Chemistry Quiz #1 Flashcards
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is Matter?
Anything that has mass and takes up space (volume)
Solids
Liquids
Gasses
Plasma
What are the properties of Solids?
Solids…
Hold their own shape
Have mass
Take up space

What are the properties of Liquids?
Liquids…
Take the shape of their container
Have mass
Take up space

What are the properties of Gasses?
Gasses…
Spread out to fill the entire space given
Have mass
Take up space

What are the properties of Plasma?
Lightning is a plasma
Plasma is a lot like gas, but the particals are electrically charged

What are the properties of particles in solids? (list 2)
Are packed tightly together
Have very LITTLE energy
What are the properties of particles in liquids? (list 2)
Are loosely packed
Have MEDIUM energy levels
What are the properties of particles in gasses? (list 2)
Move freely
Have LOTS of energy
What are the properties of particles in plasma? (list 2)
Are electrically charged
Have EXTREMELY high energy levels
What determines the state of matter of a substance?
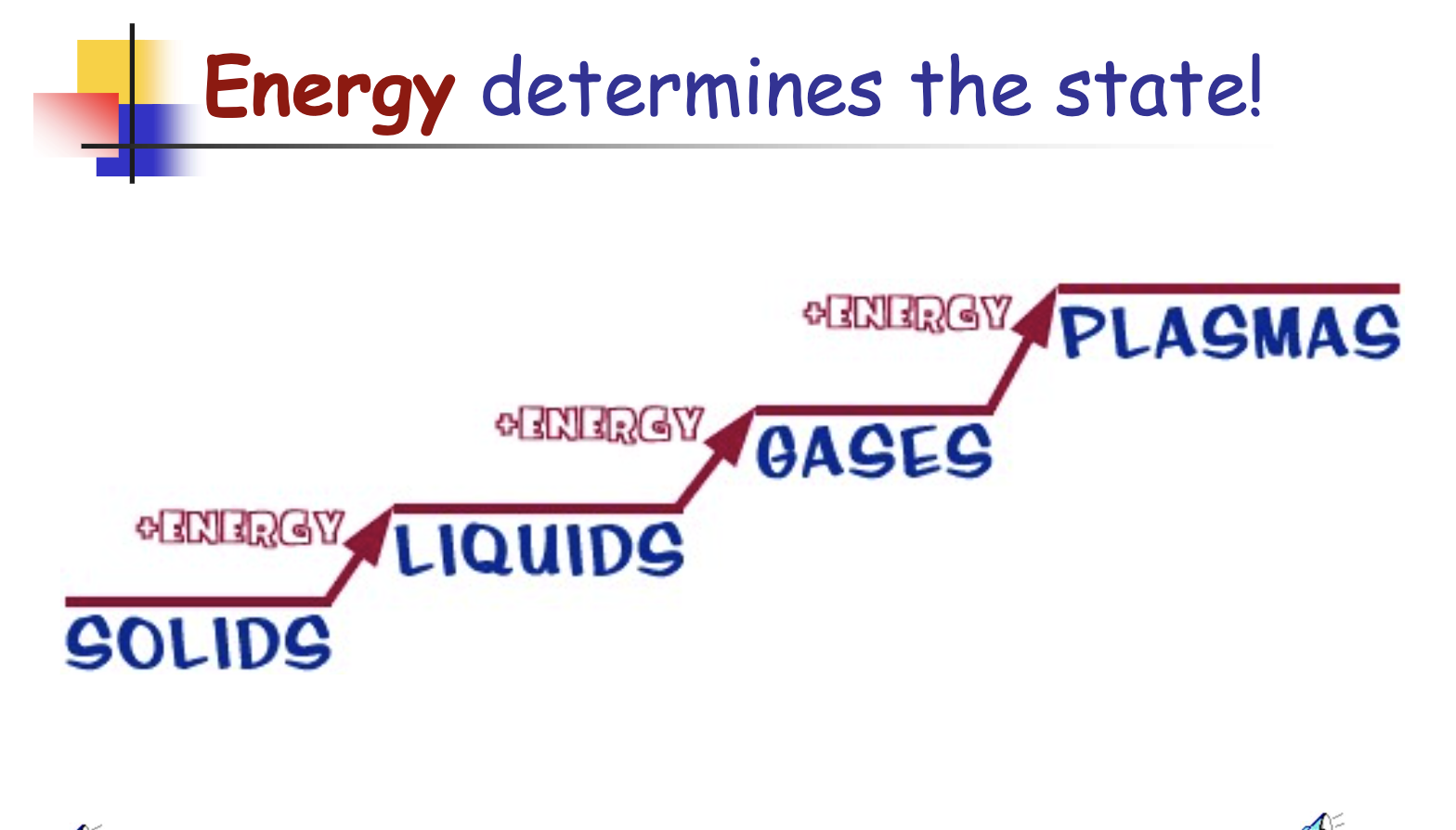
Energy.
