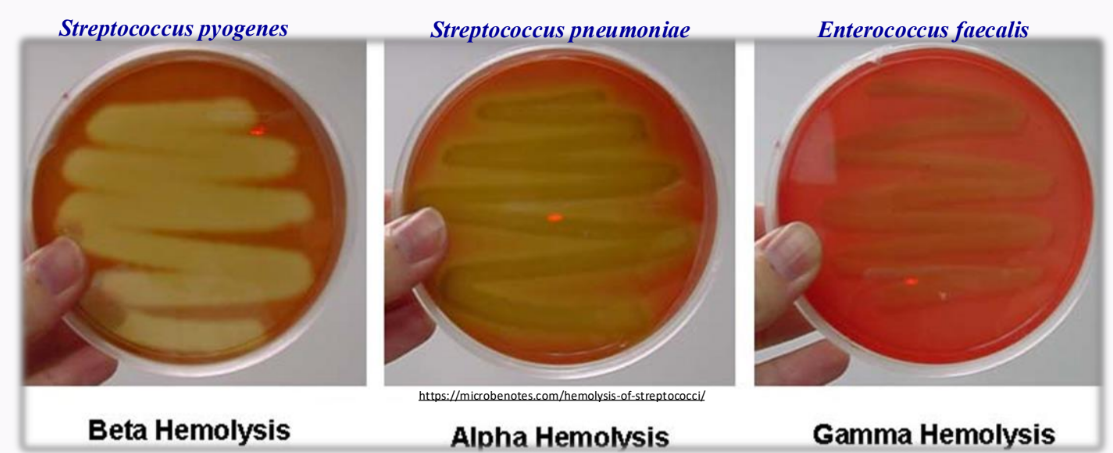
________Hemolysis - complete
_________ - partial only
_________ - non hemolytic
Beta, Alpha, Gamma
_______________ - breaks down blood
Hemolysis
a type of culture media used for investigative study for quantitative/qualitative data; of prescribed composition of used _______ of vitamins, amino acids and antibiotics.
assay, assay
a type of culture media that is used to determine qualitative/quantitative production of such a compound by an organisms
assay
_____________ -a type of culture media (assay) that uses three sugars: _______, ________, and _____________
Triple sugar iron medium
glucose, sucrose, and lactose
it utilizes glucose as it changes to color yellow
another example of assay that is used for antibiotic testing
Disk diffusion assay or Kirby-Bauer test
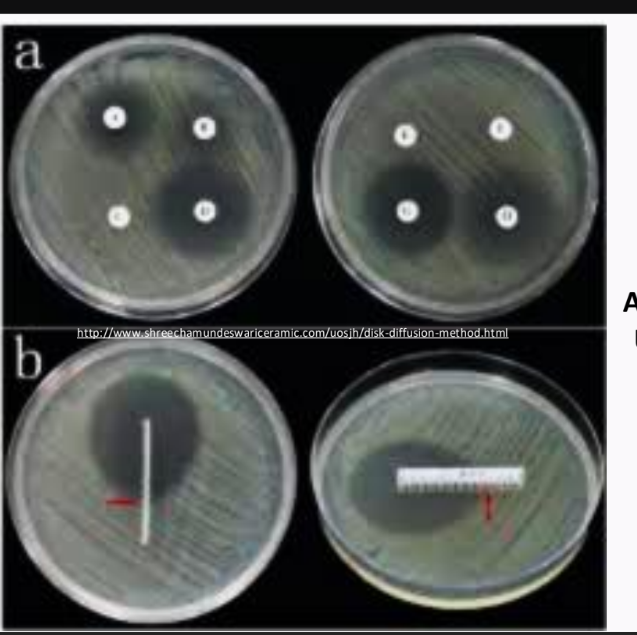
Enumerate the isolation techniques
plating
enrichment culture
serial dilution
single-cell isolation technique
membrane filter technique
______________ - a macroscopically visible (surface/subsurface) growth of cluster of microorganisms on a solid medium
colony
different types of plating
streak
spread
pour
types of plating and its corresponding place of growth
____________ - surface agar
____________ - surface agar
_____________ - subsurface/surface agar
streak
spread
pour
__________ - can be seen in the surface only; most commonly used
streak plating

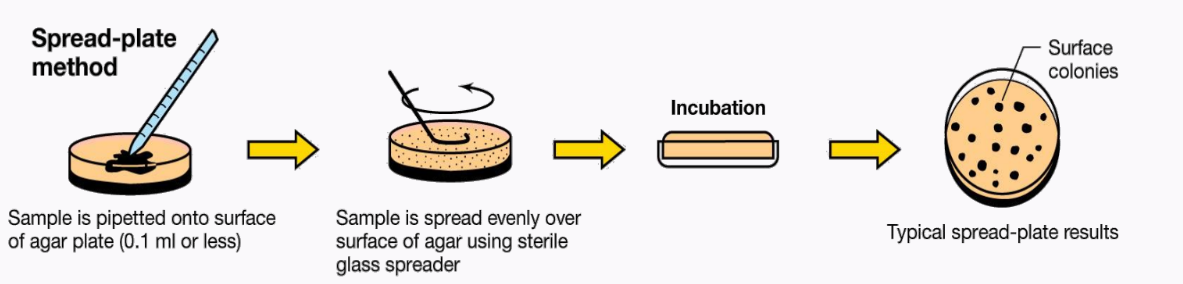
