Examination of the cardio-respiratory system in dogs & cats
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What respiratory/cardiac conditions are associated with certain breeds?
Myxomatous degenerative valvular disease (= Mitral valve disease) in CKCS or small breed dogs
Tracheal collapse in Yorkshire terriers
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) in Dobermanns & giant breeds of dogs
Cats —> hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
What history questions do you need to ask?
Vaccination & worming status
Travel outside the UK
Indoor vs outdoor
Environment (urban vs rural)
Other pets or animals in the environment (foxes, slugs etc.)
Diet / appetite / thirst / V+ / D+ / PUPD
Access to toxins
Any change in weight / condition etc.
What questions would you ask about a dogs cough?
When is the dog coughing - at night before bed? when excited?
Dry cough or productive (retch/ swallow)
Are they coughing anything up
What questions would you ask about a dogs breathing?
Laboured breathing —> Dyspnoea
When first noticed? episodic / continuous / getting worse?
Orthopnoea (posture to optimise breathing)
Any change in Bark / Meow?
Nasal discharge? Blocked?
Tachypnoea
What questions would you ask about exercise?
How much normally? changes?
Reluctant to exercise?
Slowing down?
What questions would you ask about collapse?
When?
Describe, loss of consciousness?
Colour of tongue / gums?
Flaccid / rigid? Any muscle movement?
What would the first steps be with a respiratory patient?
Observe behaviour
Assess respiratory rate before handling (normal 20 – 30 breaths a minute)
Assess respiratory effort (hyperpnoea if increased, orthopnoea)
Record respiratory rate (not possible if panting, panting = probably NOT dyspnoeic)
What are the signs of orthopnoea?
standing /sitting to breathe
air-hunger stance
elbows abducted
What are the different types of dyspnoea?
Inspiratory / Expiratory or Both
Obstructive versus Restrictive
Upper vs Lower Airway
If airway noise (stridor, stertor etc. will be upper airway problem)
What would you check for in a cardio patient?
Peripheral perfusion
Colour of mucus membranes (if cyanotic, assess response to O2 & do not stress)
Capillary refill (CRT) (normal <2 seconds)
Warmth of extremities
What are the signs of forward heart failure?
What is a ddx for these clinical signs?
Lethargy, exercise intolerance
Weak femoral pulses, unable to detect distal pulses (metatarsal)
Pale MM, slow CRT
Cold extremities
Possibly hypothermia
Weak precordial impulse on palpation
Heart sounds “quiet” or “distant” on auscultation
“Cardiogenic shock” (obstruction)
What is forward heart failure more likely in?
Dilated cardiomyopathy
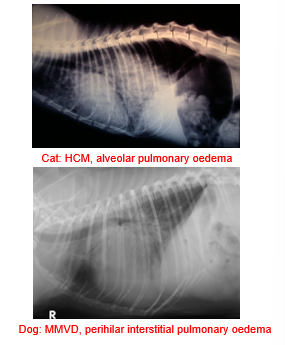
What are the signs of left sided CHF (pulmonary oedema)?
Tachypnoea, both inspiratory and expiratory, restrictive breathing pattern
Cough in dogs due to left atrial enlargement
+/- soft inspiratory crackles on auscultation (don't rely on this - not present with bad oedema)
What are the signs of right sided CHF?
