OCR GCSE paper 1 computer science
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What does the CPU do?
Processes data and instructions by constantly repeating the fetch-execute cycle
What are the parts of the CPU?
control unit, arithmetic logic unit, register
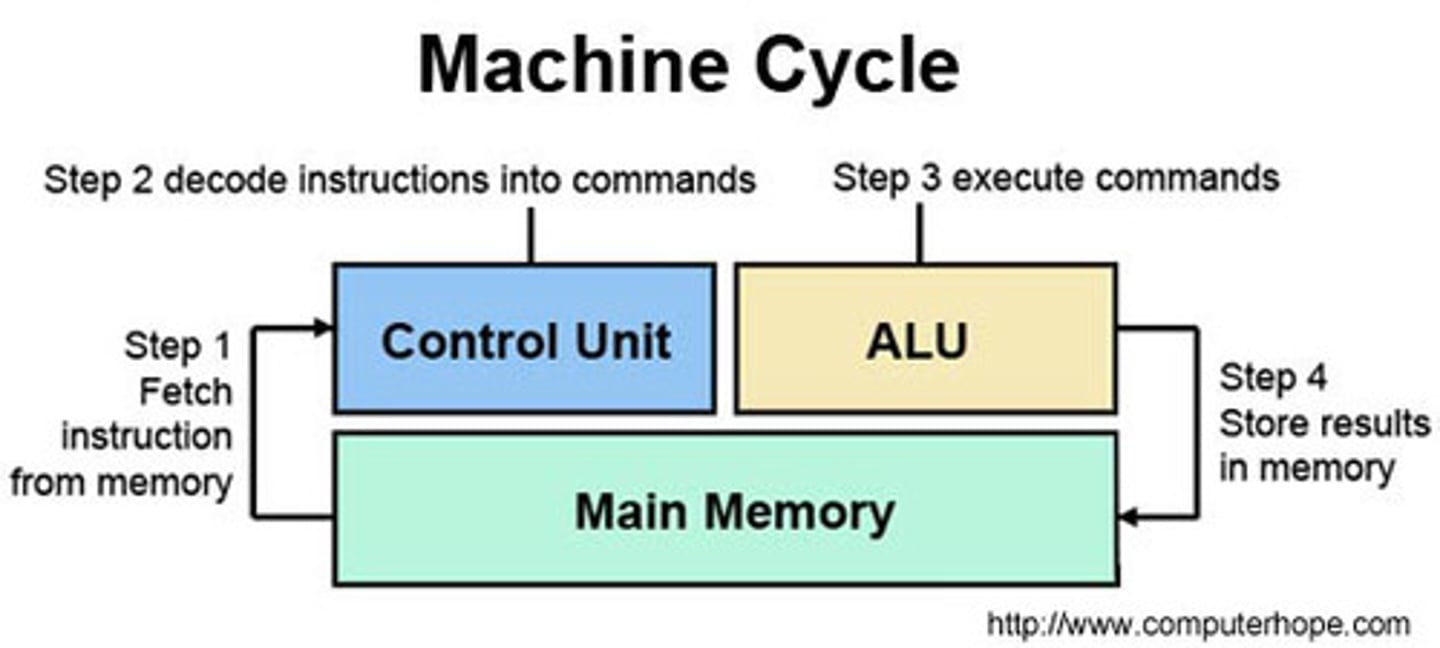
What does the control unit do (CU)?
sends controls signals to direct the operation of the CPU, Control signals and timing signals are sent to the ALU and other components i.e RAM
also decodes instructions as part of the F-E cycle
What does the ALU do?
performs simple calculations and logical operations
What is a register?
temporary storage space for one instruction or address, different registers are used in the F-E cycle
How does a computer with Von Neuman architecture work?
stores both program and instructions in the same memory(RAM)
What are the names of the 5 registers in the F-E cycle?
program counter, memory address register, memory data register, current instructions register, accumulator.
What does the PC do?
tracks the RAM address of the next instruction to be fetched
What does the MAR do?
Stores the address of the data to be fetched from or the address where the data is to be stored.
What does the MDR do?
The MDR stores the instruction that has been transferred from RAM to the CPU.
What does the CIR do?
stores the instruction that has been fetched from RAM, and is about to be decoded or executed.
What does the accumulator do?
The ACC stores the result of mathematical or logical calculations.
