Parts of the Brain - AP Psych
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biological Bases of Behavior Unit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
cerebral cortex
body’s info-processing center; originates distinctly human traits
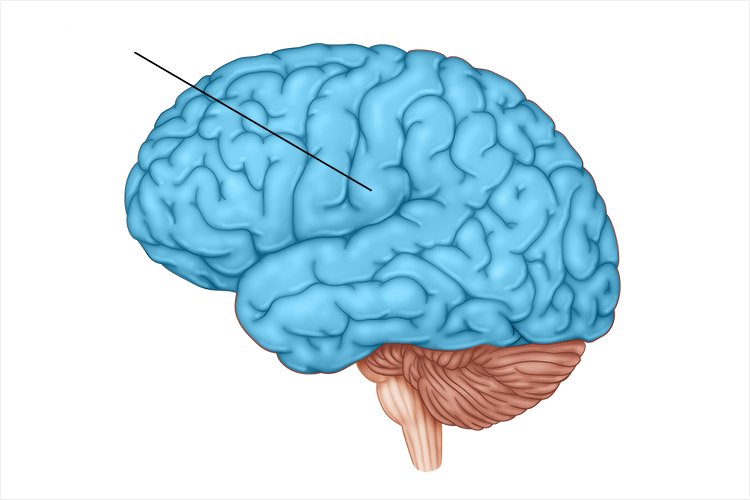
thalamus
directs messages to sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and the medulla; receives info from all senses except smell; located at top of brainstem
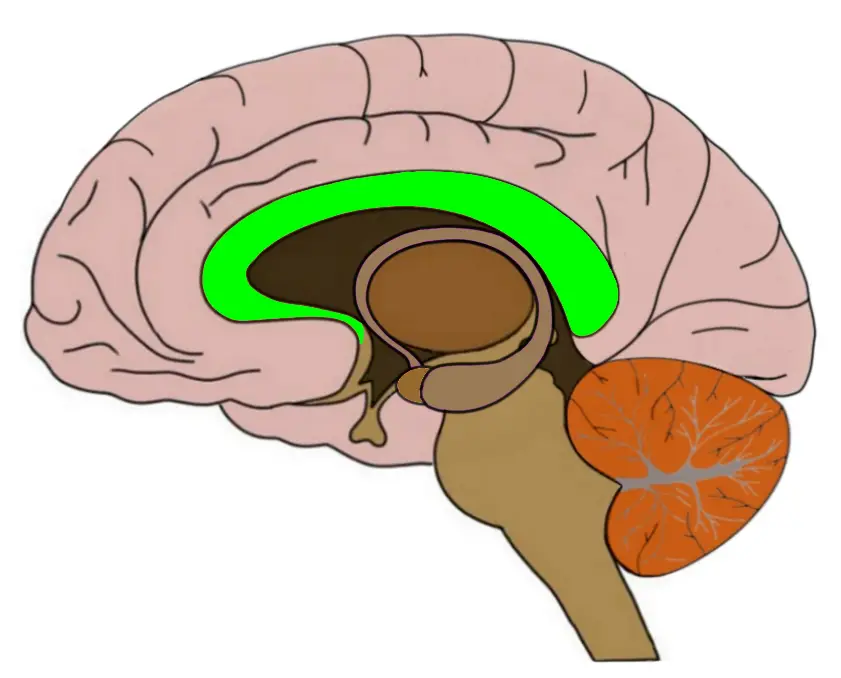
corpus callosum
neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
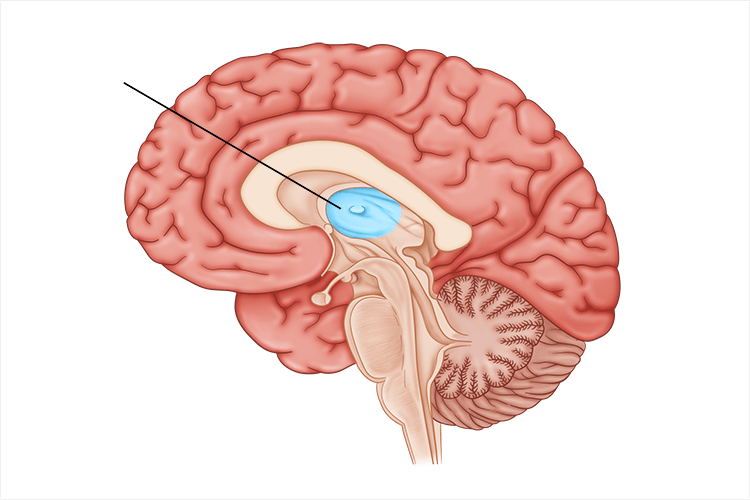
hypothalamus
directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temp) and helps govern endocrine system via the pituitary gland; also linked to emotion and reward
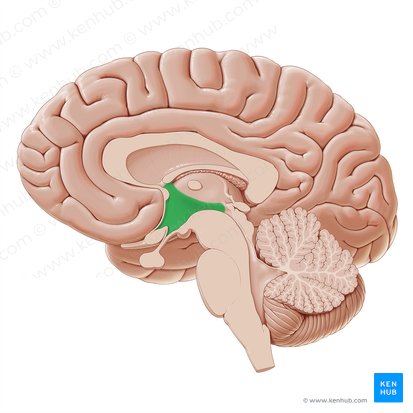
amygdala
linked to emotions like fear and anger and coordinates fight or flight
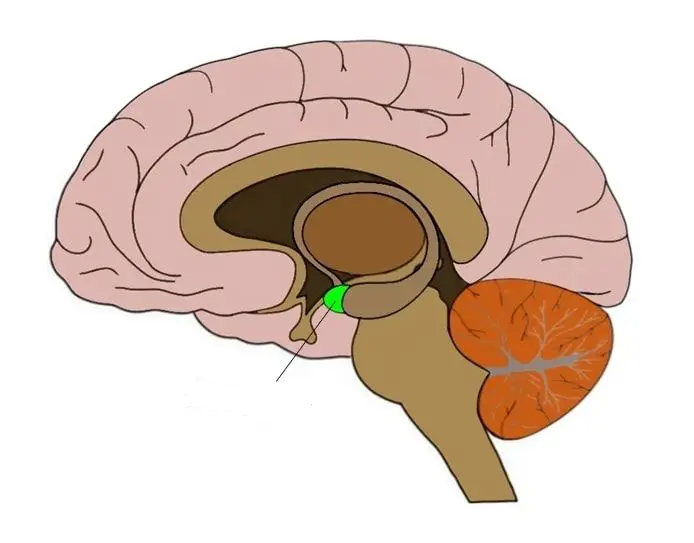
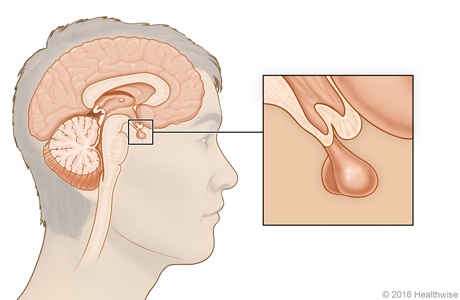
pituitary gland
