Muscle Anatomy and Physiology
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parts of a muscle cell, how muscles contract/relax and all cellular level mechanisms needed to make that happen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle?
produce movement
maintain posture
main body temperature
What is the the dense layer of connective tissue that surrounds an entire skeletal muscle called?
Epimysium
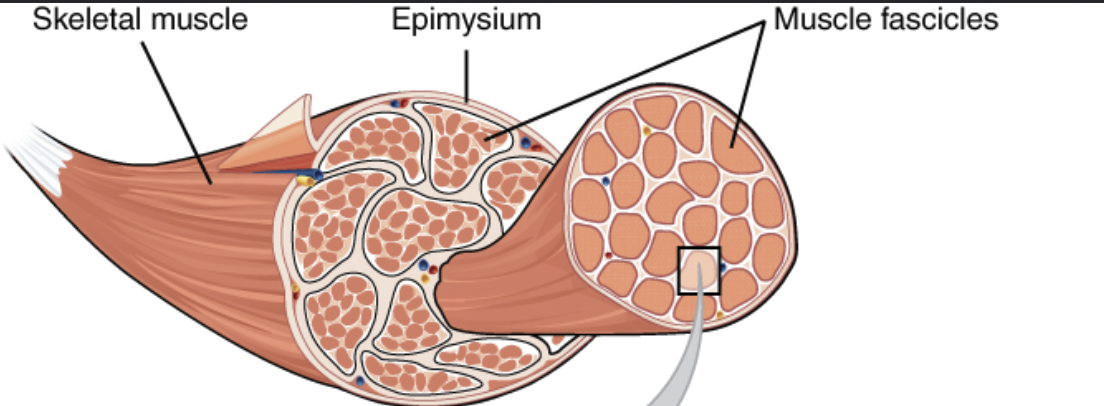
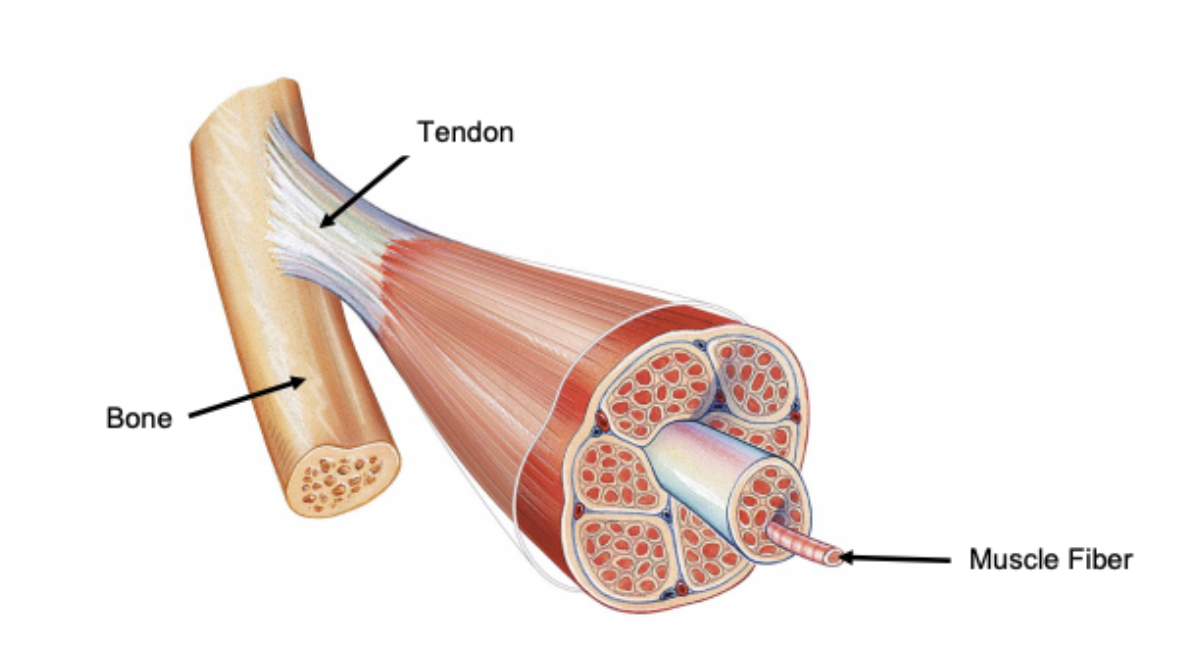
What is the name of the structure that is considered an extension of the epimysium which connects muscle to bone?
