Chem 7-10
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
1
New cards
triple covalent bond
a covalent bond sharing six electrons
2
New cards
Metalic bonds
A
3
New cards
Wavelength
the distance from one point to the next similar point.
4
New cards
Amplitude
The distance from the origin to the crest or the trough on a wave.
5
New cards
Frequency
the number of waves to pass in a period of time.
6
New cards
Electromagnetic spectrum
range of all electromagnetic radiation
7
New cards
Electromagnetic waves
radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, cosmic rays, gamma rays
8
New cards
Photons
packets of light. each frequency carries its own specific amount of energy (quantized).
9
New cards
E=hv
Equation for energy
10
New cards
3x10^8
Speed of light
11
New cards
c=lv
speed of light equation
12
New cards
Bright-light spectrum
each element when excited will give off light and when refracted it will have its own distinct separate lines of color, each with its own frequency.
13
New cards
l (lamda)
wavelength symbol
14
New cards
h
planks constant symbol
15
New cards
v
frequency symbol
16
New cards
c
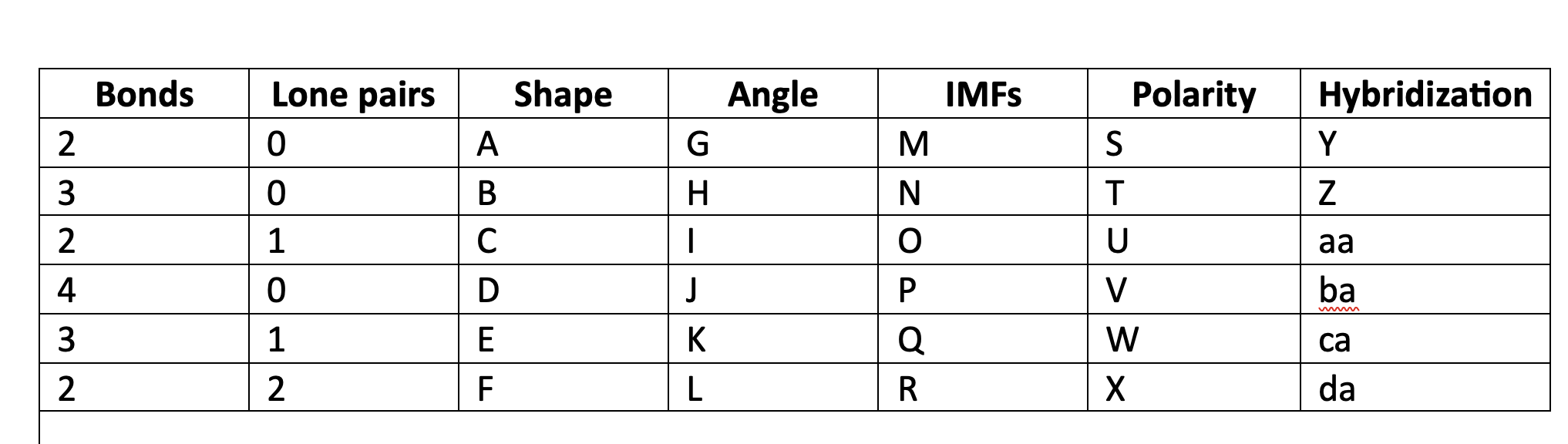
speed of light symbol
17
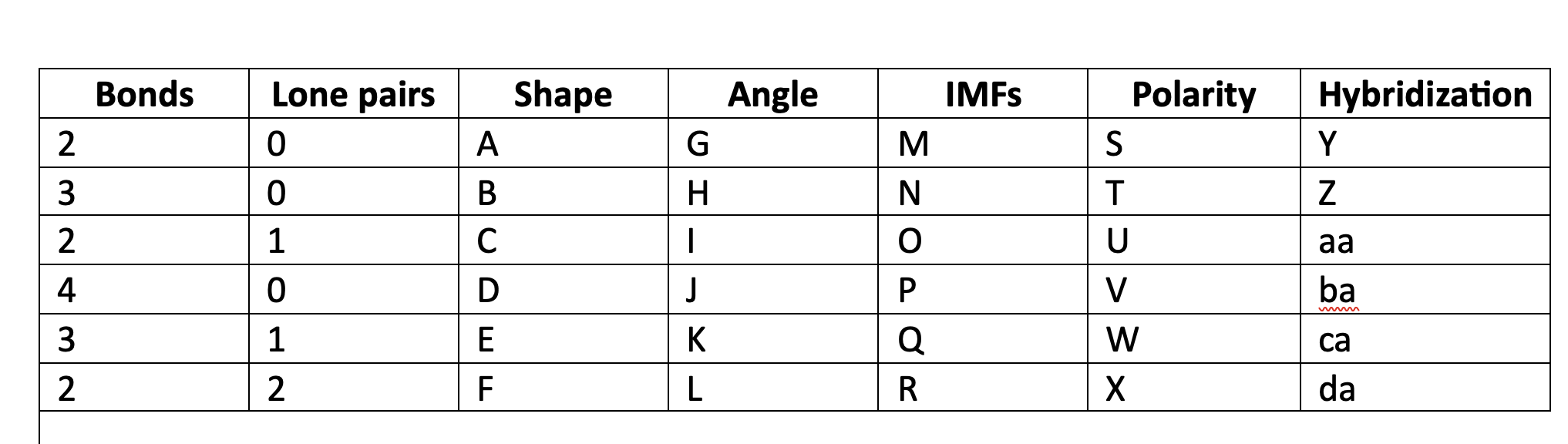
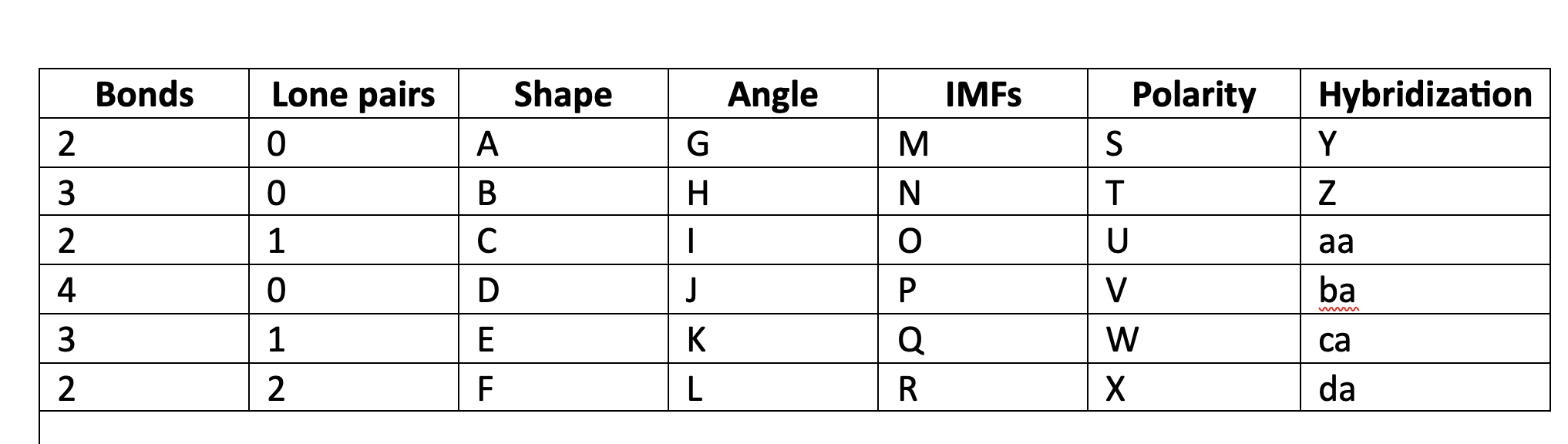
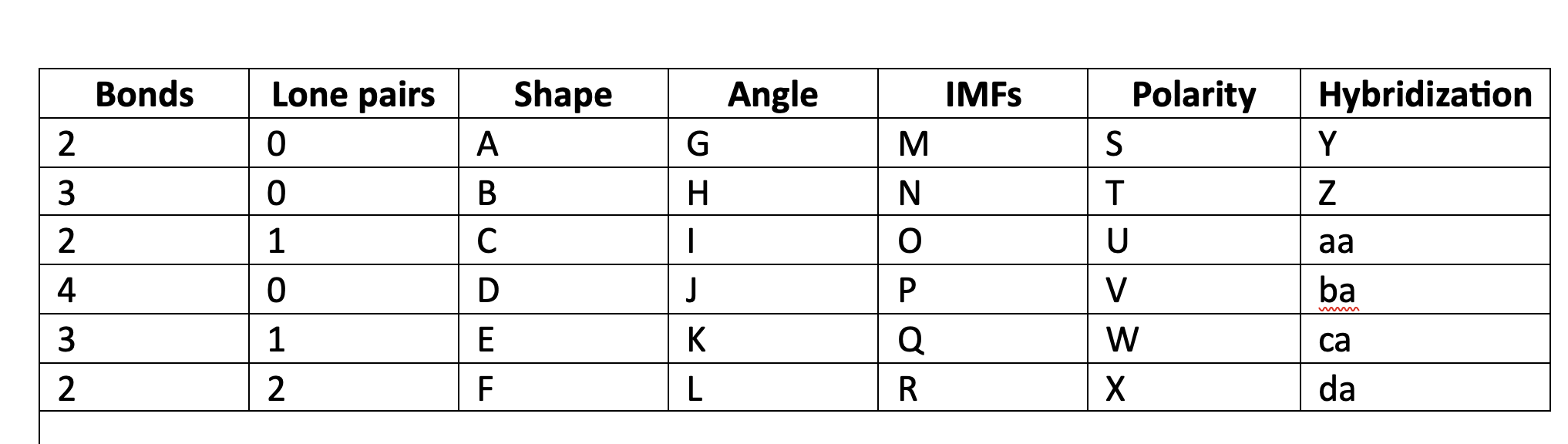
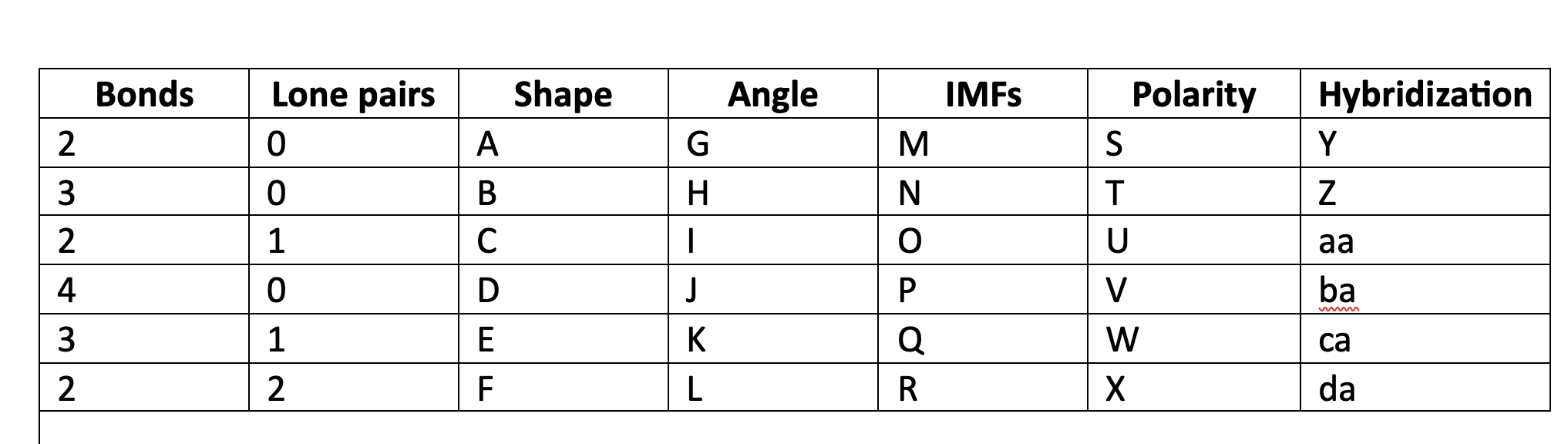
New cards
ground state
when electrons are in its lowest energy configuration
18
New cards
excited atoms
atoms that have absorbed a specific amount of energy. electrons have been bumped up to upper energy levels and are unstable.