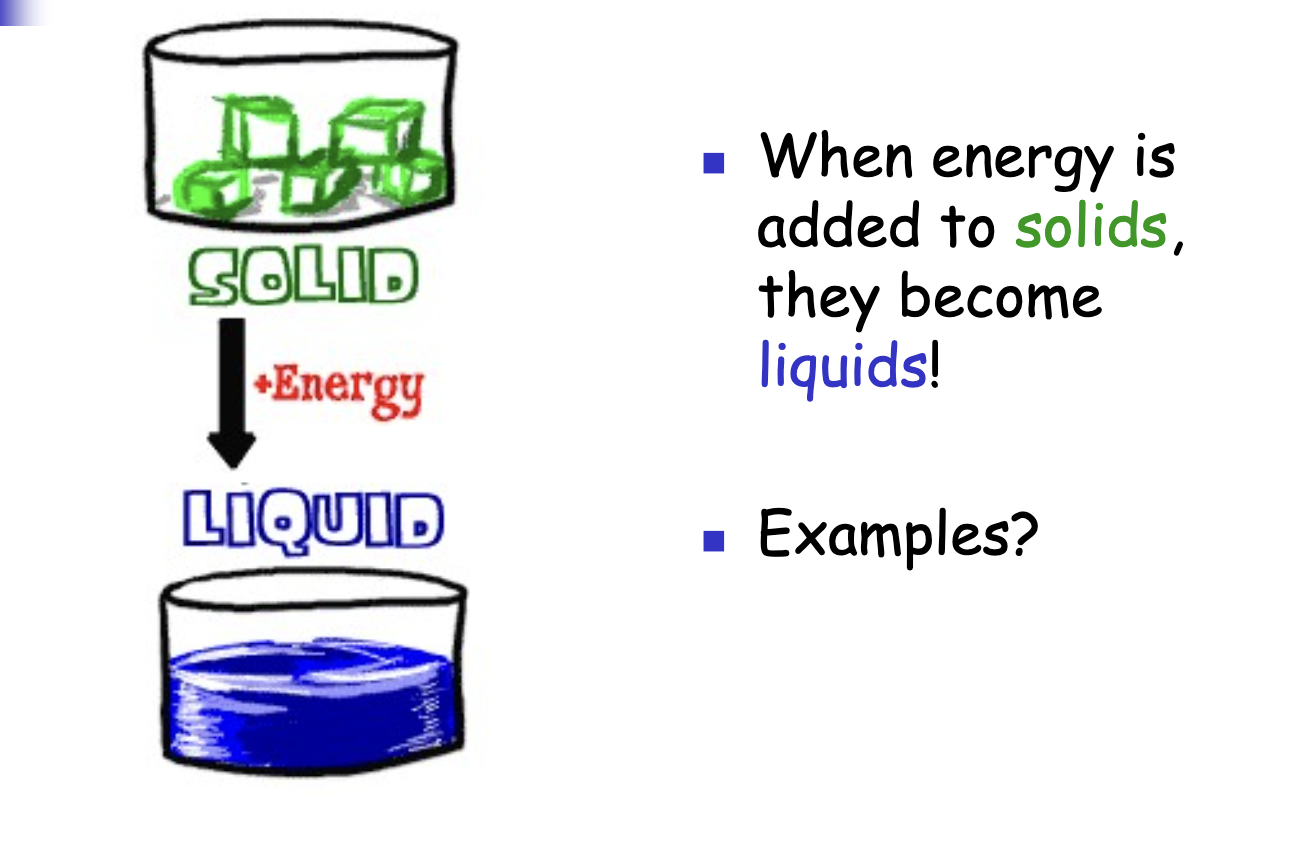
Solid + Energy = ?
Adding energy to a solid causes it to become a liquid.
Example: Ice melting and becoming into water.
