Y10 Science Exam SEMESTER 1
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
wasn't super rushed and last minute what are you talking abt
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
DNA
Is short for deoxyribonucleic acid, and is the basis of inheritance, which determines what traits are passed down, and is made up of nucleotides and found in the nucleus of all cells that have one. Is in the shape of a double-sided helix, and has two sugar-phosphate walls connected by nitrogen bases connected by hydrogen bonds
Function of Nucleus
To perform all regular functions done in order to keep a cell alive, such as cellular respiration
Base Pairing Rule
The rule which allows for cellular division, in which the nitrogen bases of adenine, thymine, guamine, and cytosine pair in a specific way, which code genes (in which adenine pairs with thymine, and guamine pairs with cytosine)
Nucleotide
The building block of DNA, which is made up of a phosphate, deoxybrose sugar, and a nitrogenous base
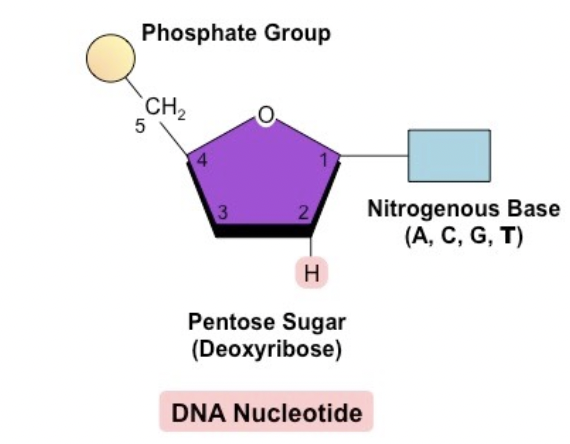
Chromosome
A large length of DNA tightly wrapped around proteins (histones), which contains many genes, and is found in the nucleus. Usually has 23 different versions in a human body. Extremely information dense in order to make being pulled apart for cell division easier. Different organisms have different amounts (frogs have 13)
Centromere
The constriction point of a chromosome in which the two sides connect in the middle, and is used in cell division to split the chromosome in half
The relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA
DNA is substance which includes information on how the body should work and be built. Chromosomes are made up of long strands of tightly wound DNA around histones, which are incredibly information dense and found in the nucleus. Genes are sections of DNA which code a specific thing, and make up chromosomes
Process of DNA replication
DNA molecule unwinds from chromosome
DNA molecule unzips (gets cut in half)
Two separate strands form
Each side of the DNA acts as a template for new strands using spare nucleotides in the cell
Each new side zips up (is put back together)
Identical copy of DNA is created
Mitosis
The process by which a cell splits it’s chromosomes in half to create double the amount of chromosomes, in order to create two daughter cells (would be diploid cells represented by 2n). Used for growing (e.g., from baby to adult), repairing (e.g., broken bones) and replacing (old/damaged cells)
Meiosis
The process by which a cell splits it’s chromosomes in half to create double the chromosomes, which are then split between 2 daughter cells, then into 4 daughter cells (meaning each has half the amount of chromosomes). These cells are known as gametes, represented as haploid/n, and are for sexual reproduction
Fertilisation