19
New cards
ionization energy
the energy required to remove a mole of electrons from a mole of gas atoms.
20
New cards
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
we don’t know the momentum or position of a particle.
21
New cards
Orbital
an area of high probability of finding an electron
22
New cards
n, l, m, s
quantum numbers (letters)
23
New cards
energy level
principal (first) quantum number
24
New cards
sublevels
the shape of an orbital
25
New cards
s, p, d, f
sublevels (listed)
26
New cards
double lobes
shape of a P orbital
27
New cards
circular
shape of s orbital
28
New cards
sublevels
second quantum number
29
New cards
orientation around the x, y, z axes
third quantum number
30
New cards
spin
fourth quantum number
31
New cards
hund’s rule
electrons fill one orbital at a time (only two electrons in one orbital) with opposite spin
32
New cards
Cr, Cu
Hund’s rule exceptions
33
New cards
Electron configuration
the procedure of organizing electrons in atoms from the orbital with the highest energy. assumed to be in the ground stateAufbau principle
34
New cards
shielding effect
inner electrons block outer electrons therefore the larger the atom, the more ______
35
New cards
Aufbau principle
electrons fill one sub level to the next.
36
New cards
valance electrons
electrons in the outer energy level
37
New cards
4s1 3d10
Cu last two terms of e configuration
38
New cards
4s1 3d5
last two terms of Cr configuration
39
New cards
core electrons
electrons that are not in the outer energy level
40
New cards
Pauli exclusion principle
no 2 electrons can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers.
41
New cards
Atomic radius
1/2 the distance between two nuclei of two like atoms in a solid crystal
42
New cards
electronegativity
the attraction that an atom has between a shared pair of electrons and its positive nucleus.
43
New cards
e affinity
energy change for adding an electron to an atom in a gaseous state
44
New cards
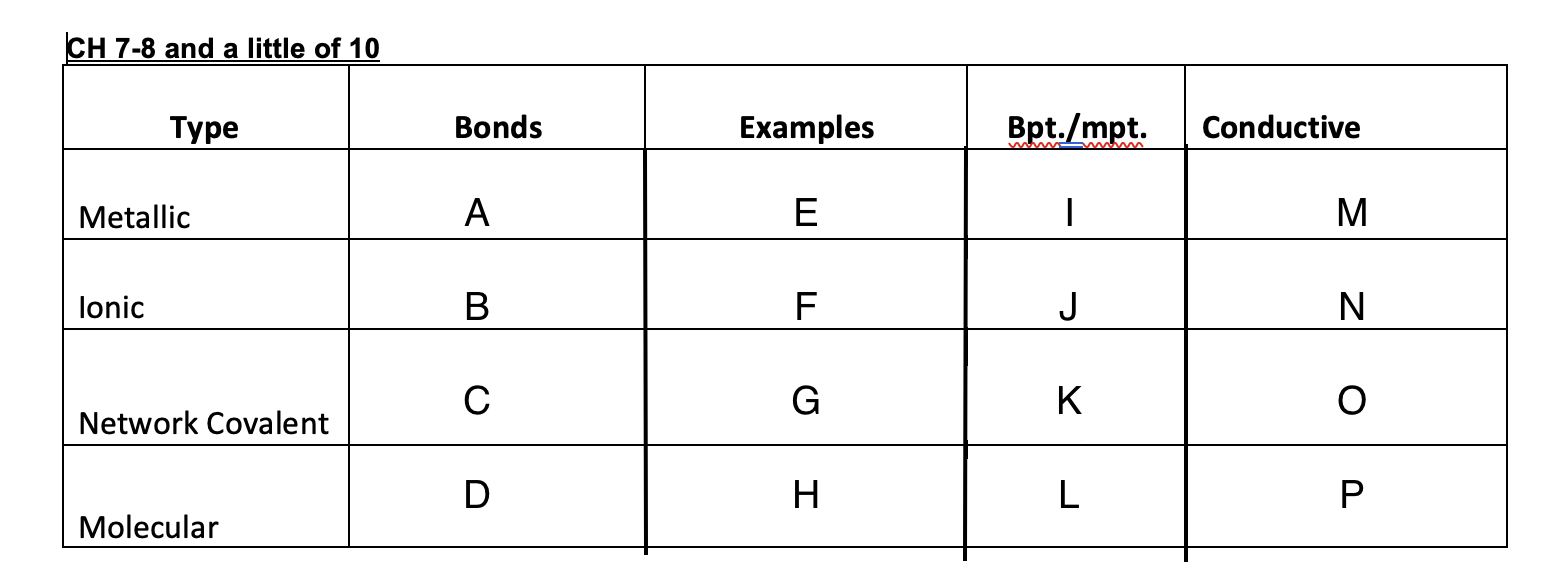
Ionic bonds
B
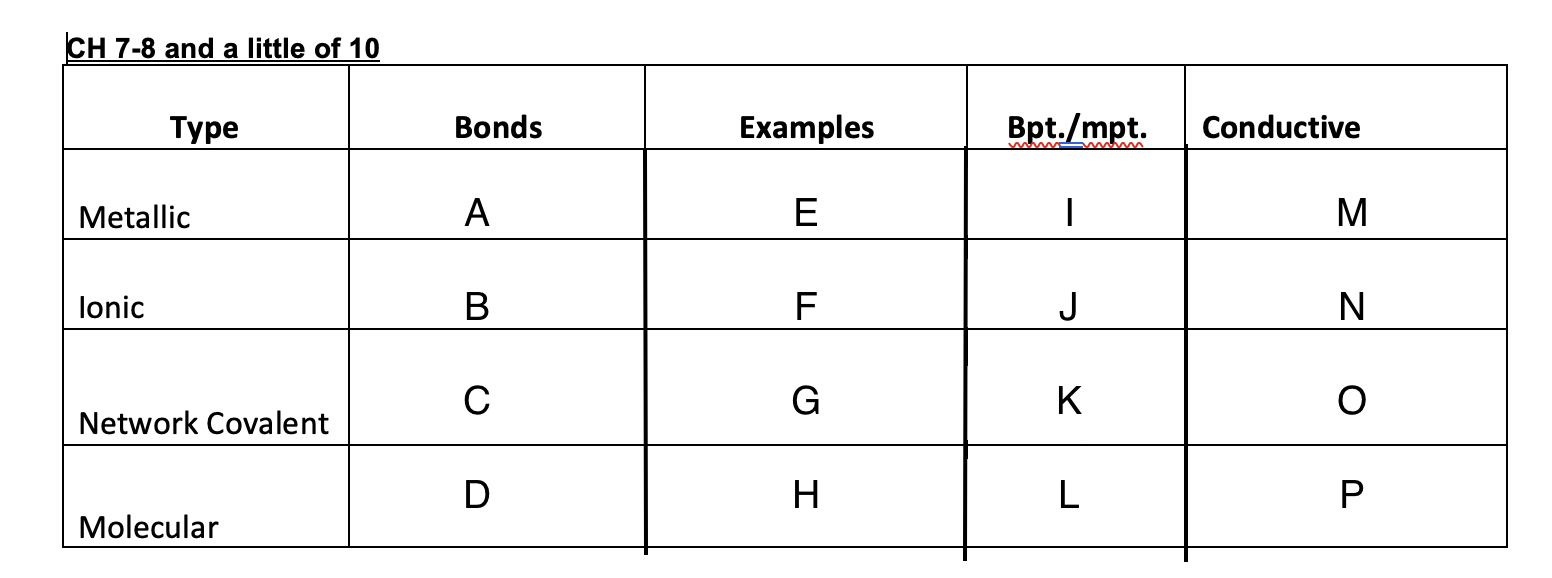
45
New cards
1000s of covalent bonds
C
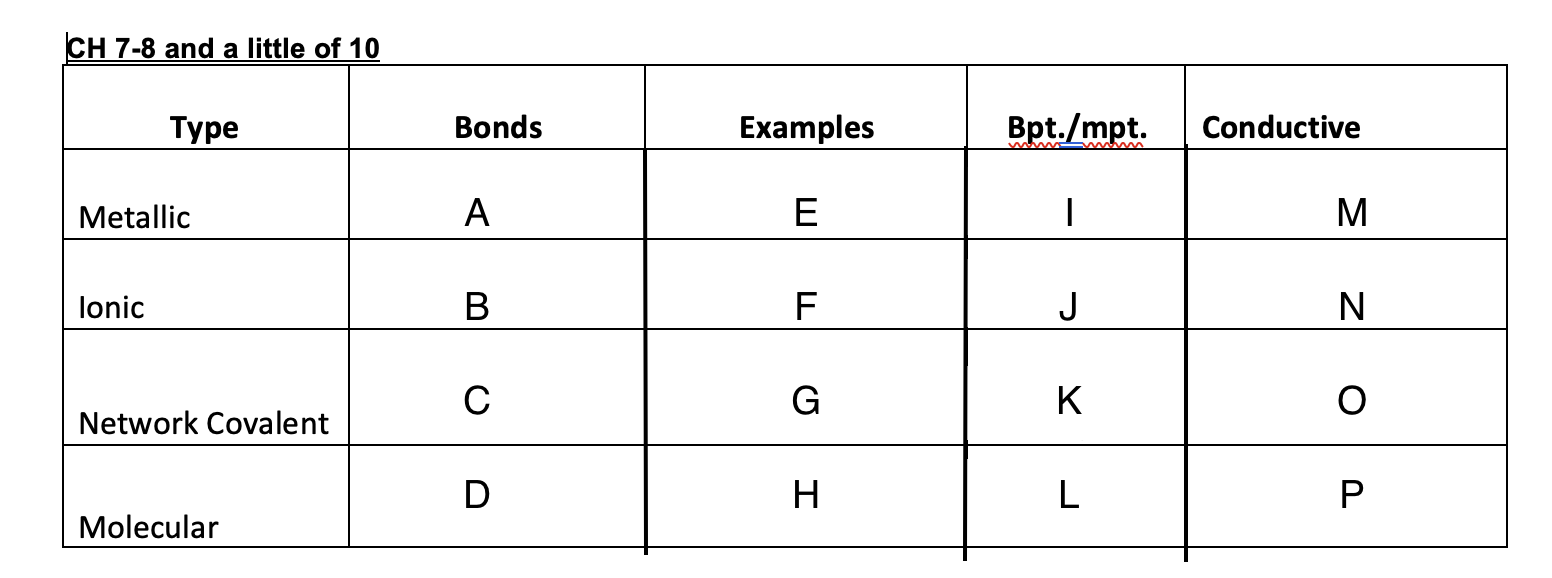
46
New cards
Intermolecular force
D
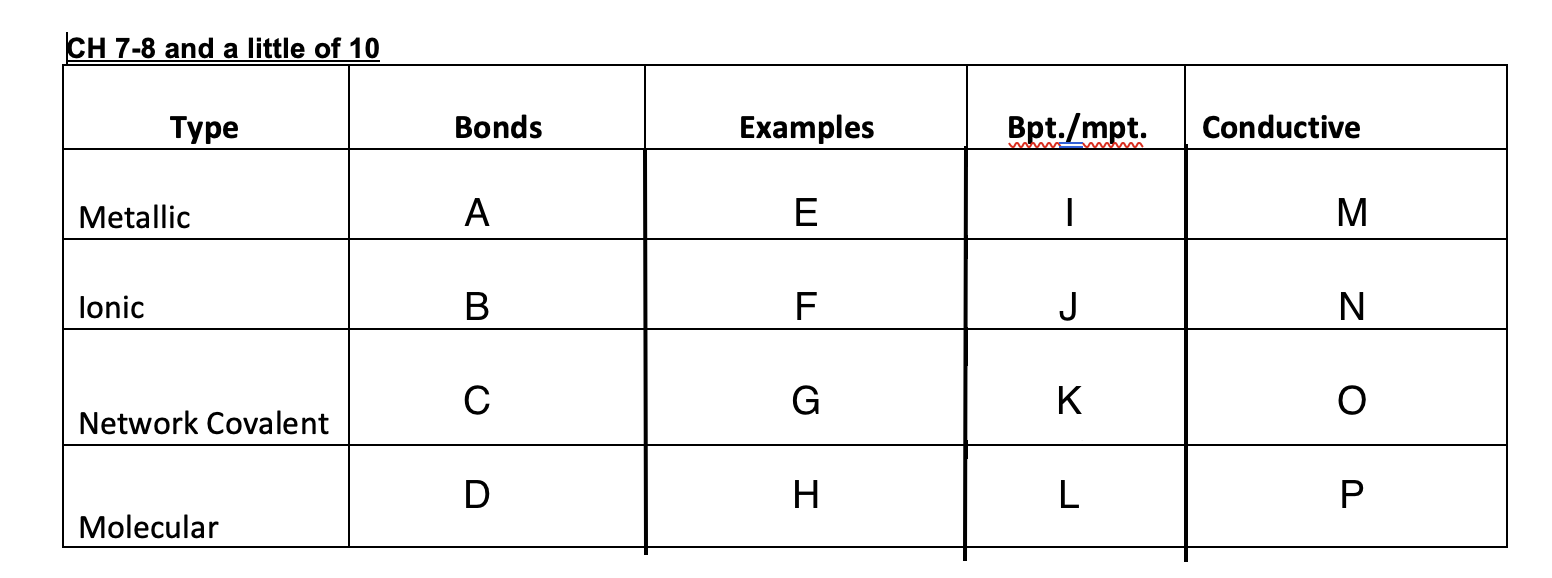
47
New cards
Cu, Ag, K, Pb
E
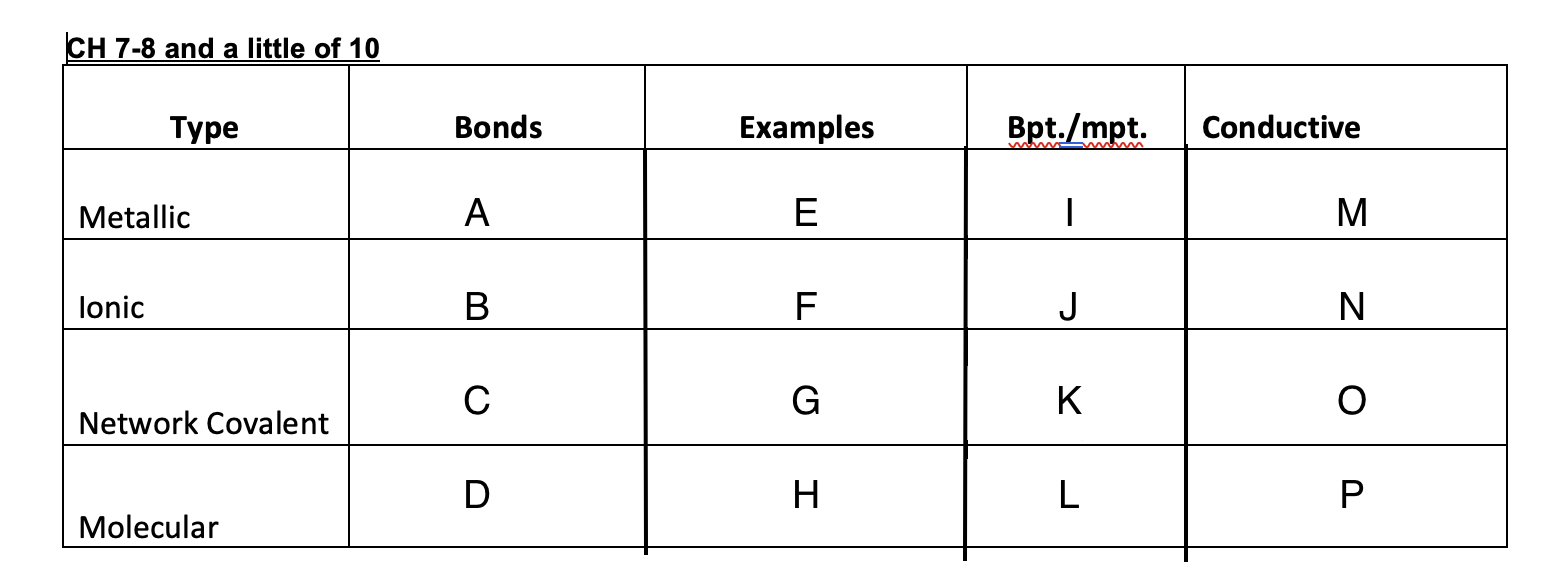
48
New cards
NaCl, MgSO4,
F
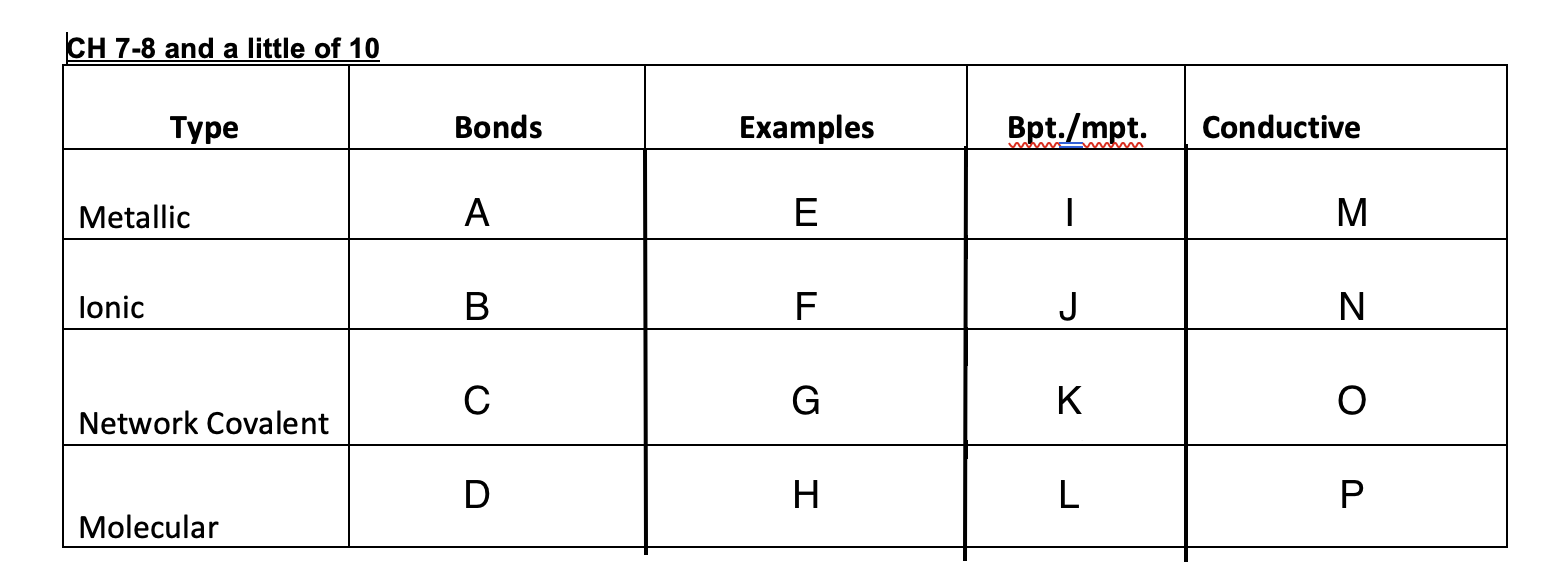
49
New cards
Graphite, glass, diamonds
G
