AP Computer Sciences Principle
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Algorithm
specific and logical sets of instructions to solve a problem or achieve a specific result
High level language
easier for humans to read and write
easier to debug
less abstractions
Low level language
closer to machine or assembly language
requires more knowledge
harder to debug
more abstractions
Binary
number systems consisting of 1s and 0s
Hexadecimal
16 symbols 0-9 and A-F
Abstraction
process of making something simpler or easier
Source code
programming statements saved in a file
Syntax error
a mistake in which the rules of the programming language are not followed; mistakes a programmer makes when writing (grammar, keywords, symbols)
Runtime Error
mistake that occurs during the execution of a program that ceases the execution
Logic error
mistake in the algorithm or program that causes it to behave incorrectly or unexpectedly
Overflow error
a mistake that occurs when a computer attempts to handle or store a number that is outside of the defined range of values
Round-off errors
computer rounds numbers with decimal places
bit
smallest unit of information stored or manipulated on a computer (1 or 0)
conversions of bits
1 bit = 1 or 0
1 byte = 8 bits
1 kilo byte = 1000 bytes
1 megabyte = 1000 kilobytes
1 gigabyte = 1000 megabytes
1 terabyte = 1000 gigabytes
Digital images
are collections of pixels where each pixel consists of binary numbers
one is black (or on) and 0 is white (or off) you can create black a white pictures
metadata
data providing information about one or more aspects of the data
Colors
can represents more colors using green, red and blue lights
max value is 255 and min is 0
White (255, 255, 255)
Black (0,0,0)
Blue (0,0,255)
red (255, 0, 0)
Analog signal
exists throughout a continuous interval of time and takes on continuous range of values
Digital signal
discrete sequence
Data compression
used in Mp3, mp4, rar, zip, jpg
used to make a data package smaller or decompress the package to original form
useful for saving disk space and reduce the bandwidth used when sending data
takes strings of bytes and compresses it down to smaller sets of bytes
Lossless algorithms
can reconstruct the original message from compressed message
quality is important
typically used for texts
Lossy algorithms
removes repeating data bits
permanently removes and can not restore
file speed is more important
used more related to images yet when enlarged you can see compression loss, music difference in quality, and video frames
List
data type that holds a collection of values
aList {3,7, 11],
separated by commas
also called arrays
elements
individual items in a list accessed by position using an index
index positions
always integers and are enclosed with square brackets
INSERT command
causes elements to the right of the indicated index position, i, to shift right one position to make room for the new element
APPEND command
will add the new element to the end of the list so no index position is needed; size of list increases by one
REMOVE command
deletes the element at the provided index position and shifts the remaining elements on position to the left
size of list decreases by one
length
the length of a list is the number of elements in the list
FOR EACH item IN list command
loop that will automatically repeat the code for each element in the list
this is called traversing a list
Strings
text fields that are just a series of characters and are denoted with quotation marks around the string filed
any character, number, or symbol
ex. “Hi”
Integers
whole number
floating-point numbers
whole number and decimal
5.5
Variables
placeholders for values a program needs to use
to assign a value to a variable an equal sign is used
let color = “green”
let month ← “April”
variable ← expression
Modulus operator
calculates the remainder
13 MOD 2 = 1
20 % 6 = 2
Boolean values
can only be true or false
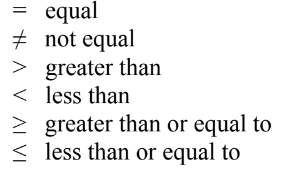
Relational operators
==: equal
! =: not equal to
>: greater than a>b
<: less than a<b
>=: greater than or equal to
<=: less than or equal to
Logical operators and the order they are evaluated
1) parentheses
2)) relational operators
3) logical operator not (Opposite)
4) logical operator AND (together)
4) Logical operator OR
Sequential
statements that are executed as written in order in the program
needs to be in correct order
Selection statements
use if (condition) structure to evaluate condition of Boolean values
Iterative
repetitive statements or loops until condition is met
While loop
control structure in programming that repeats a block of code as long as specified condition is true
For loop
used to repeat a block of code a specific number of times
ex. for (Let i = 0; i< ; i++)
let i=0 starts counter at 0
i <5 keeps looping while i is less than 5
i++ increases i by 1 each loop
Repeat Until (condition) loop
condition to evaluate at each iteration of the loop
loop will continue to run while condition evaluates to false
Math functions
Math.abs (x): absolute value
Math.PI constant of pi
Math.pow (x,y) return value of x to power of y
Math.pow(x): returns x rounded to nearest value
Math.sqrt(x): return square root of x
extracting codes
console.log(“funny”.substr(0,3)); outputs fun
loops
sequence of instructions that are repeated until a condition is reached
Push code
adds a values to the end of an array
Splice code
removing/ replacing things
Nested conditionals
an IF statements within another set of IF statements
when the outer IF statement is executed, the inner IF statement may also get executed

Linear search
check each individual record starting from beginning and going to the end to find the desired data or to determine it is not in the data set
works on any list, sorted or unsorted
binary search
more efficient than linear searches
data must be sorted (ascending order)
divides and conquer into two equal parts
Procedures
also called functions
sections of code that will be executed only when they are called by main program or another procedure
Parameters
allowing calling program to send values to procedure
makes procedures more flexible
Calling a procedure
when the procedure is called the program will pause at that location and execute the code in the procedure
when procedure finishes, control returns back to the line of the code where the call ocurred
Return statement
end a procedure before the end of the code is reached '
no other code will be executed after the return statement
send a value back to calling program
DISPLAY ()
We do not know how this procedure is coded, only that we can use it multiple times, pass it different types and values to print, and that it works.