The process by which two gametes/haploid cells combine and from a diploid zygote, which contains genetic info passed down from both parents, half of the amount of total chromosomes from each parent
Homologous Chromosome
Two chromosomes inherited from each parent that have the same purpose (same genes coding same things), and are similar in height, length and centromere location, though having different alleles due to being inherited from different parents. Are paired together in a karyotype and placed in order of height, and are only not found between and X and Y chromosome
Why meiosis involves two divisions
The first division cuts the original cell in half, and creates two diploid cells
The second division cuts each diploid cell in half to create four haploid cells which are each half one diploid cell, allowing two different gametes to make one diploid
Diploid Cell
A cell which has two copies with each chromosome, one from each parent
Haploid Cell
A cell with half the amount of cells of a diploid cell, meaning it has one chromosome of each type
Allele
An alternate form of a gene, such as colour of eyes
Karyotype
A visual display of all of a person’s chromosomes, arranged from longest to shortest in their homologous pairs. Sex chromosomes are found at the end, generally with male karyotypes having XY chromosomes, and female having XX
Amounts of Chromosomes in other Animals
Goldfish - 25 types
Fruit fly - 4 types
Cat - 19 types
Inheritance
The process by which genetic information is passed down from parents to children
How Gregor Mendel contributed to Inheritance
Created three key principles of inheritance, being:
Inheritance is determines by genes passed onto offspring
Offspring inherit one gene for each trait
A trait may not show up in one offspring, but can still appear in the next generation (recessive genes)
Phenotype
The physical expression of genes on the body, and can be influenced by external factors. For example, being short (even if having tall genes due to poor nutrition)
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, which is made up of two alleles (e.g., Aa)
Homozygous
Refers to when the genotype for a trait is made up of two of the same alleles. Has two types, dominant (where the two alleles are dominant), and recessive (where two alleles are recessive). Also known as true-bed, e.g., AA, aa
Heterozygous
Refers to when the genotype for a trait is made up of two different alleles, and the dominant trait is shown (e.g., Aa). Also known as hybrid
Sex-Linked Inheritance
The passing down and inheritance of genes found on sex chromosomes. X-linked refers to traits on the X-chromsome, and vice versa for Y-linked
Why biological men are more likely to get X-Linked Traits than biological women
Due to biological men generally having one x-chromosome, meaning that they only need one copy of the trait, whether recessive or dominant, while biological women usually have two x-chromosomes, meaning dominate alleles can overpower recessive alleles
