Unit 2.5 Nervous system, Homeostasis, The Eye and The Plant Response
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is the central nervous system (CNS)
The Brain and Spinal cord
What are the sense organ?
It is a group of receptor cells that detect specific stimuli (change in environment and internal). It then sends the information to the central nervous system along neurones
Give an example of stimulus
Chemical, temperatures, light and sound
What is a nerve
A group of neurones that transfer information as electrical impulses in the nervous system
What is a nerve
A group of neurones that transfer information as electrical impulses in the nervous system
What is the nervous system made up of
The brain, spinal cord and nerves
What is the function of the nervous system
Allows an organism to rapidly react to the environmental and internal change
What is the function of sensory neurone
Carries the impulse from sense organs (receptors’) to the central nervous system
What is the function of motor neurones
Carry impulses from the central nervous system to effectors
Describe reflex
Very rapid
Automatic
Protective mechanisms
The brain is not involved
Give some example of reflexes
Pull hand away from pain
Blink
Pupil constrict in bright light
What does the reflex arc involves
Stimulus
Receptors
Coordinator
Effector
Response
What is the role of coordinator
Coordinate information from the receptor and transmits impulses to the effector
Describe the reflex arc
Stimulus —> Receptor —> Sensory Neurones —> Relay Neurones —> Motor neurone —> Effector —> Response
Outline the function of relay neurone
Carries impulses from sensory neurones to motor neurones within the central nervous system
What is a synapse
A small gap between neurones across which a nerve impulses is transmitted via neurotransmitter
Why is reflex automatic?
Impulse does not travel through the neurones in the Brian
Why is reflex fast?
Impulse must only cross through two synapses (which slows them down) in the spinal cord
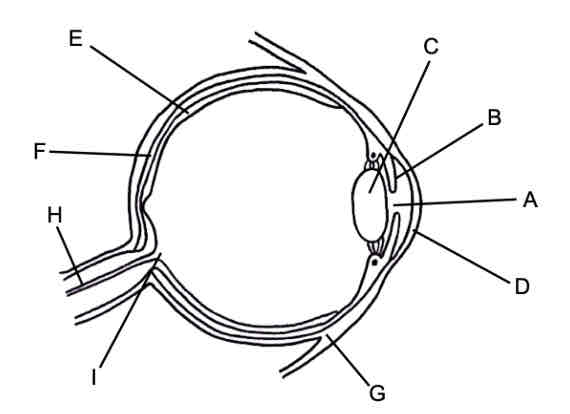
Label the eye
A = Pupil
B = Iris
C = Lens
D = Cornea
E = Retina
F = Choroid
G = Sclera
H = Optic nerves
I = Blind spot
Outline the structure and function of the cornea
It is a transparent outer covering of the eye and it refracts the light entering the eye
Outline the function of iris
It controls the size of the pupil to layer how much light enters the eye
What is the pupil
A hole that allows light to enter the eye
Outline the function of the lens
it is a transparent disc that can change shape to focus light into the retina
Outline the function of choroid
It absorbs light, preventing internal reflection
Outline the function of the sclera
Maintain eyeball shape
Outline the function of the retina
It converts light energy into neural signal which are sent to the brain via the optic nerve
What is the function of the optic nerve
It transmits nerve impulses to the brain from the retina
What is the blind spot
It is where the optic nerve connects, no receptor cells here.
What are plant tropisms
The growth response of a plant to a stimulus
What is a positive tropisms
The growth of a plant towards a stimulus
What is a negative tropism
The growth of a plant away from a stimulus
What are the 2 main type of plant tropism
Geotropic - a plant’s growth response to gravity (grow in the direction of gravity (down))
Phototropic - a plant’s growth responses to light (grow in the direction of light)
What are auxins
Auxin is the plant hormones, it is the hormones that control the plant growth in root and shoot.
Where are auxin produced
Meristem
What direction do the root and shoot of a plant grow in
Root = geotropic
