Tsunami
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:59 PM on 4/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
what are seismic sea wave?
* an abnormally long wavelength wave produced by sudden displacement of water
2
New cards
what is a near field tsunamis?
* tsunami that strikes areas adjacent to its point of origin
* there is little warning
* there is little warning
3
New cards
what is far field tsunami?
* tsunami that strikes areas distant from its point of original
* can impact multiple countries around
* can impact multiple countries around
4
New cards
what are masses that may cause tsunamis?
* the seafloor shifting up or down
* a submarine and/or subaerial landslide
* a pyroclastic flow
* an air blast form an explosive volcanic eruption
* a meteorite impact
* a submarine and/or subaerial landslide
* a pyroclastic flow
* an air blast form an explosive volcanic eruption
* a meteorite impact
5
New cards
are tsunamis large tsunamis?
* not tsunamis
6
New cards
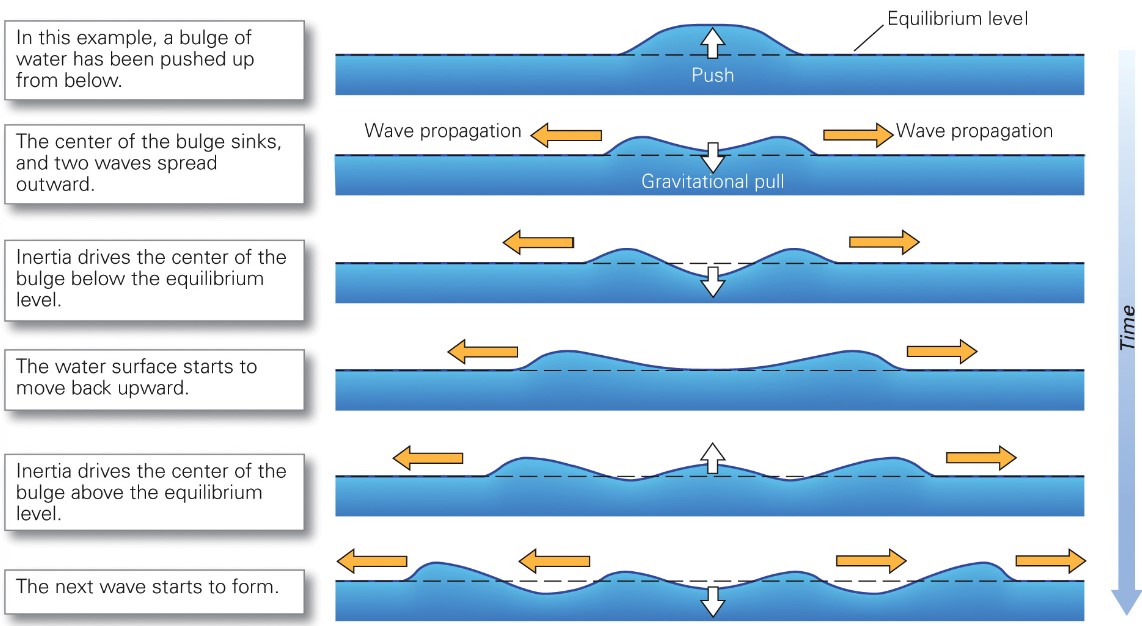
what are tsunami wave train?
