1.3 and 1.4 PLTW MI Review
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
killed/inactivate vaccines
A harmless pathogen that consists of recognizable antiges; typically boosters or larger doses
what kind of vaccine is used for rabies or polio?
killed/inactivate
live, annuated (weakened)
A weakened form of a pathogen typically involving a strong immune response (fewer boosters); SMALL risk of disease agent mutating back to pathogen form
what kind of vaccine is used for measlers, mmr, and varicella?
live, attenuated
similar pathogen
Uses pathogen that is less dangerous than the target pathogen, but produces an immune response that will also protect against the target pathogen
a scientist saw a similar infection on a cow’s udder as an almost exact replica of the disease: smallpox. What kind of vaccine is this an example of?
similar pathogen
subunit
Often associated with genetic engineering, genes for microbial antigen are inserted into plasmid then cloned into appropiate host cells (such as yeast). Host cells produce microbial antigen, which is the purified for vaccine production
what kind of vaccine is used for hepititis B?
subunit
DNA/RNA vaccines
DNA (or mRNA) instructins for the microbial organism are delivered to your cells, which then produce the antigen themselves via protein synthesis, leading to an immune response
what kind of vaccine is used for COVID and HIV?
DNA/RNA vaccines (COVID- mRNA and HIV- DNA)
toxoid
a purified toxin produced by the microbe is used to elicit an immune response
what kind of vaccine is used for tetanus?
toxiod
Passive Immunity