Shoot = phototropic
Why is homeostasis important
It ensures the optimum conditions for enzymes and cellular processes in body is reached
What type of chemical helps to ensure optimum condition are reached within the human body
Hormones
What is a hormones
A cell signalling molecule produced by endocrine glands and released into the blood, it travels to a target organ and binds, imitating a response
State the three condition within the human body that must be controlled by homeostasis
Temperature
Blood glucose concentration
Water level
Why must body temperature be controlled
Because enzymes works best at their optimum temperature (37 degree)
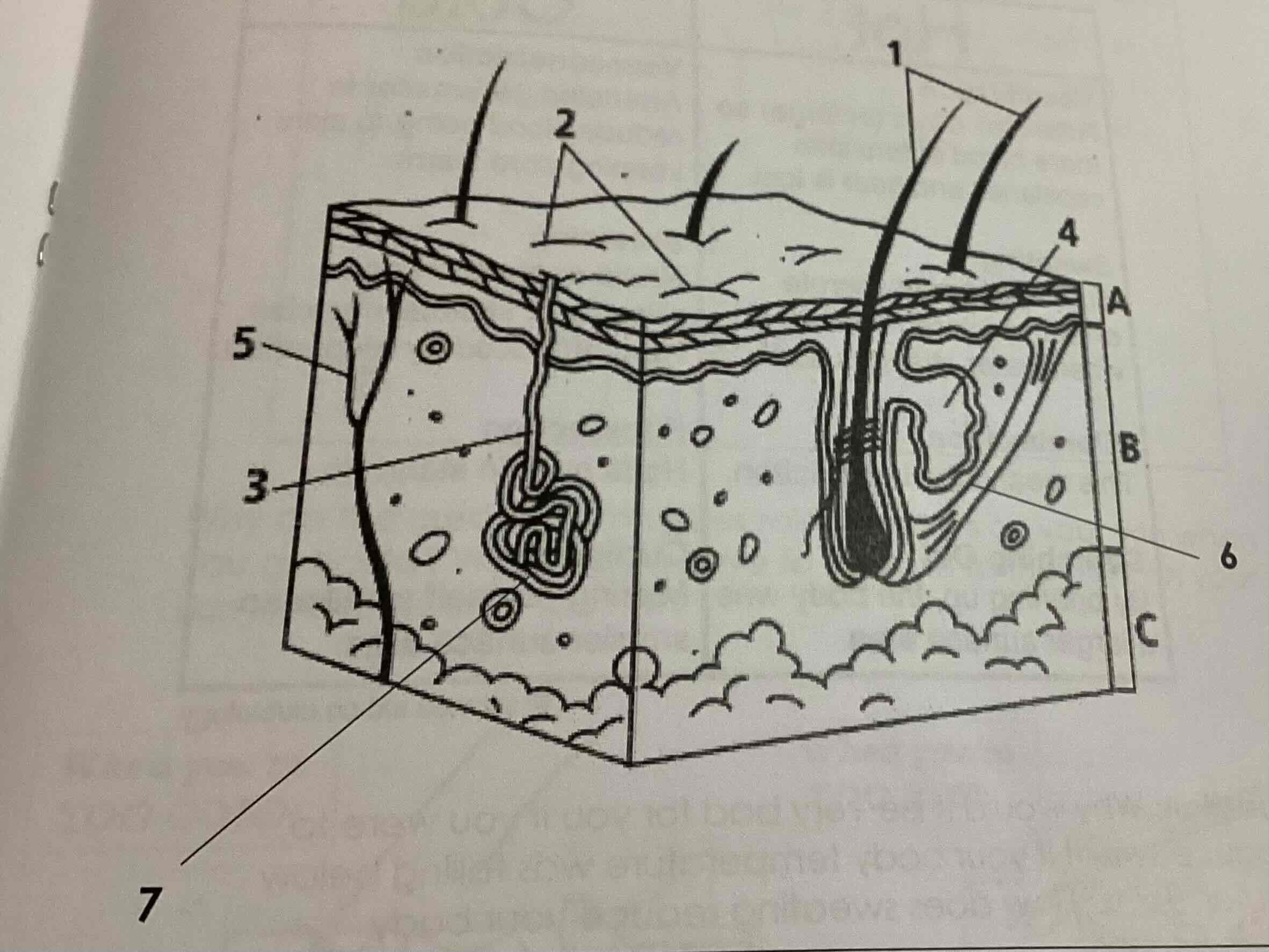
Label

Outline the response of the human body to an increase in temperature above 37 degree [3]
Vasodilation
Sweating
Erector muscle relax, hair lies flat
What structure in human body produce sweat
Sweat glands
How does sweating help to reduce body temperature
Heat energy is used to evaporate sweat. Increased heat transfer from the skin to the environment decreases the body temperature
What is vasodilation
Dilation of blood vessels near the skin surface, blood flows closer to the skin surface and greater heat loss to the surrounding
Outline the response of the body to a decrease in temperature below 37 degree [4]
Vasoconstriction
Shivering
Hair erector muscle contract
Little to no sweat is produced
How does shivering help to increase body temperature
Involuntary contraction of muscles generates heat energy from respiration
How does the contraction of hair erector muscles help to increase body temperature
Hairs stand on the end creating pockets of air between hairs and a layer of insulation
What is vasoconstriction
Constriction of blood vessels near skin surface, less blood flows close to the skin surface and less heat is loss to the surroundings
Why must blood glucose concentration must be controlled
If blood glucose concentration is too high, it can cause dehydration and type 2 diabetes
If blood glucose concentration is too low, the rate of cellular respiration can decrease
Which organ is responsible for the maintenance of blood glucose concentration
Pancreas
Describe what would happen if someone did not eat for a while and what would happen if someone suddenly takes a sugary drink
It you did not eat for a while, chemoreceptor will detect the blood sugar level is low, so the pancreas will produce glucagon ta breaks the glycogen in your liver to convert it into glucose so the blood sugar is maintain at the certain range
If you rook a sugary drink, then the chemoreceptor will detect the blood sugar level too high, so the pancreas will produce insulin to convert glucose in the liver into glycogen to reduce the blood sugar level.
Why does someone’s glucose level increase when eat glucose
The glucose taken are absorbed into the blood stream
What is the control of blood glucose concentration an example of
Negative feedback
What is diabetes
A condition where the homeostatic control of blood glucose levels stops working.
What is the cause of type 1 diabetes
Immune system attacks and destroys insulin producing cells, therefore pancreas does not produce enough insulin
How can type 1 insulin be treated [3]
Daily insulin injection
Managing diet
Regularly testing blood glucose level
What is the cause of type 2 diabetes
Person develops insulin resistance (often due to obesity)
How can type 2 diabetes be treated [3]
Managing diet
Regular exercise
Drugs
Describe the effect of alcohol on the body
Decrease reaction time
Cause liver damage and cardiovascular diseases
Name the receptor that reacts to the flashing of intense light
Retina