a type of plating technique that is spread evenly over surface of agar using sterile glass spreader
spread-plate technique
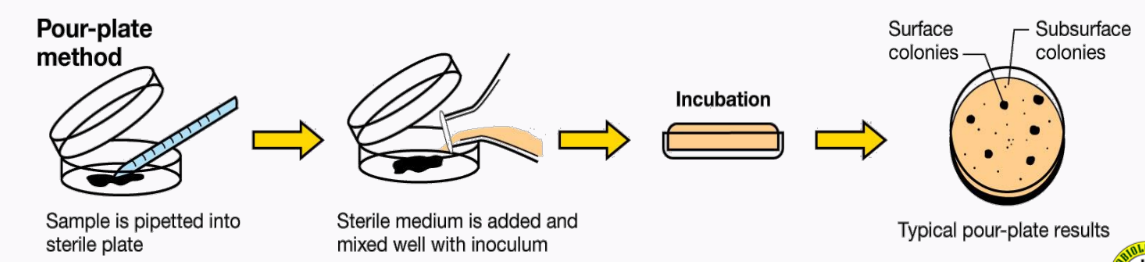
a plating technique that uses a sterile medium and is mixed well with inoculum
pour-plate technique
an isolation technique that isolates specific types of microorganisms by a combination of nutrient and physical conditions
enrichment culture
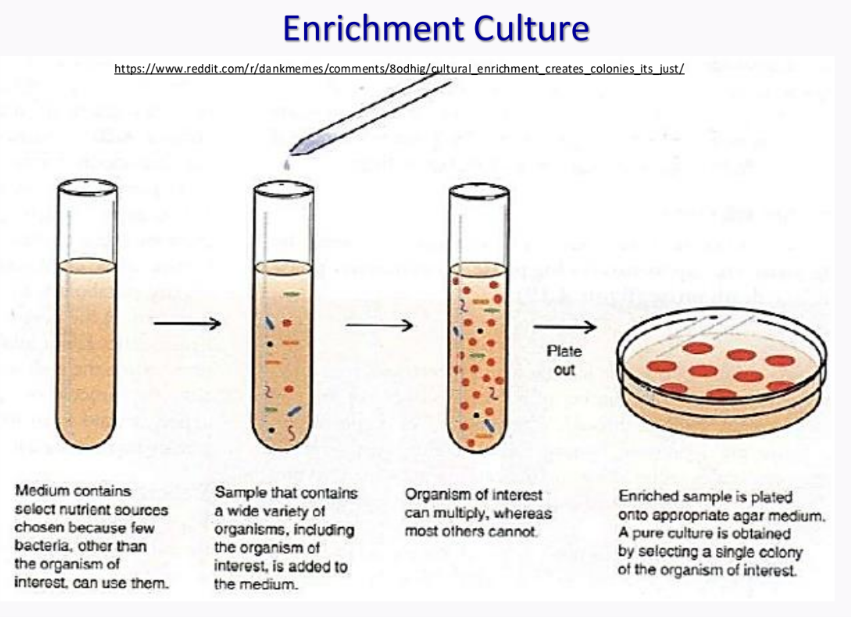
______________ - used for the isolation of unusual physiological types of microorganisms which are present in small numbers and which grow slowly
enrichment culture
_________________ - used if the desired microorganism is present at higher level than any other microorganism
serial dilution
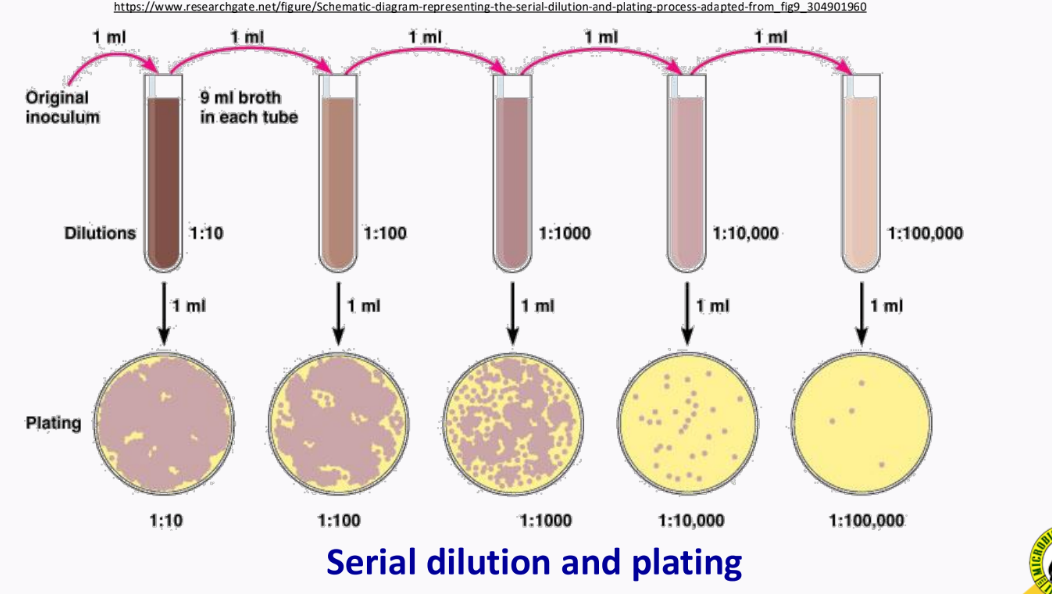
______________ - used this type of isolation technique when studying organisms from the soil
serial dilution (coupled technique: serial dilution + plating)
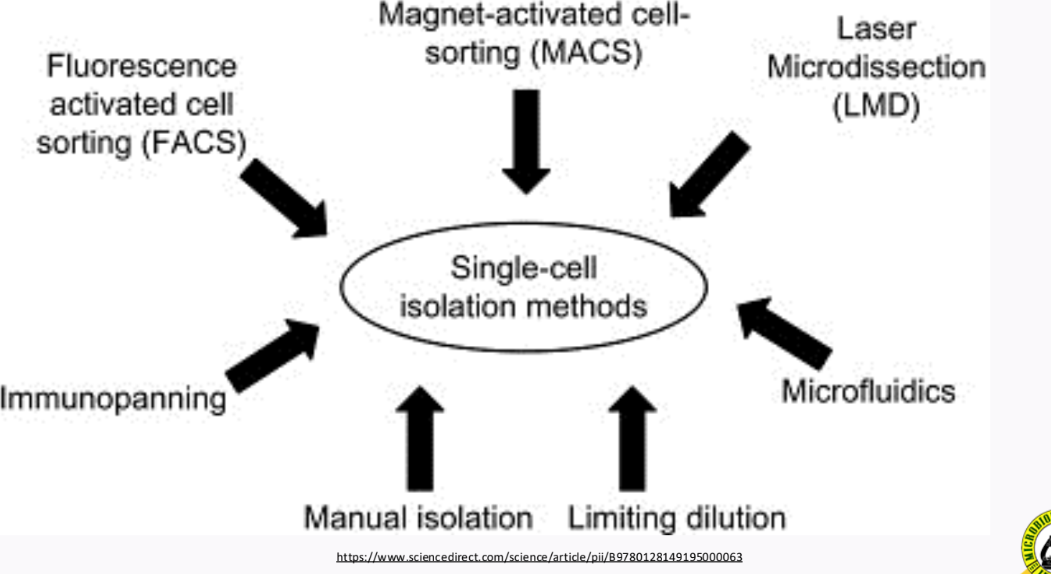
__________ uses a micropipette or microprobe to physically pick a single cell and transfer it on an agar medium
Single-cell isolation technique
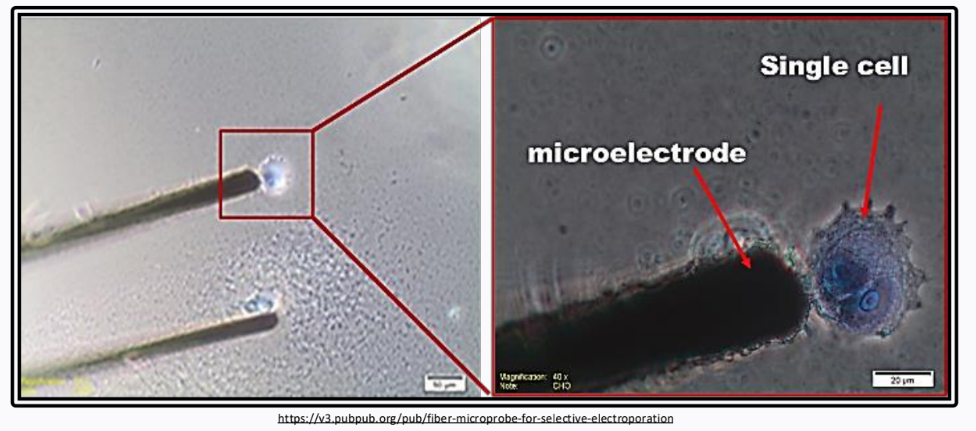

different single-cell isolation techniques
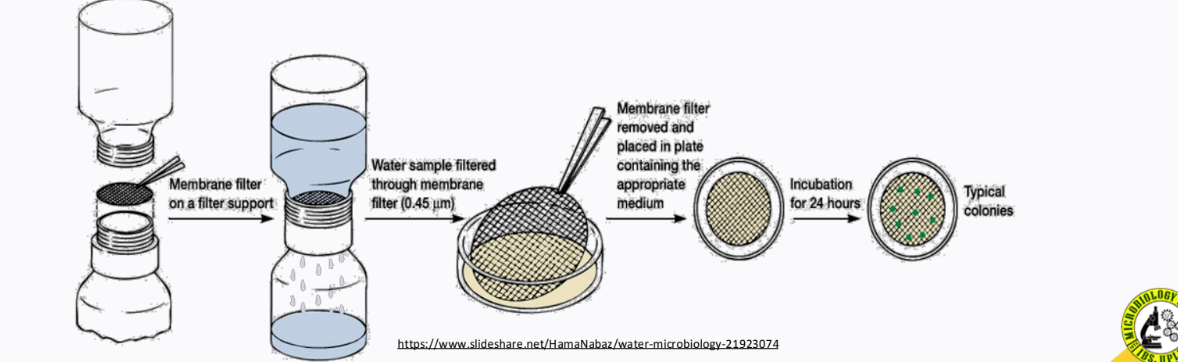
_______________ - an isolation technique that is used for samples with low population
Membrane Filter Technique
Steps in preparing pure cultures (for preservation)