X-Linked Notation
The X chromosome will be shown as an X, with the allele in superscript (e.g., XA or Xa)
Scalar Quantity
A quantity which only measures magnitude/amount, like grams being the amount of mass, and metres being amount of distance
Vector Quantity
A quantity which measures both magnitude, and direction, like displacement being amount of distance and direction from starting point
V
Symbol for velocity/final velocity/speed (m/s)
S
Symbol for distance/displacement
T
Symbol for time (s)
U
Initial velocity (m/s)
A
Acceleration (m/s/s)
How to convert from m/s to km/h and vice versa
m/s → km/h is x3.6
km/h → m/s is divide by 3.6
Acceleration
Uses the symbol a, and is the rate of change of speed over time, using the unit ms-2 -(or m/s/s). Can be a negative if something slows down. Uses the formula a = (v-u)/t, where v=final velocity, u=initial velocity, and t=time
Displacement-time graph
A graph that shows the distance of someone/thing from an initial starting point. A flat area shows them standing still
Velocity-time graph
A graph that shows the velocity of an object over time. A flat point shows an object moving at a constant speed, and a point of 0 velocity means an object is stationery. If velocity goes below 0, an object is moving backwards
How to Interpret Displacement-Time Graph
Velocity: Using rise/run
Distance: Add up lengths of the line itself
Displacement: Final point displacement - First point displacement
Avg. Speed: Distance/time in between edges of distance (e.g if one edge is at 1 second, and another is at 5 seconds, then divide by 4)
Force
A push, pull, or twist, which causes an object to change in some way, and is measured in Newtons (N)
Can make it start/stop moving, speed up, slow down, change direction, or change shape
Newton’s First Law
An object which is in motion will remain moving until opposed, and an object at rest will stay at rest until moved. Can be seen in examples like a magician pulling a tablecloth, or a ball on a skateboard
Also known as the law of inertia
Newton’s Second Law
Force is equal to mass times acceleration, meaning that more accelerations is more force, and more mass requires more force to accelerate
Can be simplified as “F=ma”, where F=force, m=mass in kgs, and a=acceleration
Newton’s Third Law
For every action, there is an equal opposite reaction
Means that each force applied causes another force to react to it (referred to as applied forces and reaction forces)
Newton’s Third Law - Examples
When a tennis racquet hits a ball, the net of the racquet tries to spring the ball back
When anything with weight is on the ground, the ground pushes against it with a normal force
When a gun is shot, the acceleration of the bullet pushes the gun back
Formula for Force
F=ma, force = mass x acceleration
Weight
