Macroeconomic aims and issues: inflation and deflation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is inflation and how is it calculated
sustained increase in the GPL
calculated using a percentage change in the country’s CPI
on average, prices are rising for a sustained period of time

what is mild/low inflation
inflation rate that is single digit and does not distort relative prices severely
CB typically target about 2-3%
what is galloping inflation
price level increasing at a higher rate at double or triple digits
cause money to lose its value at a rapid rate
what is hyperinflation
extremely high (more than triple digit) rate of inflation
people lose confidence in the currency
→ currency ceases to function as a medium of exchange
people may resort to barter trade
what is disinflation
slowing rate of price increases or falling inflation
what is deflation
falling prices or negative inflation wh
what is stagflation
a period of
rising prices
coupled with no or negative growth in real GDP/GNP
and high or rising unemployment
what is anticipated inflation
effect of anticipated inflation on individuals and businesses
inflation rate that is steady and expected
when inflation is anticipated, individuals and businesses are able to accurately predict the inflation which will take place
what is unanticipated inflation
effect of unanticipated inflation on individuals and businesses
inflation that is volatile and unexpected
occurs when economic agents (households, firms, government) make errors in their inflation forecasts
and actual inflation ends up well below or significantly above expectations
difficult for individuals and businesses to correctly predict the rate of inflation for the near future
what does CB do with regards to inflation
monitors inflation rate ti ensure an environment of low inflationary pressures conducive to sustainable economic growth
outline inflation in SG
what about SG makes it prone to inflation
impact of inflation in SG
SG: small and open economy, import reliant
exposed to global events
eg strong recovery in global growth and demand with the arrival of covid-19 vaccines
increase in price of gas and oil on the back of a SS crunch and geopolitical tensions
pandemic-related disruptions to the world’s supply chains
covid 19 border curbs → tighter labour market → increase in wages → increase in CoP
Impact
CoL increase
local i/r
bank loans affected by i/r hikes overseas
GST hike
rise in GPL due to rise in COP
outline the causes of inflation
demand-pull inflation
cost-push inflation
explain cause of demand pull inflation
caused by persistent rises in AD
associated with booming economy
reflected by continuous shifts of the AD curve to the right
Sources of DD-pull inflation
non-GPL factors that cause an increase in autonomous C, I, G and NX
eg monetary or fiscal stimulus
positive expectations about future income/sales
rising property prices
expectations about inflation
economic growth in other countries
etc
explain price adjustment process for demand-pull inflation
eg increase in NX; assume economy is operating along intermediate range of AS curve
increase in AD as NX is a component of AD
rightward shift of AD curve from AD0 to AD1
shortages in the economy created as current spending exceeds current production levels at initial GPL P0
firms respond to the rise in demand partly by raising prices and partly by increasing output
because as economy approaches full employment, fewer idle FoPs like labour and raw materials
competition for fewer idle FoPs becomes greater → firms bid up factor prices
As each additional unit of output becomes costlier to produce, prices have to increase to ensure that production remains profitable
increase in RNY from Y0 to Y1 is accompanied by an increase in GPL from P0 to P1
what can cause inflation to persist
taking example of the export boom
export boom → households and firms have greater confidence in the future
expect income and sales to continue to increase in the future
households and firms have incentive to buy more and invest more in current time period
→ increase in autonomous C and autonomous I
→ AD increases further (another rightward shift of AD curve)
GPL will increase further
higher demand pull inflationary pressures
what does extent of increase in GPL depend on
how much spare capacity economy has
whether economy is operating on horizontal range of AS curve, intermediate range of AS curve or vertical range of AS curve
extent of increase in GPL if economy is operating on horizontal range of AS curve
Case 1: horizontal range, low levels of RNY/output
a lot of available spare capacity
firms can easily expand output (increase production) to meet increases in demand without increasing prices
firm can increase production without firms bidding up prices of FoPs to hire more FoPs
output rises without pressure on price to increase, firms don’t have to pass on any increase in CoP to consumers
extent of increase in GPL if economy is operating on intermediate range of AS curve
fewer idle FoPs
firms compete and bid up prices of factor inputs
the closer to Yf, resources become decreasingly idle → GPL rises faster
each additional unit of output becomes much costlier to produce
the closer to Yf, price increases by a increasingly greater extent for a given increase in AD
extent of increase in GPL if economy is operating on vertical range of AS curve
full employment level reached
impossible increase output
only pressure on price to increase
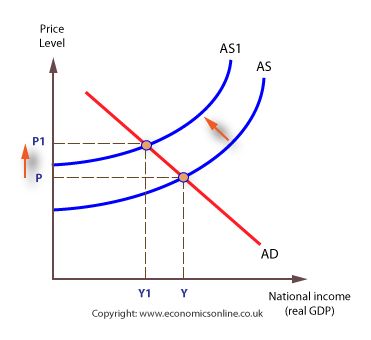
what is cost-push inflation
sustained increase in GPL caused by persistent falls in AS, independent of level of AD
continuous upward shifts on AS curve
and/or leftward shifts of AS curve
explain price adjustment for cost-push inflation
if there is an increase in the CoP due to eg an increase in the price of oil
AS will fall
AS curve shifts upwards from AS0 to AS1
shortages at prevailing price level P0 and firms will take the opportunity to raise prices
outline sources of cost push inflation