master gland that secretes hormones that tell other glands to secrete their hormones; regulates growth
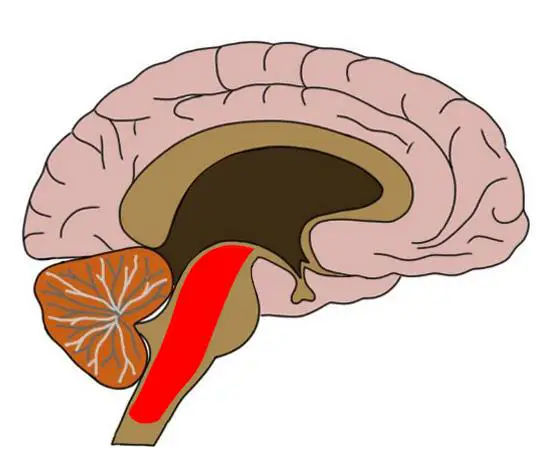
brainstem
reticular formation, pons, medulla
reticular formation
plays a role in controlling conscious arousal and helps filter out unnecessary stimuli
pons
plays a role in regulating sleep (sleeping, waking, REM) and coordinating facial expressions
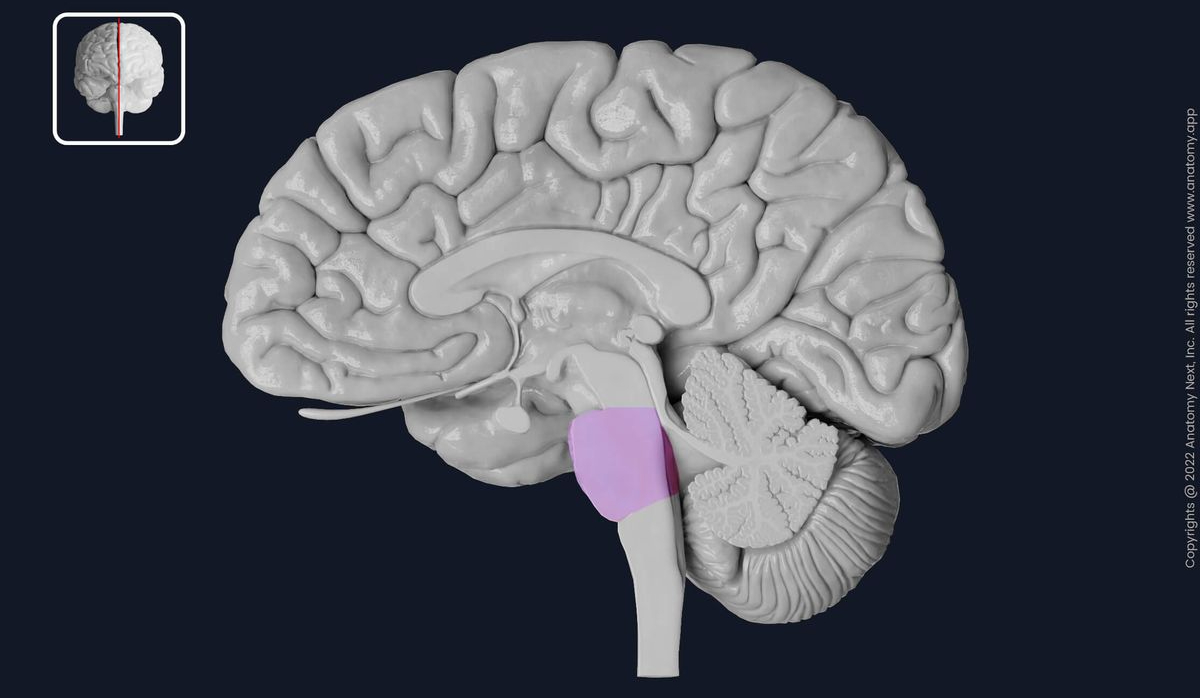
medulla
controls heart beat and breathing
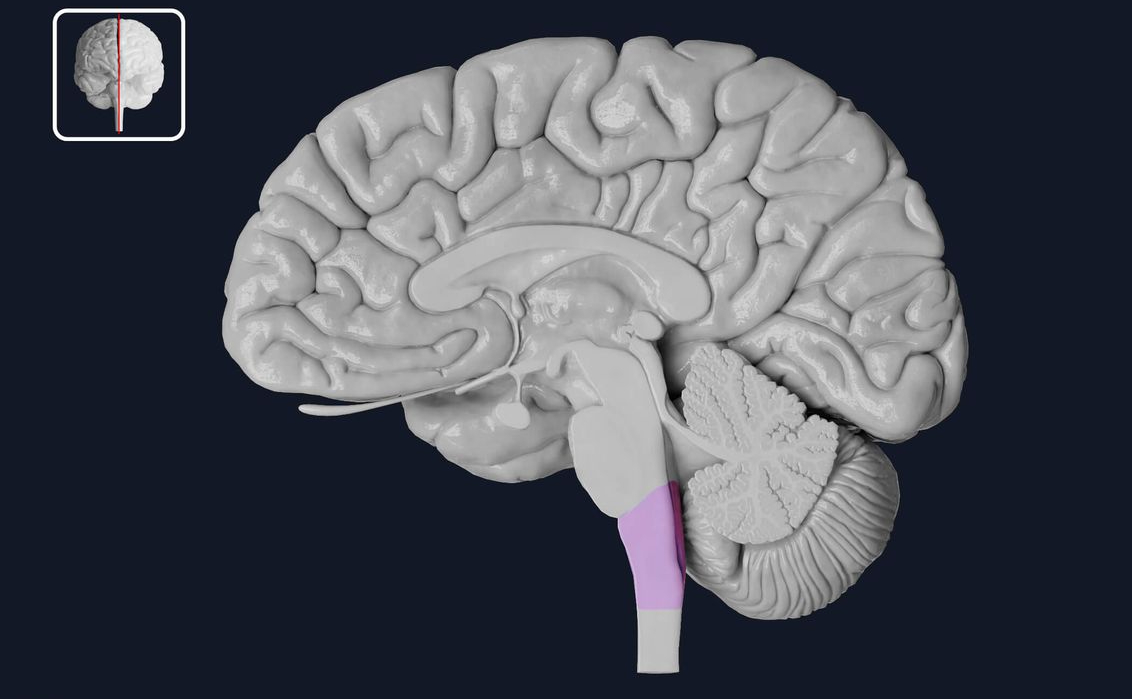
brainstem