* groups of waves
* consistent w/ earthquakes
* consistent w/ earthquakes
7
New cards
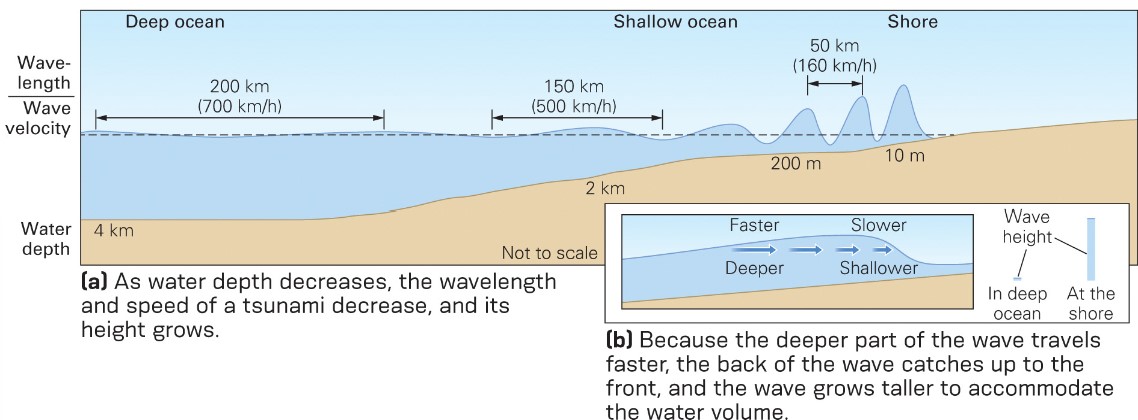
what are the tsunami wave characteristics?
* long wave lengths
* velocity dependent of water depth
* the wave is so big that there is frictional interaction w/ the ocean bottom
* wave slows down in shallower water → more friction
* wave increases its height as the water becomes shallower near the coast
* velocity dependent of water depth
* the wave is so big that there is frictional interaction w/ the ocean bottom
* wave slows down in shallower water → more friction
* wave increases its height as the water becomes shallower near the coast
8
New cards
wave height depends on?
* the distance between source and location
* the amount of water pushed by a mass
* the shape and velocity of the mass pushing the water
* the amount of water pushed by a mass
* the shape and velocity of the mass pushing the water
9
New cards
what creates waves refraction interference?
islands
10
New cards
are tsunami waves big or small while crossing open ocean?
* small
11
New cards
what creates towering waves as they approach shore?
shoaling
12
New cards
wave velocity across open oceans?
* around 700 km/hr
13
New cards
does wave velocity slow or speed up as they enter shallow water?
slow
14
New cards
how are big waves caused?
* water at rear of wave catches up to slower water, increasing height
* front slows down, back catches up → cause big wave
* front slows down, back catches up → cause big wave
15
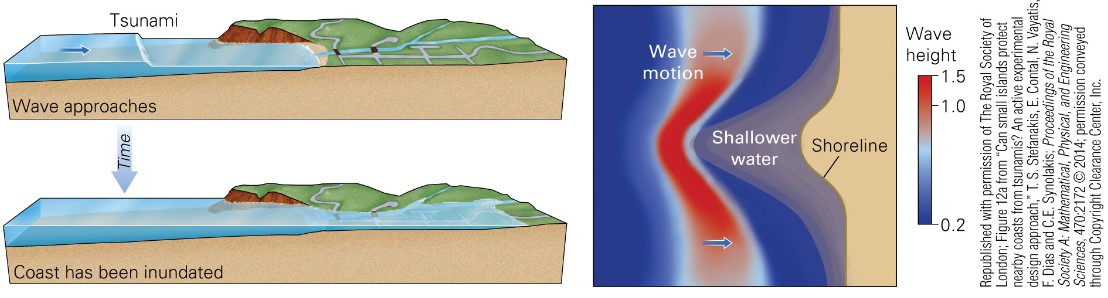
New cards
what can prevent water from flowing inland?