What is the main idea of the F-E cycle?
instructions are fetched from RAM to the CPU, to be decoded (understood) and executed (processed) by the CPU.
How does the F-E cycle work?
1. The Program Counter (PC) register displays the address in RAM of the next instruction to be processed.
This value is copied into the Memory Address Register (MAR).
2. The PC register is increased by 1. This prepares the CPU for the next instruction to be fetched
3. The CPU checks the address in RAM which matches the address held in the MAR.
4. The instruction in RAM is transferred to the Memory Data Register (MDR).
5.The instruction in the MDR is copied into the Current Instruction Register (CIR).
6. The instruction in the CIR is decoded (understood) and executed (processed).
Any result of an execution is stored in the Accumulator (ACC) register.
7. The cycle repeats by returning to the first step and checking the program counter for the address of the next instruction.
What is cache memory?
Temporary storage for frequently accessed data
How does cache memory improve storage?
because it is close to the CPU than the RAM, so it can provide data and instructions to the CPU at a faster rate.
disadvantage of cache memory
Costly so most computers have a small amount
What is clock speed?
Clock speed is the measure of how quickly a CPU can process instructions, measured in GHz
How does clock speed improve performance?
The faster the clock speed, the faster the computer can perform the FDE cycle resulting in better performance because more instructions can be processed each second.
What is a core?
a complete set of CPU components(CU, ALU & registers). Each core can perform is own FDE cycle.
How does the number of cores improve performance?
A computer with more cores will have a higher performance because it can process more instructions at once
disadvantages of having more cores?
if one core is waiting for another core to finish processing the performance may not increase at all
What is an embedded system?
a computer system built into a larger machine to provide of control. uses both hard and software, perform specific tasks, have often low storage and processing power.
What does an embedded system do?
perform a specific pre-programmed task which is stored in ROM
What is a network?
A network is two or more computers linked together so that they can communicate with each other
What is a LAN?
Local Area Network- computer system are geographically close together (i.e. same building).
The network infrastructure of a LAN (i.e. servers & routers) is usually owned and managed by the network owner.
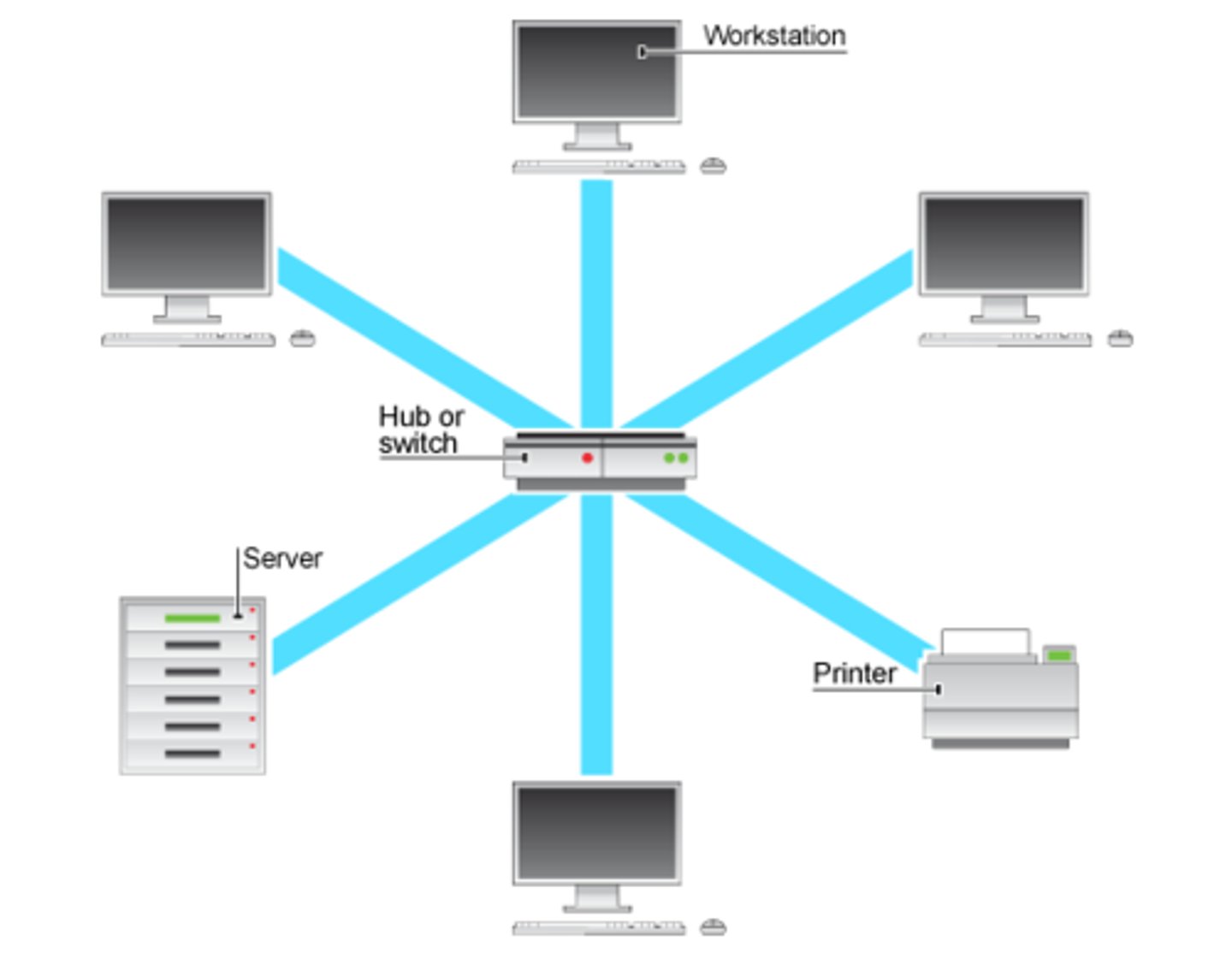
What is a WAN?
Wide Area Network- computer systems are geographically distant to each other. use 3rd part communication channels
Advantages of a LAN