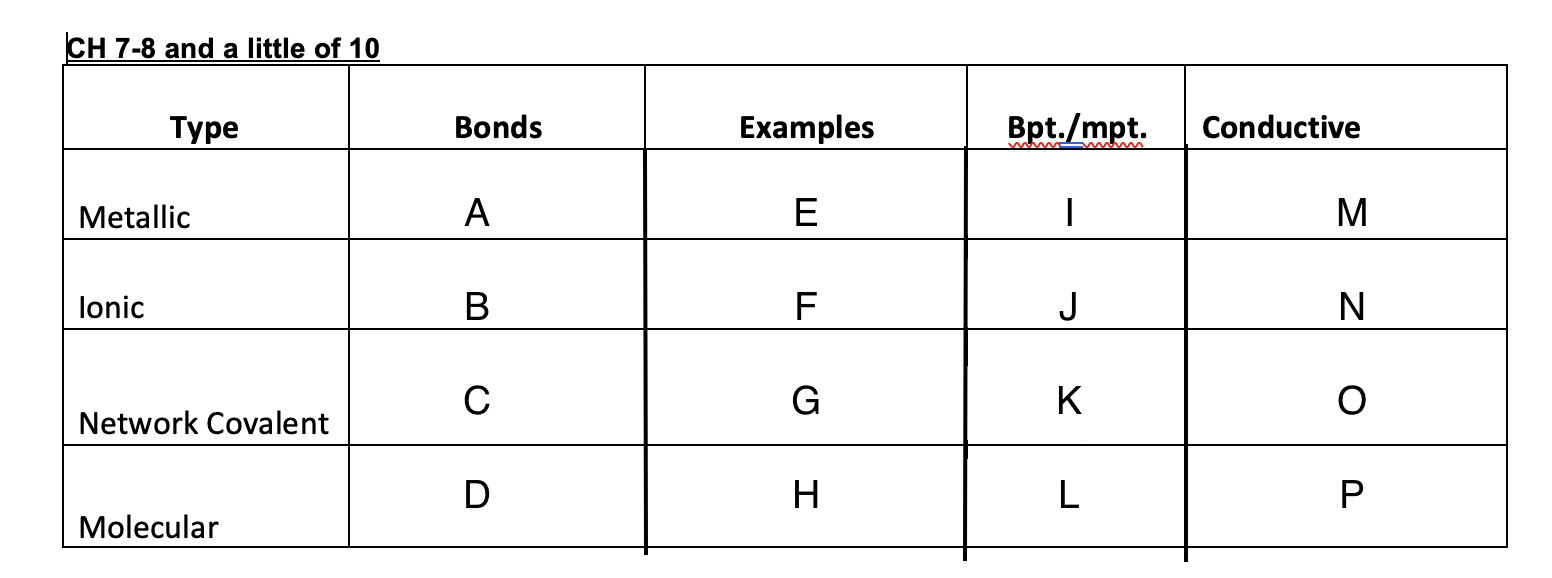
50
New cards
Ice, dry ice, sugar, organic solid
H
51
New cards
High
I
52
New cards
High
J
53
New cards
High
K
54
New cards
low
L
55
New cards
Yes
M
56
New cards
No
N
57
New cards
Graphite-yes, diamond-no
O
58
New cards
No
P
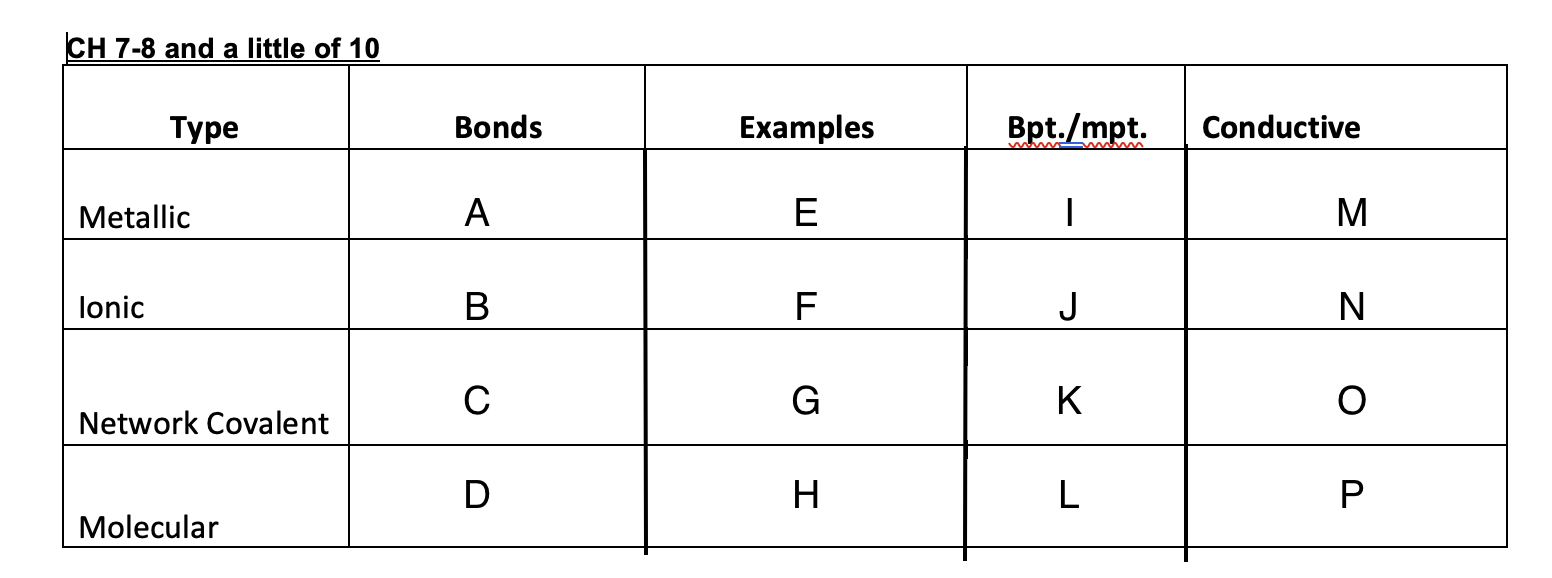
59
New cards
crystal lattice, metallic bond, network covalent, molecular
4 types of crystal solids
60
New cards
Crystal lattice
a regular and repeated structure. organized
61
New cards
ionic bonds
an electrostatic attraction due to opposite charges
62
New cards
Metallic bond
an attraction of positive ions to a sea of electrons
63
New cards
Network covalent
crystal in which thousands of atoms are covalently bonded to each other. giant molecule
64
New cards
molecular
solid held together by weak intermolecular forces
65
New cards
valence electrons
electrons in the outer or highest occupied energy level
66
New cards
lewis dot structures
shows valance electrons as dots
67
New cards
octet rule
atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to have the same configuration as the closest noble gas.
68
New cards
covalent bond
an attraction of a shared pair of valence electrons to the positive nuclei.
