Waves
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Transverse wave
oscillations are perpendicular to direction of energy propagation
Longitudinal wave
oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy propagation
Example of a transverse wave
Light
Example of a longitudinal wave
Sound
Amplitude
Max displacement of particles from equilibrium (middle) position
Unit for amplitude
Metres
Wavefront
The front of wave / same point on each wave
What is frequency
number of waves passing any point each second / number of vibrations per second of source
Frequency unit
Hertz
A hertz is
s^-1
Wavelength
Distance between two successive points in phase (e.g. two peaks)
Wavelength unit
Metres
Period
Time taken for one complete vibration of the source/particles
Period unit
Seconds
All waves can be…
Reflected and refracted
Waves transfer…
Energy and information without transferring matter
Doppler effect
Change in observed frequency/wavelength of a wave when its source is moving relative to an observer
When does Doppler effect happen
When source of wave moves relative to observer
What happens when a source of waves moves relative to an observer
Waves at front of source are bunched together; waves at back are spread out
What do you observe if a source of waves is moving away from you
Increased wavelength / decreased frequency
Order of EM spectrum
Radio micro IR visible UV X-ray gamma
EM wave with highest wavelength / lowest frequency
Radio
EM wave with highest frequency / lowest wavelength
Gamma
Use of radio waves
Broadcasting, communications
Use of microwaves
Cooking, satellite transmissions
Risk of microwaves
Internal heating of body tissue
Protective measure for microwaves
Shielding on microwave ovens to prevent microwaves reaching user
Use of infrared
Heaters, night vision equipment
Risk of infrared
Skin burns
Protective measure against IR
Wear sunscreen to reduce IR reaching skin
Use of visible light
Optical fibres, photography
Risk of visible light
Damage eyes
Use of UV light
Fluorescent lamps, detecting fake cash
Risk of UV
Blindness, damage to surface cells
Protective measure against UV
Wear sunscreen
Use of X rays
Medical imaging
Risk of x rays
Small chance of cancer after accumulated exposure
Use of gamma rays
Sterilising food and medical equipment
Risk of gamma rays
Cancer, mutation
Protective measure against gamma rays
Wear film badge, keep source in lead-lined box
What do film badges do
Show when wearer is overexposed to radiation
What is the law of reflection
i = r
What is refraction
When wave passes boundary between two different media and undergoes a change in direction
What does change in direction (refraction) depend on
Difference in density between media
When would light be refracted towards the normal
Less → more dense
When light slows down it bends…
Towards the normal
When would light be refracted away from the normal
More → less dense
What parts of the wave change when refracted
Speed and wavelength (not frequency)
What is the normal
Line perpendicular to the boundary
Why should you use a set square in ray box practical
Draw normal correctly
Why should you use sharpened pencil in ray box practical
Accurately mark in the middle of beam
What do you need to measure angles accurately
Perpendicular normal; sharp pencil; high res protractor
Safety for ray box practical
Don’t look directly into light, don’t touch box if too hot, keep liquids away
Relationship between refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction (Snell’s law)
N = sin i/ sin r
What is n in snells law
Refractive index
How do u know sin i is on top of sin r
I is before r in alphabet
How can you check the refractive index is right
Always larger than 1
What kind of materials have a higher refractive index
More optically dense materials e.g. diamond
What kind of materials have a lower refractive index
Less optically dense materials e.g. glass
Total internal reflection
Light reflected instead of refracted when moving from denser to less dense medium
2 conditions required for TIR
i>c; incidence material denser than second material
Optical fibres are used in
Communications, endoscopes
What is an endoscope used for
Examine inside the body e.g. stomach
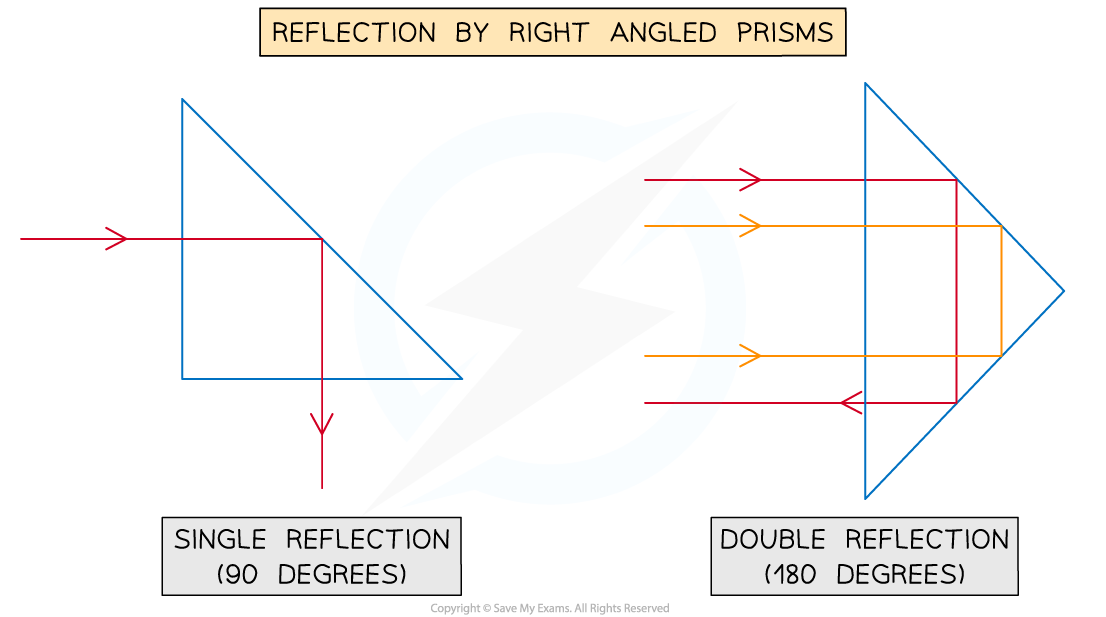
What are prisms used in
Binoculars, telescopes, cameras, periscopes
Reflection by right angled prisms
Critical angle
Angle of incidence where angle of refraction is 90 (along the boundary)
Relationship between refractive index and critical angle
sin c = 1/n
How would you find refractive index given the critical angle
N = 1/sin c