It enables: digital communication between people,
the sharing of digital information,
the sharing of peripheral devices such as printers and scanners,
computers to be updated with the latest software from a central point,
distributed processing - the ability for a single program to be run simultaneously at various computers.
Disadvantages of LAN
requires a bit of 'expertise' to install and maintain a large network which can be costly.
Viruses may be able to infiltrate the network and infect every computer
There are a number of security issues from unauthorised access to data
What is the internet?
The internet is a worldwide collection of inter-connected networks, not owned or managed by any one group of people.
Anyone can access the internet.
What is an IP address?
Internet Protocol- Every networked computer or device has a separate, unique IP address
e.g. 65.123.217.14
The current addressing system is called IPv4

How does the Domain Name System (DNS) work?
1) a webpage request is sent to a Domain Name System server on the internet.
2)The DNS looks up the domain name in a database to find the IP address of the website which will then allow your browser to request the data/files in order to load the page.
3)If the DNS doesn't find the domain name, it forwards the request onto another DNS connected to the internet in order to try to locate the page.
What is a client-server network?
clients make requests to a server and it completely dependent on it to provide and manage the info
What are the advantages and disadvantages of client servers?
Can be controlled centrally,
easy to back up data and update software, hardware and software can be shared across the network
Traffic congestion will slow the network down,
If there is a fault the whole network will fail,
I t technicians may be required to manage and maintain the network
What is a peer-to-peer network?
where data is shared directly between systems without requiring a central server. it is optimal for sharing files.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of peer-to peer?
Simpler to set up as no server required,
Clients are not dependent on a server,
Can share files quickly between systems,
No central device so backups must be performed on each individual system,
Performance will decrease with more devices connected
What is a data packet?
when data is broken into smaller parts when data is sent across a network. Each packet is redirected by routers until it arrives at its destinations, they could split up and choose alterative routes.
What is the contents of a data packet?
Header- Source & address, destination, packet number, protocol
Payload- The data
Trailer- checks for any errors
What is a network topology?
The layout of a computer system on a local network
What is a star topology?
