Chemistry (6.2): Nitrogen compounds, polymers and synthesis
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Ammonia formula
NH3
amines
organic chemicals where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced with alkyl chains
Primary amine
RNH2
Secondary amine
RNHR’
Tertiary amine
RNR’R’’
Naming amines suffix
amine
Are amines bases or acids?
weak bases
Lewis base
electron pair donor
Bronsted-Lowry base
proton acceptor
What do amines react with?
dilute inorganic acids (e.g. HCl)
What is produced when HCl reacts with a base?
chloride salt and water
What is produced which primary amines react with HCl?
alkylammonium salt
alkylammonium salt
a compound where the hydrogens on an ammonium ion have been substituted by alkyl chains
Name of salt formed when an amine reacts with HCl
alkylammonium chloride
Name of salt formed when an amine reacts with nitric acid
alkylammonium nitrate
Name of salt produced when amines react with sulfuric aicd
alkylammonium sulfate
What chemicals are used to prepare aliphatic amines?
haloalkane, ammonia and ethanol
ammonia + haloalkane →
ammonium salt
ammonium salt + ammonia →
amine + ammonium salt
quaternary ammonium salt
each hydrogen on the ammonium ion has been replaced with an alkyl chain
How do you prepare aromatic amines?
reduce a nitroarene
What are the conditions for preparing aromatic amines?
Tin, conc HCl, reflux at 100 degrees C, strong alkali (NaOH)
What kind of reaction is the preparation of aromatic amines?
neutralisation
amino acid general formula
RCH(NH2)COOH
what functional groups do amino acids have?
amine and carboxylic acid groups
What does the amine group on an amino acid act as?
a base
Why does the amine group of an amino acid act as a base?
due to the lone pair of electrons
What does the carboxylic acid group of an amino acid act as?
a weak acid
amphoteric
can act as both an acid and a base
isoelectic point
when there is no net electrical charge due to each zwitterion having an internal balance of charge
What happens when an amino acid is in acidic conditions?
amino acid acts as a base and accepts a proton from the acid and becomes positive
What happens when an amino acid is in alkaline conditions?
amino acid acts as an acid and donates a proton to the hydroxide ion and becomes negative
What does the carboxylic acid functional group of an amino acid react with?
metal oxides
alkalis
carbonates
alcohols
acid + amino acid →
ammonium salt
amide
a class of compound with a functional group made of an acyl group which is directly attached to an amine
primary amide general formula
RC(O)NH2
How are amides related to carboxylic acids?
hydroxyl group has been substituted for an amine group
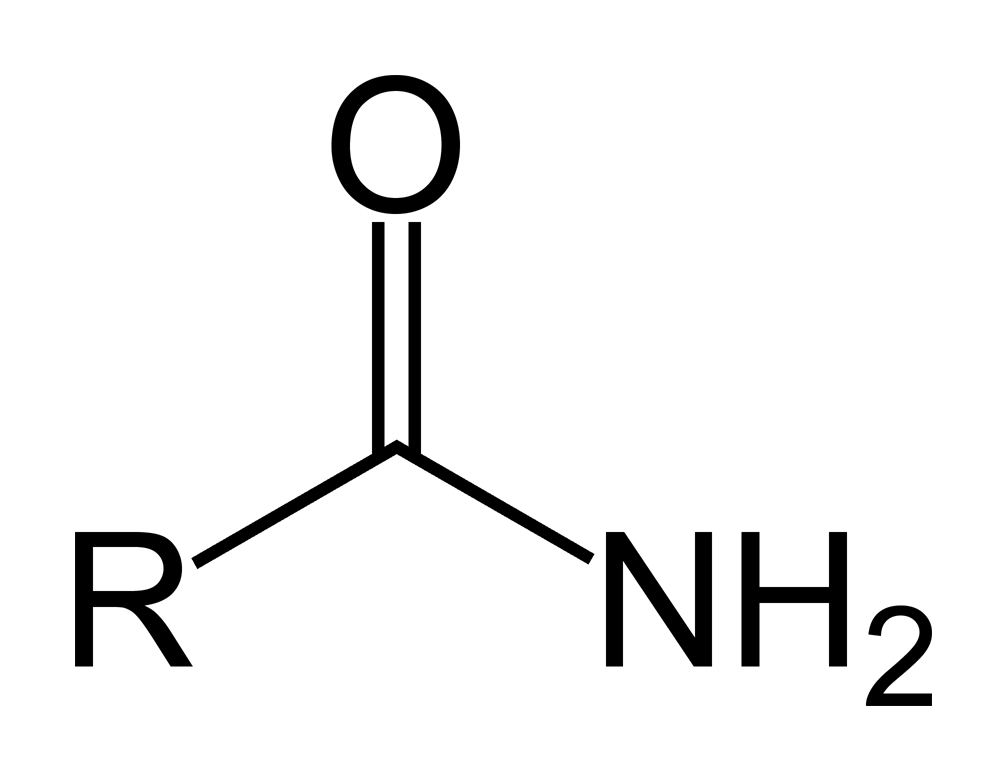
What is this?