INPUT()
It accepts data from the user, usually from the keyboard.
When the programming language sees this command, it will pause the program and wait for something to be typed on the keyboard.
APIs
application programming interface
provides the information needed to set up the interface and use the newly connected software
Libraries
prewritten programs to provide commonly needed functionality
Instance of a problem
a specific example of a problem
Decision problem
yes or no answer
Optimization problem
should find the best solution for the problem
Limits of algorithms
can’t run in a reasonable amount of time with our current algorithms
some can’t solve problems efficient enough
Heuristic approach
approach may not be optimal or the best but is close enough to use as a solution
Random
happens, done, or chosen by chance instead of following a system, plan, or rule; used frequently for testing
Simulation
computer model used to mimic real world events
Decidable problem
an algorithm that can be written that results in a correct yes or no answer for all inputs
ex. determining if a number is even or odd
min or max value
sorting
Undecidable problem
does not have an algorithm that can give a yes or no for all cases of a problem
ex. program verification
security
AI
Halting problem
problem of finding out whether a program will halt or run indefinitely
Internet
worldwide system of computer networks
routing
process of finding a path from sender to receiver
bandwidth
measure of max amount of data that can be transferred through a channel or network connection
bits per second determines how quickly you can download and upload files from the internet
Internet protocol (IP)
responsible for addressing and routing your online requests
Transmission control protocol (TCP)
protocol that defines how computers send packets of data to each other
User datagram protocol (UDP)
protocol that allows computer applications to send message without checking for missing packets to save on time needed to retransmit missing packets (loss is acceptable)
Hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP)
communication protocol to transfer data between webservers and other computing devices
Fault tolerant
the ability of a network to continue operating without interruption if one or more components fail
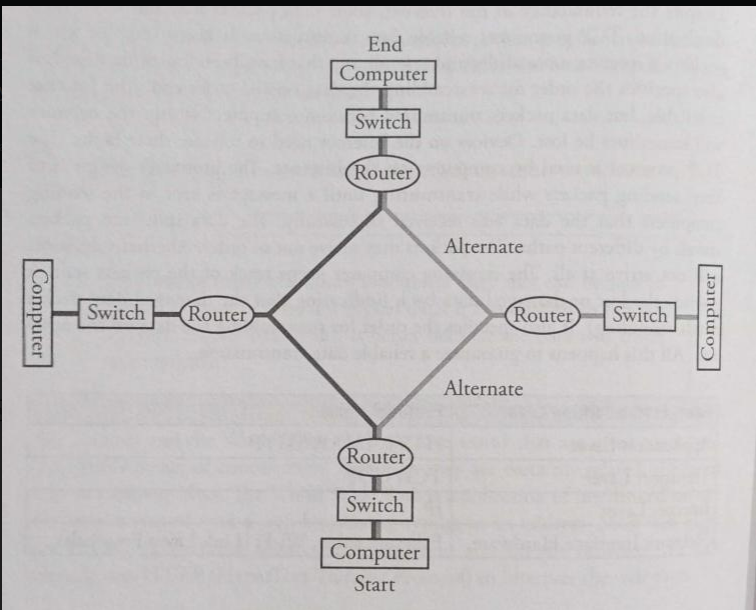
Redundancy
a network system designed where components are duplicated so if a component fails the network will still work
Hardware failure
stops working due to an issue with the physical components
Operational failures
any issue or breakdowns in operation of a business, machine, system
Sequential computing
slower than parallel or distributed computing but is required when tasks must be completed in a specific order
Parallel computing
takes as long as the longest of the tasks done in parallel
parallel and sequential portion
multiple processors
Distributed computing
allows problems to be solved that could not be solved on a single computer because of either the processing time or storage needs involved
multiple devices
Machine learning and data mining
help find patterns and identify insights in data leading to new innovations
cloud computing
offers new ways for people to communicate making collaboration easier and more efficient
Digital divide
decreases people’s ability to access news, connect socially, and learn about political events
due to education, income, geography, digital literacy, dexterity
can be solved by: universal access, community access centers, well trained staff, accessibility
Bias
intentional or unintentional prejudice for or against certain groups of people
Crowdsourcing
allows people to share information and ask anyone who accesses the site for feedback, to help solve problems, find employment, or funding
Citizen science
practice of using the general public to help in gathering, analyzing, or sorting specific data
Legal/ ethnical concerns
material created by someone else that you use in any way should always be cited
devices that monitor/ collect data have ethical concerns
creative commons
provides a way for creators of software, images, music, videos, and other computational artifact to share their creations
Digital data
easy to find, copy, paste, ensuring you have written permission from the creator or owner is important
Open source software
software that is freely shared, updated, and supported by anyone who wants to do so
Open access
availability of open databases in varies fields
Personally identifiable information (PII)
any information that identifies you
Digital footprints and fingerprints
are the trail of little pieces of data we leave behind as a sign of our presence as we go through our daily lives.
Cybersecurity
has a global impact because now anyone from anywhere can attempt to gain unauthorized entry to someone else’s computer, data, servers, or network.
Security
strong passwords
multifactor authentication
Phishing
attacks create e-mail and or websites that look legitimate hoping to induce a persons to click on the malicious link