Each computer system is connected to a central device (i.e. switch) and transfers data packets there. The switch looks at the destination address and transfers the data packets directly to the intended computer
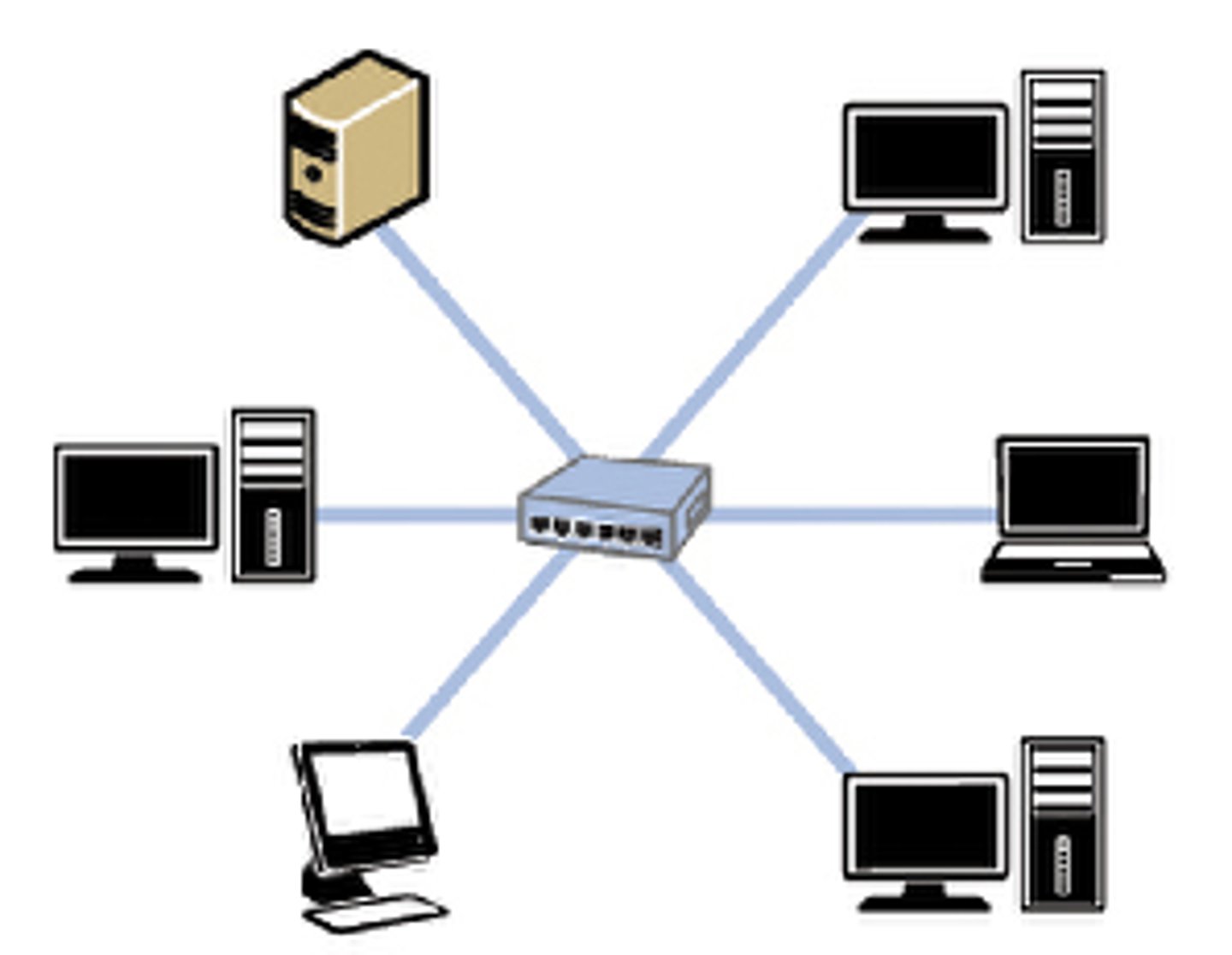
What are the advantages and disadvantages of star topology?
improved security- as data packets are sent directly to + from the switch
transfer speeds are fast
extra hardware is required
if the central system fails (switch) who networks is unstable until fixed
What is a mesh topology?
each computer system is connected to every other computer system.
Data packets are transferred to the destination address along the quickest path, travelling from node to node.
If a pathway is broken, there are many alternative paths that the packets can take.