responsible for automatic survival functions (breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness)
spinal cord
how brain communicates with body
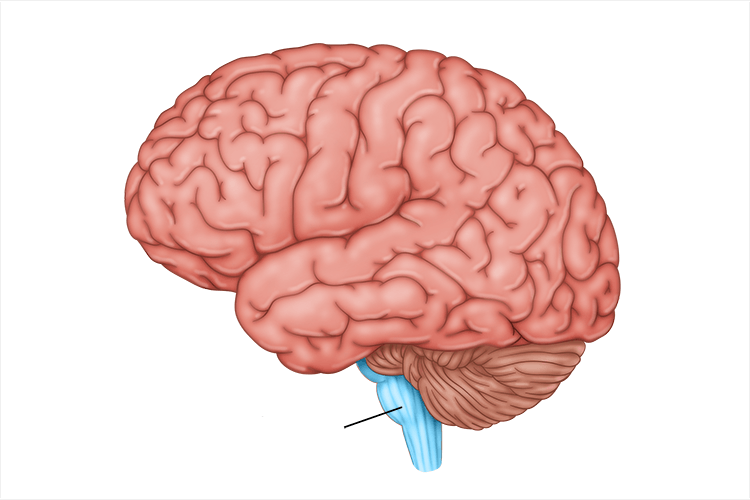
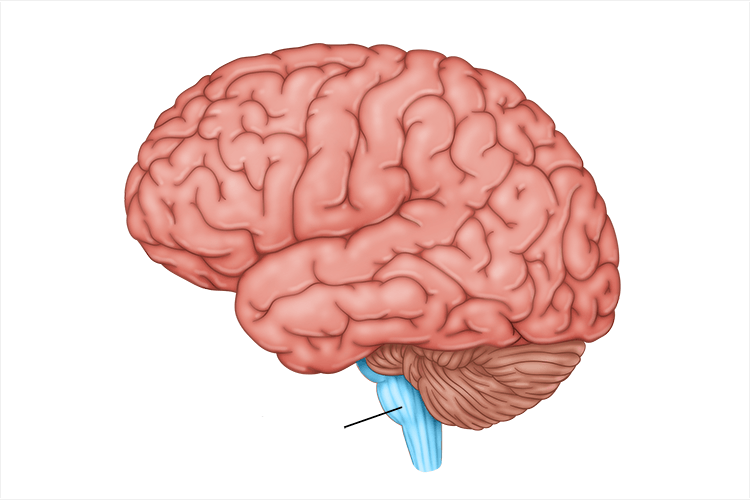
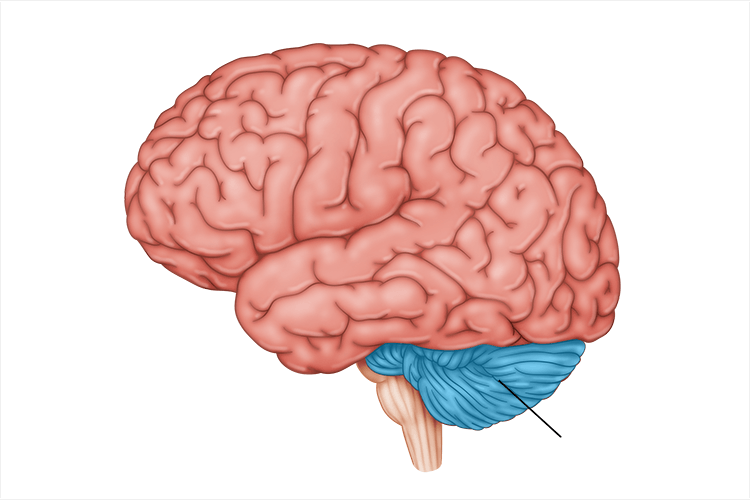
cerebellum
processes sensory input, coordinates movement output and balance, and nonverbal learning and memory
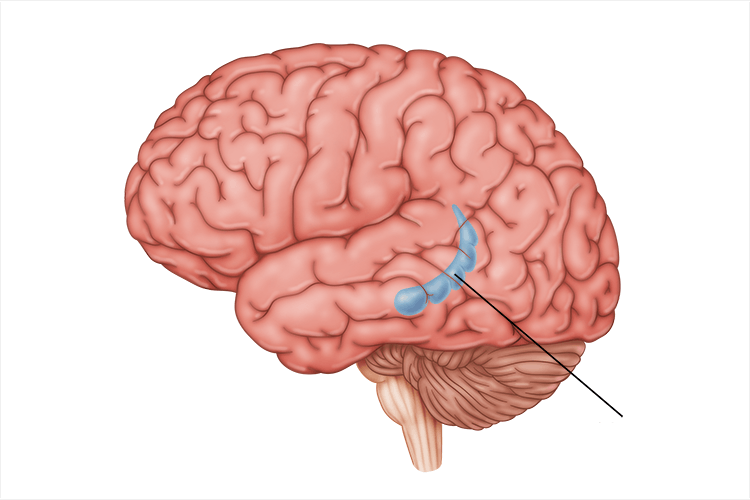
hippocampus
critical role in formation, organization, and storage of new memories (declarative memories)
hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus
limbic system
limbic system
associated with emotions, drives, and conscious memories
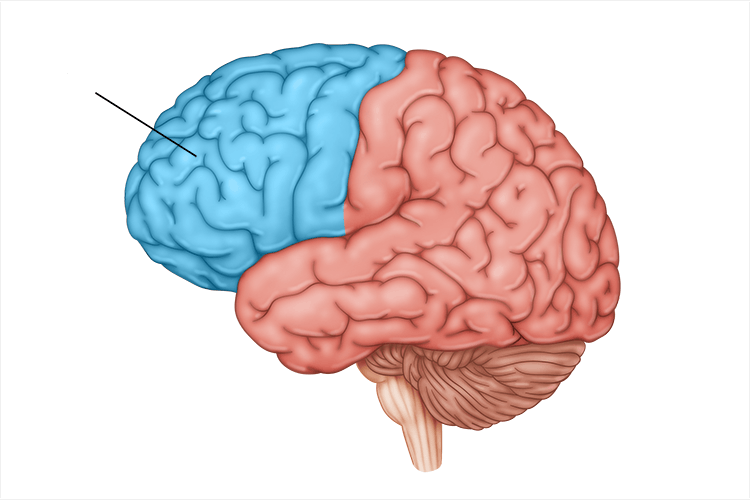
frontal lobe
involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgements
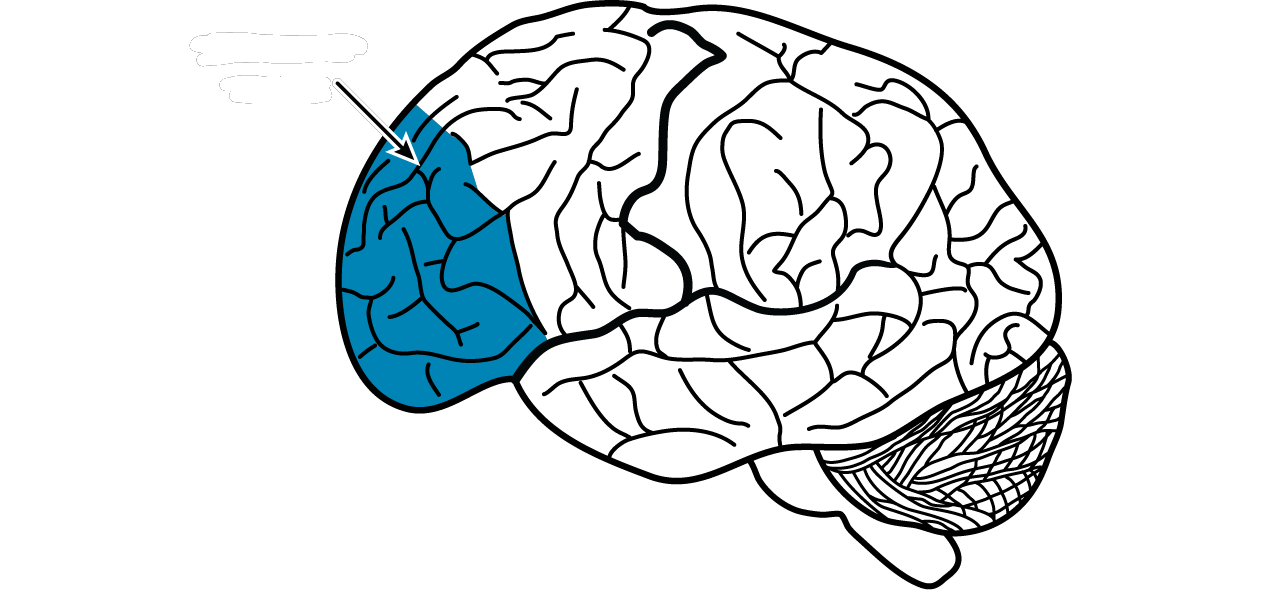
prefrontal cortex
associated with planning and complex cognitive behavior, personality expression, decision making, and moderating social behavior
motor cortex
controls voluntary movements; part of frontal lobe