Ascites (positive fluid wave on ballottment)
Distended jugular veins
Positive hepatojugular reflux —> putting gentle pressure on the caudle abdomen will lead to distention of the jugular veins —> sign of increased R sided filling pressure
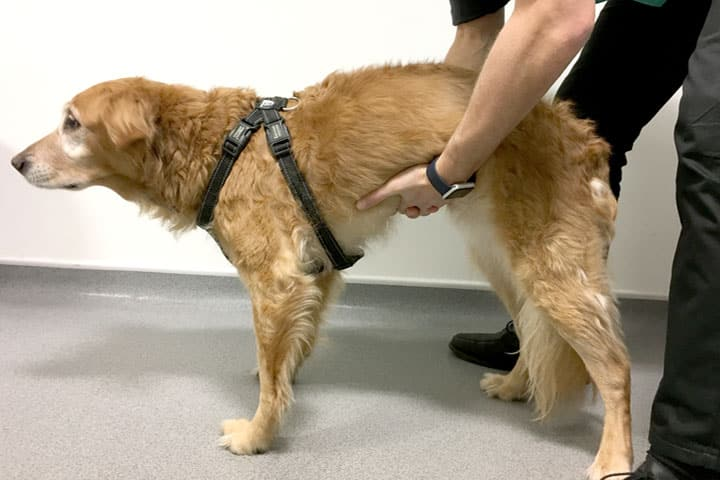
+/- pleural effusion (could be left in cat)
Rarely sub-cutaneous oedema in SA (horses and cattle)
How do you check the hepatojugular reflex?
Gentle pressure on the caudal abdomen causes increased distention / pulsation of the jugular veins
Signs of increased right sided filling pressure
What will you auscultate on the heart?
What are the normal paramotors for cats and dogs?
Record heart rate and rhythm
Sinus arrhythmia is normal in dogs
Normal heart rate in dogs: 80 – 140
Normal heart rate in cats: 120 – 200
If abnormal rhythm check femoral pulse at same time as checking HR for deficits
Listen for murmurs & gallop sounds
How do you further define a murmur?
Location (point of maximal intensity) —> Left vs Right; Apex vs Base
Timing —> Systolic vs Diastolic vs Continuous
Grade
Character, Radiation?
How do you grade a heart murmur?
I/VI —> very quiet murmur, only detected in optimal conditions
II/VI —> less loud than the heart sounds
III/VI —> as loud as the heart sounds
IV/VI —> louder than the heart sounds
V/VI —> loud heart murmur with a precordial thrill
VI/VI —> very loud murmur with a precordial thrill, which can be still detected after lifting the stethoscope off the chest wall (feel with fingers on the chest)
How do you locate heart murmurs?
Left Apex —> Mitral valve
Left Base —> Pulmonic valve/ aortic
Left Cranio-Dorsal —> Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Right side of chest —> Tricuspid valve (apex) = soft murmur/ ventricular septal defect = loud murmur (cranio-sternal)
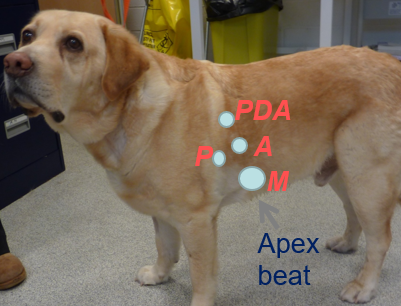
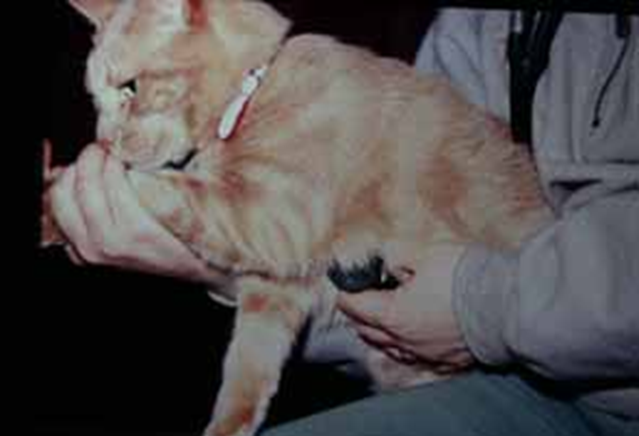
What do you need to not forget to auscultate in the heart with cats?
Sternal borders (pick them up)

How do you figure out the timing of the heart murmur and what other characteristics could you identify?
Systole —> between S1 (closure of AV valves) and S2 (closure of pulmonic & aortic valves i.e. semilunar valves)
Plateau
Blowing, Decrescendo
Crescendo-Decrescendo
Brief-mid systolic
When are heart murmurs detected?