Tendon
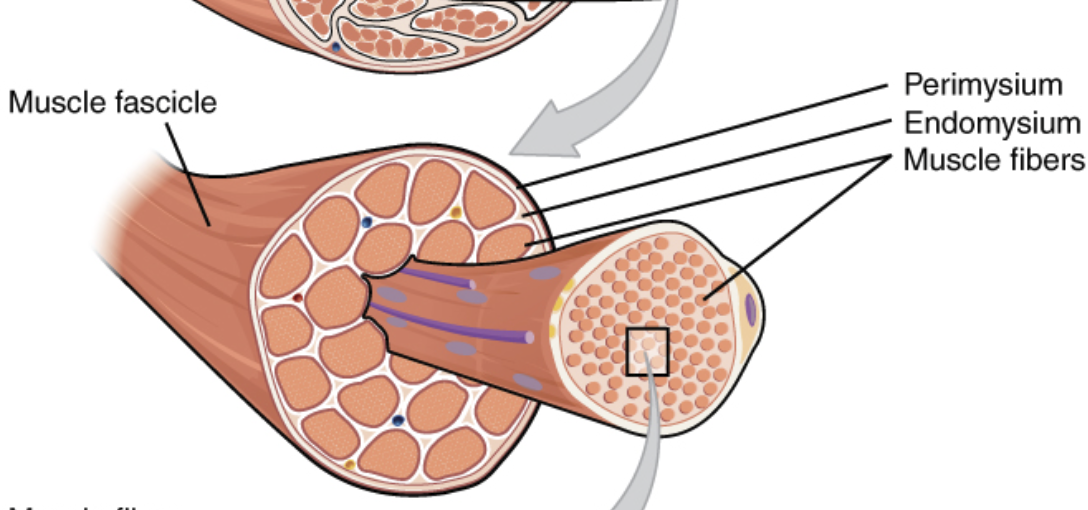
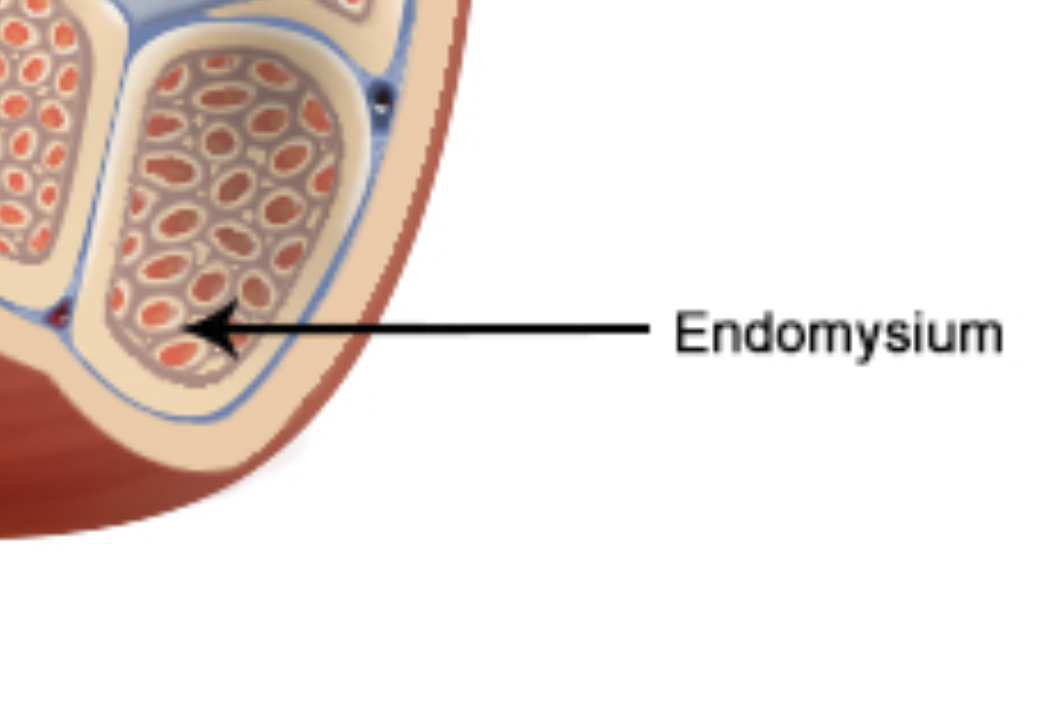
Which of the following is the name for the structure that surrounds an individual muscle fiber?