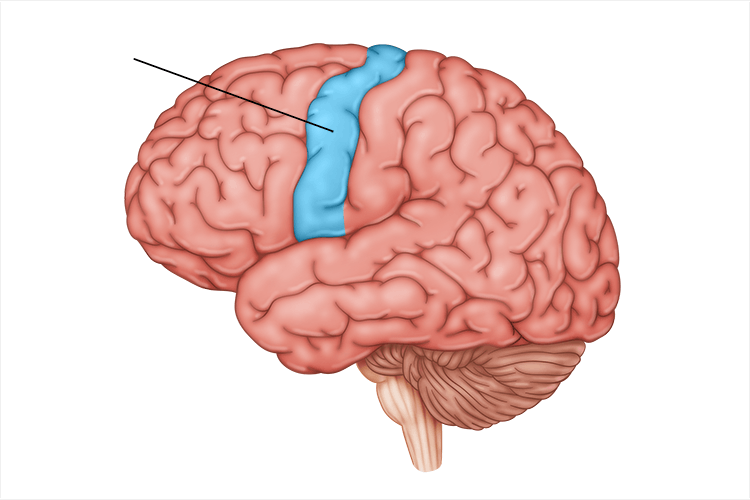
somatosensory cortex
processes body touch and movement sensations; part of parietal lobe
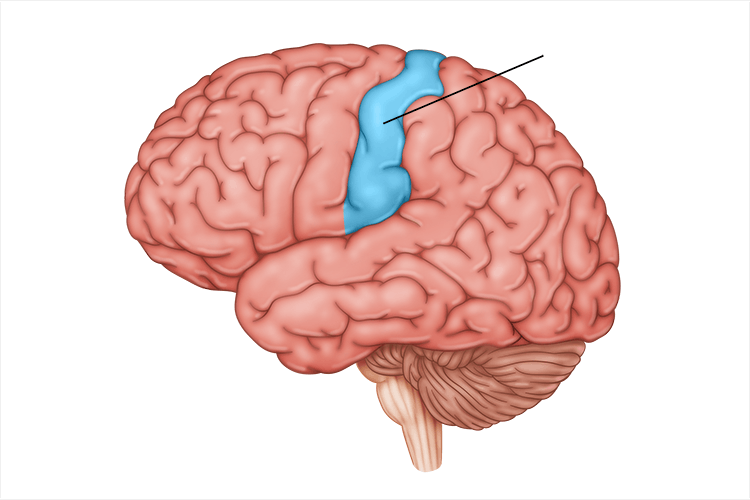
parietal lobe
receives sensory input for touch and body position
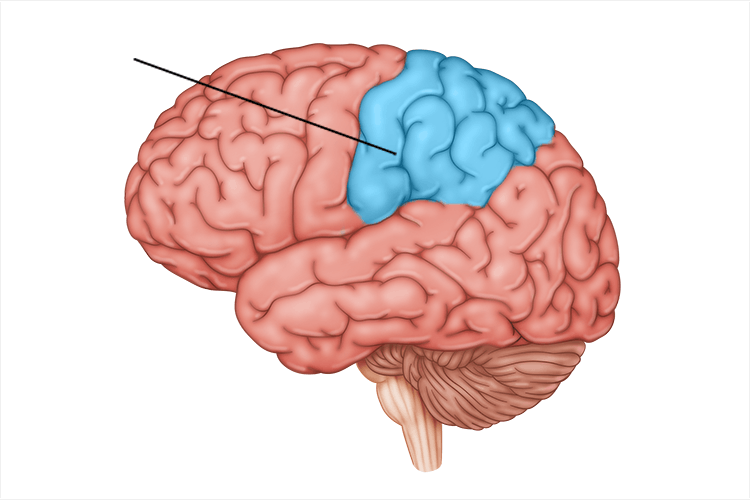
occipital lobe
receive info from visual fields
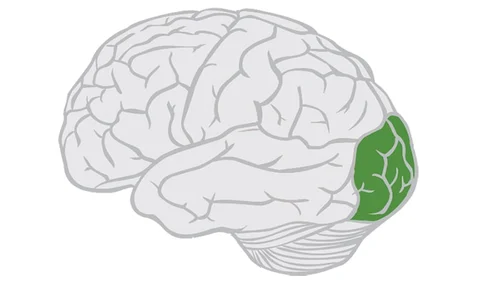
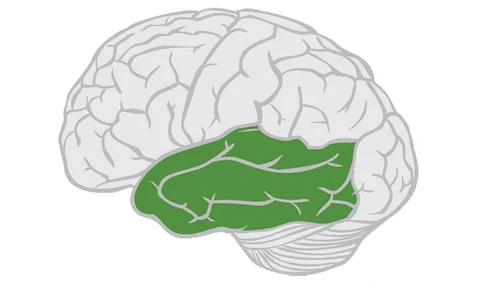
temporal lobe
includes auditory areas
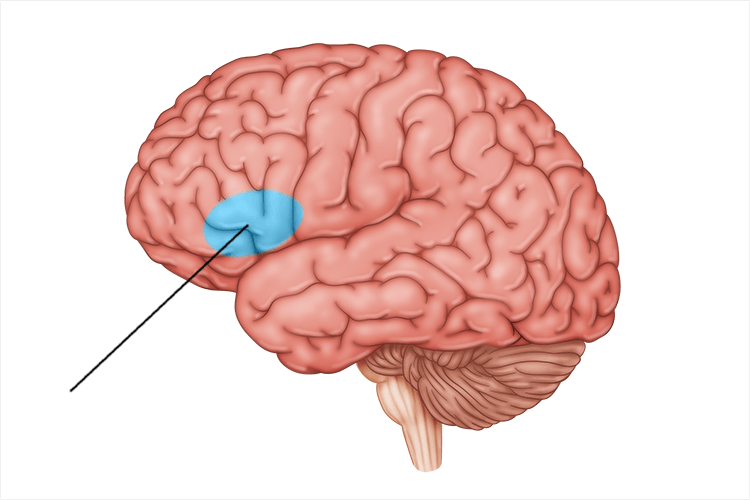
Broca’s Area