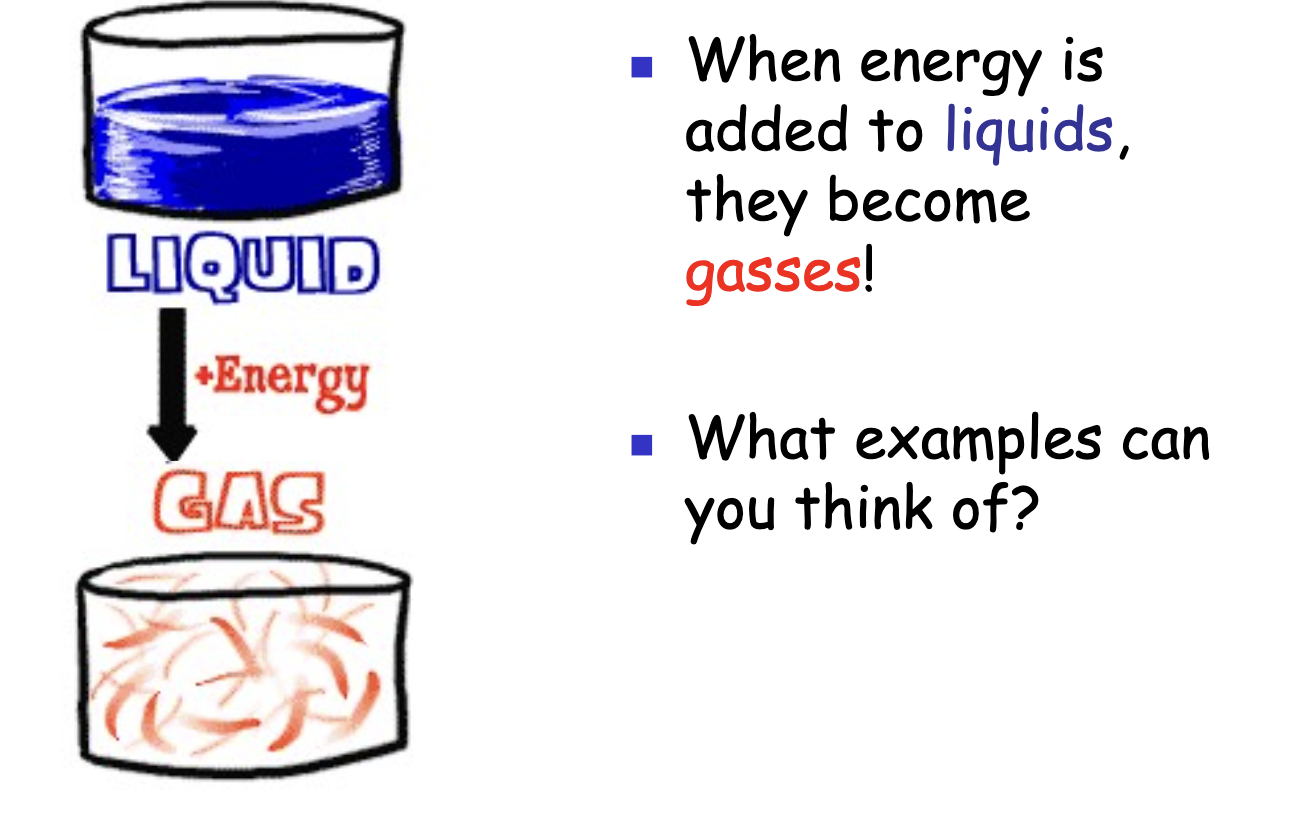
Liquid + Energy = ?
Adding energy to a liquid causes it to become a gas.
Example: Water evaporating and becoming water vapor.