* steep cliffs
* water may flow many km into gently sloping coasts
* water may flow many km into gently sloping coasts
16
New cards
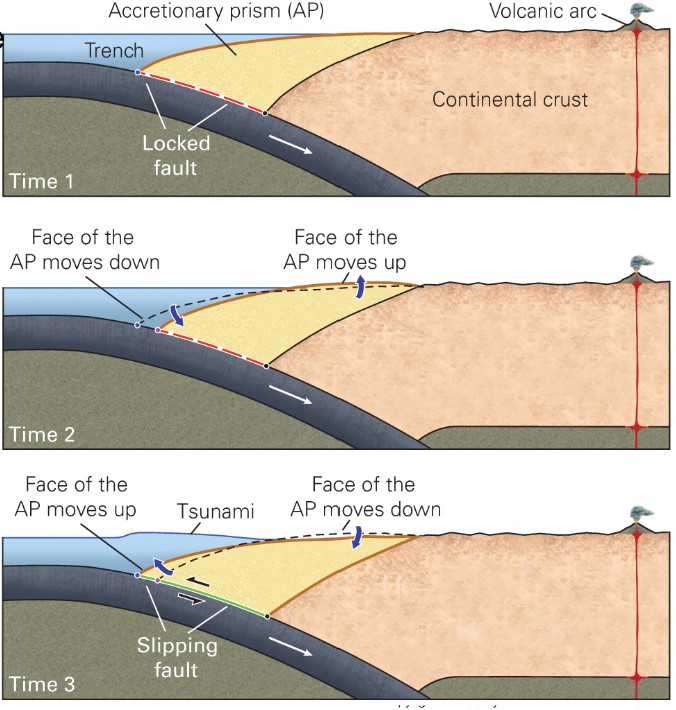
what occurs in a mega-thrust earthquake?
* Megathrust earthquakes have \n an M W > 8.6.
* at subduction zone
* Accretionary prism (AP) at \n convergent margin.
* Shortens horizontally
* Thickens vertically
* Land elevation slowly \n rises.
* Two motions occur to AP \n when slip occurs:
* Face quickly moves \n seaward.
* Land elevation quickly \n sinks.
* at subduction zone
* Accretionary prism (AP) at \n convergent margin.
* Shortens horizontally
* Thickens vertically
* Land elevation slowly \n rises.
* Two motions occur to AP \n when slip occurs:
* Face quickly moves \n seaward.
* Land elevation quickly \n sinks.
17
New cards
sumatra tsunami - Dec 26, 2004
* 9.1 magnitude subduction zone earthquake
* indian plate and burma plate
* paleoseismic studies show that giant seismic events occur every 230 yrs
* tsunami waves generated by this event rose 10 metres or more above sea lvl
* 230,000 deaths
* indian plate and burma plate
* paleoseismic studies show that giant seismic events occur every 230 yrs
* tsunami waves generated by this event rose 10 metres or more above sea lvl
* 230,000 deaths
18
New cards
Chile Tsunami - may 26, 1960
* caused by 9.5 magnitude earthquake in subduction zone along the coast of Chile
* 2000 people killed in Chile: 5700 people killed around the Pacific
* Hilo, Hawaii, 61 deaths
* Japan, 185 deaths
* left a sand layer over the soil in a farmer’s field
* alarm sys was placed after this
* 2000 people killed in Chile: 5700 people killed around the Pacific
* Hilo, Hawaii, 61 deaths
* Japan, 185 deaths
* left a sand layer over the soil in a farmer’s field
* alarm sys was placed after this

19
New cards
how can volcanoes generate tsunamis?
* caldera collapse
* submarine eruption
* debris cloud collapse may trigger tsunamis
* debris displaces sea surface when it falls
* flank collapse
* submarine eruption
* debris cloud collapse may trigger tsunamis
* debris displaces sea surface when it falls
* flank collapse
20
New cards
do volcanos generate big tsunamis?
* only small vol of water it moved
* generate (relatively) small tsunamis
* only impact local area
* generate (relatively) small tsunamis
* only impact local area
21
New cards
Krakatau Eruption - 1883
* in Sunda Strait
* tsunami killed 36,000 on Sumatra and Java
* pyroclastic flow may have displaced sea surface
* tsunami killed 36,000 on Sumatra and Java
* pyroclastic flow may have displaced sea surface
22
New cards
how frequent and severe are flank collapse?
*
23
New cards
what is example of flank collapse generated tsunami?
* Anak Krakatau 2018
* 400 deaths
* 7,000 injured
* 47,000 displaced from homes
* 400 deaths
* 7,000 injured
* 47,000 displaced from homes
24
New cards
what percentage of tsunamis are caused by fast-moving landslides or rock avalanches?