Endomysium
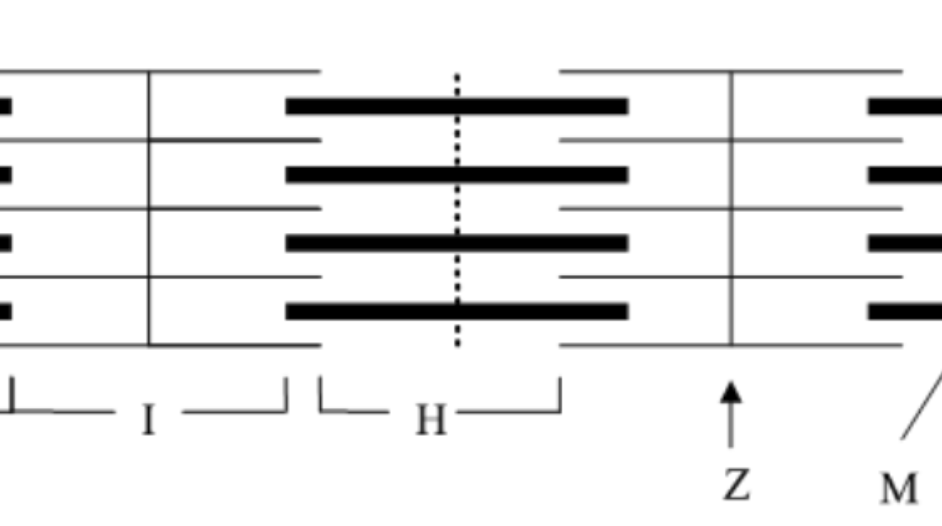
Which of the following best describes the term sarcomere?
thousands of contracting units found in each myofibril
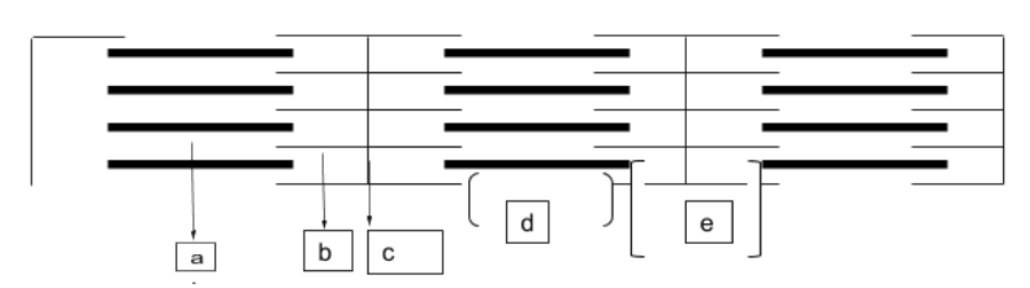
Match everything up