A force, which can be measured in Newtons. Is equal to an object’s mass multiplied by the acceleration of gravity, which on Earth is 9.8ms-2 uses the formula Fg = mg, where Fg=weight, m=mass, g = acceleration of gravity (9.8m/s/s on earth)
Inertia
The tendency of an object to not change their motion in any way (whether it be slowing down, speeding up, or changing direction)
Periodic Law
The law created by Dmitri Mendeleev, in which he states that by arranging elements in order of their atomic number, patterns in their properties are formed. Through this, he arranged the periodic table in groups and properties to show the patterns (like valence electrons, and outer shells)
Alkali metals + Properties
Most of Group 1. One of the most reactive groups, forming a cation, and has a charge of 1+ when stable. Are soft, low density, low in melting/boiling points, and become more reactive as you go down, as the more outer shells an atom has, the less attraction is has toward the valence electrons (as they are far away), allowing it to lose the electrons easier
Earth Alkaline Metals + Properties
All of Group 2. One of the second most reactive groups, forming cations with a charge of 2+. Are soft, low density, low in melting/boiling points, and become more reactive as you go down, as the more outer shells an atom has, the less attraction is has toward the valence electrons (as they are far away), allowing it to lose the electrons easier
Transition Metals
The elements between group 3 to 12, being able to form cations, and are fairly unreactive when compared to alkali metals and halogen, though can react. Are strong and hard, high density, and have high melting/boiling points
Halogens
The elements in the 17th group of the periodic table. Form anions with a charge of 1-. Are brittle when solid, have low melting/boiling points, and become less reactive as you go down the group, due to having less attraction to pull in electrons as there are more outer shells in the way
Noble Gases
The elements of Group 18 which are completely unreactive due to having a full valence shell.
Valence Electron Shell
Outermost electron shell, which either seeks to be removed (Cations), to be filled (anions), or nothing (noble gases)
Electron shell filling order
2, 8, 8, 2, which after Calcium, becomes 2, 8, 18
Group
The vertical columns which are number 1-18, and groups elements that have the same charge when gaining stability (e.g., potassium and sodium both get a charge of +1 as they are in the same column), and have similar properties
Period
The horizontal rows which are numbered from 1-7 which group elements with the same amount of outer shells. In the first row, there are only 2 elements, due to the first outer shell only being to contain two electrons
Charges of Groups 1, 2, 13, 15, 16, and 17 when an ion
Group 1: 1+
Group 2: 2+
Group 13: 3+
Group 15: 3-
Group 16: 2-
Group 17: 1-
Bond Naming Process