* around 1%
* These types of tsunamis are created by fast-moving landslides (sediment) or fast-moving rock avalanches (broken bedrock) falling into the ocean and displacing a large volume of water. \n • Size of tsunami waves based on the mass of the materia
* These types of tsunamis are created by fast-moving landslides (sediment) or fast-moving rock avalanches (broken bedrock) falling into the ocean and displacing a large volume of water. \n • Size of tsunami waves based on the mass of the materia
25
New cards
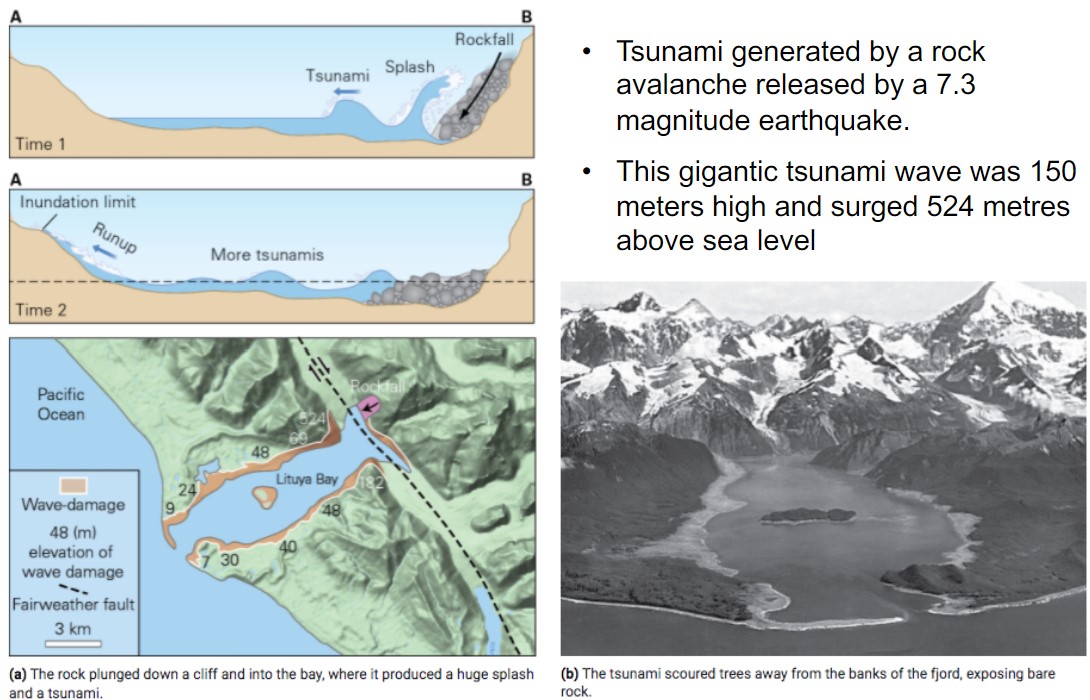
example of rock avalanche generated tsunami?
* Lituya Bay Alaska - July 9, 1958
* released a 7.3 magnitude earthquake
* wave was 150 meters high and surged metres above sea lvl
* released a 7.3 magnitude earthquake
* wave was 150 meters high and surged metres above sea lvl
26
New cards
what % of tsunami are from submarine landslide?
* around 5%
27
New cards
do submarine landslide generate big tsunamis?
* typically not as large as ones generated by landslide/rock avalanches from above sea lvl bc of the gentle slopes of the ocean floor
28
New cards
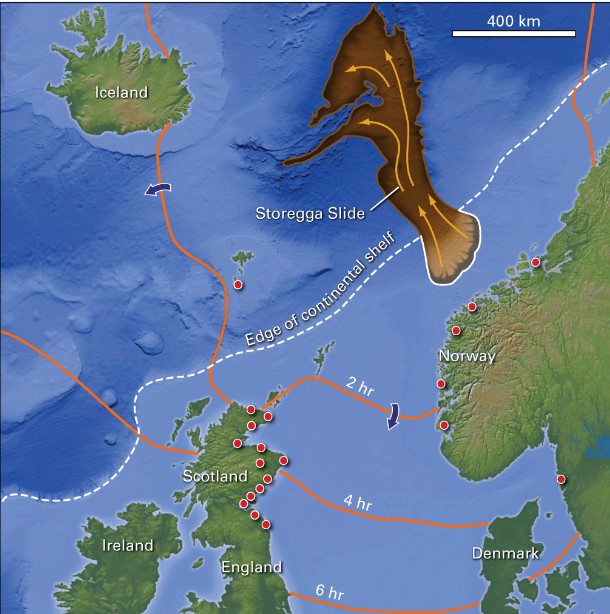
example of submarine landslide?