H zone: D
Myosin: A
Z disc: C
Actin :B
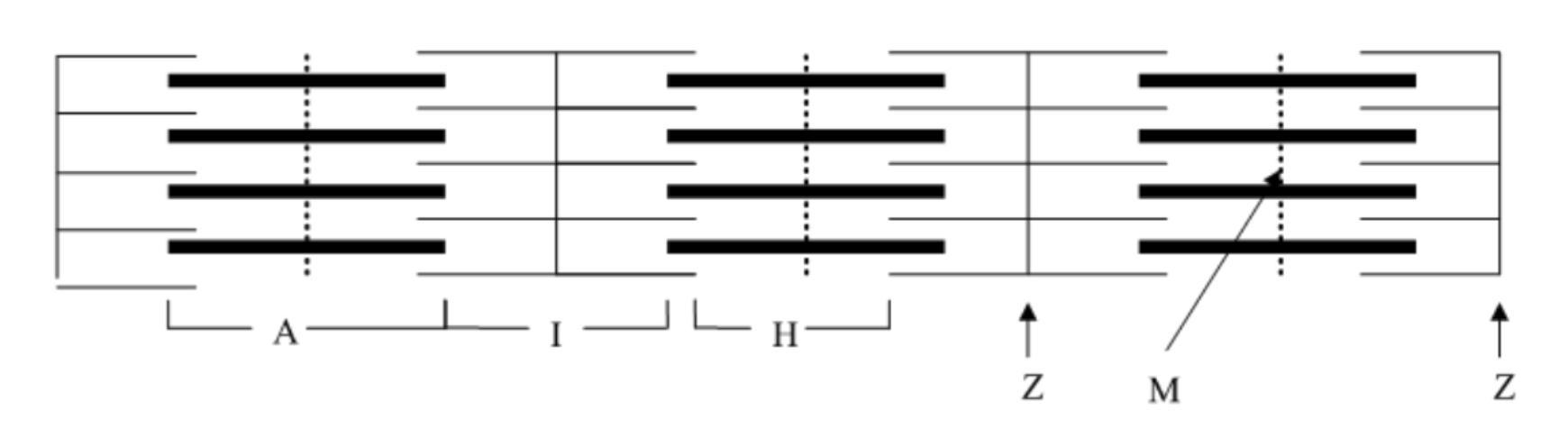
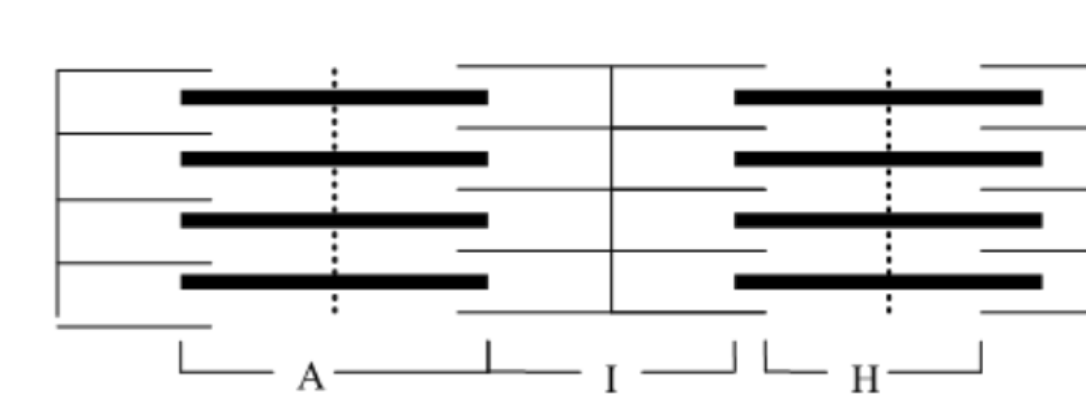
What is the name of the entire region of the sarcomere containing the thick filament called?