Ionic bonds always have the metals first, and then the non-metals second, with the neither showing how many there are (e.g., no difluoride, just fluoride). The name will have the metals, and then the non metals with the amount of the nonmetal + ide/ine/etc. (will be on valency chart). Metallic bonds can only be made of one element, so it is just that, and covalent bonds have the first as its element, and only having its number if there is more than one of it (e.g., dihydrogen monoxide in H2O)
Ionic Bonding
A form of bonding between two or more metal and non metal ions, in which the metals transfer their valence electrons to the non-metals, allowing both to become stable
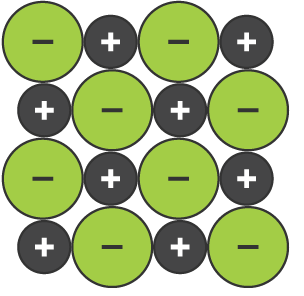
Ionic Bonding Lattice
The structure of ionic bonding, which is made up of alternating positive and negative ions that are equally spaced apart, and have a strong electrostatic attraction keeping them in place
Ionic Bonding Properties
Non-malleable due to movement the positive ions will put them closer other positive ions, and cause them to repel (same as with negative ions)
Non-conductive when solid as they are not moveable due to their strong electrostatic attraction
Conductive when liquid as they can move, and are charged particles
Have high melting/boiling points due to having strong electrostatic attractions (meaning much energy is required to break bonds)
Ion vs Neutral Atom
Neutral atoms do not have a charge, having the same amount of protons and neutrals, while ions have more or less electrons than protons
Covalent Bonding
A form of bonding between two or more non-metals share one or more electrons with each other to allow both to reach stability
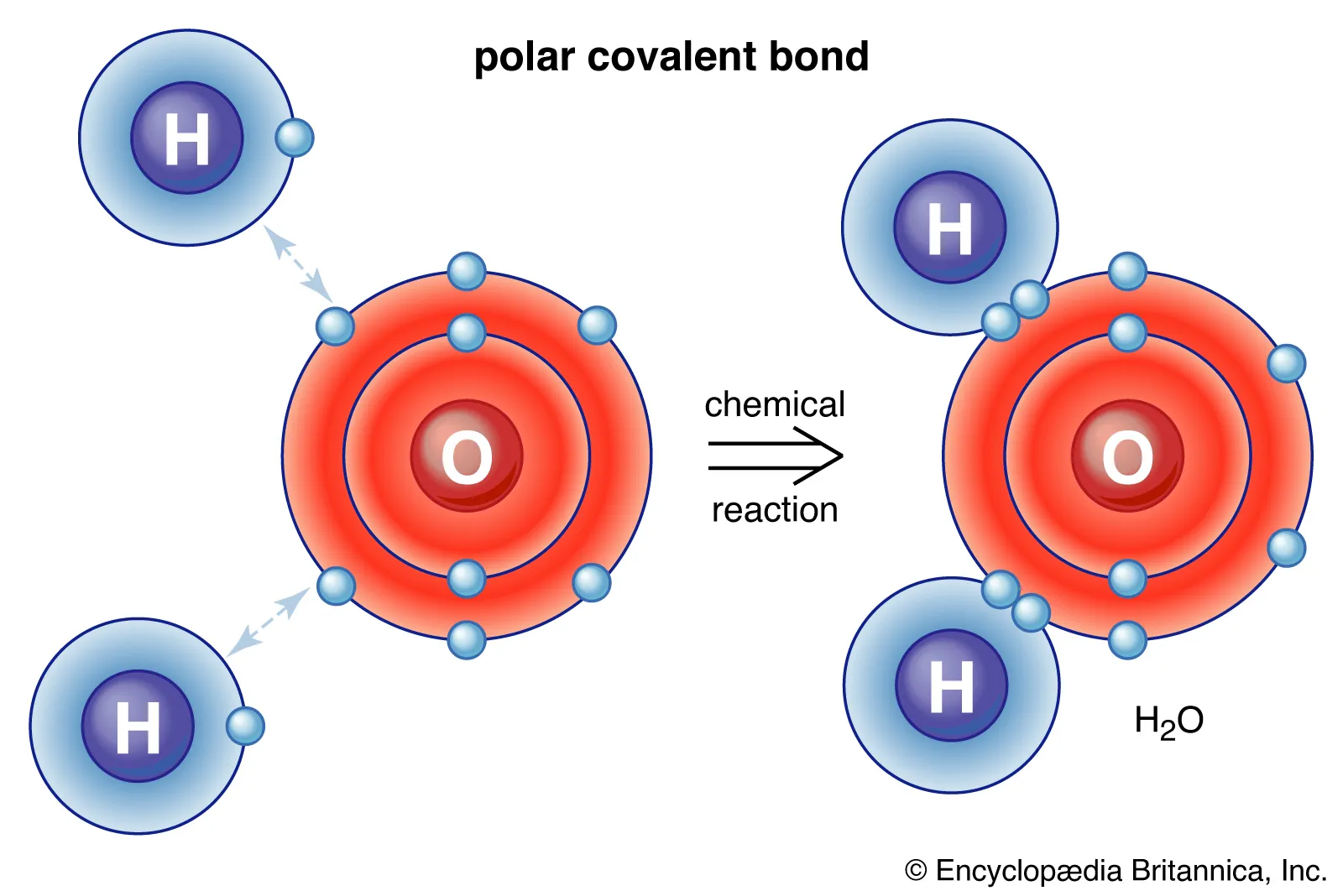
Covalent Bonding Properties
Malleable as there is only little attraction (Van Der Wall’s charges) holding multiple molecules together, only having attraction to keep one molecule intact
Non-conductive as the molecule has a neutral charge due to there being no transfer of electrons, only sharing
Low melting/boiling points for the same reason as why they are malleable (there being little attraction connecting each molecule)
Metallic Bonding
A form of bonding between two or more of the same metal, in which the metals remove their extra valence electrons and form a layer of positive metal ions, connected by a sea of delocalised electrons, giving it a high electrostatic attraction keeping it in place
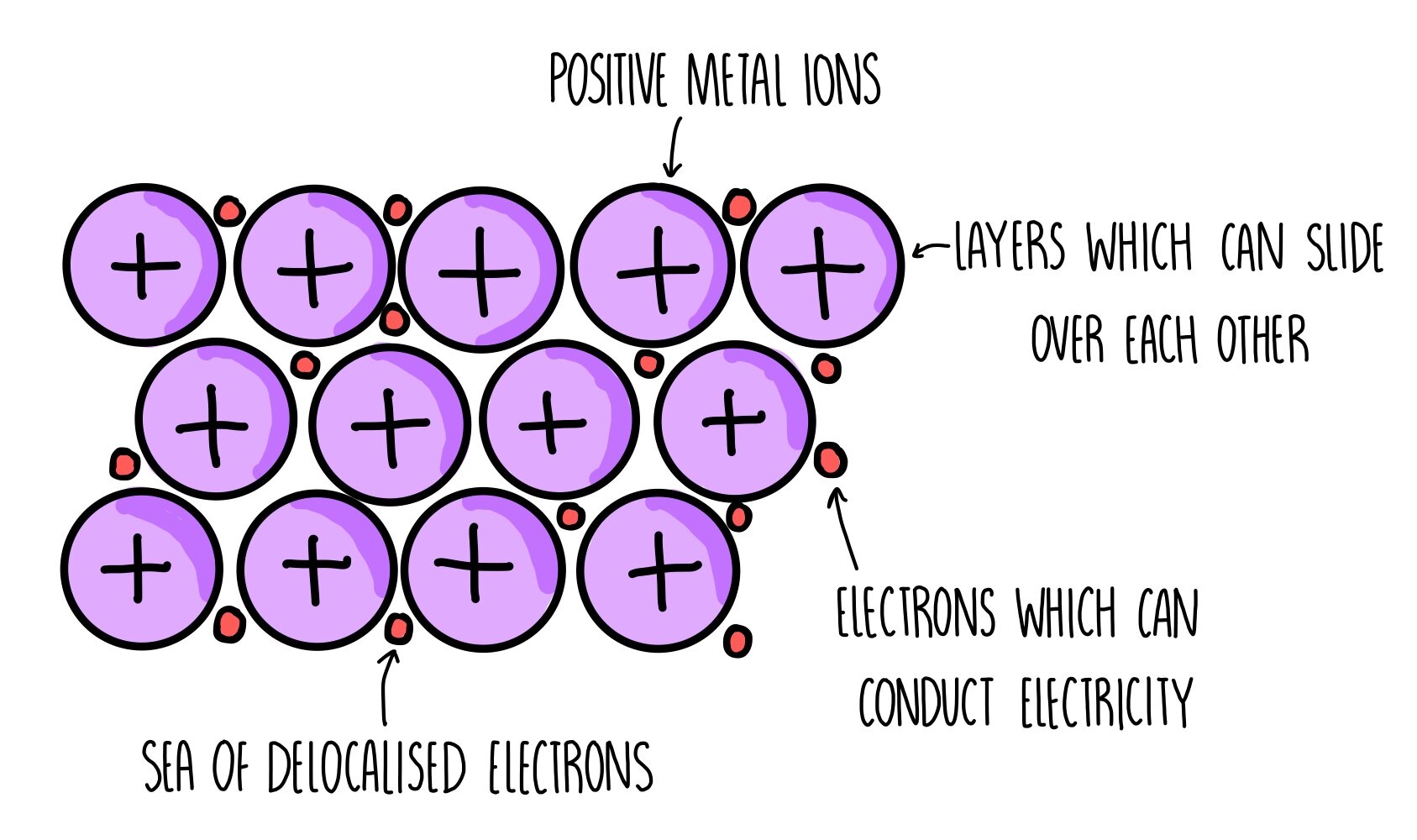
Metallic Bonding Properties
Malleable due to the sea of delocalised electrons still connecting metal ions when they move as the sea can move
Conductive due to the sea of delocalised electrons being able to carry charges
High melting and boiling points due to the strong attraction from the electrons keeping the positive metal ions together
Metalloids
The group of Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, Tallurium, and Polerium which share properties with metals and non-metals, such as being as able to be anions or cations