* Storegga slide
* tsunami laid sediment (TLS) found above sea lvl on the Shetland Islands, Norway and Scotland
* TLS consist of mud fragments ripped from the sea floor a\\layers of well-sorted sand
* we knew it happened cuz found an area of sand missing
* Papua New Guinea landslide
* an Mw 7.0 earthquake off northern coast of Papua New Guinea
* 15-m-high wave front devasted northern coastline; 2,000 people died, 1,000 injured, 10,000 displaced
* tsunami generated
* region is remote, isolated and lacks modern medical facilities
* infection and post traumatic stress created long impact
* tsunami laid sediment (TLS) found above sea lvl on the Shetland Islands, Norway and Scotland
* TLS consist of mud fragments ripped from the sea floor a\\layers of well-sorted sand
* we knew it happened cuz found an area of sand missing
* Papua New Guinea landslide
* an Mw 7.0 earthquake off northern coast of Papua New Guinea
* 15-m-high wave front devasted northern coastline; 2,000 people died, 1,000 injured, 10,000 displaced
* tsunami generated
* region is remote, isolated and lacks modern medical facilities
* infection and post traumatic stress created long impact
29
New cards
example of tsunamis from meteorite impact?
* 66 Ma, a 14-km-diameter asteroid struck the Yucatan Peninsula.
* Impact created the 150-km-diameter Chicxulub crater.
* Impact ended the Mesozoic Era and the Age of Dinosaurs.
* Mega-tsunamis were generated from the impact and falling debris.
* Impact created the 150-km-diameter Chicxulub crater.
* Impact ended the Mesozoic Era and the Age of Dinosaurs.
* Mega-tsunamis were generated from the impact and falling debris.
30
New cards
what can we do in trough arrives on shore first?
* we can tell that all the water runs away from shore providing some warming
31
New cards
how can offshore coral reef play role in tsunami?
* if coastal area surrounded by it, can provide some protection by forcing wave to break on reef
32
New cards
how does lack of warming impact region?
* difficult to disseminate info between and within countries
33
New cards
what is the time between waves?
* typic more than 30 mins
34
New cards
which waves are the worse?
* second or third waves often worse than first
35
New cards
rising water hazards
* boats carried inland as anchor and chains are lost
* larbors fill like bathtubs
* larbors fill like bathtubs
36
New cards
water moving onshore issue
* vehicles, trees, and debris and tumbled and crushed
* buildings are crushed or carried off foundations
* buildings are crushed or carried off foundations
37
New cards
drawback from tsunamis?
* debris and sediment are tumbled and crushed
* sand stripped from beach
* human and animal fatalities occur at all stages
* sand stripped from beach
* human and animal fatalities occur at all stages
38
New cards
tsunami aftermaths?
* tsunamis destroy power lines, roads, bridges, water and gas line; fires starters
* essential services cant reach victims
* debris rots and molds
* crops destroyed, salt deposition in soils
* contamination of water supplies
* disease due to water rotting things
* essential services cant reach victims
* debris rots and molds
* crops destroyed, salt deposition in soils
* contamination of water supplies
* disease due to water rotting things
39
New cards
relief and recovery?
* tsunami relief and recovery are challenging:
* roads are buried or damaged
* communication sys destroyed
* hovercraft may be the only to way to access communities
* ships often become floating hospitals
* roads are buried or damaged
* communication sys destroyed
* hovercraft may be the only to way to access communities
* ships often become floating hospitals
40
New cards
near-field tsunami warming system?