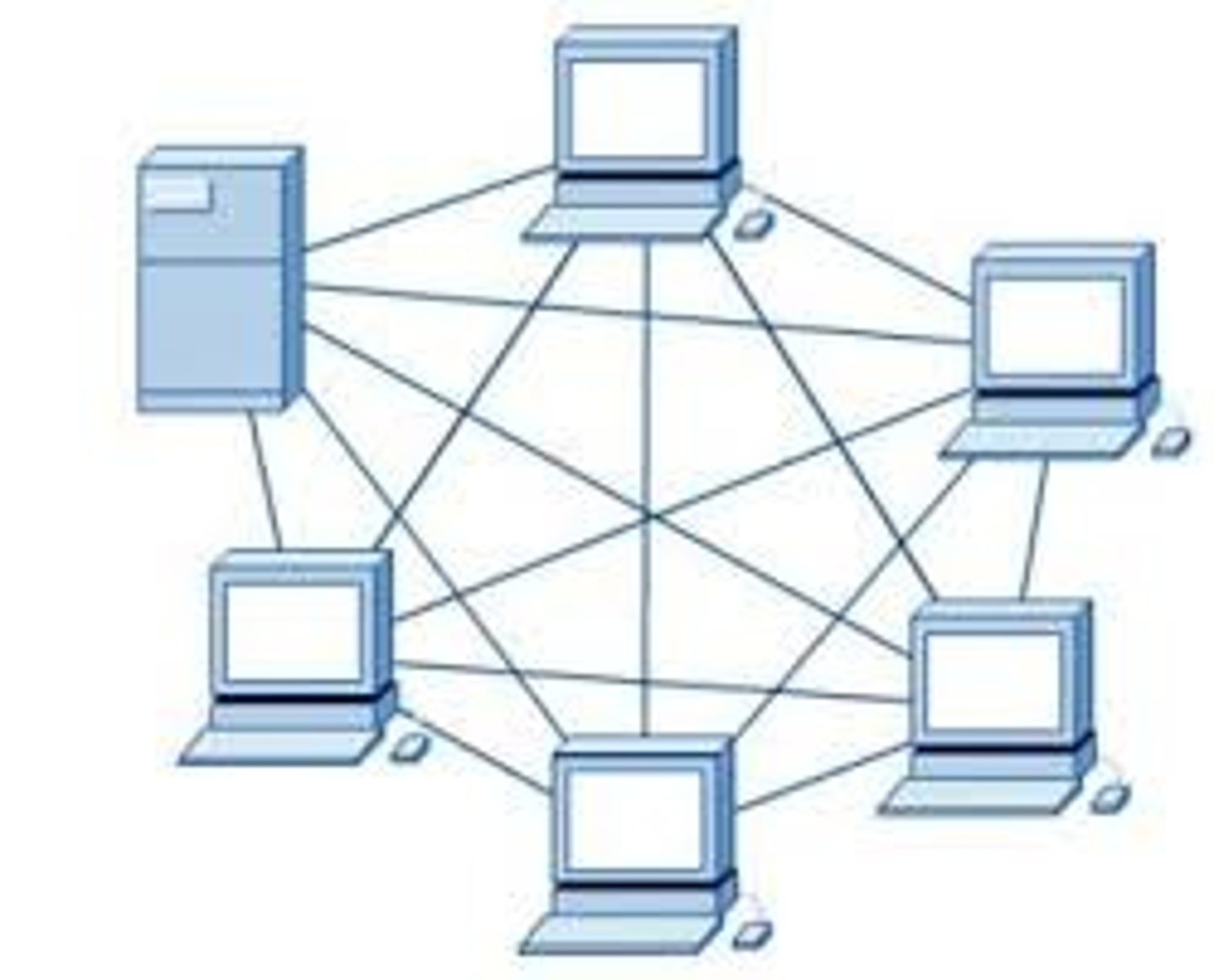
What are the advantages and disadvantages of mesh topology?
:) If one cable or system fails then data packets can take an alternative route,
withstand large amounts of data traffic-as there are many connections,
New systems can be added to the network without disrupting the entire topology.
:( expensive to install and maintain- large amount of cables
What are the factors that can affect the performance (speed) of a network?
The bandwidth available*
Interference (e.g. thick walls)
Applications being used
Number of users at the same time
Distance to travel / signal strength
Server / CPU Performance
Number of data collisions
Amount of data to transfer
What is a wireless access point (WAP)?
provides a link between wireless and wired network, it creates a wireless local area network which allows Wi-Fi enables devices to connect

What do routers do?
they transfer/ receive data packets between networks, and use the IP address to find the best route

What does a switch do?
Connects devices together,
receives data packets, reads the destination address and forward it directly to its destination, generates a list MAC addresses of devices connected to it
What is a network interface controller (NIC)?