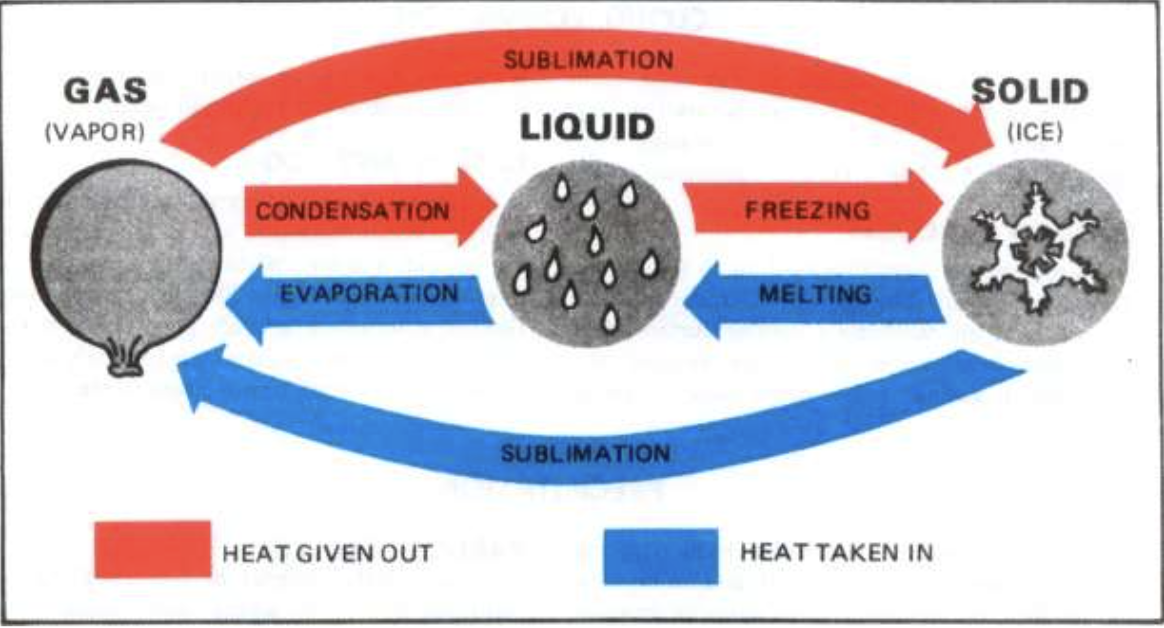
Changing States — What are the different names for matter changing states?
State change
Phase change
Physical change
What are the different kinds of state change?
Gas → Liquid: Condensation
Liquid → Solid: Freezing
Gas → Solid: Sublimation
Solid → Liquid: Melting
Liquid → Gas: Evaporation
Solid → Gas: Sublimation
What is the Particle Model?
It is a theory of how scientists think that matter is made up. It can be used to explain why matter behaves the way it does.
What are the 5 main points of the Particle Model?
Matter is made up of tiny particles.
All particles in one type of matter are the same. Different types of matter are made up of different particles.
The particles in matter are separated by empty space.
The particles in matter are in motion. Increasing the temperature increases the amount of motion.
The particles in matter are attracted to one another. These attractions get stronger when particles are close together.
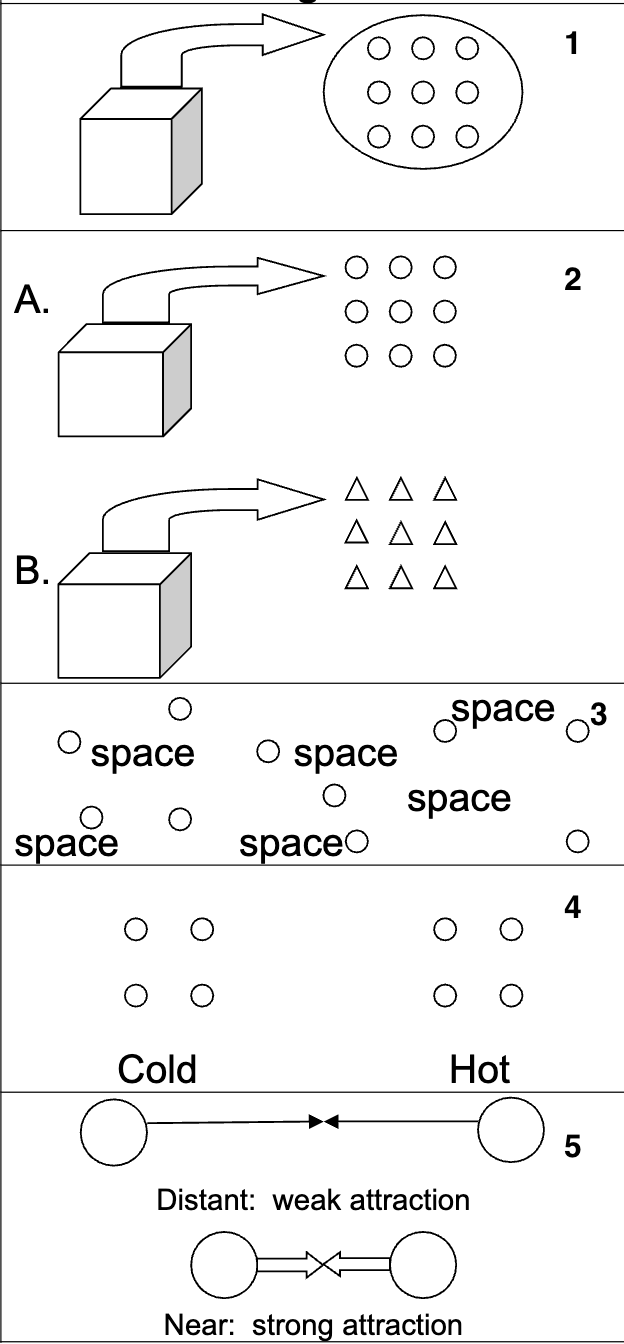
How does the particle theory explain solids?