* arrival of tsunami less than 30 mins after tsunami trigger
41
New cards
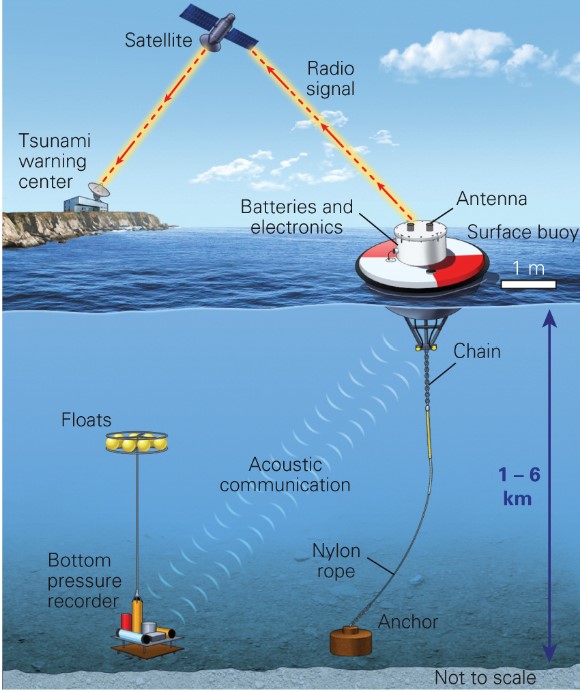
what are some far-field tsunami warming system?
* travel time of tsunamis in the Pacific Ocean can be accurately calc based on topography of the ocean floor
* tidal sensors and ocean-bottom sensors can detect waves as they move across the ocean
* downside: cannot forecast the actual height of a tsunami wave
* tidal sensors and ocean-bottom sensors can detect waves as they move across the ocean
* downside: cannot forecast the actual height of a tsunami wave
42
New cards
some adaptations to tsunami hazards?
* land-use zoning
* engineering structs to resist erosion
* orient streets and buildings at right angle to the waves
* well-rooted vegetation
* engineering structs to resist erosion
* orient streets and buildings at right angle to the waves
* well-rooted vegetation
43
New cards
tsunami hazards adaptations in Japans?
* seawall with stairway evacuation route used to protect a coastal town in Japan
* water gate used to protect Okushiri Island → they automatically close within secs after earthquake shaking triggers seismic sensor
* tsunamis stones in Japan warm not to build below certain elevations
* tsunami inundation map increase public awareness
* water gate used to protect Okushiri Island → they automatically close within secs after earthquake shaking triggers seismic sensor
* tsunamis stones in Japan warm not to build below certain elevations
* tsunami inundation map increase public awareness
44
New cards
tsunami from Cascadia Subduction-Zone earthquakes
* cascadia subduction zone located 1,900 km offshore southern british columbia
* sequences of tsunami-laid sediment (TLS) indicate historic tsunami impacts along the Pacific Northwest coastline
* Mud → contains the remains of marine plants
* tsunami → laid sand
* peat at the base → consists of partially decayed saltwater marsh plants
* sequences of tsunami-laid sediment (TLS) indicate historic tsunami impacts along the Pacific Northwest coastline
* Mud → contains the remains of marine plants
* tsunami → laid sand
* peat at the base → consists of partially decayed saltwater marsh plants
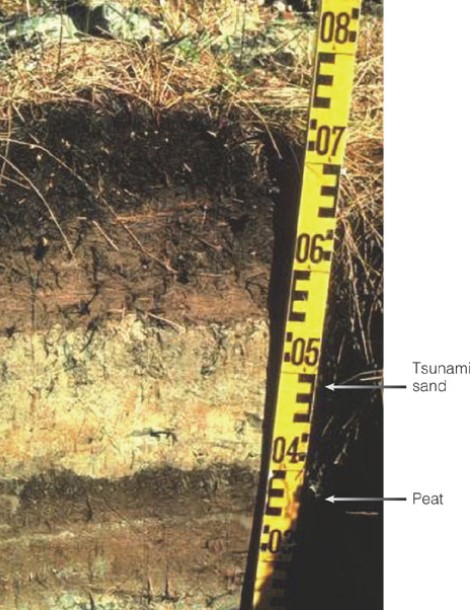

45
New cards
huge tsunami-flattened forest are now below sea level why?