An internal piece of hardware that allows a device to connect to a network, it also includes a MAC address used when sending data across a LAN
what are the 3 types of transmission media?
Ethernet cable, fibre optic cable, copper cables
How is an ethernet cable used?
typically used on LAN to transfer data between nodes and hardware i.e. switches.

How is a fibre optic cable used?
used to send data quickly along a WAN, v fast but more expensive and fragile

What is a copper cable?
old and slow affected by EM interference

What is cloud storage?
a network of servers accessed on the internet- they run applications store data, remote processing
data is stored on large servers owned by a hosting company

Adv and disadv cloud storage?
very convenient, can be accessed from different devices, huge capacity, portable
if connection fails/server attacked data could become inaccessible
What do wired connections require?
require physical cable(e.g. copper or fibre optic) & an NIC to connect to a network
What do wireless connections require?
require a wireless NIC (WNIC) as they use no cables, slower and can be affected by distance and obstacles (e.g. walls, weather)
What is a protocol?
A protocol is a set of rules that allow devices on a network to communicate with each other.
defines rules for data transmission
What is TCP (transmission control protocol)
TCP is a protocol that allows packets to be sent and received between computer systems.
It breaks the data into packets and reassembles them back into the original data at the destination.
What is an IP (internet protocol)?
IP is a protocol in charge of routing and addressing data packets. This ensures data packets are sent across networks to the correct destination.
It is also an addressing system - every device on a network is given a unique IP address so data packets can be sent to the correct computer system.
What is HTTP (hyper text transfer protocol)?
used to transfer web pages over the Internet so that users can view them in a web browser.
What is HTTPS (hyper text transfer protocol secure)?
HTTPS is a more secure version of HTTP that works with another protocol called SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to transfer encrypted data.
What is FTP (File Transfer Protocol)?
FTP is used to transfer files across a network. It is commonly used to upload or download files to/from a web server.
What is SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)?
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a protocol used to send emails to a mail server and between mail servers
What is POP (Post Office Protocol)?
POP and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) are both protocols for receiving and storing emails from a mail server.
POP will delete an email from the email server once it has been downloaded to a device.
IMAP syncs the message with an email server so it can be accessed by different devices.
What is IPv4?
IPv4 is a 32-bit address, represented in denary, that allows for over 4 billion unique addresses.
It has four 8-bit segments of denary values (from 0 to 255) separated by full stops.
EG:
145.13.218.102
What is IPv6?
IPv6 is a 128-bit address, represented in hexadecimal, that allows for an undecillion unique addresses.
It has eight 16-bit segments of four hexadecimal values (0000 - FFFF), separated by colons.
EG:
736E:1029:A4B3:902D:77B2:72FF:AE62:0912
What is a MAC address?
a unique hexadecimal number assigned to each network interface card/controller inside a networked device such as a router or laptop.
A MAC address is a 48-bit address made up of six 8-bit pairs in hexadecimal, separated by dashes.
While an IP address may change, the MAC address can't be changed. MAC stands for Media Access Control.
what is one advantage of using a layer to construct network protocols?
it is self contained, layer can be taken out and added without effecting other layers
What is malware?
Malware is any type of harmful program that seeks to damage or gain unauthorised access to your computer system.
What is a virus?
A virus can replicate itself and spread from system to system by attaching itself to infected files.
deletes/corrupts data
What is a worm?
-A worm can replicate itself and spread from system to system by finding weaknesses in software.
-uses up all the bandwidth
What is a trojan?
A trojan is malware disguised as legitimate software so users are tricked into installing it.
A trojan secretly gives the attacker backdoor access to the system.
Trojans do not self replicate or infect other files
What is spyware?
Spyware secretly records the activities of a user on a computer.
The main aim of spyware is to record usernames, passwords and credit card information.
All recorded information is secretly passed back to the attacker to use.