69
New cards
single covalent bonds
a covalent bond sharing two electrons
70
New cards
double covalent bonds
a covalent bond sharing four electrons
71
New cards
unshared electrons
orbitals of electrons, usually in pairs, not shared b/w two atoms
72
New cards
resonant structures
two or more valid electron dot formulas for a single molecule
73
New cards
sigma bond
bonding orbitals that overlap head to head. there is one _____ in either a single, double, or triple bond
74
New cards
pi bond
bonding orbitals that overlap side by side. occur in double and triple bond
75
New cards
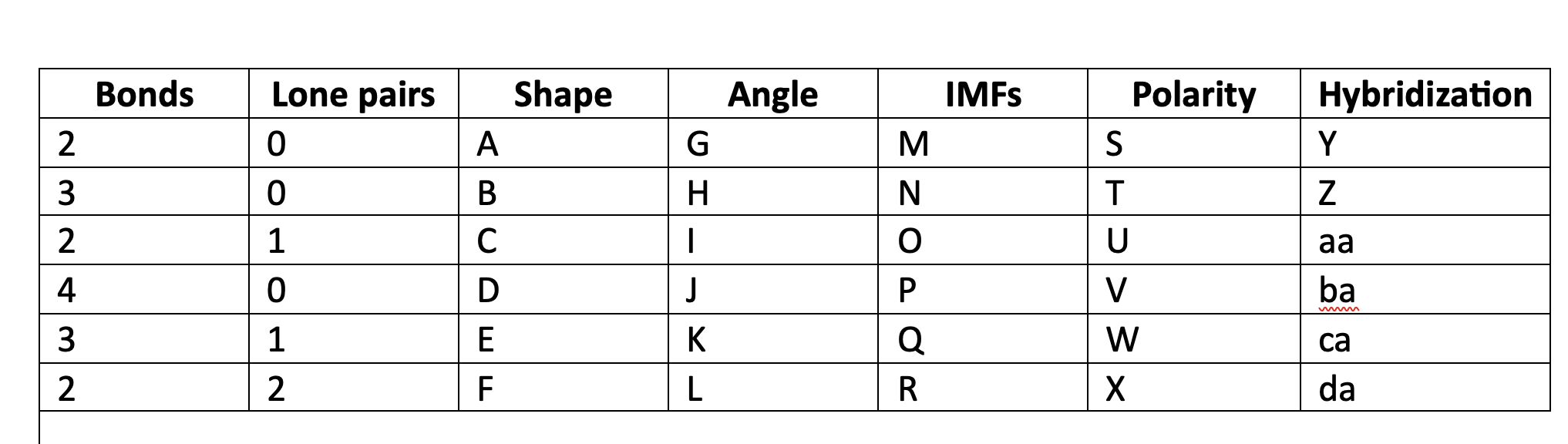
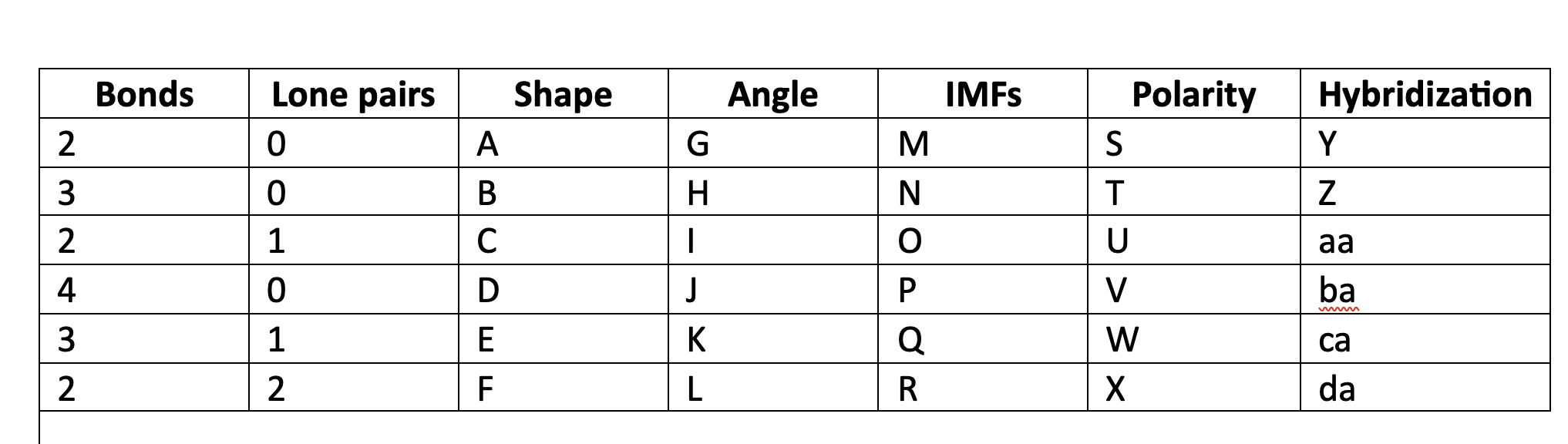
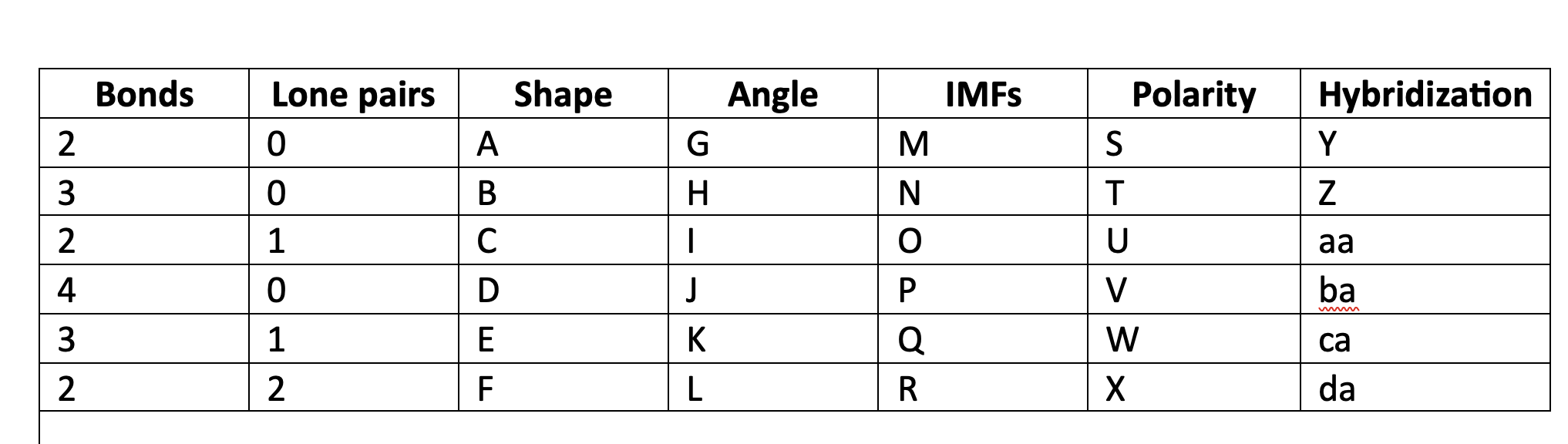
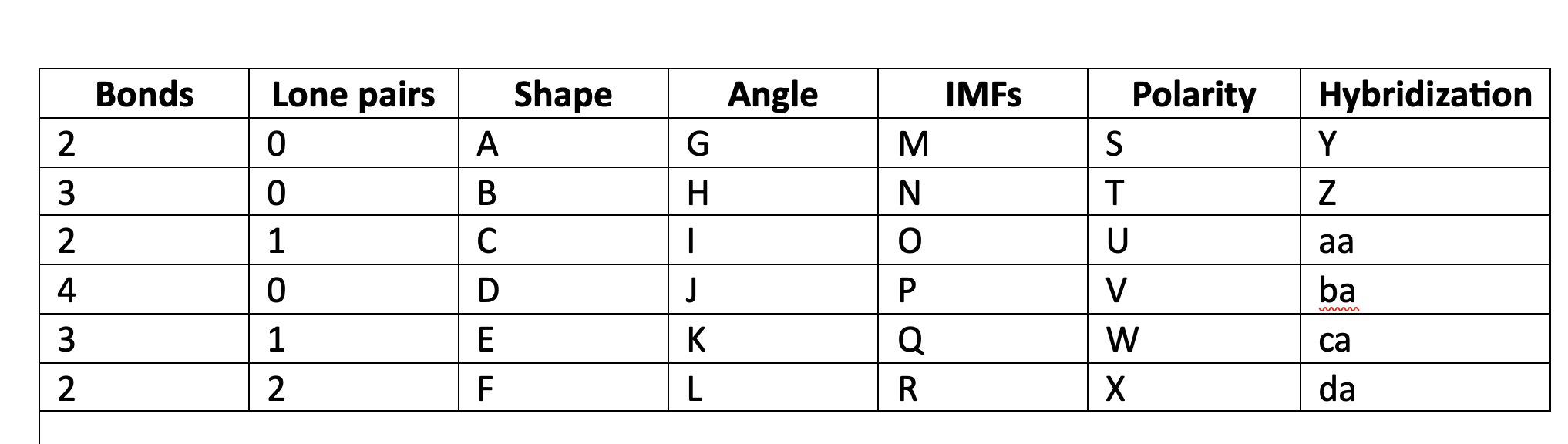
Valence shell electron pair repulsion
VSEPR acronim meaning
76
New cards
VSEPR
orbitals of electrons, bonding and nonbonding, will move geometrically as far away from each other as possible.
77
New cards
linear
A
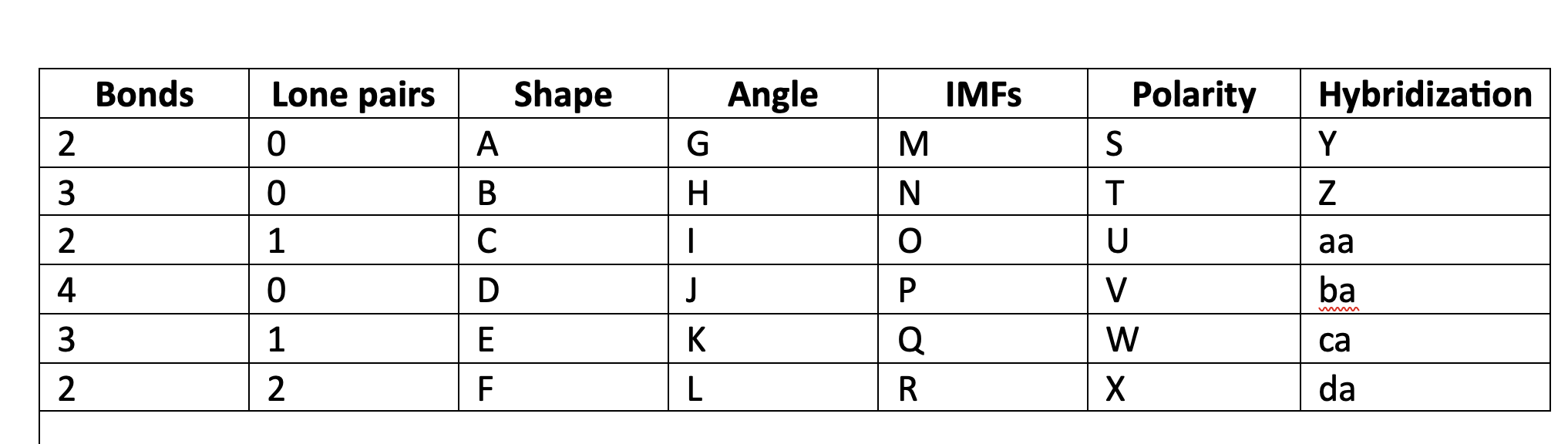
78
New cards
trigonal planar
B
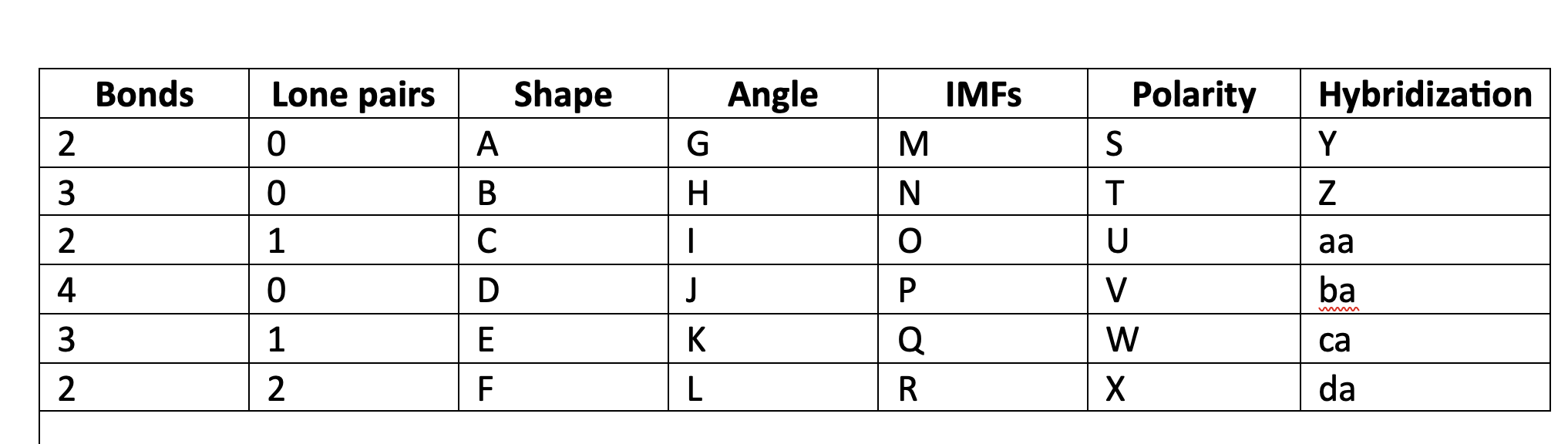