Observations:
Definite shape and volume
Can be compressed only slightly
Explanation:
Strong attractive forces hold particles in place in an orderly manner, close together.
How does the particle theory explain liquids?
Observations:
Flows easily
Definite volume
No definite shape
Can be compressed only slightly
Explanation: Weaker attractive forces allows for movement in a less orderly manner.
How does the particle theory explain gasses?
Observations:
No definite shape or volume
Can be greatly compressed
Explanation: Very weak forces of attraction, particles are far apart and move fast.
What are the 2 main Properties of Matter?
We use the properties of matter to help identify and classify substances
The two main properties of matter are physical properties and chemical properties
What are Physical Properties?
The characteristics that can be observed (using our senses) or measured (using equipment) during experiments.
Physical Properties that can be observed with our senses are…
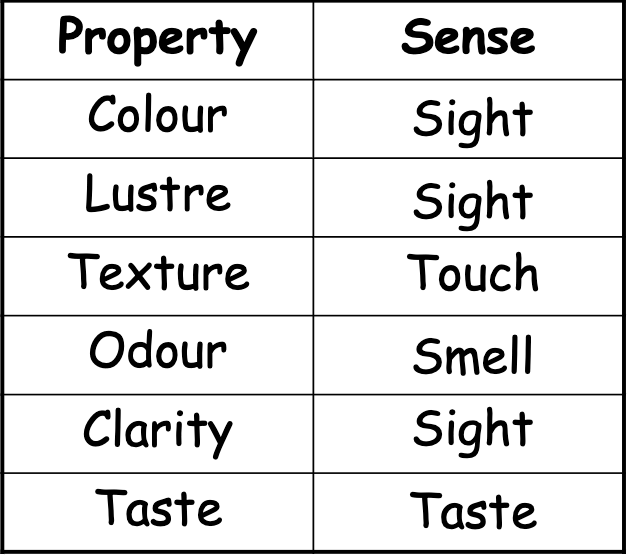
Physical Properties — State of Matter
Is the substance solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature?
Physical Properties — Hardness
The ability of a solid to resist being scratched or dented.
Physical Properties — Malleability
The ability of a solid to be hammered or bent. If it bends, it is malleable. If it breaks, it is brittle.
Physical Properties — Melting Point
The temperature(s) at which a substance will change form a solid to liquid
For example, ice melts at 0 degrees Celsius.
Physical Properties — Boiling Point
The temperature(s) at which a substance will change form a liquid to a gas.
For example, water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
Physical Properties — Solubility
The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
For example, Kool-Aid dissolves in water.
Physical Properties — Viscosity
How easily a liquid flows. The thicker a liquid, the more viscous it is.
For example, honey is viscous.
Physical Properties — Density
The amount of mass per unit of volume.
For example, the density of water is 1g/mL
Physical Properties — Crystal Form
Is the substance made up of regular patterns?
Physical Properties — Ductility
When a substance can be pulled out to form wires.
For example, copper is a ductile metal.
What are Chemical Properties?
They describe the behaviour of a substance when it reacts with another substance to become a new substance.
Chemical Properties — Combustibility
The ability of a substance to burn or explode. If a substance is combustible, it will burn (also called flammable). If a substance is not combustible, it will not burn (non-flammable).
Chemical Properties — Reaction with Acid
The ability of a substance to react with an acid. When the substance reacts, a gas may form or a colour change occurs, and a new substance is formed.
What are the 2 changes of matter classified as?