* bc of displacement during an earthquake of the coastal bulge offshore
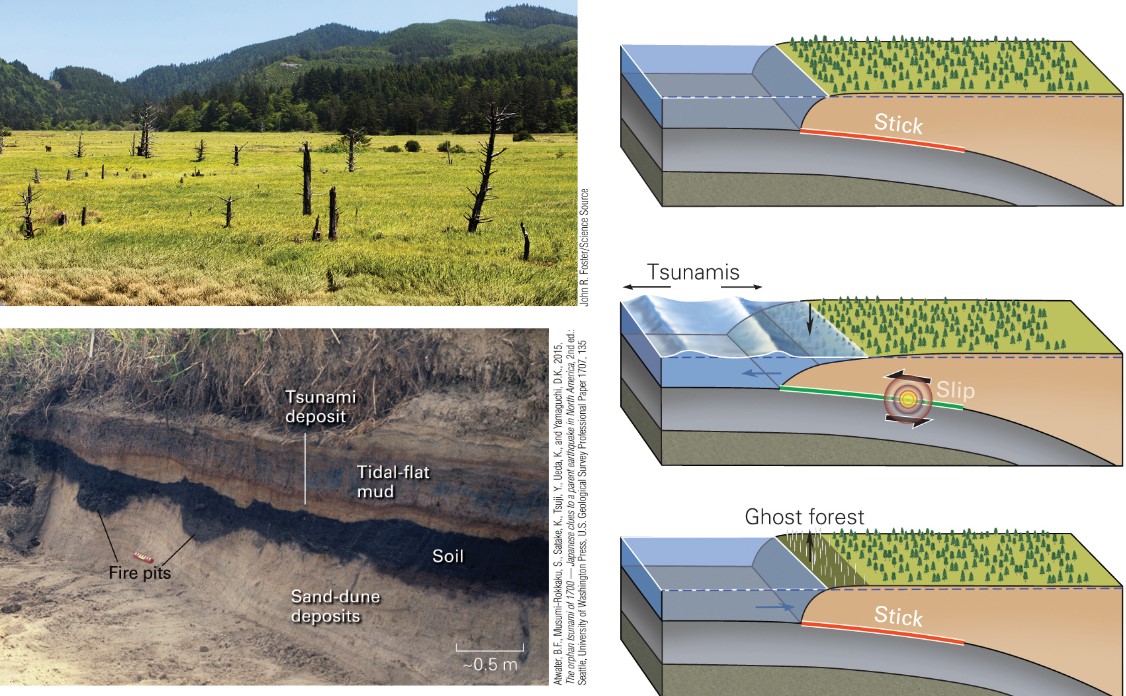
46
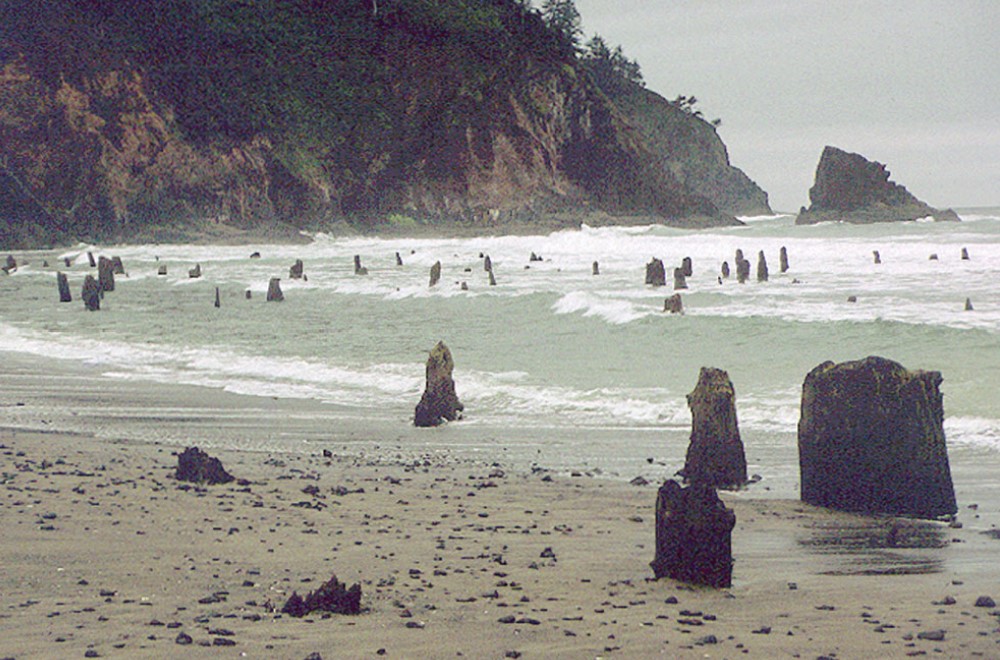
New cards
example of forest that got flattened?
* ancient Sitka spruce forest in the bay at Neskowin, Oregon, was felled by a giant tsunami following a large subduction-zone earthquake of 1700