controls motor function and speech production; only in left hemisphere
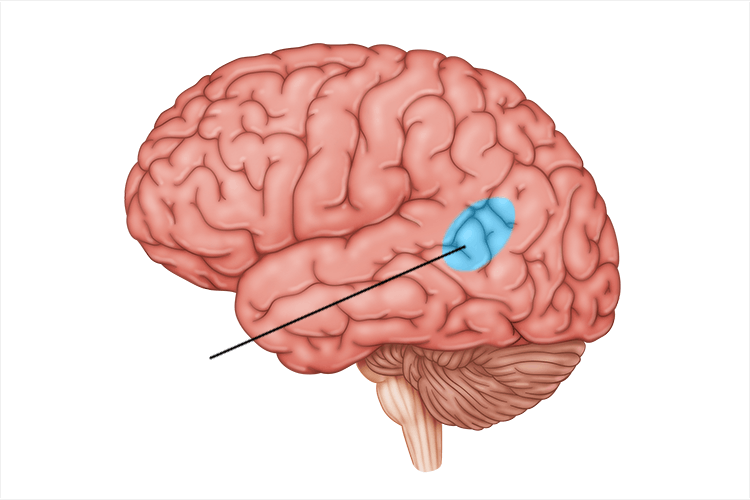
Wernicke’s Area
language comprehension; only in left hemisphere
plasticity
brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
dual processing
the principle that info is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
cerebrum
largest part of the brain consisting of two hemispheres that enable perceiving, thinking, and speaking (left hemisphere controls right side of body); evolutionarily newest part of brain