When turbulent vs laminar flow is present in heart / great vessels
What is the equation to determine if blood is turbulent?

If Reynolds number is more than 2000 = turbulent
Describe murmurs in puppies & kittens
Innocent murmurs
Usually < grade 3/6
Usually apical
Diminish with growth
Disappear by 16 – 20 weeks old
Due to change in foetal to adult haemoglobin
Hard to distinguish from congenital heart disease
How do you listen for diastolic gallops?
S3 and S4 (not audible in SA)
Use bell of stethoscope with very little pressure over left apex
Will hear Lup-Dup-Te
What would be the cause of S3 and S4?
S4 is detected in animals which depend on atrial contraction to achieve ventricular filling e.g. with abnormal LV relaxation, in feline hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
S3 is heard when early diastolic filling is abruptly decelerated in a stiff, poorly compliant LV, and filling pressures are high e.g. dilated cardiomyopathy
What do you need to be aware of with respiratory auscultaton?
Be aware of referred sounds from the URT (especially in brachys)
Check larynx and trachea (palpation & auscultation)
Bronchovesicular lung sounds —> normal respiratory sounds (harsher when faster respiratory rate / panting)
What abnormal lung sounds do you need to identify?
Crackles (inspiratory) —> smaller airways opening
Wheezes (expiratory) —> narrowed airways
What can you identify when you percuss the thorax?
(percuss both sides of chest)
Identify any asymmetry / areas of increased / decreased percussion resonance
Pleural effusion —> increased dullness
Pneumothorax —> increased resonance
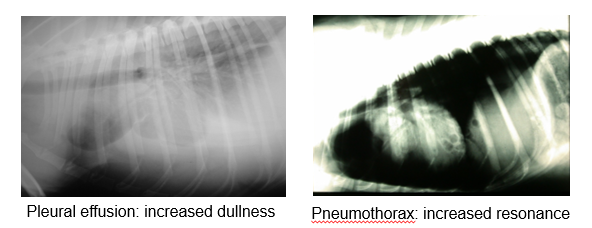
What can thoracic compressibility be useful for?
More useful in cats than dogs
Useful to detect cranial mediastinal masses
Also less compressible with significant pleural effusion
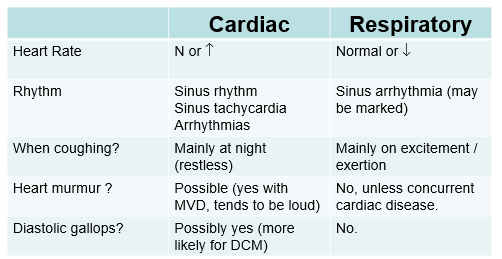
How you distinguish between cardiac and respiratory disease when a patient has a cough?
What is the commonly used classification of severity of heart disease?
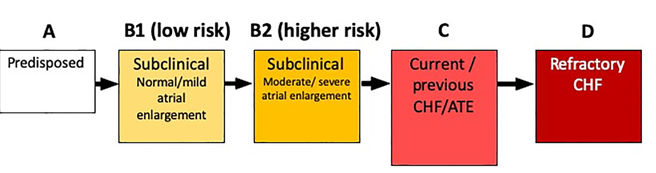
ABCD classification
(heart dx DOES NOT equal heart failure)
Describe the ABCD classification
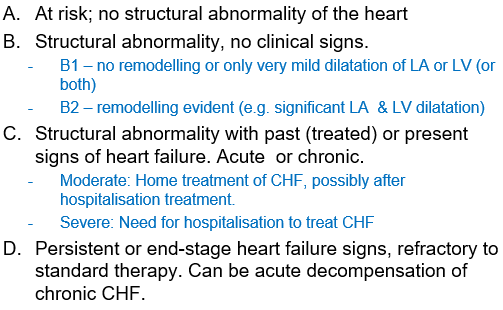
*for mitral regurgitation (MMVD = myxamatous mitral valve dx)
What is the ABCD classification for feline cardiopyopathies?