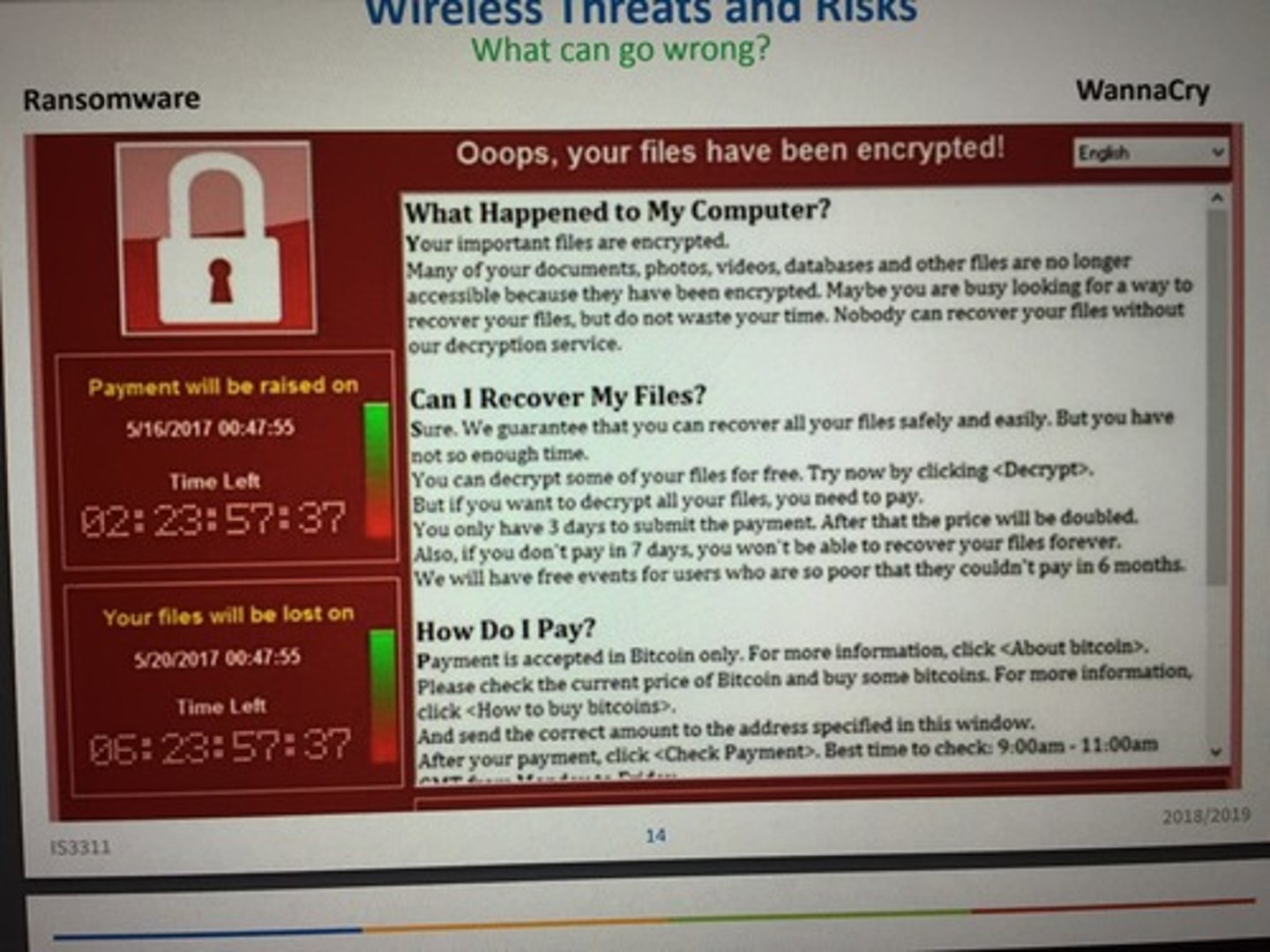
What is a ransomware?
Ransomware locks files on a computer system using encryption so that a user can no longer access them.
The attacker demands money from the victim to decrypt (unlock) the data.
Attackers usually use digital currencies like bitcoin which makes it hard to trace them.
What is a SQL injection?
A SQL injection is when a malicious SQL query (command) is entered into a data input box on a website.
If the website is insecure then the SQL query can trick the website into giving unauthorised access to the website's database.
An SQL injection can be used to view and edit the contents of a database or even gain administrator privileges.
What is a Dos attack?
attack is when a computer repeatedly sends requests to a server to overload the system. A server overload will slow the system and may take websites offline temporarily.
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack is a coordinated attack using a botnet of infected systems to overload a server with requests. A botnet is a large group of devices controlled and used maliciously by an attacker.
What is brute force attack?