A band
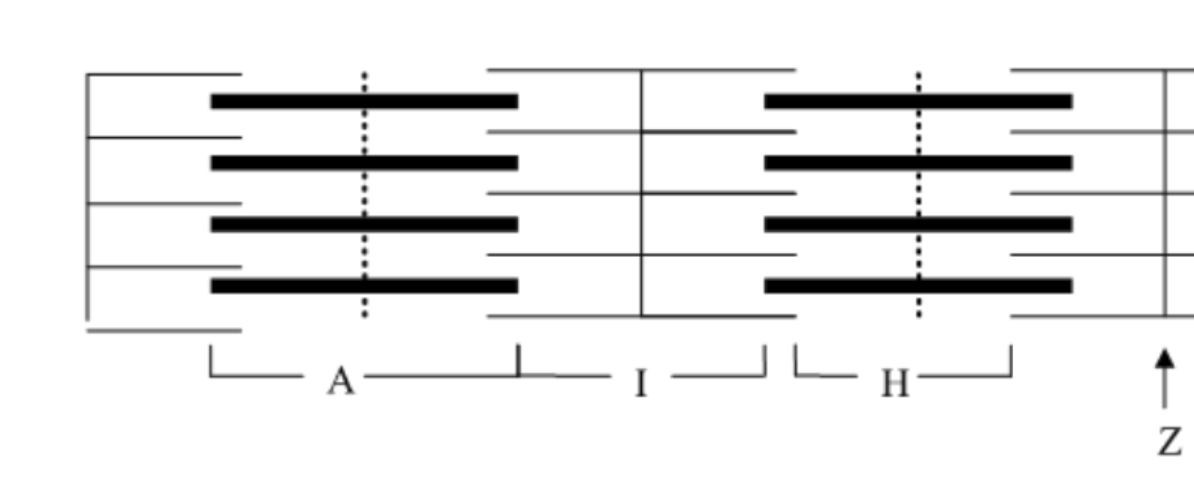
What is the name of the region of the sarcomere that always contains only thin filaments?
I band
What is the name of the area in the center of the A band that contains no thin filaments?
H zone
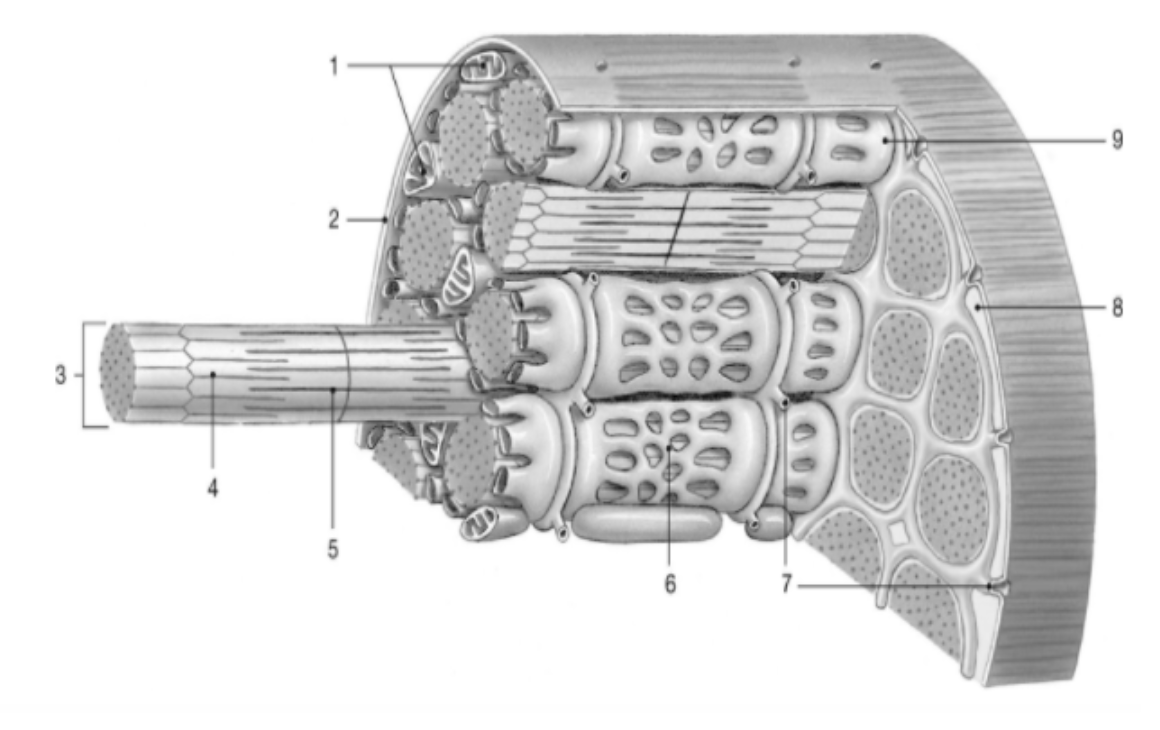
Match the correct part of the muscle cell.