Matter can undergo changes. These changes can be classified as:
Physical Changes
Chemical Changes
What is a Physical Change
During a physical change,
No new substance is formed
All the substances remain the same (although they appear in a different form)
A physical change can normally be reversed.
Examples:
Dissolving (Salt is dissolved into water)
Change of state (Ice melts to become water)
Expanding or crushing (Chalk is crushed into powder)
What is a Chemical Change?
When matter undergoes a chemical change,
At least one new substance is formed
A chemical change normally cannot be reversed.
Examples:
A piece of paper is burned (paper becomes ash)
A tin can rusts (tin becomes rust)
What is the evidence for a physical change?
Change of state
Colour stays the same
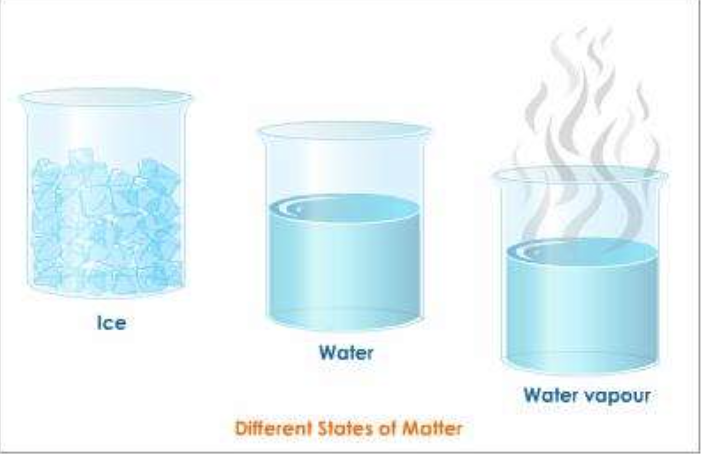
What is the evidence for a chemical change?
A new colour appears
Heat or light is given off (energy)
Bubbles of gas are formed
A solid material (called a precipitate) formed from two liquids
The change is difficult to reverse
What is density?
A measure of how tightly packed and how heavy the molecules are in an object; the amount of matter within a certain volume.
All substances have a unique density.
How is density calculated?
Density (p) equals mass (m) divided by volume (V)