79
New cards
bent
C
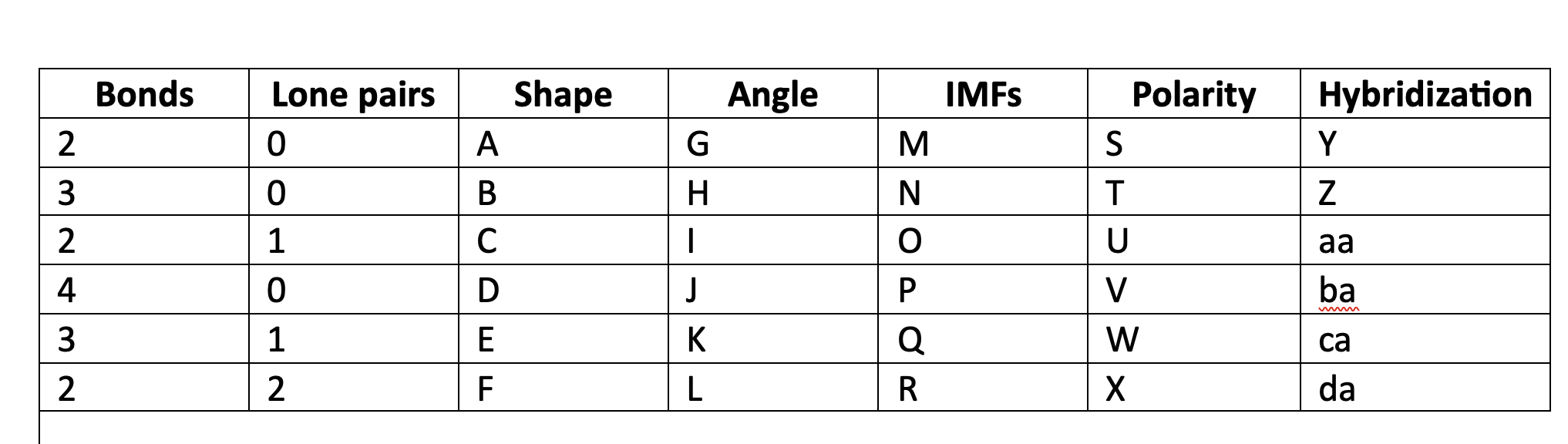
80
New cards
tetrahedral
D
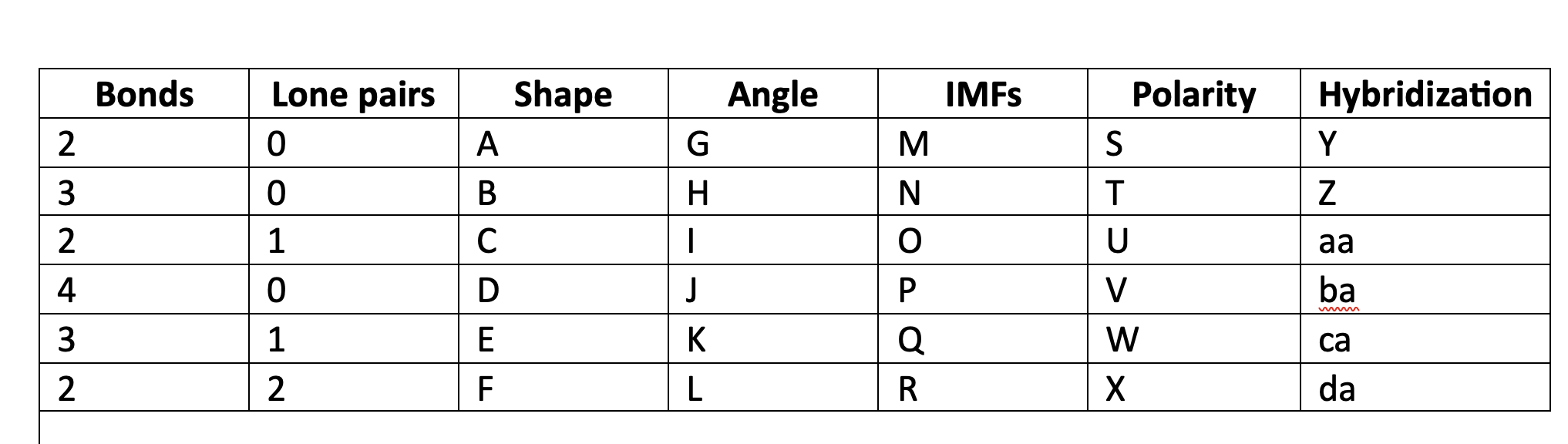
81
New cards
trigonal pyramidal
E
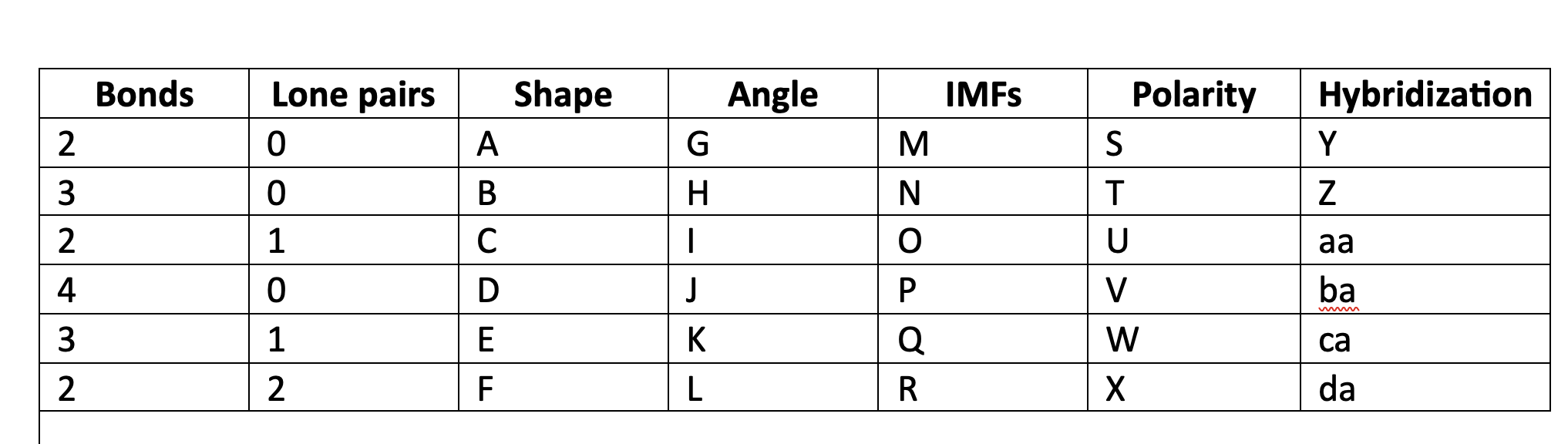
82
New cards
bent
F
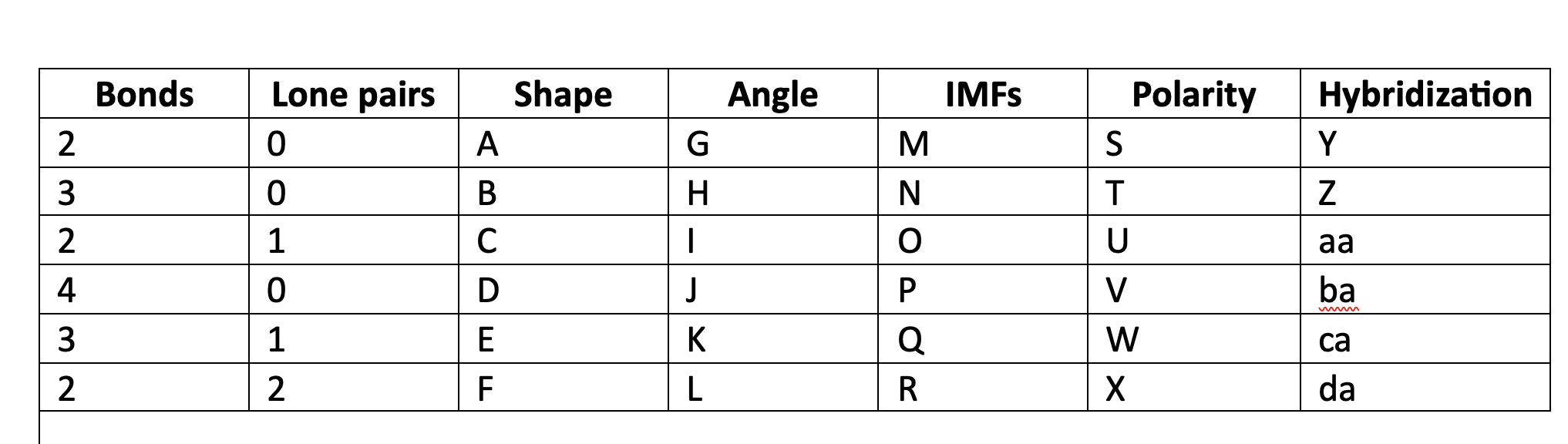
83
New cards
180
G
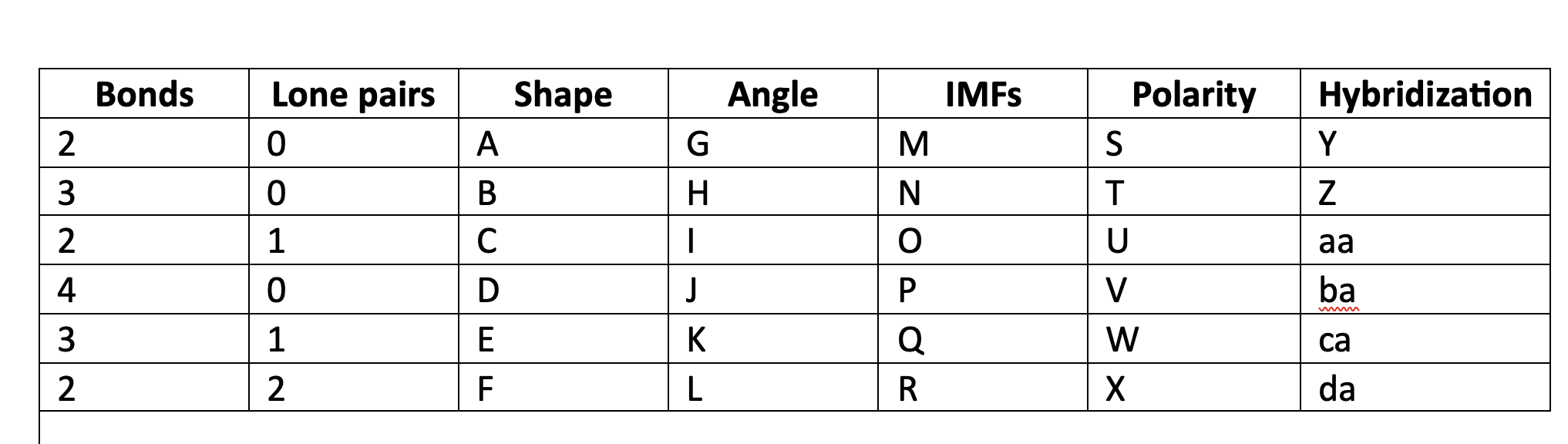
84
New cards
120
H
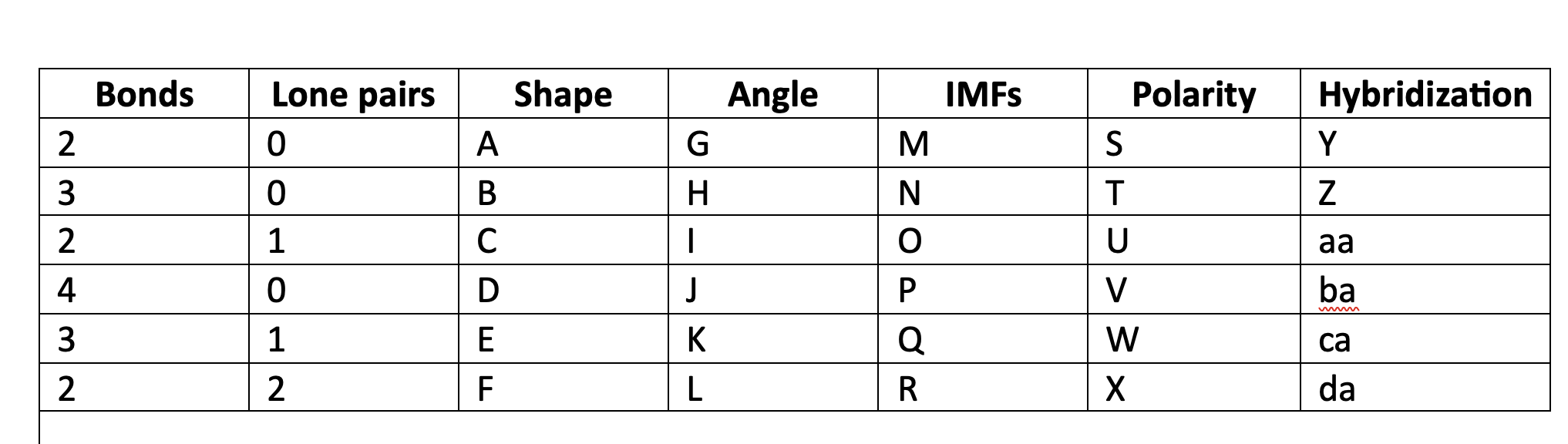
85
New cards
less than 120
I
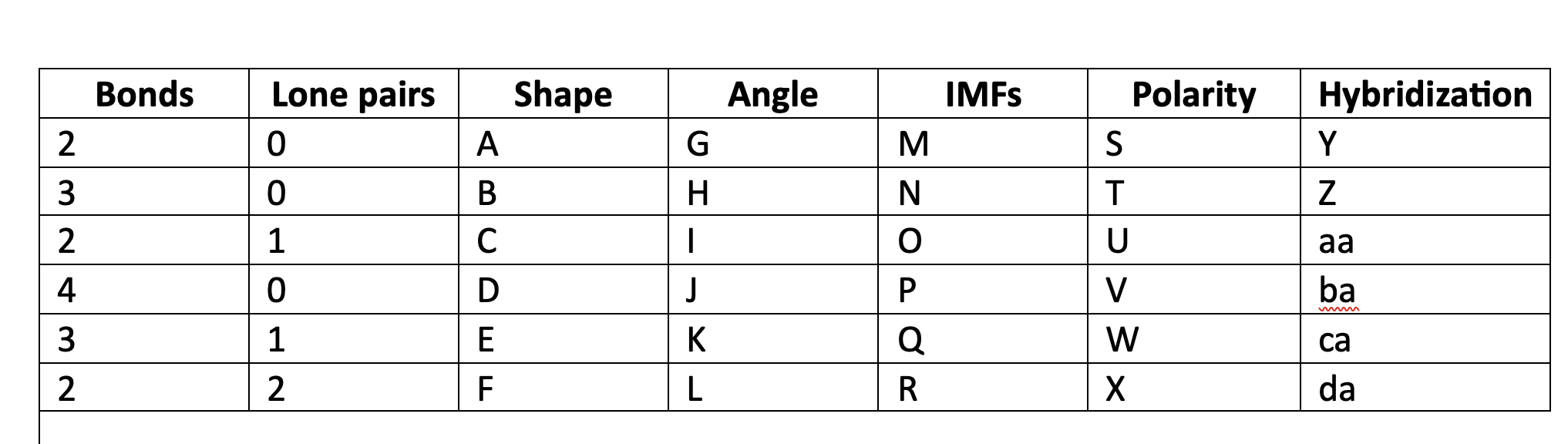
86
New cards
109\.5
J
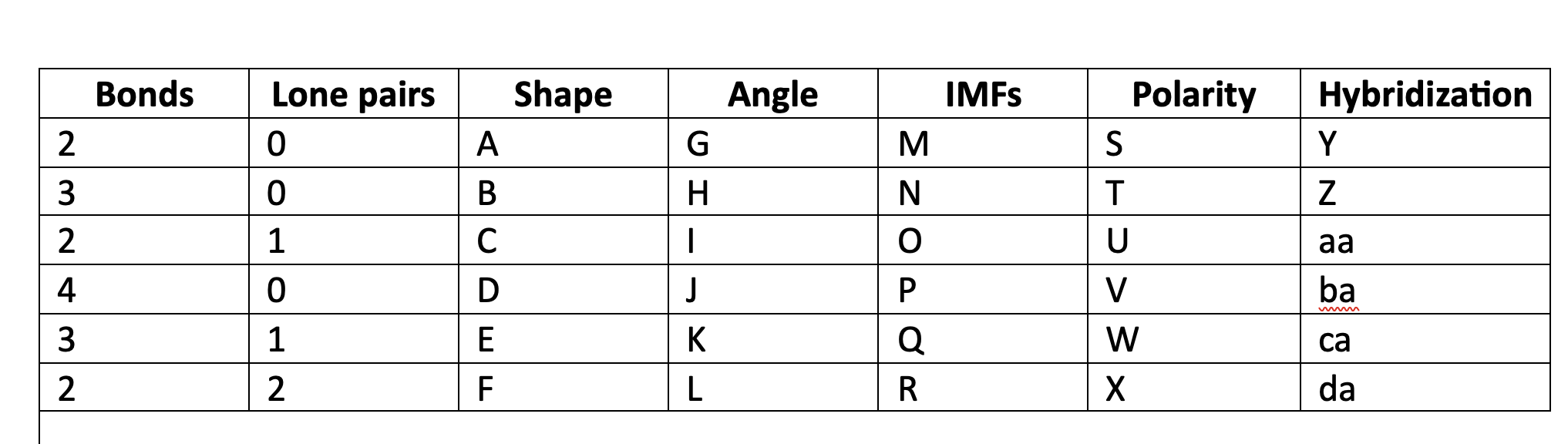
87
New cards