Actin: 4
Myosin: 5
Myofibril: 3
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum: 6
What are the interactions between actin and myosin filaments of the sarcomere responsible for?
Muscle contraction
Which of the following best describes the term Z line?
boundary between sarcomeres
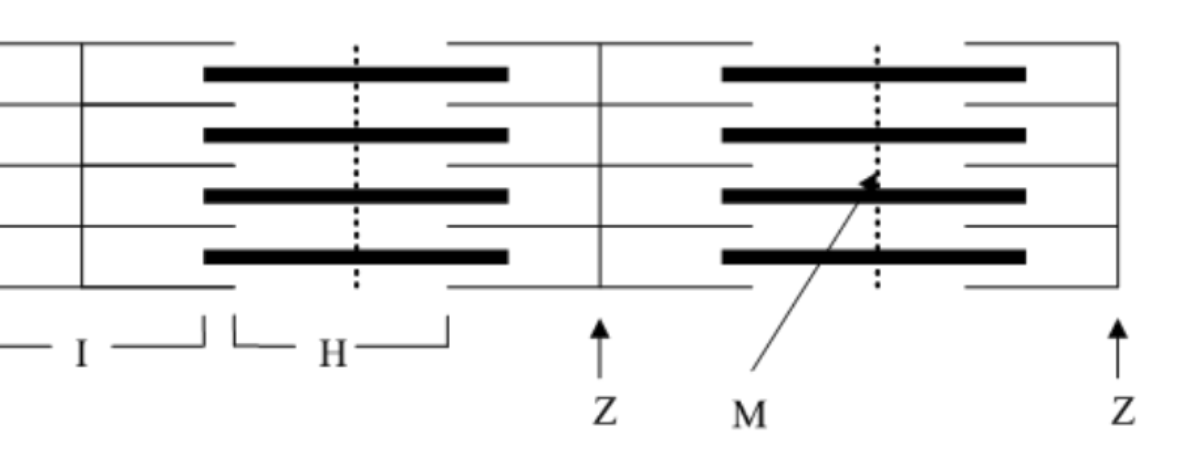
At rest, what are the active sites on the actin blocked by?
tropomyosin molecules
Which of the following is true regarding contraction of a sarcomere?
Which of the following is true when a skeletal muscle fiber contracts?
Since each myofibril is attached at either end of the muscle fiber, when sarcomeres shorten, the muscle fiber:
Shortens
In response to action potentials arriving along the transverse tubules, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases
calcium ion
What happens when calcium ions bind to troponin?
tropomyosin moves to expose “active sites” on actin
Which of the following become connected by myosin cross-bridges during muscle contraction?
thin filaments and thick filaments
How many of the following terms are smaller than a myofibril?
Myosin
Actin
Muscle fiber
Muscle fascicle
Troponin
Tropomyosin
4 because of Actin, Myosin (protein filaments that make up the Myofibril) Troponin, and Tropomyosin (Proteins involved in muscle contraction, also smaller than the myofibril)
What is the name of the connection between a muscle fiber and a neuron?
Neuromuscular junction
Which molecule provides energy for the muscle to contract?
ATP
Write a paragraph explaining the sliding filament theory. Be sure to include the following terms in your explanation:
Myosin
Actin
Sarcomere
Calcium
Troponin
Tropomyosin
ATP
ADP
Phosphate (P)
Nerve Impulse
When a nerve impulse is sent into a muscle, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions which bind to the troponin molecules in actin thin filaments. This causes the tropomysoic to move; thus, exposing the actin active sites. Once the myosin heads connect to those active sites using the energy released from the hydrolization of ATP, which removes a phosphate atom, thus turning it into an ADP molecule that will be sent to the mitochondria to be re-phosphated. All of this occurs within the individual sarcomeres, wherein the actin and myosin are located. The ultimate connection of myosin heads to actin site and enabling the corssbridges allows for the event called a "powerstroke" leading to muscle contraction.
Muscle Contraction
Calcium ions diffuse into nerve cell.
Causes neurotransmitter acetylcholine to be released.