isolation
transfer the desired colony to a slant/stab
Verify the purity (pure culture, check if gram (+) or gram (-)
microscope
restreak on agar medium (check phenotype if still the same)
physiological and biochemical test (normally: rapid kit)
Make stock cultures
the objective of culture preservation: to retain the ___________ of the stock culture for a ______ period of time while maintaining its _________
viability, long, purity
Culture preservation methods
periodic transfer to fresh media
overlaying cultures with mineral oil
freeze drying (lyophilization)
freezing with liquid nitrogen
drying
periodic transfer of fresh media (sub culture); considerations:
time _________ of transfers
proper______
proper storage ______
interval (has limitations; 4-5 transfers)
medium
temperature
in this culture preservation method it limits the availability of oxygen
Overlaying cultures with mineral oil
what does limiting the availability of oxygen do in a culture?
it reduces the metabolic rate of the culture
Some reminders in overlaying cultures with mineral oil
allow it to grow (culture) before placing the mineral oil
after allowing it to grow, proceed to overlay with mineral oil
place in a refrigerator
Advantages of overlaying cultures with mineral oil
prevents ____________
simple
enables one to remove some __________ under the oil and inoculate it in a _________ medium and still preserve the initial culture
dehydration
growth, fresh
disadvantages of overlaying culture with mineral oil:
___________ of microorganisms varies with species
not all possible to be stored
viability
A culture preservation method that involves rapid drying in frozen state (temp: -20°C)
lyophilization/freeze-drying
process of freeze-drying
freeze dry until H20 molecules are removed for preservation and needs a vacuum pumpad
advantages of freeze-drying (lyophilization)
_______- term survival
_________ opportunity for changes in the characteristics of culture
_________ storage containers
long
less
small
a culture preservation method that uses temperature around -196°C (cryopreservation)
freezing with liquid nitrogen
considerations for freezing with liquid nitrogen
cryoprotective agent (______)
liquid-nitrogen refrigerators
pulverized in form
exposed to ice crystals; reason for protecting it with _________
glycerol - cuz coating siya
a culture preservation method (____________) - in which samples are grown on sterile paper disk saturated with nutrient, then the disks are allowed to air dry and stored aseptically, drying temperature = 45°C
drying
limitations of drying as a culture preservation method
only used for spore- and cyst- formers
______________ organizations which maintain authentic pure cultures of microorganisms
culture collection
______________ provides “________” (first strain isolated from a species) strains to microbiologists
culture collection, type