greater than 109.5
K
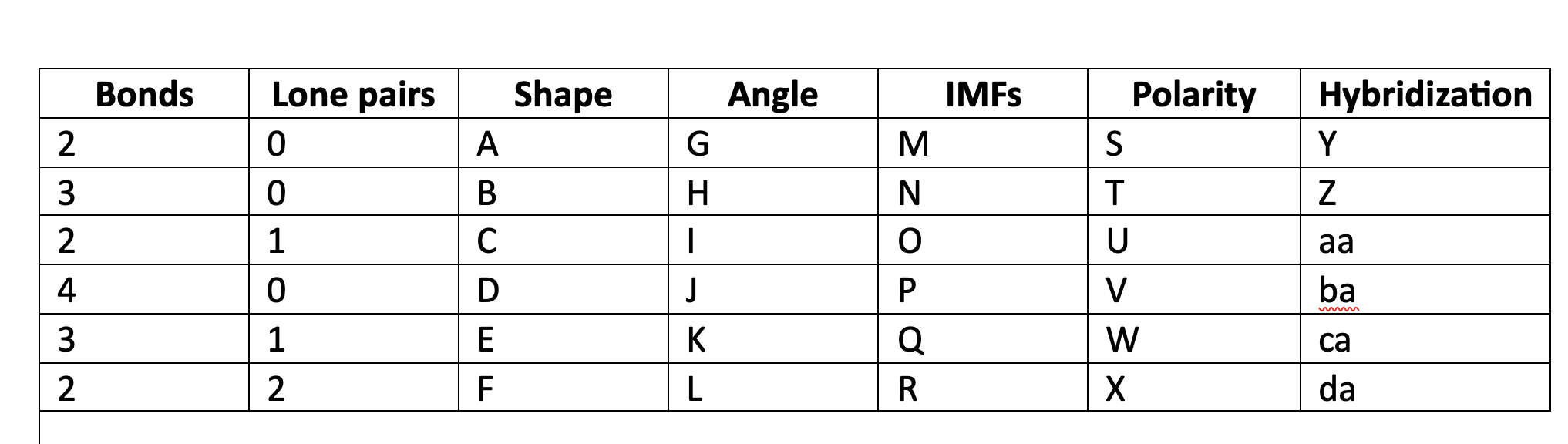
88
New cards
less than 109.5
L
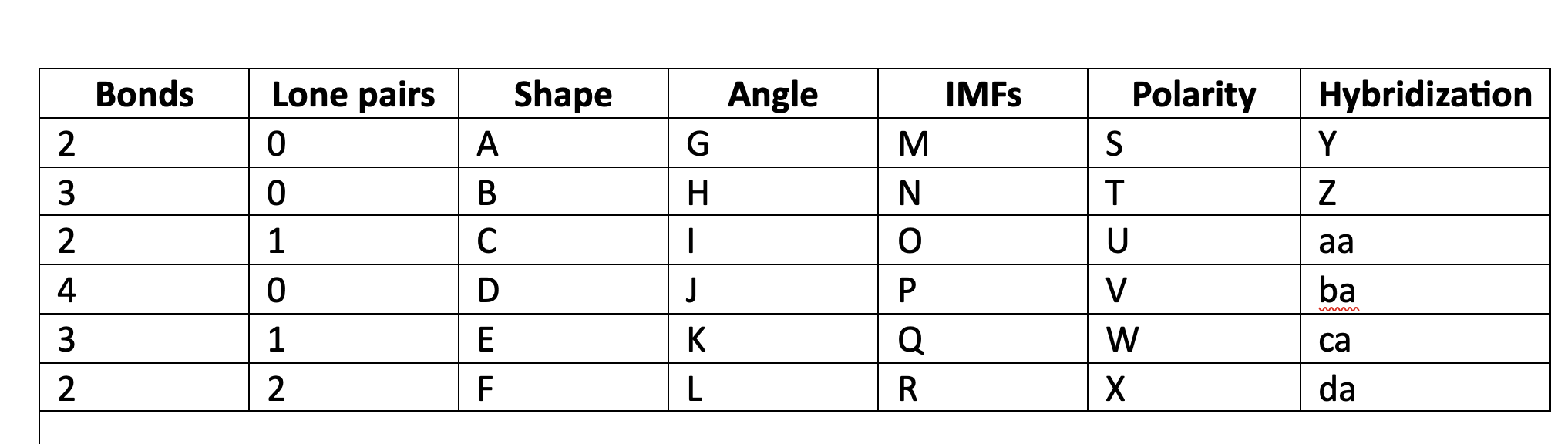
89
New cards
LDF
M
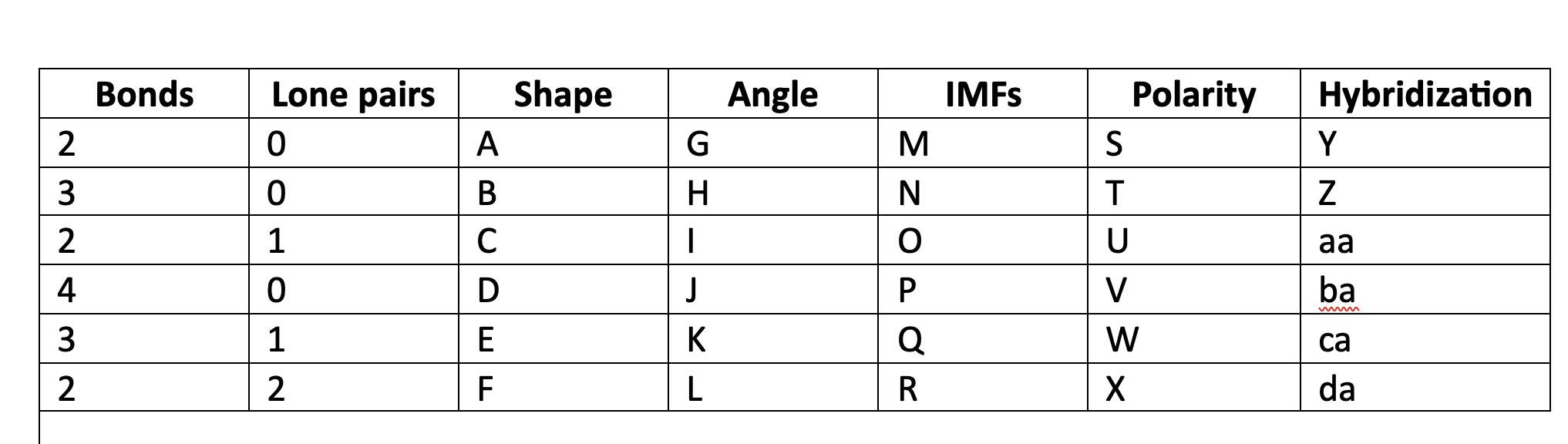
90
New cards
LDF
N
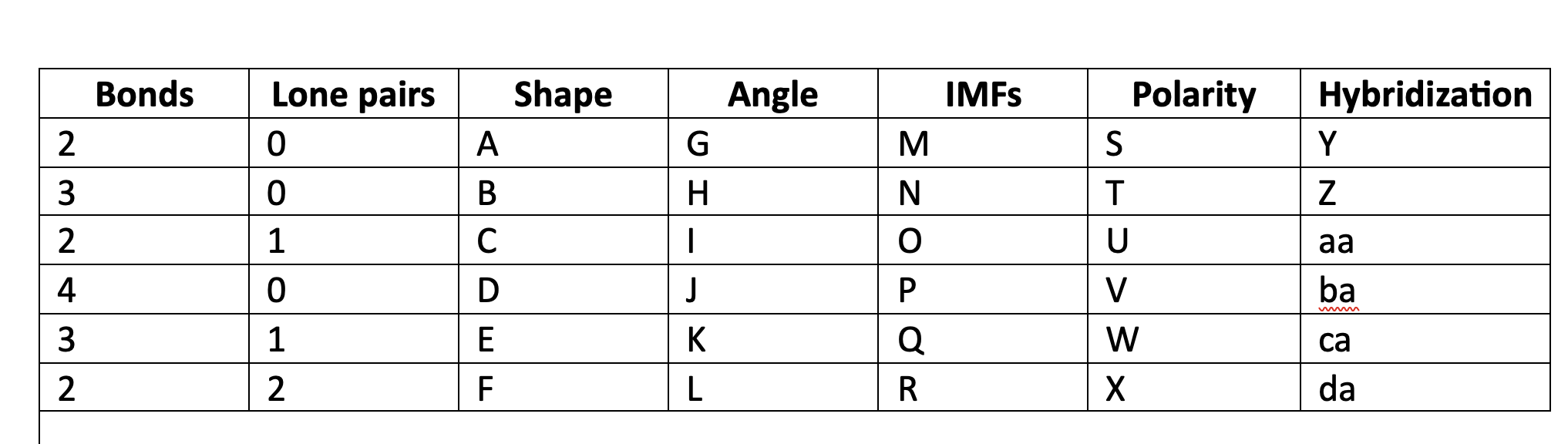
91
New cards
LDF, Dip-dip, h-bond
O
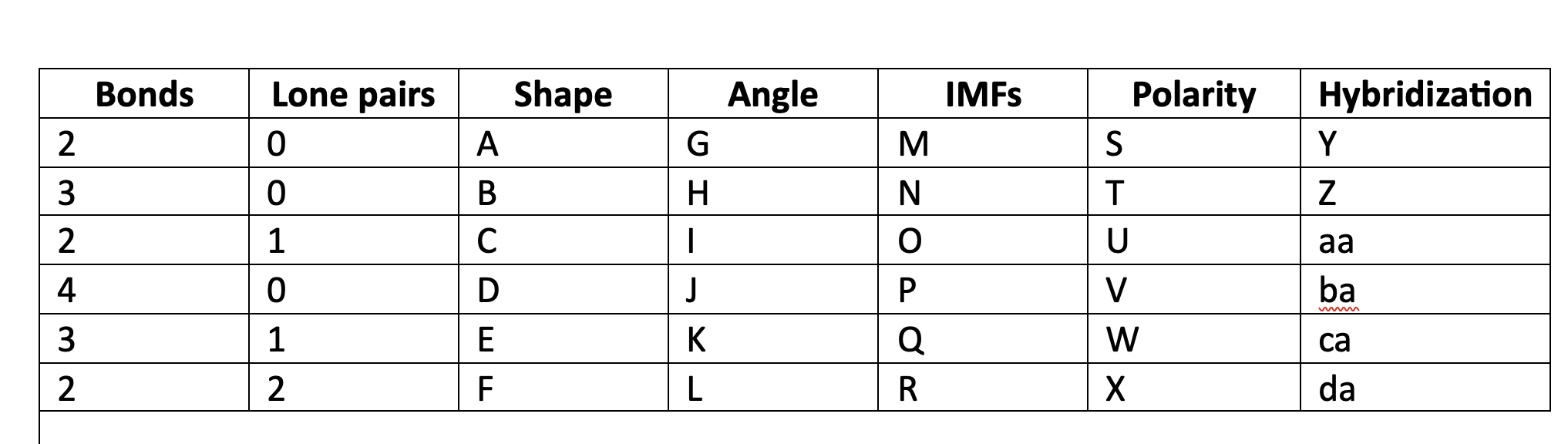
92
New cards
LDF
P
93
New cards
LDF, Dip-dip, h-bond
Q
94
New cards
LDF, Dip-dip, h-bond
R
95
New cards
NP
S
96
New cards
NP
T
97
New cards
polar
U
98
New cards
NP
V
99
New cards
polar
W
100
New cards
polar
X