Every possible combination is tested in order from start to finish. This is not a quick method but it should break the password eventually and can be sped up if multiple computer systems are used at the same time

What is phishing?
-fake emails sent to a person
-person enter personal data
what is pharming?
software that redirects user to fake website
person enters personal data
What is a penetration test?
Penetration tests are carried out as part of ethical hacking.
The purpose of a penetration test is to review the system's security to find any risks or weaknesses and to fix them.
What is a firewall?
A firewall manages incoming and outgoing network traffic
Each data packet is processed to check whether it should be given access to the network by examining the source and destination address.
Unexpected data packets will be filtered out and not accepted to the network.
What are other tasks of a firewall?
-Blocking access to insecure / malicious web sites.
-Blocking certain programs from accessing the internet.
-Blocking unexpected / unauthorised downloads.
-Preventing specific users on a network accessing certain files.
what are uses of secure passwords?
-Usernames must be matched with a secure password to minimise the chances of unauthorised users accessing a system.
-at least 8 characters
-must be regularly changed
What are user access levels?
-used to only allow certain users to access and edit particular files
-Eg: read-only and read write.
What is encryption
-process where data is scrambled
-data cannot be intercepted
What is physical security?
eg: locks. biometrics, CCTV, keycards
What is an OS?
An operating system (OS) is software that helps to manage the resources of a computer system and provide the interface between the user and the computer's hardware.
What are the 5 main tasks of the OS?
Memory management & multitasking, peripherals management & drivers, user management, file management, user interface(GUI)
How does the OS carry out memory management and multi tasking?
Because programs must be temporarily stored in RAM for the CPU to be able to process them.
The OS transfers programs in and out of memory from the hard drive (or virtual memory) when processing is required - programs are removed from RAM when closed to free up space for other tasks.
The operating system can only perform one process at a time, but through memory management it can appear that more than one process is being executed - this is called multitasking.
What is a peripheral?
an external device connected to a computer system to input or output data.
How does the OS carry out peripheral management & drivers
Data is transferred between external devices and the processor and this process needs to be managed by the operating system.
A device driver is a program that provides an interface for the OS to interact and communicate with an external device. Drivers are hardware dependent and OS-specific. The driver translates the OS' instructions into a format the specific hardware can understand.
Because the CPU and the peripheral will process data at different speeds, a buffer is typically used to temporarily store data until it can be processed.
How does the OS carry out user management?
The OS allows users to create, manage and delete individual accounts. User accounts can be granted different access rights such as an administrator or guest.
The OS will manage security settings such as allowing passwords to be reset and can also be used to monitor login activity.
How does the OS carry out file management?
The operating system creates and maintains a logical management system to organise files and directories (folders).
File management allows files to be named, renamed, opened, copied, moved, saved, searched for, sorted and deleted. It also allows users to set access rights for specific files and to view file properties.
How does the OS carry out user interface (GUI)
allowing a human/user to interact with the computer system. The way in which a user can navigate a computer system is known as human-computer interaction
How does the graphical user interface provide a user interface?
(GUI):
Icons are displayed to represent shortcuts to applications and files.
Multiple windows can be opened at the same time and switched between.
A folder and file system is displayed and manipulated allowing for copying, searching, sorting and deleting data.
The interface can be customised, such as changing font sizes and the desktop background.
The taskbar allows shortcuts to be pinned for quick access.
Menus can be opened from the Start button to display files and shortcuts.
System settings can be accessed such as network and hardware options.
Advantages primary storage?
very quick- directly accessed by CPU
Typically smaller in storage size.
Sometimes called 'main memory'.
Includes RAM and ROM.
What the characteristics of secondary storage?
Slower because it is not directly accessed by the CPU.
Typically larger in storage size.
Used for the long-term storage of data and files because it is non-volatile.
Includes magnetic, optical and solid state storage.
What is volatile memory?
Volatile storage is temporary - data is lost whenever the power is turned off.
EG: RAM
What is non-volatile storage?
Non-volatile storage saves the data even when not being powered. Data can be stored long-term and accessed when the computer is switched on. EG: ROM
Why do Computers need Primary Storage?
Primary storage is low-capacity, internal storage that can be directly accessed by the CPU.
Program instructions and data must be copied from the hard drive into RAM to be processed by the CPU because primary storage access speeds are much faster than secondary storage devices like the hard drive.