A type of immunity in which antibodies are passed on from another outside source to fight internal disease (often used when a patient is incapable of producing their own antibodies)
Active Immunity
A type of immunity in which antibodies are self-made.
Examples of passive immunity
Breastfeeding (natural) and monoclonal antibodies (artificial)
Examples of active immunity
[Natural] infection and vaccination [artificial]
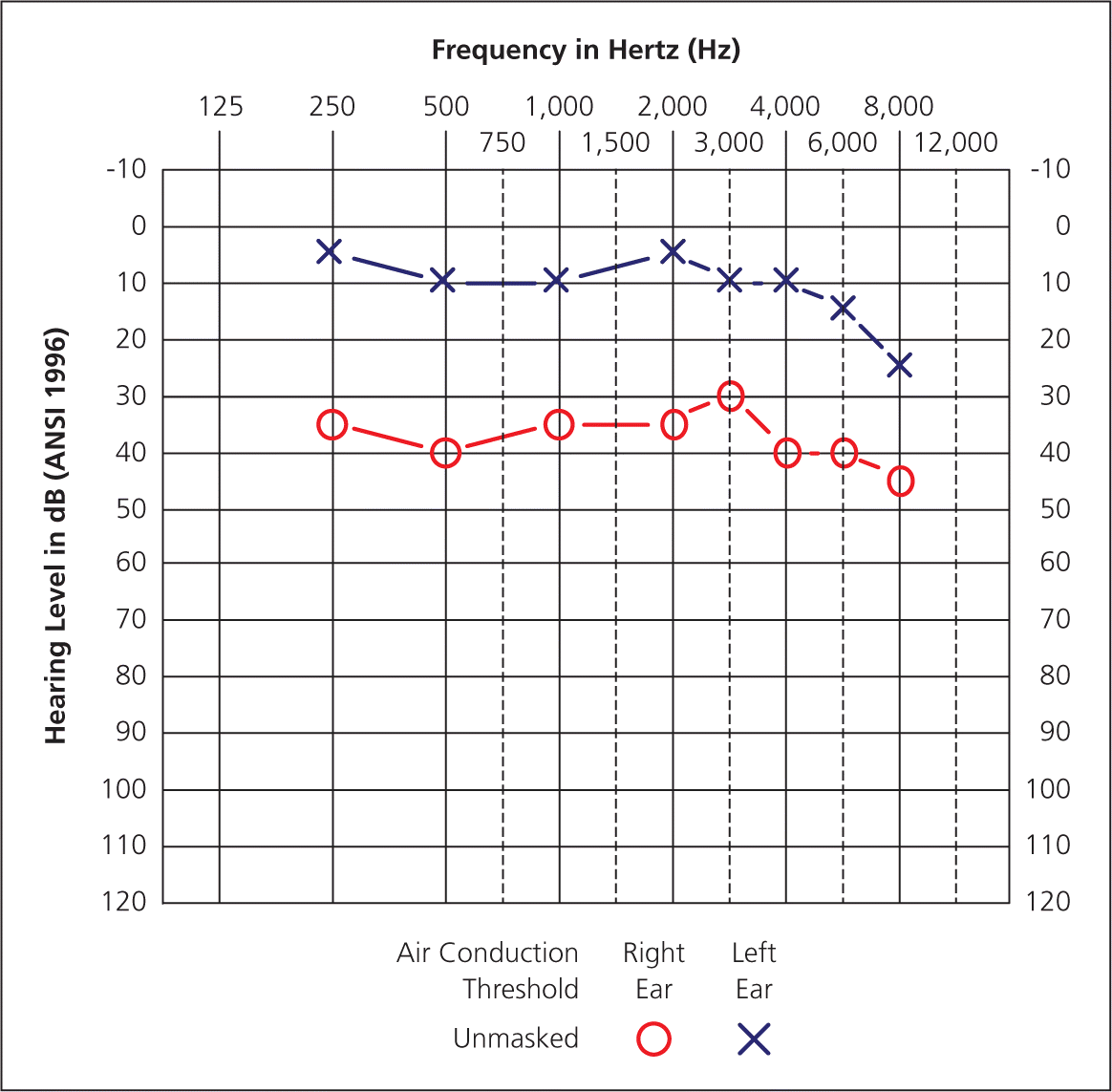
What kind of hearing loss does this graph represent? What kind of graph is it?
This graph is a pure tone test. It represents a person with mild to moderate sesorineural hearing loss in their right ear
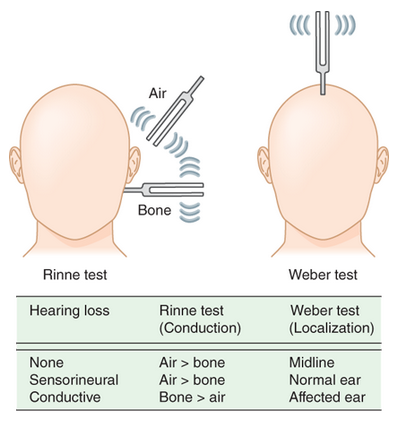
Weber & Rinne Test
Test comparing hearing loss through bone conduction vs. air conduction; measures sesorineural hearing loss.
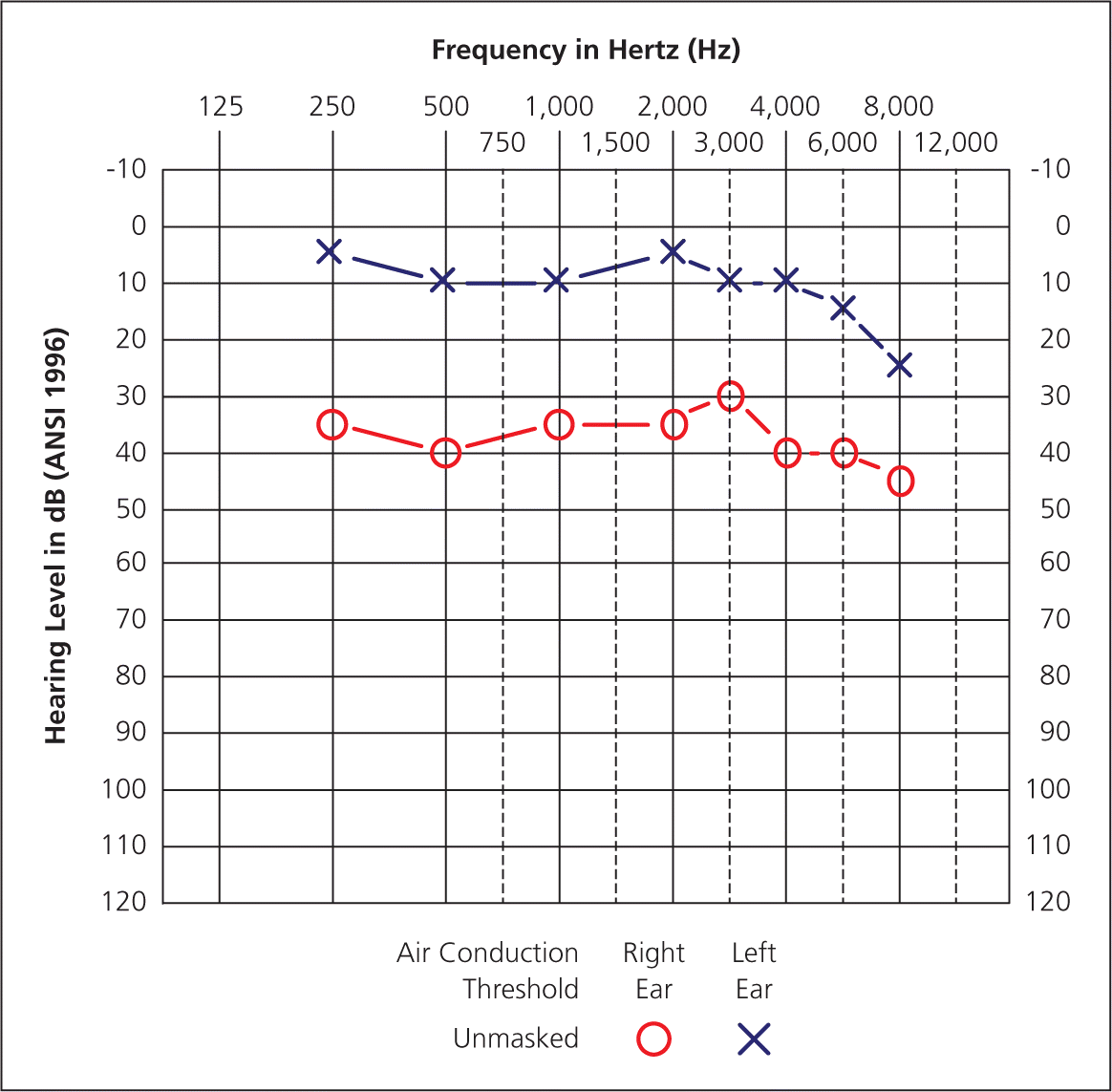
Pure Tone Test
Graph representing sensorineural and conductive hearing loss at different frequencies.
Meniere’s diseae
A disorder caused by build of fluid in the chambers in the inner ear.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Affects inner ear: caused by inner ear (nerve pathway) damage
Conductive Hearing Loss
Affects outer and middle ear: caused by something physically stopping sounds rom getting through outer ear or middle ear
Edward Jenner
Scientist credited for the first vaccination (small pox and cow pox)
Recombinant DNA technology
Process of cutting and recombining DNA fragments (DNA is composed of the same nucleotides in all species which allows for the DNA to be combined to two different species; plasmid)