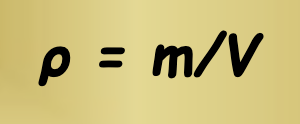
Mass is measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg)
Volume is measured in millilitres (mL) or (cm3)
When mass is in kg, the volume is in L or m3
When mass is in g, the volume is in mL or cm3
What are Liquid Layers?
If you pour together liquids that don’t mix and have different densities, they will form liquid layers.
The liquid with the highest density will be on the bottom
The liquid with the lowest density will be on the top
Objects or substances with a HIGHER density will sink below objects or substances with a LOWER density.

Determining Density — regularly-shaped objects:
Find mass
Determine volume using appropriate formula
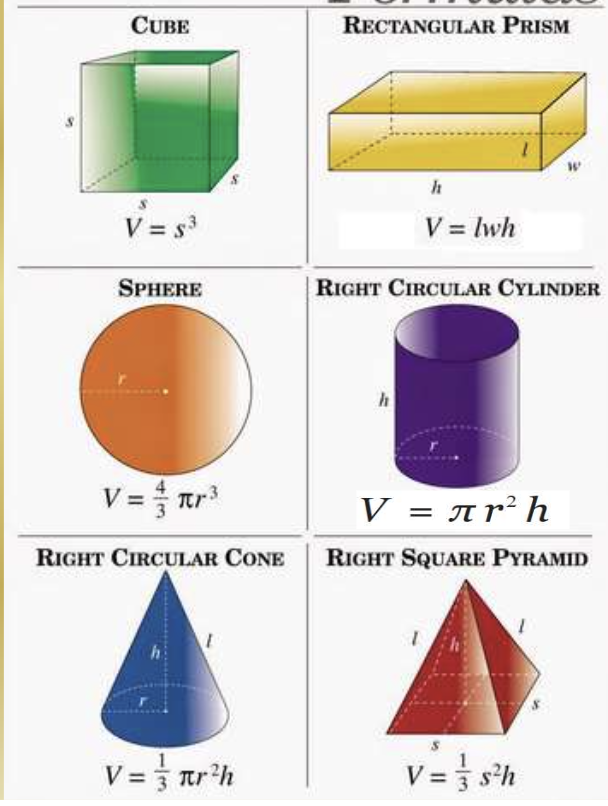
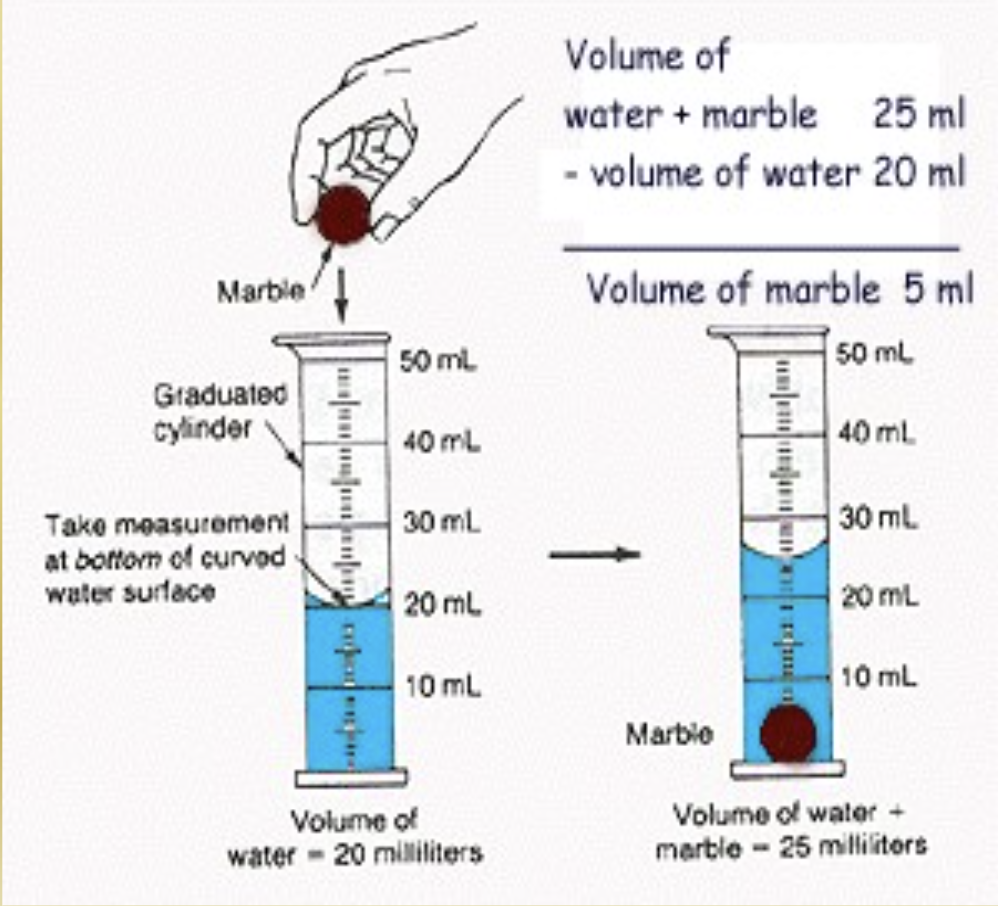
Determining Density — irregular shapes:
Find mass
Determine volume by measuring how much water is displaced by the object
Volume of the water with the object subtracted by volume of the water without the object.
What is GRASP?
Given — What is the given question?
Required — What are you looking for/trying to find?
Analyze — Write the formula
Substitute and solve — Solve using the formula
Paraphrase — Therefore…
What is electrolysis?
A process that uses electricity to break down water (H2O) into its elements (Hydrogen and Oxygen).