Acetylcholine binds to sarcolemma, which makes it permeable to Calcium (Ca2+).
Ca2+ assists in the muscle contraction and relaxation
Neuromuscular junction
Nerve cell is meets muscle fiber.
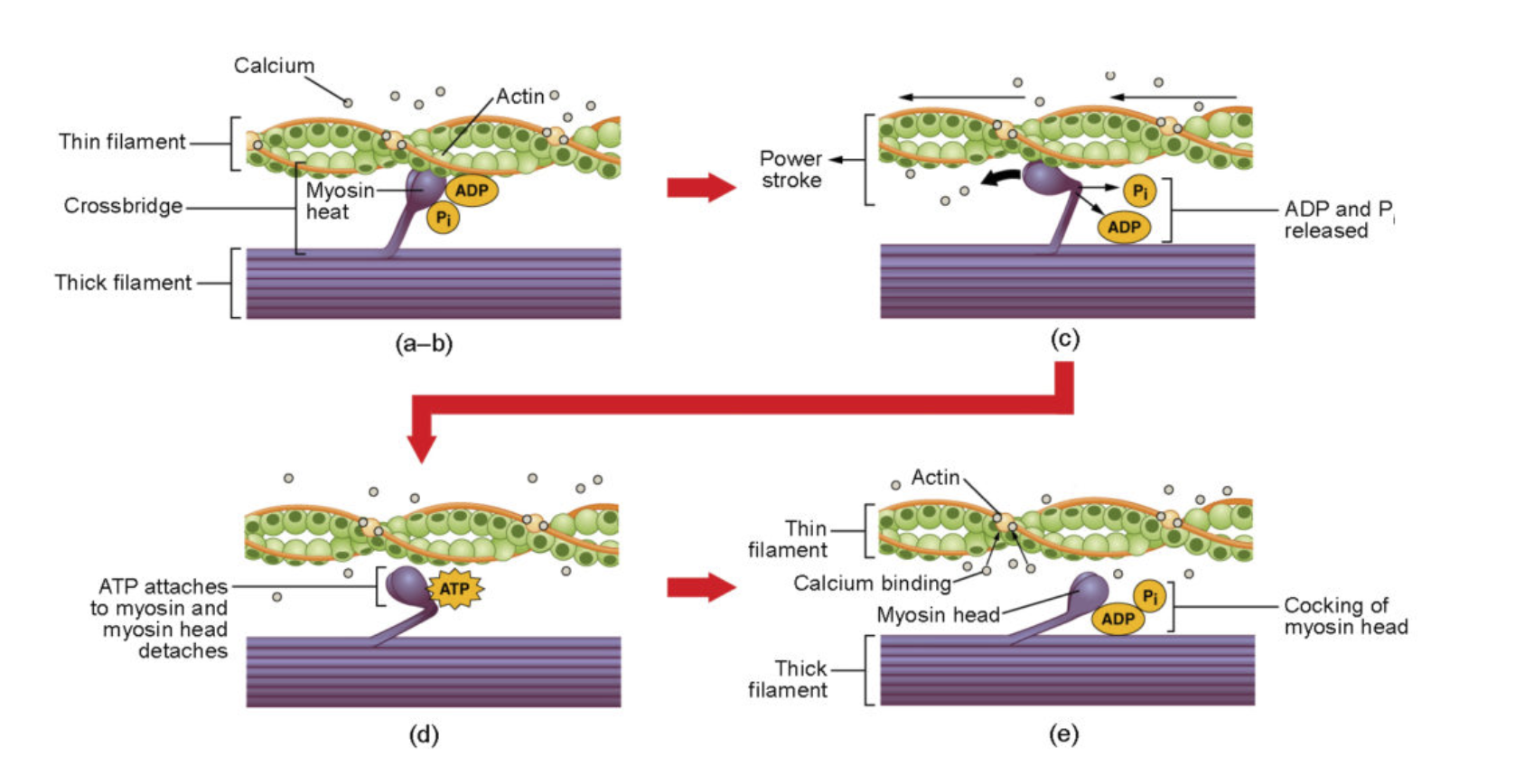
Molecular Level of Muscle Contraction