47
New cards
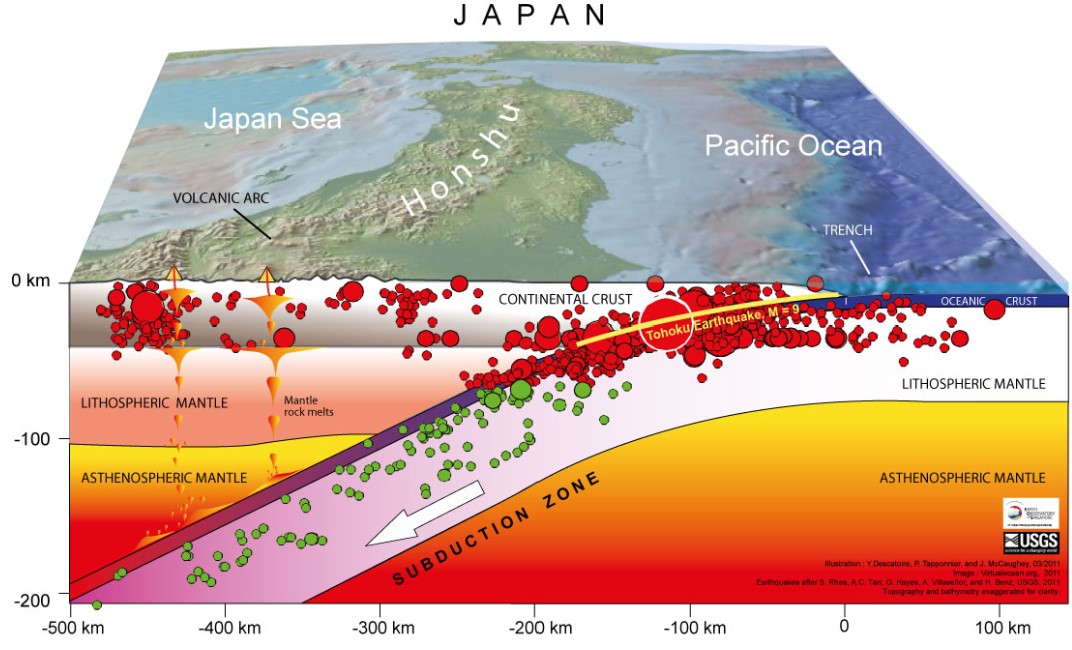
Japan earthquake
* March 11 2011
* Magnitude 9.0 earthquake
* subduction zone earthquake
* generated a tsunamis that swept across the pacific ocean
* Magnitude 9.0 earthquake
* subduction zone earthquake
* generated a tsunamis that swept across the pacific ocean