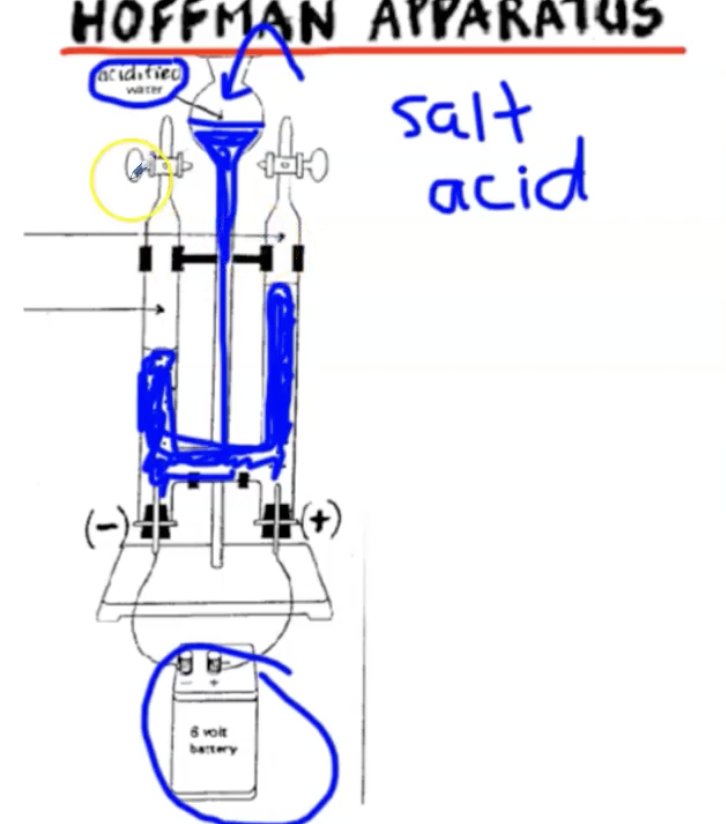
What is a Hoffman Apparatus?
A piece of equipment that is used to perform electrolysis.
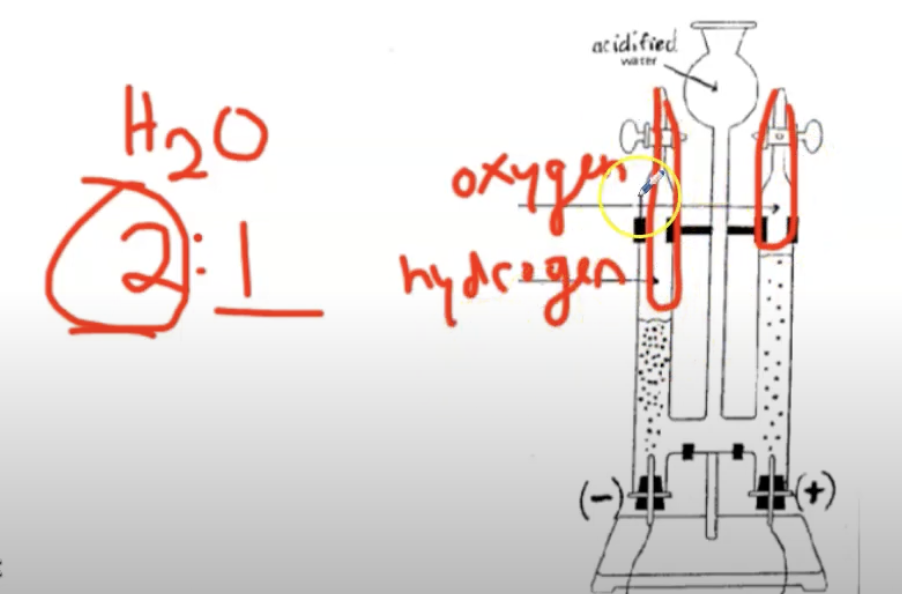
Oxygen is collecting on the right, and hydrogen is collecting on the left because the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in water is 2:1.
The formula for water is…
H2O
If there is no number after the element, it is the same as it being a 1. (H2O1).
This tells us the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in water (2:1).
This formula tells us that a water molecule has more hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms.
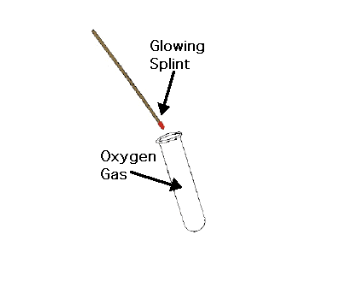
Standard Oxygen Gas Test
Place a glowing splint into the gas…
→ Split bursts into flames (POSITIVE for Oxygen)
→ No change is seen (NEGATIVE for Oxygen)
Standard Hydrogen Gas Test
Place a burning splint into the gas…
→ The splint has a burst of flames and a loud “POP” sound is heard (POSITIVE for Hydrogen)
→ No change is seen (NEGATIVE for Hydrogen)

Standard Carbon Dioxide Gas Test
Place a burning splint into the gas…
→ The flame goes out (POSITIVE for Carbon Dioxide)
→ No change is seen (NEGATIVE for Carbon Dioxide)
Atom
A particle of a substance that cannot be broken down by physical or chemical changes.
Element