primary amide
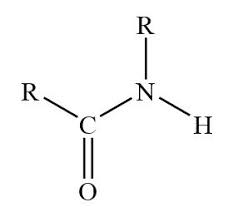
What is this?
secondary amide
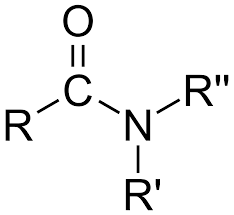
What is this?
tertiary amide
polyamides
condition polymer made from carboxylic acid and an amine
carboxylic acid + amine →
polyamides
How do you name primary amines?
suffix amide
optical isomers
molecules which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
chiral carbon
has four different groups attached to it
When are optical isomers formed?
when there is a chiral centre
repeat unit
the arrangement of atoms that occurs many times in a polymer
condensation polymerisation
the chemical reaction to form a long-chain molecule by elimination of a small molecule like water
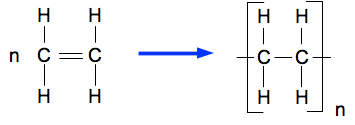
What does this show?
addition polymerisation
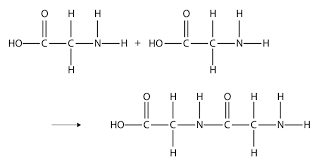
What does this show?
Condensation polymerisation
What are polyesters made from?
dicarboxylic acid and a diol or a molecule that contains both an alcohol and a carboxylic acid group
Types of condensation polymer (2)
polyesters
polyamides
What are polyamides made from?
dicarboxylic acid and a diamide
Under what conditions do polyesters undergo hydrolysis?
acidic or basic
Products of the acid hydrolysis of polyesters
diol and dicarboxylic acid
Products of the base hydrolysis of polyesters
diol and the salt of the dicarboxylic acid
Under what conditions do polyamides undergo hydrolysis?
acidic or basic
Products of the acid hydrolysis of polyamides
diammonium salt and a dicarboxylic acid
Products of the alkali hydrolysis of polyamides
diamine an
nitrile functional group
-CN
-CN
nitrile functional group
Reactions to extend carbon chain length
haloalkane + KCN
carbonyl + HCN
Friedel-Crafts reactions (acylation and alkylation)
What type of reaction is the reaction between a haloalkane and KCN?
nucleophilic substitution
haloalkane + KCN →
nitrile + halide ion
What type of reaction is the reaction between carbonyl and HCN?
nucleophilic addition
Why is the solvent ethanol when a haloalkane is mixed with KCN and heated under reflux?
ensures that the nucleophile is the cyanide ion
carbonyl + HCN →
hydroxynitrile
Reactions of nitriles (2)
reduction
hydrolysis
What are the reagents when nitriles undergo reduction?
hydrogen gas, nickel catalyst, increased temp (150) and pressure
What is formed when nitriles undergo reduction?
amines
RCN + 2H2 →
RCH2NH2
What can be used as a reducing agent in the reduction of a nitrile?
LiAlH4
What are the conditions for the hydrolysis of nitriles?
strong acid catalyst and heating under reflux
What are formed when nitriles undergo acid hydrolysis?
carboxylic acids
What do Friedel-Crafts reactions allow?
electrophilic substitution to occur on an aromatic ring
Friedel-Crafts reactions (2)
acylation
alkylation
Alkylation
occurs when hydrocarbon chains are added to an organic compound
Reagents for alkylation
aromatic compound, haloalkane and a strong Lewis acid catalyst
What kind of reaction is alkylation?
electrophilic substitution
Acylation
when RCO- is added to an organic compound
What are the reagents of acylation?
benzene, acyl chloride and a strong Lewis acid catalyst
distillation
a technique used to separate miscible liquids or solutions
heating under reflux
used to ensure that volatile compounds are not lost from the reaction mixture
recrystallisation
a method for purifying organic compounds
How are the tubes attached to the condenser in distillation?
water out at the top and cool water in at the bottom
What techniques are used to purify an organic solid? (2)
filtration under reduced pressure
recrystallisation
How to check purify of an organic compounds
measuring melting points
What kind of funnel is used for pressure filtration?
Buchner funnel
Steps of filtration
connect tubing to vacuum pump and check suction
put Buchner funnel into top of filter flask
connect tubing to filter flask
start suction
place filter paper into top of funnel and dampen with distilled water
poor reaction mixture into centre of funnel
Stages of recrystallisation (4)
dissolve product in hot solvent
solution undergo gravity filtration
hot filtrate allowed to cool
purified organic product collected by vacuum filtration
How do you measure melting points?
melting po