Subcutaneous (injection)
Injection to the subcutaneous tissue (third layer of skin)
ex. MMR
Intramuscular (injection)
Injection to the muscle (4th layer of skin)
ex. COVID
intradermal
Injection to the dermis (2nd layer of skin)
ex. TB
True or False: Oral vaccines don’t exist
False: Oral vaccines are availabe for a few dieases (ex. rotavirus)
Herd Immunity
Resistance to the spread of an infectious disease within a population that is based on pre-existing immunity of a high proportion of individuals as a result of previous infection or vaccination.
Cohort Study
Taking the participants and studying them through a long period of time to attempt to find the origin for the epidemic
Case Control Study
Case: People with disease
Control: People without disease
Two groups are studied and compared through retrospection; observational studies
Epidemiology
The study and analysis of the distribution, patterns, etc. of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
blunt ends
sticky ends
Sticky ends are cuts of DNA that have DNA fragments on either side of the cut made by the restriction enzyme. Sticky ends are easier to combine with other DNA
Ideal cut for vaccination (plasmid to recombinant DNA)
1 for Bacteria
2 for Viruses
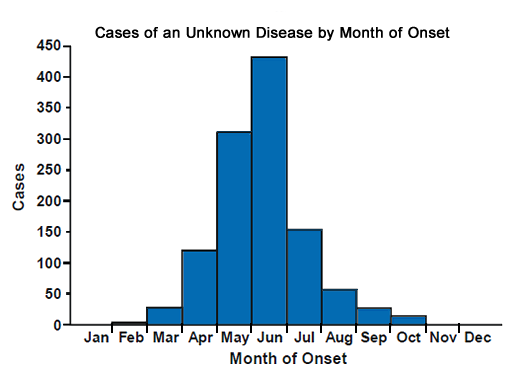
What does this graph represent?
An epicurve
Lygase
Acts like tape when binding sticky ends
Restriction enzymes
Acts like scissors cutting the preferred gene to add to the plasmid
To check if the recombinent DNA was successful you:
run it on PCR. If the gene was properly attatched, PCR will show two fragments at the same location.